AP Macroeconomics Practice E#1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Which of the following typically occurs during an
expansionary phase of a business cycle?
(A) Nominal interest rates decrease.
(B) Income taxes decrease.
(C) The price level decreases.
(D) Government transfer payments increase.
(E) Employment increases.
(E) Employment increases.
Economic growth refers to an increase in which of
the following?
(A) Government spending
(B) Consumption spending
(C) Nominal gross domestic product
(D) Potential real gross domestic product
(E) Household wealth
(D) Potential real gross domestic product
If both the nominal interest rate and the expected
inflation rate increase, what will happen to the
real interest rate?
(A) It will increase because the expected inflation
rate has increased.
(B) It will increase because the nominal interest
rate has increased.
(C) It will increase if the expected inflation
rate increases by more than the nominal
interest rate.
(D) It will decrease because the nominal interest
rate has increased.
(E) It will decrease if the expected inflation
rate increases by more than the nominal
interest rate.
(E) It will decrease if the expected inflation
rate increases by more than the nominal
interest rate.
Which of the following statements is true about an
expansionary fiscal policy?
(A) It decreases demand for loanable funds.
(B) It decreases the equilibrium price level.
(C) It decreases the equilibrium real interest rate.
(D) It increases aggregate demand.
(E) It increases the money supply.
(D) It increases aggregate demand.
Which of the following will most likely result
from deflation?
(A) Increased nominal interest rates
(B) Increased business profits
(C) Increased real value of fixed incomes
(D) Decreased purchasing power of cash
(E) Decreased real wealth
(C) Increased real value of fixed incomes
Which of the following is a defining characteristic
of a fractional reserve banking system?
(A) The existence of a central bank with
a monopoly on money creation
(B) The use of paper money backed by
a commodity such as gold or silver
(C) The fact that banks retain an amount of bank
reserves that is less than the amount of
customer demand deposits
(D) The requirement that banks maintain a certain
percentage of their reserves as a deposit in
an account at the central bank
(E) The regulations that separate investment
banking from commercial banking
(C) The fact that banks retain an amount of bank
reserves that is less than the amount of
customer demand deposits
A negative aggregate supply shock will result in
which of the following in the short run?
(A) An increase in the price level and a decrease
in the unemployment rate
(B) A decrease in the price level and an increase
in the unemployment rate
(C) A decrease in both the price level and real
output
(D) An increase in both the price level and real
output
(E) An increase in both the price level and the
unemployment rate
(E) An increase in both the price level and the
unemployment rate
Which of the following combinations of fiscal
and monetary policies will correct a severe
recession?
(A) Increasing income tax rates and decreasing
the money supply
(B) Increasing both the income tax rates and the
money supply
(C) Decreasing both the income tax rates and the
money supply
(D) Decreasing income tax rates and increasing
the money supply
(E) Decreasing income tax rates and increasing
the federal funds rate
(D) Decreasing income tax rates and increasing
the money supply
Which of the following would decrease the
United States net exports to South Korea?
(A) South Korean computer companies sell more
computers to the United States.
(B) South Korean insurance companies provide
fewer services to the United States.
(C) South Koreans spend more vacations in the
United States.
(D) United States banks provide more banking
services to South Korea.
(E) United States smartphone companies sell
more smartphones to South Korea.
(A) South Korean computer companies sell more
computers to the United States.
An increase in the purchases of newly constructed
houses will result in which of the following?
(A) Aggregate demand will decrease as a result of
a decrease in the price level.
(B) Aggregate demand will increase as a result of
an increase in investment spending.
(C) Aggregate demand will increase as a result of
an increase in exports.
(D) Aggregate demand will not change, since
consumer spending has not changed.
(E) Aggregate demand will not change, since
investment spending has not changed.
(B) Aggregate demand will increase as a result of
an increase in investment spending.
Suppose that a country's nominal gross domestic
product (GDP) was $1,000 in year 1 and $2,000
in year 2. If year 1 is the base year and real GDP
in year 2 was $1,000, which of the following
is true?
(A) Prices fell by 50% between year 1 and year 2.
(B) Prices doubled between year 1 and year 2.
(C) Prices remained the same between year 1 and
year 2.
