Anomalies of Placenta and Cord
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord refer to?
abnormal structures or functions that differ from the normal anatomy or physiology during pregnancy. These issues can lead to complications that affect both fetal development and maternal health.
TYPES OF PLACENTA ANOMALIES?
1. Abruptio Placenta
2. Placenta Previa
3. Placenta Previa
4. Placenta Bilobata/Bilobe
5. Placenta Bilobata/Bilobe
6. Placenta Accreta
7. Placenta Increta
8. Placenta Percreta
9. Placental insufficiency (Placental Dysfunction)
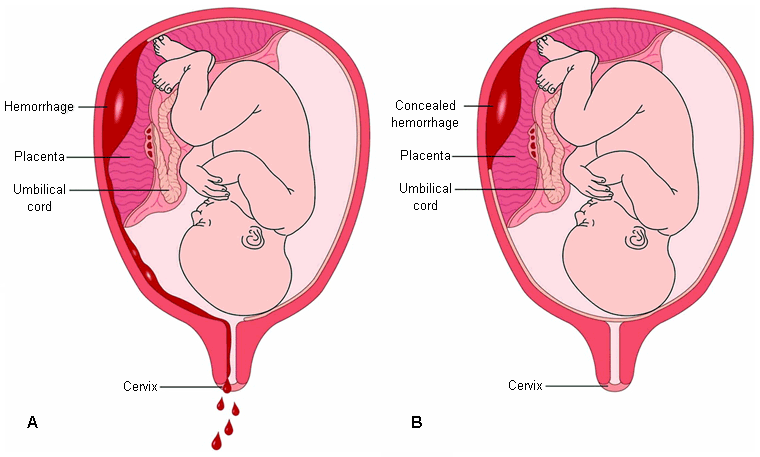
Placenta Abruptio
Premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall, leading to potential risks for both mother and baby.
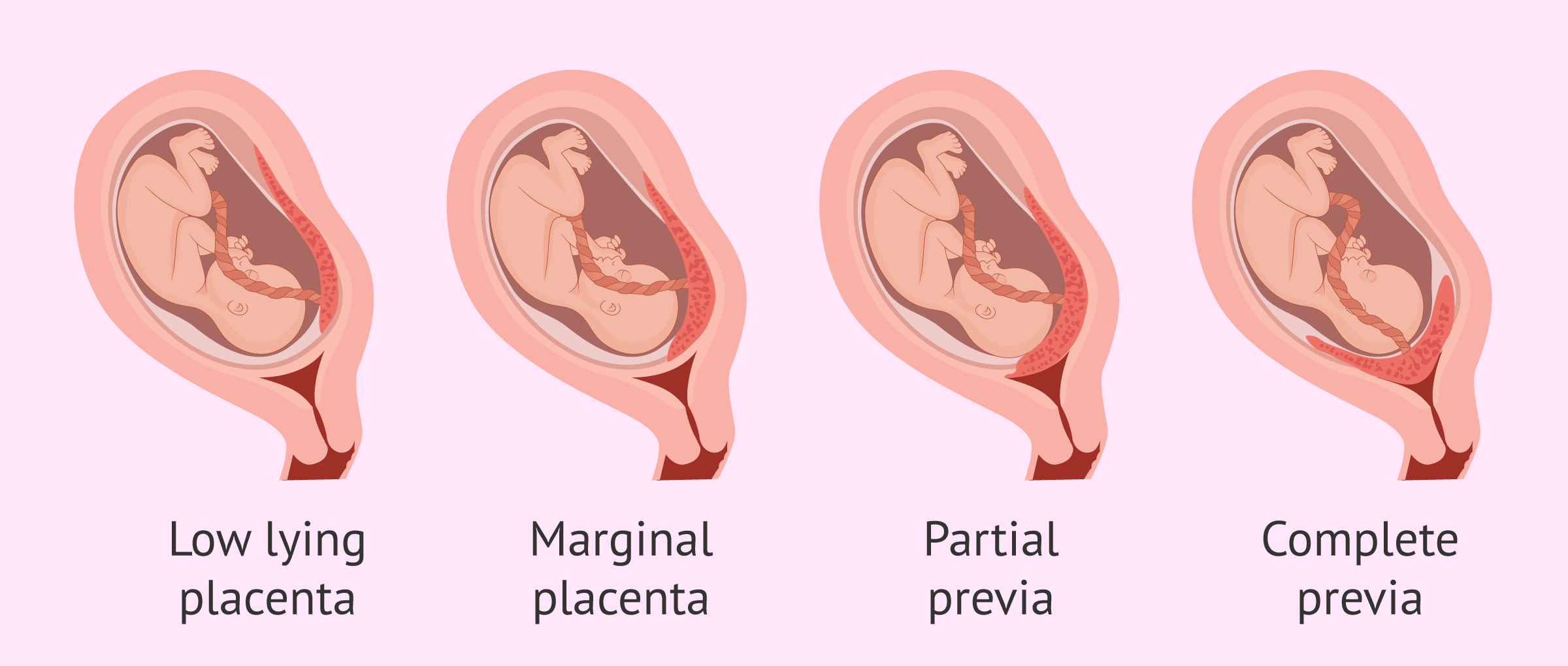
Placenta Previa
Abnormal positioning of the placenta in the lower part of the uterus, which may block the cervix.
