BIO 110 - Darwinism
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is evolution?
Change over time
Various processes that transformed ancestral life forms into many species existing today
What is organic evolution?
Change of organisms over time
Age of the solar system
10-20 billion years old
Age of the earth
4.5-5 billion years old
When did life appear?
4 billion years ago
Spontaneous generation?
Idea that organisms could “spring” from non-living material. (Not true)
Domestication of dogz
14,000 years ago artificial selection began by humans choosing desired traits and putting it into that organism
Results of artificial selection
Extreme sizes (Great Dane = big, Chihuahua = small)
Extreme form (Dachshunds=short leg, English bulldog= short snout, hard to breathe)
Homology
Similarity in structure between different species, parts of an organism, or between the different parts of a single organism, often attributable to common ancestry.
Comparative Morphology
Animals like whales + bats have similar bones in forelimbs
Who was George Cuvier?
States that a higher being (God) created the organisms today + multiple catastrophes killed them.
Explanation of dinosaurs
Who was Jean Lamarck?
Animals inherited acquired characteristics.
Was not born w/ a trait but passed on to offspring.
When environments changed organisms changed behavior to survive.
Ex. Giraffe stretching neck w/ nervous fluid to eat leaves.
Offspring inherits it + neck neck continues to stretch
Charles Darwinnn
Born Feb, 12, 1809 in Shrewsbury England.
British naturalist famous for theories + evolution + natural selection
Star pupil of John Henslow (botanist)
What happened on Darwin’s Voyage?
(1831-1836) - Naturalist on the HMS Beagle on British science expedition around the world.
South America - Found fossils of extinct animals similar to modern species
Galapagos Islands - noticed many variations among plants+animals of the same type as those in South America. Formed the theory of evolution.
What is the Galapagos Islands?
Volcanic islands far off coast of Ecuador.
All creatures descended from species that arrived on islands elsewhere
Galapagos finches and Darwin
Darwin observed these animals w/ various lifestyles + body forms
When he returned - there were 13 species
This helped him create the theory of natural selection
What is Darwin’s main theory?
Population can change over time when individuals differ in one or more heritable traits responsible for differences in ability to survive+reproduce
What are Darwins theories?
Evolution is real.
Evolution was gradual
Primary mechanism for evolution was natural selection
Millions of species alive today came from 1 original life form through branching process(speciation)
What is Natural selection?
Differential survival + reproduction of classes of organisms that differ from one another in one or more usually heritable characteristics.
Never due to chance
Animals that best adapted to their environment
Malthus- Struggle to survive
Darwins inspiration
Thomas Malthus = Argued that as population size increases, resource decrease.
Struggle to live intensifies + conflict increases.
The point of Darwin’s work
Biological evolution doesn’t change individuals.
Changes entire population
Traits in population vary among individuals
Evolution is change in frequency of traits
Individual of species does not evolve - population of species evolved
Why was Darwin afraid?
The theories he wrote were not published because the Anglican Church could be offended.
Until Alfred Russel Wallace came up w/ the same theories. He forced this man to publish his theory to gain credit.
Alfred R. Wallace
Naturalist who had the same ideas as Darwin
Prompted Darwin to publish his theories in formal paper to gain credit before him.
What is evolutionary selection?
variation within species occurs randomly + survival or extinction of each organism is determined by organism’s ability to adapt to environment.
Organisms adapt w/ traits they already have
What is adaptation 💩
Any heritable characteristic of organism improving its ability to survive + reproduce in its environment
Used to describe process of genetic change in population, influenced by natural selection
What is “On the Origin of the Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life” ?
(1859), A book where Darwin put his theories.
After OOS was published Darwin continued to write botany, geology + zoology
Was Darwin’s work still controversial to others?
Many did not like the idea that monkey’s were their ancestor.

What is the Gene Pool?
All of the genes in the population
Genetic resource that is shared (in theory) by all members of population
Variation in Phenotypes
Each kind of gene in gene pool may have two or more alleles
Individuals inherit different allele combinations
This leads to variation in phenotype
Types of Gene Mutations
1. Lethal mutation - lead to death
2. Neutral mutations - no benefit/harm
3. Advantageous mutations - these are beneficial to the organism
Natural selection is the…
Difference in the survival and reproductive success of different phenotypes
Acts directly on phenotypes and indirectly on genotypes
What are the 4 basic ideas that form the theory?
Organisms can produce large #s of offspring
Offspring are variable in appearance and function, some of this variation is heritable
Competition plays a role in which individuals survive
Survival and reproduction of individuals is not random
What is survival of the fittest?
Whoever creates the most offspring or produces the most.
What comes out of Natural selection?
A shift in the range of values for a given trait in some direction (directional)
Stabilization of an existing range of values
Disruption of an existing range of values
What is Directional Selection?