(D) More goods and services were produced in
year 2 than in year 1.
(E) Fewer goods and services were produced in
year 2 than in year 1.
(B) Prices doubled between year 1 and year 2.
To decrease the money supply, a country's central
bank can do which of the following?
(A) Sell government bonds.
(B) Decrease the discount rate.
(C) Decrease the required reserve ratio.
(D) Increase taxes.
(E) Increase government spending.
(A) Sell government bonds.
Which of the following types of unemployment is
caused by a recession?
(A) Hidden
(B) Frictional
(C) Seasonal
(D) Structural
(E) Cyclical
(E) Cyclical
If the United States government increases deficit
spending, which of the following will occur as a
result of the change in the interest rate?
(A) The United States dollar will appreciate in
foreign exchange markets.
(B) Household savings in the United States will
decrease.
(C) The United States exports will increase.
(D) The demand for United States dollars will
decrease.
(E) Private investment in plant and equipment in
the United States will increase.
(A) The United States dollar will appreciate in
foreign exchange markets.
In the short run, a reduction in the money supply
will cause
(A) a rightward shift in the aggregate demand
curve
(B) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand
curve
(C) a rightward shift in the aggregate supply
curve
(D) a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve
(E) a movement along the aggregate demand
curve
(B) a leftward shift in the aggregate demand
curve
. How will an increase in demand and a
simultaneous decrease in supply affect the
equilibrium price and quantity of a good in
a market?
Price Quantity
(A) Increase Increase
(B) Increase Indeterminate
(C) Decrease Increase
(D) Decrease Indeterminate
(E) Indeterminate Indeterminate
(B) Increase Indeterminate
An increase in government spending financed
by increased borrowing will most likely change
the real interest rate and the gross private
domestic investment in which of the
following ways?
Real Gross Private
Interest Rate Domestic Investment
(A) No change No change
(B) Decrease Increase
(C) Decrease Decrease
(D) Increase Decrease
(E) Increase Increase
(D) Increase Decrease
If real interest rates in the United States fall
relative to real interest rates in Great Britain,
which of the following will occur?
(A) British investors will buy more United States
securities.
(B) British exports to the United States will
increase.
(C) The supply of dollars will decrease.
(D) United States investors' demand for British
pounds will decrease.
(E) The British pound will appreciate relative to
the dollar.
(E) The British pound will appreciate relative to
the dollar.
A country's economy is currently in equilibrium
at point R. Which of the following policy actions
could the country's government take to achieve
potential output (YP) ?
(A) Decreasing the money supply
(B) Decreasing investment tax credits
(C) Increasing interest rates
(D) Increasing government expenditures
(E) Increasing the minimum wage
Good X Good Y
P V Q P V Q
2 2 $1 4
3 2 $2 4
Assume that an economy produces just two
goods, X and Y, as shown in the table above. If
year 1 is the base year, the consumer price index
for year 2 in this economy is
(A) 57.1
(B) 66.7
(C) 100
(D) 175
(E) 250
(D) 175
Which of the following is LEAST likely to affect
the long-run growth of an economy?
(A) Investment in physical capital
(B) Research and development
(C) Education and training
(D) A specific tax on luxury goods
(E) Stable and efficient institutions
(D) A specific tax on luxury goods
Pat deposits a portion of her wages into a personal
savings account every week. The saved money
can be considered to be primarily a
(A) means of payment
(B) unit of account
(C) store of value
(D) measure of value
(E) medium of exchange
(C) store of value
An increase in the number of which of the
following will lead to an increase in the
unemployment rate?
(A) Discouraged workers
(B) Business start-ups
(C) Self-employed persons
(D) Persons working 30 instead of 40 hours
per week
(E) Persons quitting part-time jobs to look
for full-time ones
(E) Persons quitting part-time jobs to look
for full-time ones
An economy experiences a sharp increase
in energy prices, and policy makers adopt
a stabilization policy to increase aggregate
demand. Compared with the initial short-run
equilibrium, which of the following will
definitely occur?