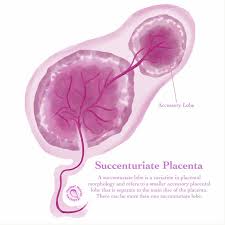
Placenta Succenturiata
Presence of an extra lobe of the placenta connected by blood vessels.
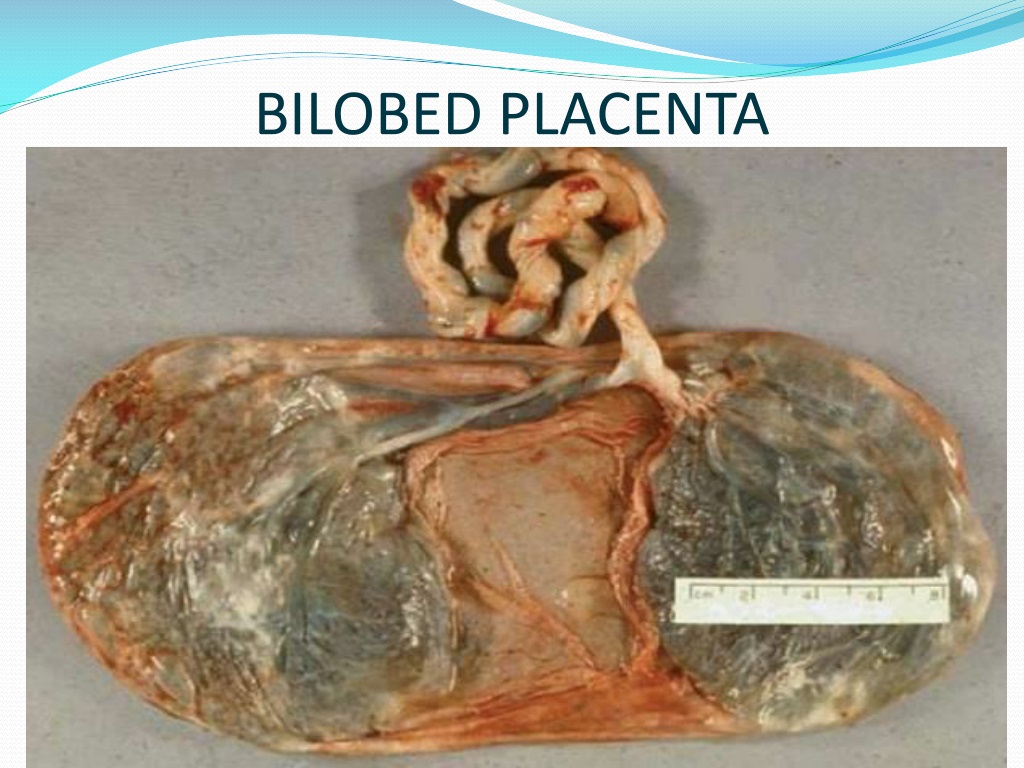
Placenta Bilobata (Bilobed Placenta)
Placenta divided into two lobes, either separated by membranes or connected by a tissue band.
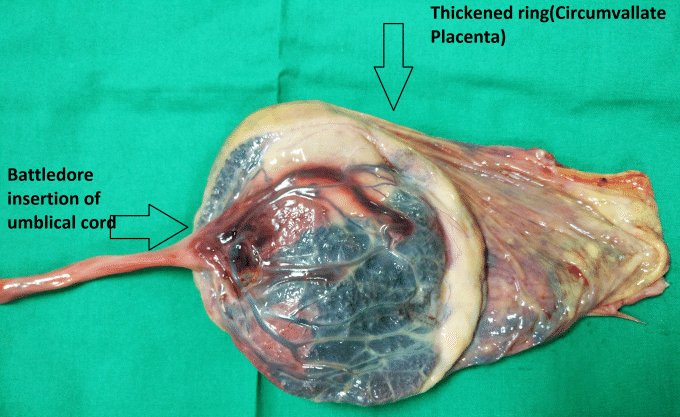
Circumvallate Placenta
Placenta with a ring-like fold of membrane around its edges, an abnormal shape.