Allele frequencies shift in one direction
Ex. The extreme right version if the species survives to reproduce
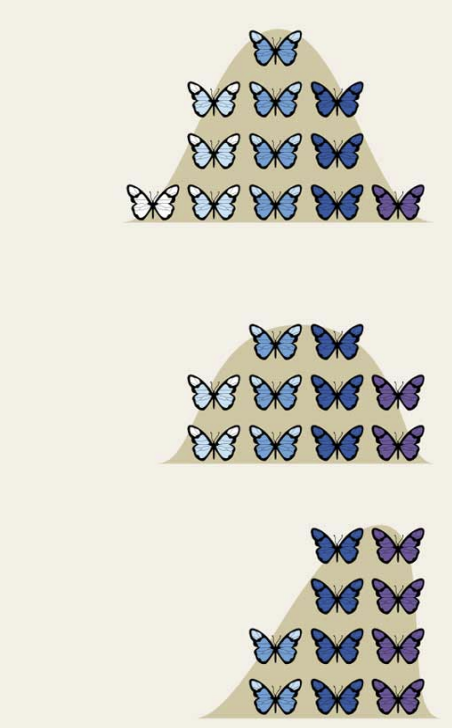

Peppered Moths, an example of directional selection?
Prior to industrial revolution in England, most common phenotype of this organism was light colored
After industrial revolution, dark phenotype became more common
Peppered moths
1800s, both colors were common.
Once factories created soot from burning coal the trees were covered.
The lighter organism were eaten by birds while the darker organism blended into the soot
What is Antibiotic Resistance?
Another Ex. of Directional Selection
First came into use in the 1940s
Overuse has led to selection of an increase in forms of bacteria
Most susceptible bacteria died out and were replaced by resistant forms
What is stabilizing selection?
Another type of selection
Intermediate forms are favored and extremes are eliminated
Middle form of species survives
The selection for Gall size
This organism has 2 major predators
Wasps preyed on larvae in small ones
Birds eat larvae in large ones
The organism that caused medium sized larvae had the highest fitness
Disruptive (Destabilizing) Selection
Forms at both ends of the range of variation are favored
Intermediate forms are selected against
Outer forms of the species survive
Disruptive Selction
In disruptive selection, extremes of visible characteristics or traits (phenotypes) enjoy a greater reproductive success than do intermediate characteristics or traits.
Ex. Pseudacraea eurytus (African butterfly)
Pseudacraea eurytus (butterfly) come in three colors
There are yellow, orange and red forms & all are the same species
All are un-edible for birds so they are not hunted by birds
BUT the middle colored (Orange) look like a different species so the birds accidentally eat them
Birds will mistakenly kill the Orange ones hence this is disruptive selection.
Sexual Selection
Another form of selection
Selection favors certain secondary sexual characteristics
Like feathers or puffy chest in woodcocks
Through nonrandom mating, alleles for preferred traits increase since they are chosen as mates more frequently
What is Gene Flow?
Physical flow of alleles into a population
Tends to keep the gene pools of populations similar
Counters the differences that result from mutation, natural selection, and genetic drift
What is Bottleneck?
A severe reduction in population size
Causes pronounced drift
Example:
Elephant seal population hunted down to just 20 individuals
Population rebounded to 30,000
Electrophoresis revealed there is now no allele variation at 24 genes
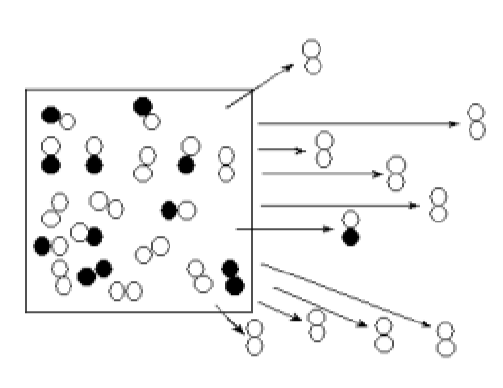
What is the founder effect?
When a small # of individuals starts a new population
By chance, allele frequencies of founders may not be same as those in original population
Effect is pronounced on isolated islands
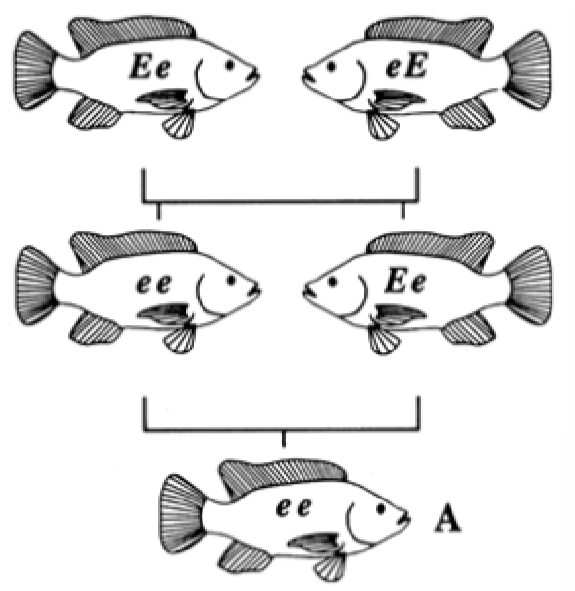
What is inbreeding?
Nonrandom mating between related individuals
Leads to increased homozygosity
Can lower fitness when deleterious recessive alleles are expressed
Amish, cheetahs are a population w/ this