(A) Lower level of output
(B) Higher level of output
(C) Lower price level
(D) Higher price level
(E) Higher aggregate supply
(D) Higher price level
Assume that the marginal propensity to consume
is 0.8. If the government increases its purchases
of goods and services by $200 and exports
decline by $50, at most the equilibrium level
of income will
(A) decrease by $250
(B) decrease by $1,000
(C) increase by $150
(D) increase by $750
(E) increase by $1,250
(D) increase by $750
An ongoing increase in the price of oil will
result in
(A) demand-pull inflation
(B) cost-push inflation
(C) expansionary fiscal policy
(D) a decrease in the prices of substitute forms
of energy
(E) deflation
(B) cost-push inflation
Assume that Country X and Country Y are trading
partners. If the average income in Country X
increases, which of the following will occur in the
foreign exchange market?
(A) The demand for Country X's currency will
increase, and Country X's currency will
appreciate.
(B) The demand for Country Y's currency will
increase, and Country X's currency will
depreciate.
(C) The demand for Country Y's currency will
increase, and Country X's currency will
appreciate.
(D) The supply of Country X's currency will
decrease, and Country X's currency will
appreciate.
(E) The supply of Country Y's currency will
increase, and Country Y's currency will
depreciate.
(B) The demand for Country Y's currency will
increase, and Country X's currency will
depreciate.
Which of the following is a monetary policy
aimed at increasing the equilibrium interest rate in
the money market?
(A) Raising taxes
(B) Lowering the discount rate
(C) Lowering the federal funds rate
(D) Selling bonds on the open market
(E) Lowering the required reserve ratio
(D) Selling bonds on the open market
Which of the following monetary and fiscal
policy mixes will reduce unemployment?
(A) Buying government bonds in the open market
and increasing taxes
(B) Buying government bonds in the open market
and decreasing taxes
(C) Selling government bonds in the open market
and increasing government spending
(D) Selling government bonds in the open market
and decreasing government spending
(E) Selling government bonds in the open market
and increasing taxes
(B) Buying government bonds in the open market
and decreasing taxes
Which of the following is correct according to the
circular flow model of an economy?
(A) Taxes received from the public equal
government spending.
(B) Imports equal exports.
(C) Total spending equals total income.
(D) Consumption plus saving equals investment.
(E) Saving plus investment equals imports plus
exports.
(C) Total spending equals total income.
If the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward
sloping, which of the following will cause
inflation?
(A) An increase in long-run aggregate supply
(B) An increase in short-run aggregate supply
(C) An increase in aggregate demand
(D) A decrease in aggregate demand
(E) A decrease in aggregate demand and
an increase in aggregate supply
(C) An increase in aggregate demand
Sam and Bill run a leaf raking and lawn mowing
business. In one day, Sam can rake 3 lawns or
mow 5 lawns whereas Bill can rake 2 lawns or
mow 6 lawns. Which of the following correctly
describes Sam's and Bill's absolute and
comparative advantages?
(A) Sam has a comparative advantage in raking
and an absolute advantage in mowing.
(B) Sam has a comparative advantage in mowing
and an absolute advantage in raking.
(C) Sam has a comparative advantage in mowing
and an absolute advantage in mowing.
(D) Bill has a comparative advantage in mowing
and an absolute advantage in mowing.
(E) Bill has a comparative advantage in raking
and an absolute advantage in mowing.
(D) Bill has a comparative advantage in mowing
and an absolute advantage in mowing.
People who have given up looking for jobs are
classified as
(A) cyclically unemployed
(B) frictionally unemployed
(C) structurally unemployed
(D) discouraged workers
(E) underemployed workers
(D) discouraged workers
Banks expand the money supply when
(A) issuing credit cards
(B) printing money
(C) cashing checks
(D) making loans
(E) accepting deposits
(D) making loans
The economy is currently in long-run equilibrium.
If the central bank increases the money supply, in
the long run the price level will
(A) increase, and output will remain at the
full-employment level
(B) increase, and output will be above the
full-employment level
(C) increase, and output will be below the
full-employment level
(D) remain unchanged, and output will remain
at the full-employment level
(E) remain unchanged, and output will be above
the full-employment level
(A) increase, and output will remain at the
full-employment level
The crowding out effect of government spending
will be large if
(A) investment is highly sensitive to changes
in the interest rate
(B) consumption is highly sensitive to changes
in wealth
(C) money demand is highly insensitive to
changes in income
(D) it takes a long time for changes in
government spending to cause a change
in equilibrium income
(E) the long-run aggregate supply curve is
horizontal
(A) investment is highly sensitive to changes
in the interest rate
When the United States dollar appreciates against
the euro, which of the following will most likely
happen?