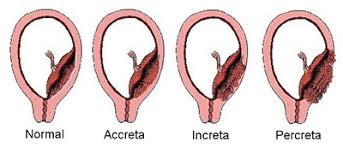
Placenta Accreta
Placenta attaches too deeply into the uterine wall, which may lead to complications during delivery.
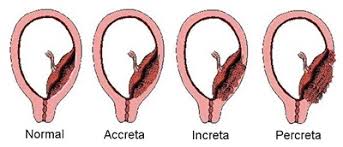
Placenta Increta
Placenta grows into the uterine muscle (myometrium), a more severe form of placenta accreta.
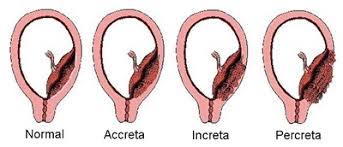
Placenta Percreta
Placenta penetrates through the entire uterine wall, potentially invading surrounding organs like the bladder.
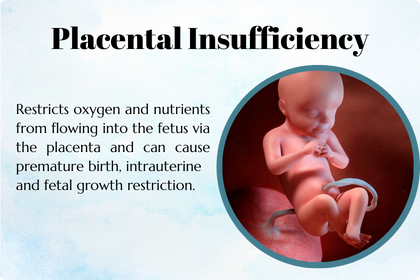
Placental Insufficiency
The placenta fails to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, potentially leading to slow growth, fetal distress, or preterm birth.
TYPES OF CORD ANOMALIES?
1. Velamentous Cord Insertion
2. Marginal Insertion of Cord "Battledore"
3. Single Umbilical Artery (SUA)
4. True Umbilical Cord Knot (TUCK)
5. Cord coil
6. Nuchal Cord
7. Cord Prolapse
8. Short Cord (<35cm)
9. Long Cord (80>cm)
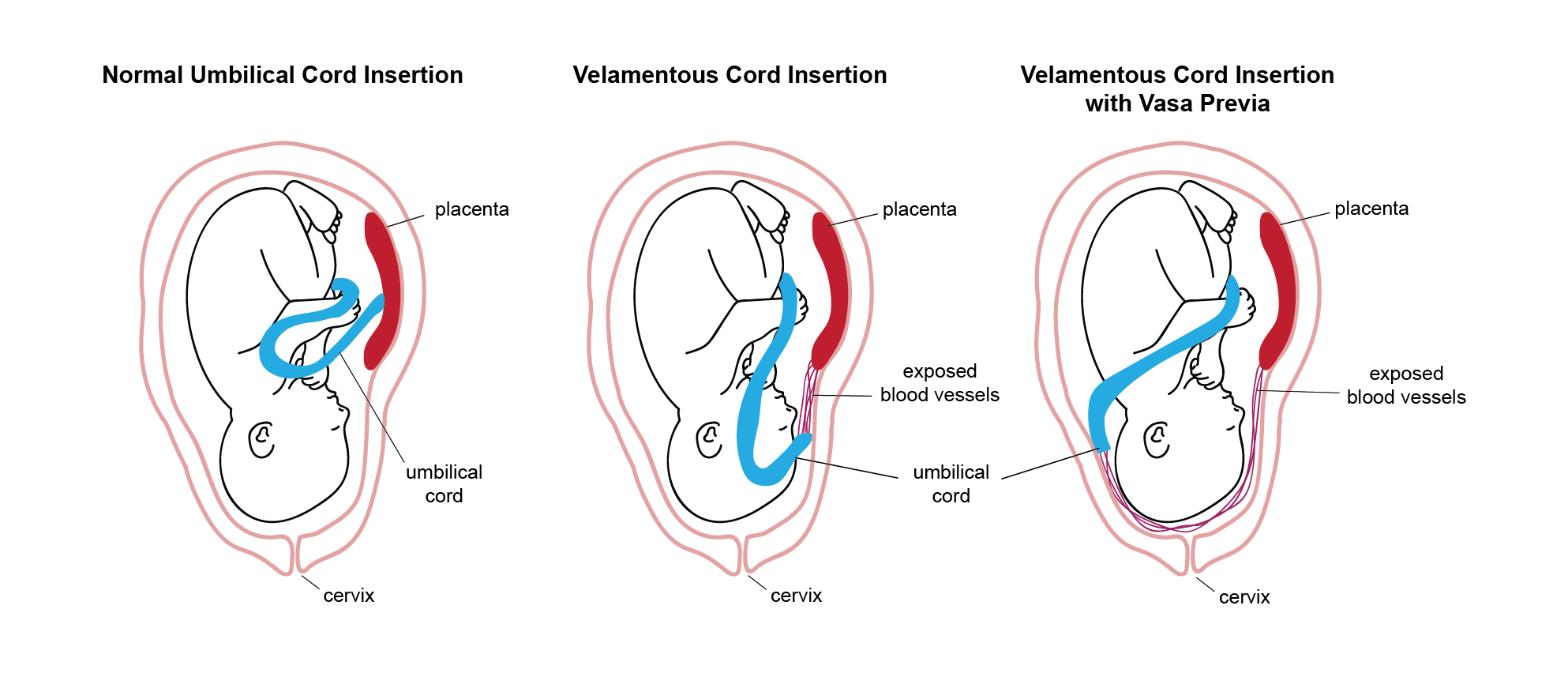
Velamentous Cord Insertion
The umbilical cord inserts into the fetal membranes, rather than directly into the placenta, increasing the risk of vessel rupture.
