PSYO 220 FINAL
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
241 Terms
primary aging
age-related physical changes that have a biological basis and are universally shared and inevitable
secondary aging
age-related changes that are due to environmental influences, poor health habits, or disease
what pattern suggests influence of secondary aging
20-34 year olds rarely die from disease, rather age interacts with other variables to influence health
determinants of health
socioeconomic, health care system, biology and genetics, physical environment
no matter what age what is happening in the brain
new synapses forming, myelinization, old connection are dying off
gradual decline in almost every measure of what throughout adulthood?
physical functioning
do mens or womens reproductive capacity decline faster?
womens
Five health practices
getting physical exercise, not smoking, drinking, over- or under-eating, and getting regular sleep
healthy lifestyle choices of early adulthood have
cumulative effects
locus of control
a person's tendency to perceive the control of rewards as internal to the self or external in the environment
internal locus of control ex)
being healthy becuase you want to be
external locus of control
something external is influencing your health, others or luck is responsible for your health behaviors
mental health problems
- anxiety and mood disorders
- personality disorders
- schizophrenia
- alcohol and substance use disorders
what are the most common mental disorders
those that are associated with intense or prolonged fear and anxiety
anxiety disorders include
phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, and panic disorder
what is the next most common type of mental difficulty
problems associated with moods
antisocial personality disorder
difficulty forming emotional attachments, lack of empathy, little regard for others
paranoid personality disorder
Suspicious
Argumentative
Reluctant to confide in others because of fears information will be "used against" him/her
Looking out for trickery
Blame others and bears grudges
histrionic personality disorder
irrational, attention seeking, inappropritae emtioanl repsonses
narcissistic personality disorder
exaggerated sense of self-importance
borderline personality disorder
unstable moods, behavior, and relationships, fear of abandonment
Schizophrenia
affects 1% of canadians
characterized by disturbances such as confused thinking, delusions and hallucinations
alcohol abuse and drug addiction
peak between 18 and 40
binge drinking
common apart post secondary student
20-34 about 38% males and 24% female
postformal thought
types of thinking that are associated with a hypothesized fifth stage of cognitive development
relativism
the idea that some propositions cannot be adequately described as either true or false
dialectical thought
a form of thought involving recognition and acceptance of paradox and uncertainty
reflective judgement
the ability to identify the underlying assumptions of differing perspectives on controversial issues
crystallized intelligence
