Material Science - Lecture 10 (Polymers)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is a polymer?
any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called monomers
mga class of mga natural or synthetic nga substance which compose of very large nga molecules called macromolecules, which kaning macromolecules are mga multiple nga mga simplier chemical units nga gitawag nga monomers
What are the categories of polymers
Natural polymers
Synthetic polymers
What is natural polymers?
These polymers are derived from natural sources and include substances such as cellulose, starch, proteins, silk, wool, and natural rubber.
They are biodegradable and renewable.
What is Synthetic Polymers?
are man-made, non-biodegradable, and usually derived from petroleum oil
polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), nylon, and polystyrene.
What are the categories of synthetic polymers based on their structure and properties?
Thermoplastics
Thermosets
Elastomers
Fibers
What are the propertied of polymers?
Strength and Durability
Flexibility
Elasticity
Thermal Stability
Chemical Resistance
Electrical Insulation
What are the applications of polymers?
Packaging
Construction
Textiles
Automobiles and Aerospace
Electrical/Electronics
Give an example of polymers being use as packaging
Polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene are widely used for bottles, bags, and films because they are lightweight, durable, and barrier potential
Give an example of polymers being use in construction
Polymers like PVC, polystyrene, and acrylics are used in pipes, insulation, flooring, adhesives, and coatings because of their strength, weather resistance, and versatility
Give an example of polymers being use as textile
Polymers like nylon, polyester, and acrylics are used in clothing, carpets, or even ropes because of their strength, elasticity, and resistance to wrinkles
Give an example of polymers being use in Automobiles and Aerospace
Polymers in this field are used to make foams and composites which are lightweight
Give an example of polymers being use in Electrical/Electronics
Polymers are used for electrical insulation, circuit boards, adhesives, and coatings because of their electrical and thermal properties
What is thermoplastics
It can be softened and processed using injection moulding, extrusion, and thermoforming to form a desired shaped of the product
It has good elasticity and strength
Give at least 5 advantages and disadvantages of thermoplastics
ADVATAGES
Recyclable and re-shapable with minimal impact on material properties
Chemical and detergent resistance
High Resistance to impact
Improved anti-slipped properties
Low-cost, high-volume manufacturing
DISADVANTAGES
Not suitable for all applications
Degrade quickly when expose to sunlight
Under high stress, it can fracture rather than deform
Long term loading can cause creep to some types of thermoplastics
More expensive than thermosets
What are the thermoplastic materials?
Polyethylene (PE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polystyrene (PS)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polycarbonate (PC)
What is polyethylene (PE)?
This is the most widely used thermoplastic because of its versatility and chemical resistance
What are the two types of polyethylene and its example?
High-density polyethylene - Milk Cartoons, detergent bottles
Low-density polyethylene - Plastic wrap, garbage bags
What is polypropylene and its example?
Just like polyethylene, it is also known for its versatility, chemical resistance, and good fatigue resistance
Straw and bottle caps
What is polyvinyl chloride and its example
Known for its durability, chemical resistance, and flame retardant properties
Pipes, electrical insulation
What is polystyrene and its example?
transparent thermoplastics with good stiffness and impact resistance
egg cartoons and disposable cutlery
What is polyethylene terephthalate and its example?
known for its excellent strength and clarity
beverages bottles and polyester clothing
What is polycarbonate and its example?
it is transparent with high impact resistance and optical properties
safety googles and eyeglass lenses
What are the manufacturing processes for thermoplastics?
Injection molding
Extrusion
Thermoforming
What is injection molding for the manufacturing of thermoplastics?
Melting the thermoplastic resin pellets and uses pressure to inject it into a mold
What is extrusion for the manufacturing of thermoplastics?
Thermoplastic is melted and pressed into a die or steel disk in a continuous profile
What is thermoforming for the manufacturing of thermoplastics?
Heating the sheets of thermoplastics and forming them either inside or outside the mold. It then cooled down and remove excess material
What is thermosets?
Once fully set, it cannot be melted or reshaped
has high dimensional stability ad strength
Give at least 5 advantages and disadvantages of thermosets
ADVANTAGES:
Allows more versatile product designs
Less expensive than metal components
Outstanding electrical insulation
Resistant to corrosion
Water repellent
DISADVANTAGES:
Cannot be reshaped once fully set
Good surface finishing is hard to achieve
Thermal conductivity is poor for housing replacements
Its rigidity ca cause product failure if used in high-vibration
What are the thermosets materials?
Epoxy resins
Phenol-Formaldehyde Resins
Urea-Formaldehyde Resins
Melamine-Formaldehyde Resins
Polyester Resins
What is epoxy resins and its application?
It offers excellent adhesion and chemical resistance
Used in coatings and adhesives
What is phenol-formaldehyde resins and its application?
It exhibits high heat resistance and electrical insulation properties
Used i circuit boards and automotive parts
What is urea-formaldehyde resins and its application?
known for being low cost and good heat resistance
Used in the production of plywood
What is melamine-formaldehyde resins and its application?
It offers heat resistance and chemical resistance
dinnerware and decorative surfaces
What is polyester resins and its application?
It is known as unsaturated polyester resins
boat hulls and construction materials
What are the different manufacturing techniques used for thermosets?
Compression Molding
Laminating
Reaction Injection Molding
What is Compression molding?
This create a hard-heat resistant plastic products
dinnerware and telephones
What is laminating?
Its products are used as a surface finish for furniture and kitchen countertops
Glass fibers and resin-impregnated paper
What is reaction injection molding
liquid thermosetting resin is combined with a curing agent and injected into the mold
Most products made by this process are made from polyurethane
What is elastomers?
It exhibits rubber-like elasticity and can return to its original shape
Have high degree of flexibility and resilience
What are the examples of elastomers?
Natural Rubbers
Polyurethanes
Polybutadiene
Silicone
Neoprene
What is natural rubber?
It is from the latex of the rubber tree and it has high elasticity and low modulus
Used in tires and automotive components
What is polyurethanes?
used in textile industry for elastic clothing like lycra
What is polybutadiene?
used for providing wear resistance in wheels of vehicles
What is silicone?
used in manufacturing medical prosthesis and lubricants
What is neoprene?
used in wet-suits and industrial belts
What are the properties of elastomers?
Elasticity and Flexibility
Resilience
Low Compression Set
Good Tear Resistance
Chemical Resistance
Temperature Resistance
Weather/Water Resistance
Electrical Insulation
What are the applications of elastomers?
Motor Vehicles - tires
Consumer products - various products
Constructions - adhesives and gaskets
Industrial products - belts and molds
Wire and cable - wire insulation
Medical products - prosthetics
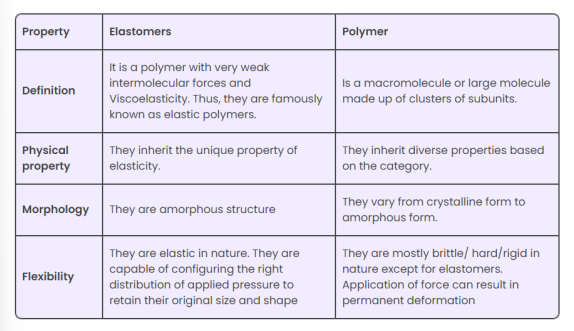
What are the difference between elastomers and polymers?