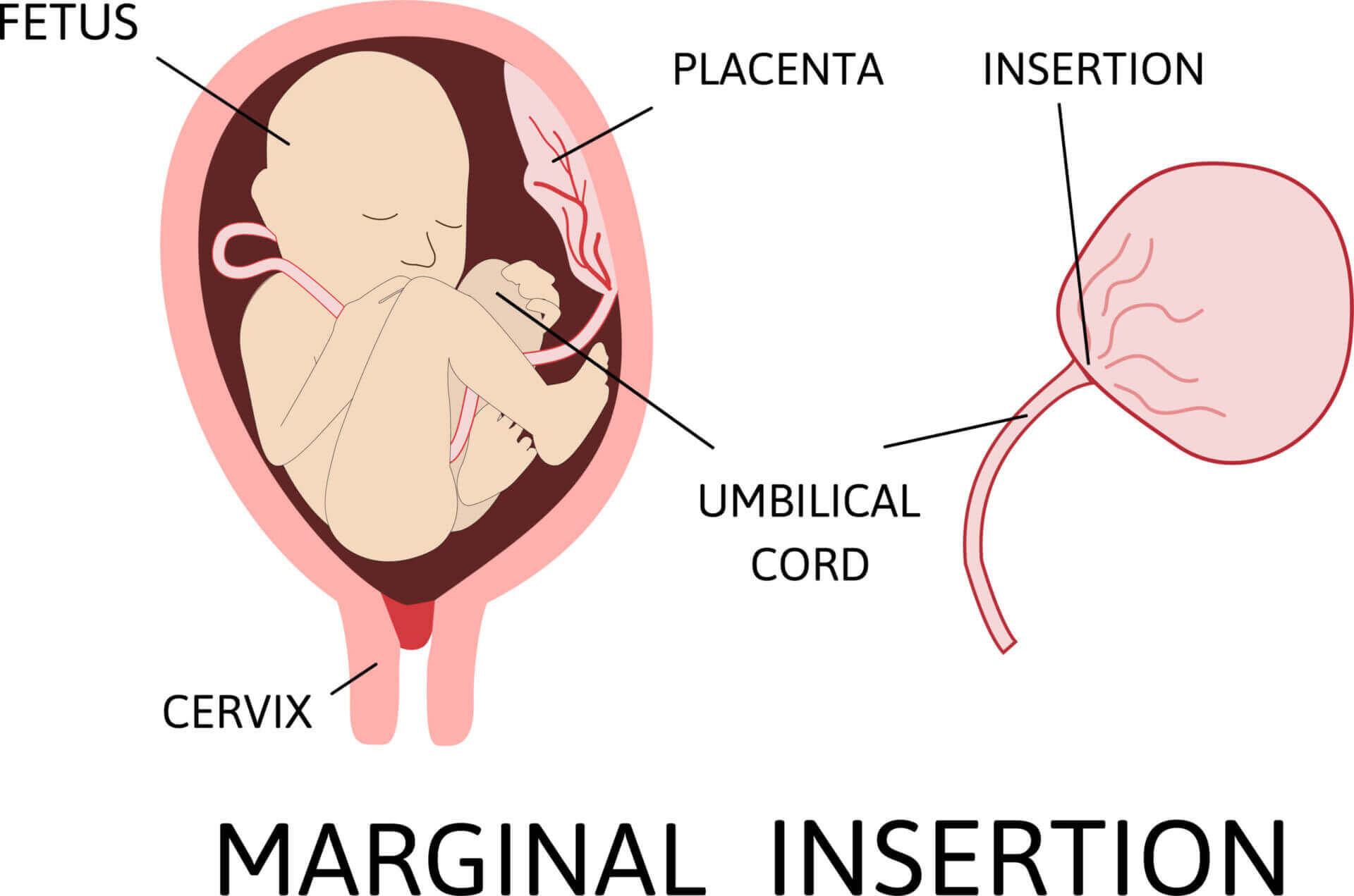
Marginal Insertion of Cord ("Battledore")
The umbilical cord attaches to the edge of the placenta rather than the center, which can lead to a higher risk of complications like premature birth.
