u1: chemistry of life
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
surface tension
water molecules near the surface are more attracted to each other than to surrounding air
result of cohesion
solvent
substance that dissolves a solute
solute
substance that dissolves in solvent
nonpolar
eg. oxygen, carbon dioxide
passes through phospholipid bilayer
polar
eg. water, ethanol
small polar can pass through phospholipid bilayer
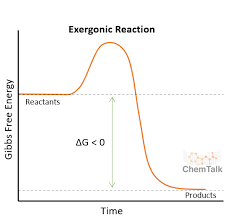
exergonic
negative ∆G (LOSE ENERGY)
releases free energy
is catabolic; breaks down
adhesion
attraction for molecules of a different kind
cohesion
attraction for molecules of the same kind
universal solvent
high heat capacity
high heat of vaporization
cohesion and adhesion
polar
importance of water for life
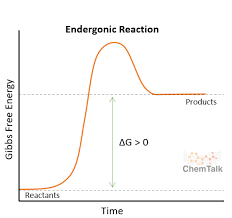
endergonic
positive ∆G (GAIN ENERGY)
requires input of energy
anabolic; forms products
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
gibbs’ free energy formula
enthalpy (order)
∆H - energy stored in bonds
entropy (disorder)
∆S
positive = more disordered
negative = more ordered
change in free energy
ΔG
organic molecules
molecules with carbon in it
hydrocarbon
molecules with hydrogen and carbon
isomers
same atoms, different arrangement
structural isomer
different covalent arrangement of atoms
geometric isomers
trans (opposite side) cis (some side)
different arrangement around bilayer
enantiomers
3d placement of atoms different
hydrogen bonds
hydrogen attracted to negative charges
weakest bond
dehydration synthesis
condensation reaction releases 1 water molecule
anabolism (requires energy)
glycosidic linkage
hydrolysis
catabolism (releases energy)
adds water molecule to break bond
rings forms
5- or 6- carbon sugars exist as either linear chains or in ring form
prefers ring form (esp aqueous solutions)
disaccharides
2 monosaccharides linked by dehydration synthesis
glycosidic linkage
oligosaccharides
a few monosaccharides together
additional functional groups bonded to proteins and lipids
polysaccharides
long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic linkage
starch (storage polysaccharide)
stores energy in plants
glycogen (storage polysaccharide)
stores energy in animals
cellulose (structural polysaccharide)
structure in cell walls
chitin (structural polysaccharide)
exoskeleton for organisms (eg. fungi, bees)
lipids
made up of nonpolar and hydrophobic hydrocarbons
triglycerides
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol
forms ester bonds (covalent)
saturated fatty acids
solid at room temp (no kink in chain)
packs tightly to build up plaque
unsaturated fatty acids
kink in cis-fat, can’t pack closely
liquid at room temperature
essential fatty acids
fatty acids needed in humans but not synthesized in the body
phospholipids
2 fatty acid + phosphate group + glycerol backbone
partially negative charge
hydrophilic heads attracted to aqueous solution
hydrophobic fatty acid tails cluster in the middle
waxes
long fatty acid chains esterified to long chain alcohols
hydrophobic, water won’t stick to surface
on feathers of aquatic birds/leaves of certain plants
steroids
closed ring structure (4 linked carbon rings)
hydrophobic & insolube in water
cholesterol
maintains fluidity in the phospholipid bilayer
synthesized in liver
primary structure
order of amino acids in a polypeptide
secondary structure
the way proteins fold, formed by hydrogen bonding
alpha helix
beta pleated sheet
tertiary structure
3d structure/properties of side chains
disulfide bridges
hydrogen bonding
van der waals interactions
ionic interactions
quaternary structure
arrangement of multiple peptide chains
hydrophobic and ionic interactions
hydrogen bonds
denaturing
destroying secondary & tertiary structure by disrupting weaker interactions
high temp
change in pH
change in solvent (eg. polar to nonpolar)