(A) European firms will pay fewer euros
for equipment purchased from the
United States.
(B) European products will become more
expensive for United States consumers.
(C) United States tourists will pay fewer dollars
for trips to Europe.
(D) The European trade deficit will increase.
(E) The United States trade deficit will decrease.
(C) United States tourists will pay fewer dollars
for trips to Europe.
Which of the following will occur in the money
market when the aggregate price level increases?
(A) The money supply will increase and nominal
interest rates will decrease.
(B) The demand for money will increase and
nominal interest rates will decrease.
(C) The demand for money will increase and
nominal interest rates will increase.
(D) The demand for money will decrease and
nominal interest rates will decrease.
(E) The opportunity cost of holding money will
decrease.
(C) The demand for money will increase and
nominal interest rates will increase.
Increases in government subsidies to encourage
investment in research and development will
affect aggregate demand (AD) and long-run
aggregate supply (LRAS) in which of the
following ways?
AD LRAS
(A) Increase Increase
(B) Increase Decrease
(C) Increase No change
(D) Decrease Increase
(E) Decrease No change
(A) Increase Increase
If an automobile was manufactured in 2006 and
sold to a consumer in 2007, what was the effect
on gross domestic product in 2006 and 2007?
2006 2007
(A) No change Increase
(B) Decrease Increase
(C) Increase No change
(D) Increase Decrease
(E) No change No change
(C) Increase No change
If the government implements an expansionary
fiscal policy, how will real gross domestic product
(GDP) and the price level be affected in the
short run?
Real GDP Price Level
(A) Increase Decrease
(B) Decrease No change
(C) No change Increase
(D) Increase Increase
(E) Decrease Decrease
(D) Increase Increase
Which of the following will most likely contribute
to long-run economic growth?
(A) High levels of household spending
(B) High levels of government spending
(C) High levels of investment in plant and
equipment
(D) Low levels of immigration to the country
(E) Low levels of foreign investment in the
country
(C) High levels of investment in plant and
equipment
Which of the following is true when interest
rates rise?
(A) The opportunity cost of holding cash
decreases.
(B) The opportunity cost of holding cash
increases.
(C) The opportunity cost of holding cash stays
the same.
(D) The money demand curve shifts to the right.
(E) The money supply curve shifts to the right.
(B) The opportunity cost of holding cash
increases.
Which of the following is an example of fiscal
policy?
(A) Decreasing income tax rates
(B) Increasing the money supply
(C) Decreasing the discount rate
(D) Selling government bonds
(E) Decreasing the required reserve ratio
(A) Decreasing income tax rates
All of the following explain why prices and wages
are sticky EXCEPT
(A) menu costs experienced by firms
(B) efficiency wages paid to labor
(C) misperceptions about relative prices by
suppliers
(D) competition in the business sector
(E) labor contracts covering multiple years
(D) competition in the business sector
Total Population 300
Working-age Population 200
Unemployed 10
Employed 90
46. The table above gives population and
labor-market data for an economy. The
unemployment rate in this economy is
(A) 3.3%
(B) 5%
(C) 10%
(D) 33.3%
(E) 50%
(C) 10%
In the short run, how would a government's
budget deficit, national debt, and real output
change if government spending increases with no
change in taxes?