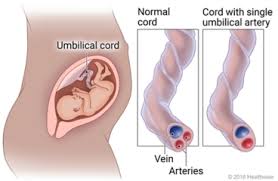
Single Umbilical Artery (SUA)
Only one artery instead of two is present in the umbilical cord, which can affect fetal development and be linked to congenital anomalies.
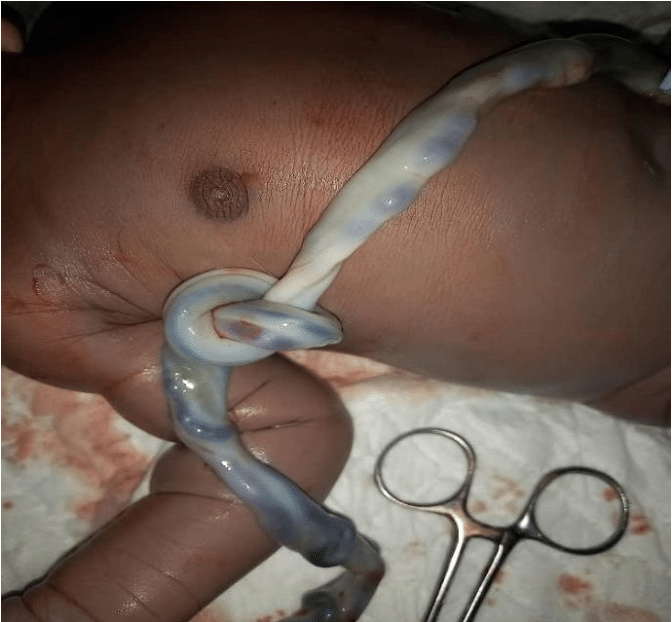
True Umbilical Cord Knot (TUCK)
A knot forms in the umbilical cord, potentially restricting blood flow and oxygen to the fetus, leading to complications like fetal distress.
Cord Coil
