Overview of the Endocrine System and Hormonal Functions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are released into the bloodstream to act on an organ in another part of the body.
Target cells
Cells equipped with compatible receptors that are able to respond to hormones.
Blood sugar control
Regulated by insulin, a hormone that helps maintain glucose levels in the blood.
Testosterone
A hormone responsible for the differentiation, growth, and function of male reproductive organs.
Estradiol
A hormone involved in the differentiation, growth, and function of female reproductive organs.
Growth hormone
A hormone that plays a key role in body growth and energy production.
Thyroid hormone
Hormones produced by the thyroid gland that stimulate all cells in the body and control biological processes.
Hormone-receptor complex
The structure formed when a hormone binds to its receptor, which then carries out the hormone's instructions.
Estrogens
A group of hormones responsible for female sexual development, primarily produced by the ovaries.
Androgens
Hormones responsible for male sex characteristics, with testosterone being a primary example.
Thyroxine
One of the main hormones secreted by the thyroid gland that stimulates growth and metabolism.
Triiodothyronine
Another main hormone secreted by the thyroid gland that controls biological processes in the body.
Endocrine system
The system made up of all the body's hormones that regulates biological processes from conception through old age.
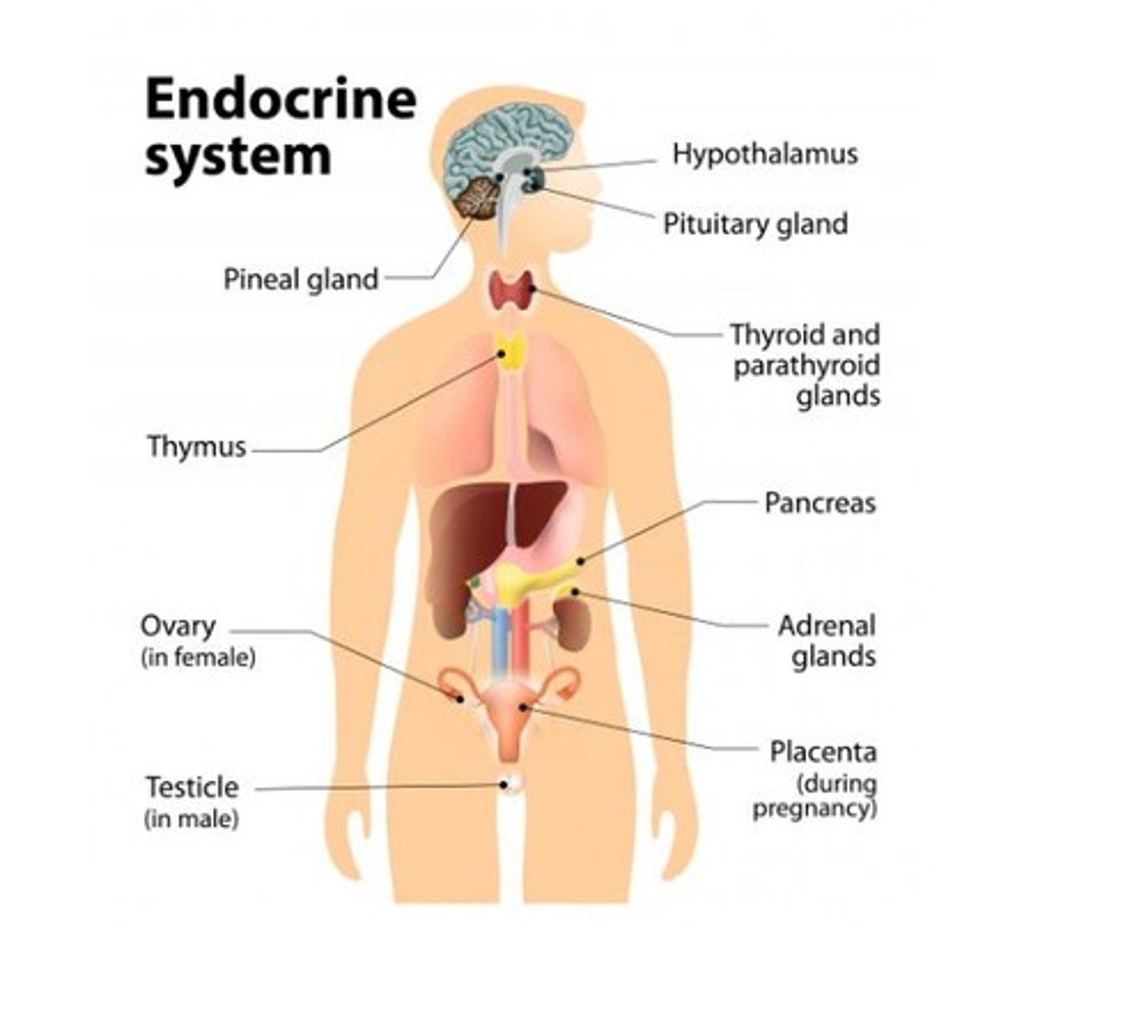
Ovaries
Female reproductive glands that produce estrogens and are part of the endocrine system.
Testes
Male reproductive glands that produce testosterone and are part of the endocrine system.
Pituitary gland
A major gland in the endocrine system that regulates various hormonal functions.
Thyroid gland
A gland that secretes hormones like thyroxine and triiodothyronine, controlling growth and metabolism.
Adrenal glands
Glands that produce hormones involved in stress response and metabolism, part of the endocrine system.
TRH
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone; stimulates the release of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and prolactin.
CRH
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone; stimulates the release of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone).
GnRH
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone; stimulates the release of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone).
GHRH
Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone; stimulates the release of GH (growth hormone).
PRH
Prolactin-Releasing Hormone; regulates pituitary gland; links nervous and endocrine systems.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Stimulates other endocrine glands; growth; milk production; reproduction.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Stimulates release of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), which regulate metabolism.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates release of cortisol, which helps in stress response, metabolism, and inflammation control.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Triggers ovulation/testosterone production.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Promotes egg/sperm development.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Regulates water balance.
Oxytocin
Involved in uterine contraction and milk ejection.
Thyroxine (T4)
Regulates metabolism.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Regulates metabolism.
Calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium.
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Increases blood calcium levels.
Cortisol
Involved in stress response.
Aldosterone
Regulates water/salt balance.
Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Involved in fight-or-flight response.
Norepinephrine
Involved in fight-or-flight response.
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose.
Glucagon
Raises blood glucose.
Somatostatin
Regulates digestion.
Melatonin
Regulates sleep-wake cycle.
Estrogen
Female sexual development; menstrual cycle; pregnancy.
Progesterone
Female sexual development; menstrual cycle; pregnancy.
Thymosin
Maturation of T-cells (immune response).
Negative Feedback
Reverses original stimulus to maintain homeostasis.
Positive Feedback
Amplifies original stimulus to achieve a specific event quickly.