Deficit Debt Real Output
(A) Increase Increase Decrease
(B) Increase Decrease Increase
(C) Increase Increase Increase
(D) Decrease Decrease Increase
(E) Decrease Increase Decrease
(C) Increase Increase Increase
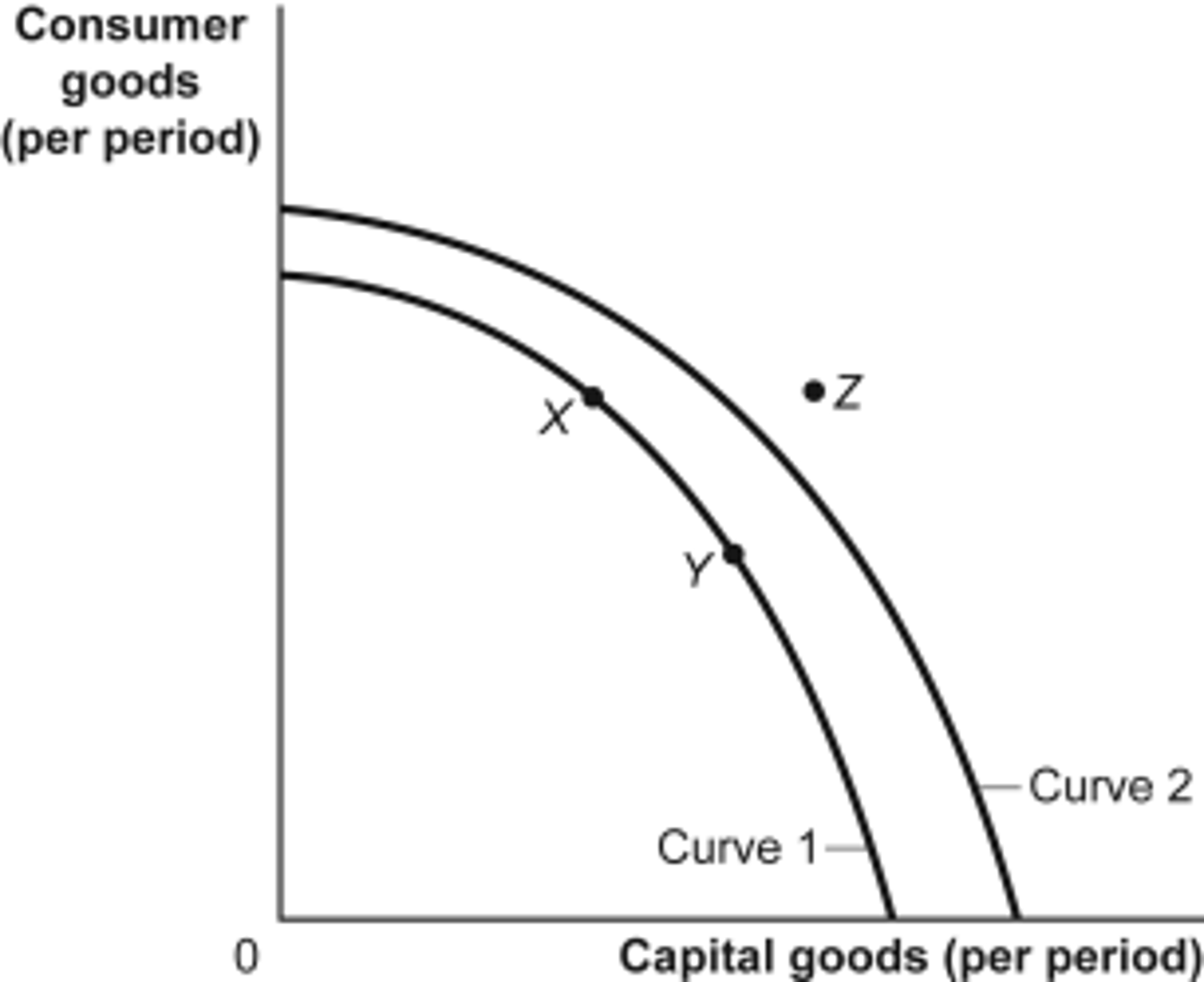
The graph above shows the production
possibilities curves (PPC) for an economy.
The concept of opportunity cost is best
represented by which of the following?
(A) A shift from PPC1 to PPC2
(B) A movement from point A to point D
(C) A movement from point B to point C
(D) A movement from point C to point E
(E) A movement from point D to point B
(C) A movement from point B to point C
If the central bank of Country Z wishes to
increase the value of its currency on foreign
exchange markets, it can do which of the
following?