The umbilical cord twists around itself; if too tight, it can restrict blood flow to the fetus.
Types of Cord Coil?
1.Single Coil: One twist or loop of the cord around itself.
2.Multiple Coils: Several twists of the umbilical cord around itself.
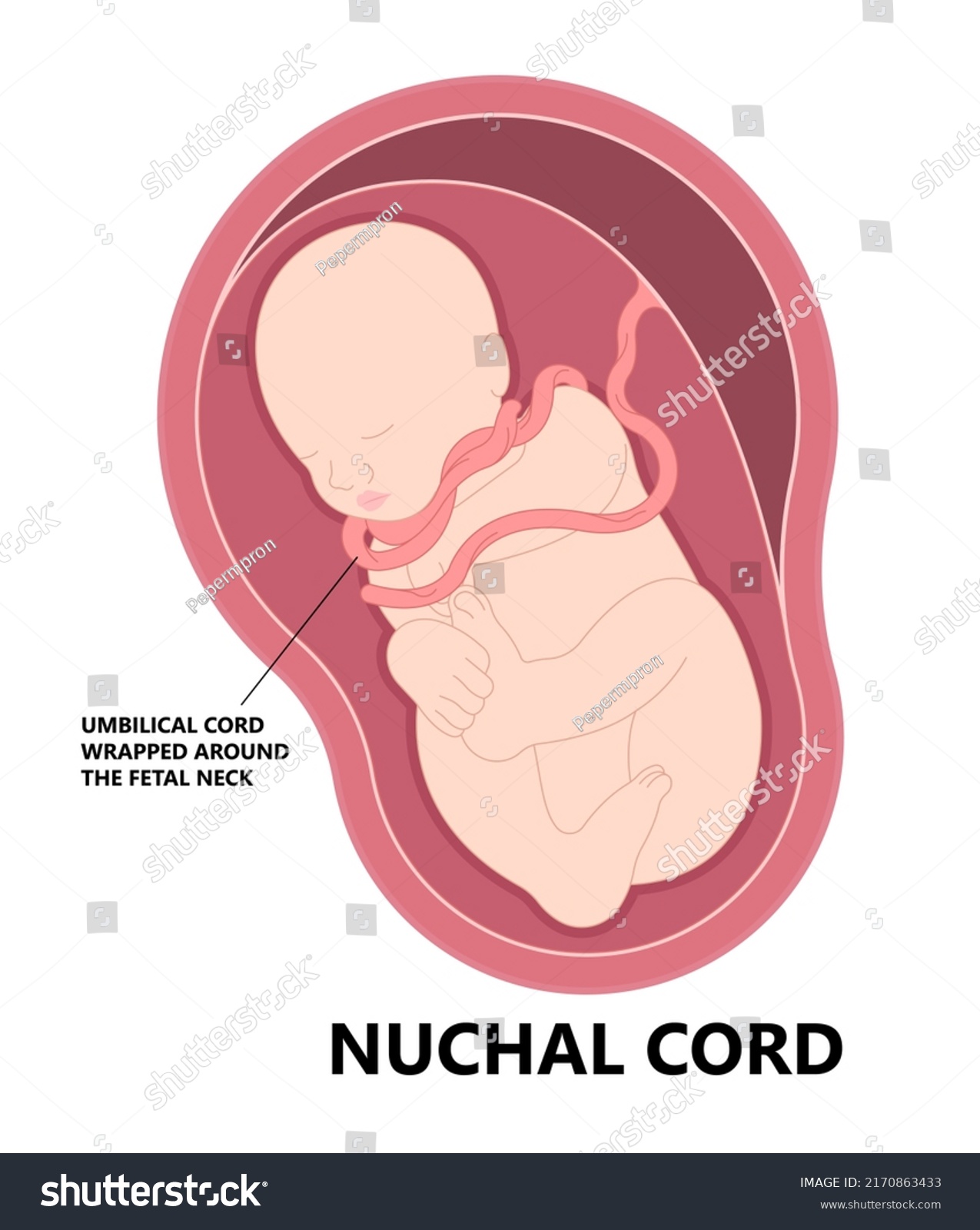
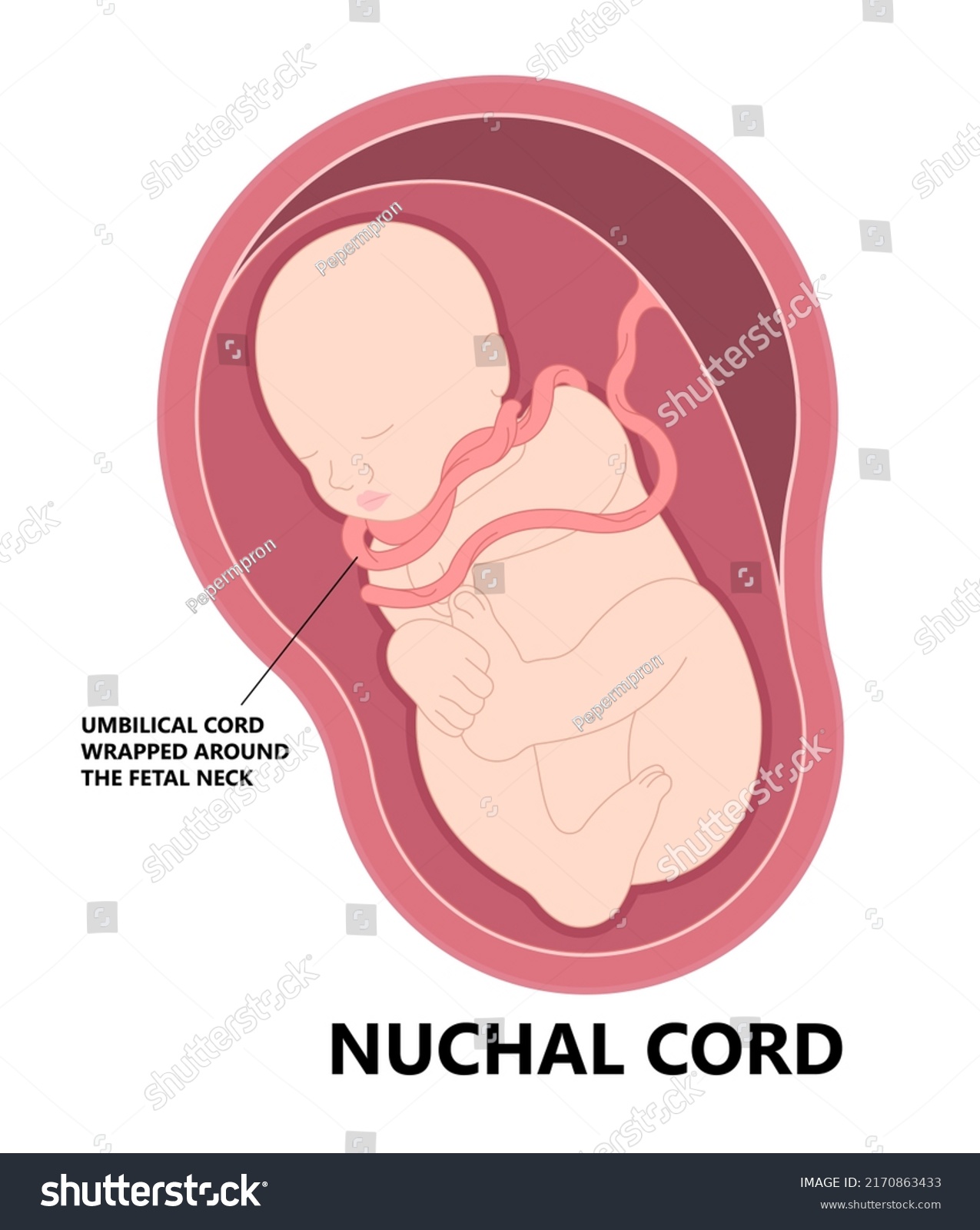
Nuchal Cord
The umbilical cord is wrapped around the fetus's neck, which may cause complications during delivery, such as cord compression.