depends heavily on education and experience
fluid intelligence
involves basic reasoning ability, memory capacity, and speed of information processing less on specific experiences
post-secondary education has become
a neccessity
percent overqualified for jobs now
40%
when do adults social connections become far more complex
between 20-40, through marriage, divorce, parenthood and career development
Erikson: Intimacy vs. Isolation
early adulthood stage in which an individual must find a life partner or supportive friends in order to avoid social isolation
intimacy
the capacity to engage in a supportive, affectionate relationship without losing one's own sense of self
what does eriksons stage success depend on
a good resolution of the identity vs role confusion crisis encountered in adolesence
life structure
the underlying pattern or design of a person's life at a given time, which includes roles, relationships and behvaior patterns
Phases of Life Structure
novice - mid-era - culmination
emerging adulthood
17-22
a new transitional stage
explore options before commiting to adult roles
unique period of life
intimate relationships form
secure base from which most young adults move out into the adult world
marriages in canada are starting to mirror
sociodemographic diversity
evolutionary theory
often cite research on sex differences in mate preferences and mating behavior to support their views
parental investment theory
says that sex differences in mate preferences and mating behaviour are based on the different amounts of time and effort men and women must invest in child-rearing
social role theory
the idea that sex differences in mate preferences and mating behavior are adaptations to gender roles
assortative mating (homogamy)
sociologists' term for the tendency to mate with someone who has traits similar to one's own
relationship quality
attachment, love, conflict management
the role of attachment
Adults create internal models of attachment to a prospective spouse that are similar to their attachment to their parents
the role of love
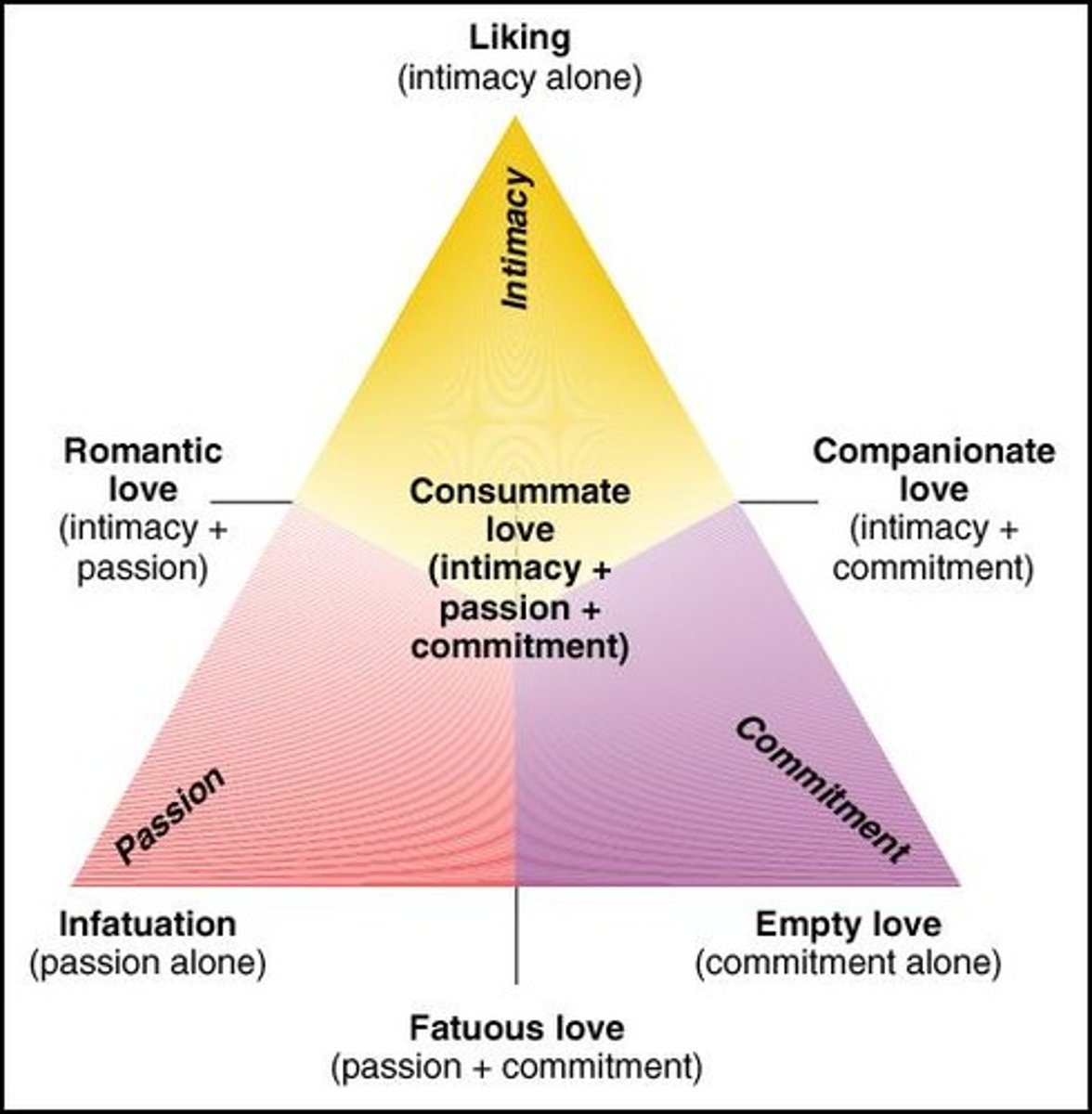
-Sternberg suggests 3 key components of love: Intimacy, passion, commitment
-When these components combine in all possible ways, the result is 7 sub-varieties of love
Sternberg's Triangular Theory of Love
intimacy, passion, commitment
stable or enduring marriages may be
validating, volatile, avoidant
couple with unsuccessful marriages may be
hostile/engaged, hostile/detached
average time marriage lasts
15 years
divorce rates highest among men and women in their
late 50s
divorce associated with
increases in mental health problems, depression
men are 3 times more likely to
become depressed following marital breakdown
divorce rate for those who cohabit before marriage is double that of
couples who did not cohabit
how many canadians are in same sex marriages
1 in 3
three dominant attachment patterns among long term singles
avoidance, anxiety, security
what percent of parents believe that is the most important thing they could do
92%
more men or women see parenting as positive?