(A) Buy the currencies of other countries
(B) Increase the domestic money supply in
Country Z
(C) Increase the income tax in Country Z
(D) Raise interest rates in Country Z
(E) Increase tariffs in Country Z
(D) Raise interest rates in Country Z
An increase in the expected inflation rate will
cause the
(A) short-run Phillips curve to shift to the left
(B) short-run Phillips curve to shift to the right
(C) long-run Phillips curve to shift to the left
(D) long-run Phillips curve to shift to the right
(E) actual inflation rate to fall below the expected
inflation rate
(B) short-run Phillips curve to shift to the right
Which of the following is most likely included in
gross domestic product?
(A) Matt gives his secondhand bicycle to his
brother.
(B) Sal paints his own bicycle.
(C) Ali buys a new bicycle.
(D) Mike buys a share of stock in a bicycle firm.
(E) Daniel bikes to school every day.
(C) Ali buys a new bicycle.
Which of the following is likely to result in an
inflow of financial capital to Country Z?
(A) A decrease in Country Z's government
budget deficit
(B) An increase in personal income tax rates in
Country Z
(C) Increased sales of government bonds by the
central bank of Country Z
(D) An increase in country Z's trade surplus
(E) Increased political instability in Country Z
(C) Increased sales of government bonds by the
central bank of Country Z
A bank has $200 million in demand deposits
and $150 million in reserves. The reserve ratio
is 20 percent. What is the maximum amount of
loans the bank can make from its reserves?
(A) $750 million
(B) $150 million
(C) $110 million
(D) $50 million
(E) $40 million
(C) $110 million
Which of the following is true about the
Phillips curve?
(A) A change in aggregate demand does not shift
the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC).
(B) A change in aggregate demand does not
cause a movement along the short-run
Phillips curve (SRPC).
(C) The LRPC shows the trade-off between
unemployment and inflation but the SRPC
does not.
(D) Changes in expected inflation affect the
LRPC only.
(E) Negative supply shocks affect the LRPC
only.
(A) A change in aggregate demand does not shift
the long-run Phillips curve (LRPC).
When the total amount the government spends
equals tax revenues in any given year, which of
the following must remain constant?
(A) The real interest rate
(B) The national debt
(C) Real gross domestic product
(D) The price level
(E) The money supply
(B) The national debt
How does the automatic adjustment mechanism
move the economy to potential real gross
domestic product (GDP) in the long run when
current real GDP is above potential GDP?
(A) Nominal wages fall, shifting the short-run
aggregate supply curve to the right.
(B) Nominal wages fall, shifting the short-run
aggregate supply curve to the left.
(C) Nominal wages do not change, shifting
the short-run aggregate supply curve to
the right.
(D) Nominal wages rise, shifting the short-run
aggregate supply curve to the right.
(E) Nominal wages rise, shifting the short-run
aggregate supply curve to the left.
(E) Nominal wages rise, shifting the short-run
aggregate supply curve to the left.
Which of the following statements about inflation
is true?
(A) The expected inflation rate is the difference
between nominal and real interest rates.
(B) Low expected inflation rates lead to high
inflation rates.
(C) Lenders lose from expected inflation.
(D) Lenders gain from unexpected inflation.
(E) Workers lose from expected inflation.
(A) The expected inflation rate is the difference
between nominal and real interest rates.
The opportunity cost of an activity is
(A) the amount of time spent on the activity
(B) the value of the benefit received from
performing the activity
(C) the value of the forgone benefit of the next
best alternative
(D) zero if the activity offered no benefits
(E) the sum of benefits from all the sacrificed
alternatives
(C) the value of the forgone benefit of the next
best alternative
Increased spending on which of the following
contributes most to long-term economic growth?
(A) Social security and other transfer payments
(B) New automobiles and homes
(C) Education and infrastructure
(D) Imported consumer goods
(E) Interest payments on national debt
(C) Education and infrastructure
If consumers in Canada increase their demand for
products that are manufactured in India, which of
the following will occur?
(A) The Indian rupee will depreciate.
(B) The Canadian dollar will appreciate.
(C) India's financial capital inflow will increase.
(D) Canada's financial capital inflow will
increase.
(E) The supply of Canadian dollars will decrease.
(D) Canada's financial capital inflow will
increase.