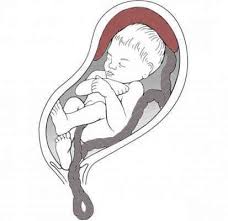
Cord Prolapse
The umbilical cord slips ahead of the baby in the birth canal, leading to compression and potential fetal distress during labor.
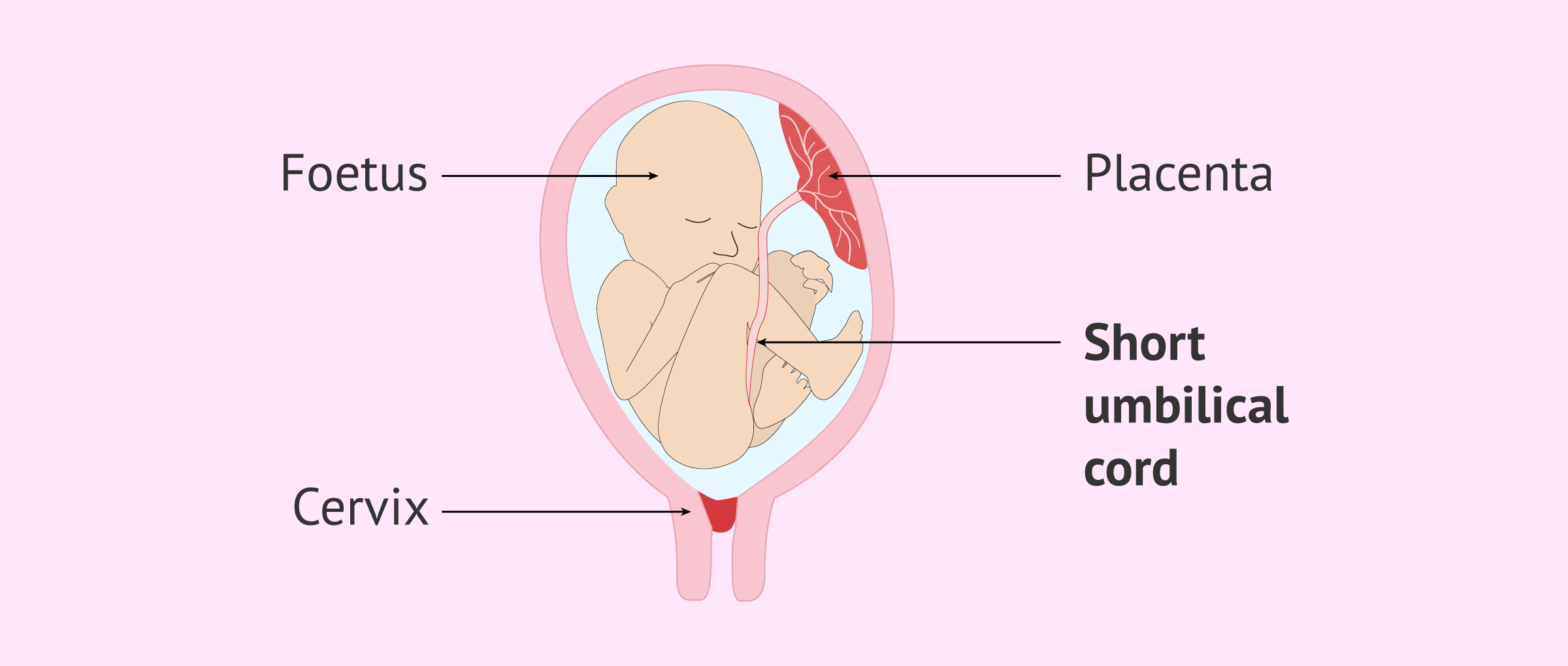
Short Cord (<35cm)
An unusually short umbilical cord, which can limit fetal movement and increase the risk of placental abruption or other complications.