men
postpartum depression
a severe mood disturbance resulting in feelings of sadness lasting a few weeks or year
what percent of mothers experience PPD
10-25%
most common reasons for not having children
doesnt fit their lifestyle, too old, infertility
what are relationships strongly influenced by
proximity and cultural influences
Holland's Personality Type Theory
realistic, investigative, social, conventional, enterprising, artistic
job satisfaction is impacted by
- perceptions of job security
- perceptions of the career as consistent with personality
- achieving work-family balance
job satisfaction at its lowest at
mid career
realistic
mechanical activities
investigative
scientists or engineers
artistic
social -artists
social
nursing and education
enterprising
high verbal - sales
conventional
bookkeeping or filing
nervous system changes in middle adulthood
white matter crests
grey matter declines until it levels off at 60
new synapses still forming but more are being lost
general rule for declining of the brain
areas of the brain that were developed last will be the first to deteriorate
cognitive tasks and activation
reproductive system in MA
climacteric
average age of menopause
50
premenopausal phase
estrogen levels fall somewhat, menstrual periods are less regular, and anovulatory cycles begin to occur
perimenopausal phase
estrogen and progesterone levels are erratic, menstrual cycles may be very irregular, and women begin to experience symptoms such as hot flashes
postmenopausal phase
no more periods for a year or more
individual differences of menopause
significant symptoms = more negative moods and most depression
connections between menopause and depression?
no
biopsychosocial view of sex with aging
chronic conditions or poor health = less sex
mental disorders
partner expectations
when does osteoperosis begin
30, but in women is accelerated by decreasing estrogen levels in menopause
risk factors for osteoporosis
age - risk increases in women over 65 and men over 70
race - white and asian highest
gender - woman higher
weight - smaller body frames
timing of climacteric - early menopause higher risk
family history
diet - low calcium
gut microbiota - imabalance
health habits - smoking and alcohol
exercise - sedentary at risk
presbyopia
normal loss of visual acuity with aging, especially the ability to focus the eyes on near objects
presbycusis
normal loss of hearing with aging, especially of high-frequency tones
when does Canadians HRQL stay relatively high for?
40 through to 70
during middle adulthood what health trends do we see an increase in
frequency of annoying aches and pains
the number who are unhappy with bodies
chronic diseases
disease related deaths
leading cause of death in MA
cancer
atherosclerosis
narrowing of the arteries caused by deposits of a fatty substance called plaque
arterial blockage = stroke
result of lifestyle not normal aging
risk factors for cancer and heart disease
smoking, BP, weight, infections, cholesterol, inactivity
diet, alcohol, herediity
whose life expectancy higher
womens even though they have more diseases and disabilities
mental health ______ with age
improves
addictive disorders go undiagnosed until
they become problematic in MA
neuro defecits in alcohol disorder people
problems with memory and language
selective optimization with compensation
ank skill not exercised is lower peak but can be improved
memory with age
forgetfulness increases with age
episodic memory with age
slows
semantic memory with age
doesnt slow (general knowledge)