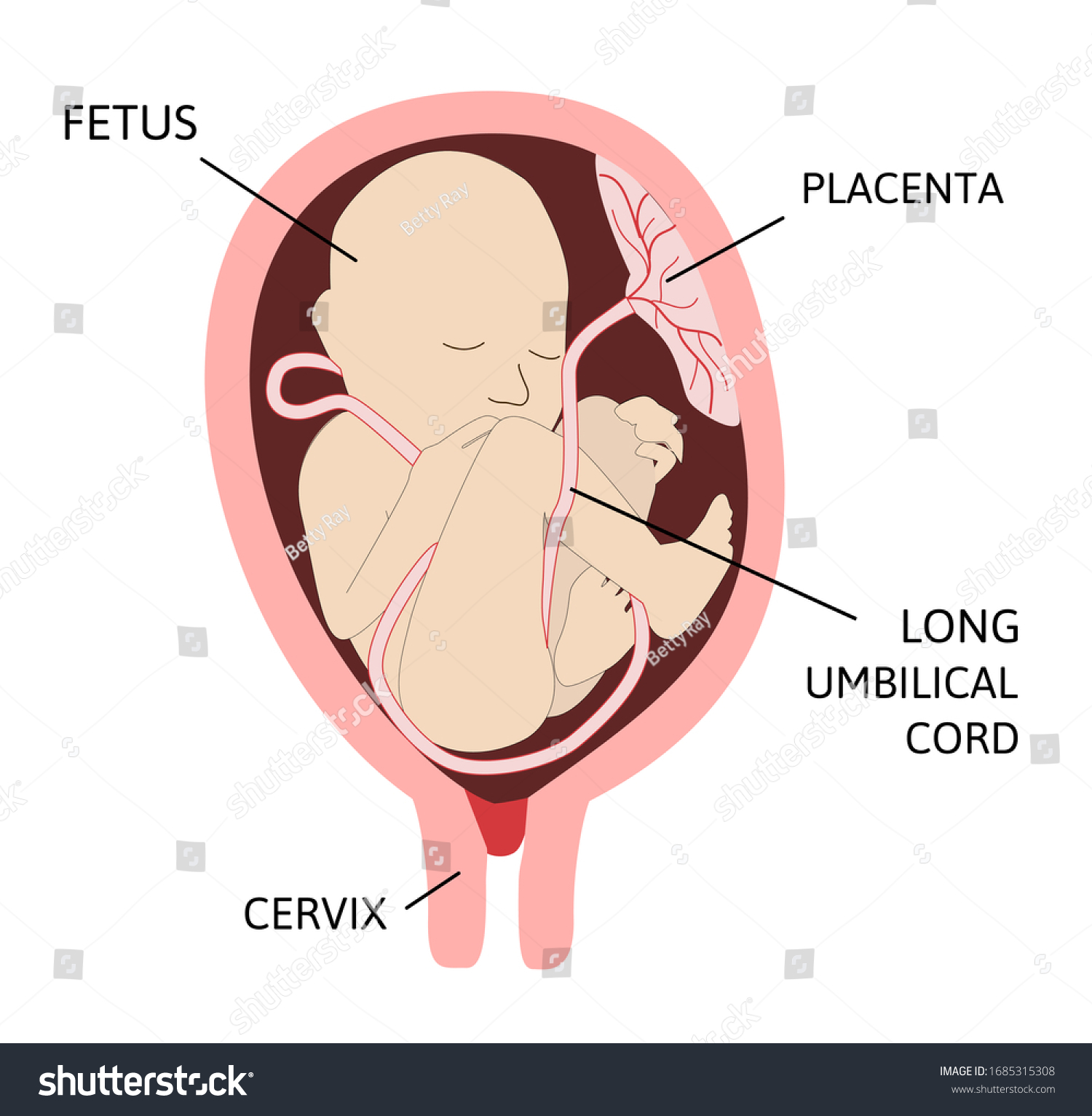
Long Cord (>80cm)
An unusually long umbilical cord, which increases the risk of cord prolapse, knotting, or entanglement.
Normal Length of Umbilical cord?
55-60 cm
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS of Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord?
- IUGR
- Fetal Distress
- Premature Labor
LABORATORY & DIAGNOSTIC TESTS of Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord?
- CBC
- Ultrasound
PHARMACOLOGIC MANAGEMENT of Anomalies of the placenta and umbilical cord?
- CORTICOSTEROIDS
- TOCOLYTICS
What are corticosteroids?
help stimulate surfactant production in the fetal lungs, promoting lung maturity and reducing the risk of breathing problems if the baby is born prematurely.
2 types of corticosteroids?
1. Betamethasone
2. Dexamethasone
What is Betamethasone?
Dosage: 12 mg IM every 24 hours for 2 doses.
Duration: Given for 48 hours to help the baby's lungs mature.
What is Dexamethasone?
Dosage: 6 mg IM every 12 hours for 4 doses.
Duration: Given for 48 hours to help the baby's lungs mature.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT for Anomalies?
1. CS
2. Hysterectomy
NURSING MANAGEMENT
ANXIETY r/t threat of preterm labor and fetal distress