Cytoskeletal proteins & inclusions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Learning objectives

protein filaments
dynamic, internal “skeleton”
three primary types
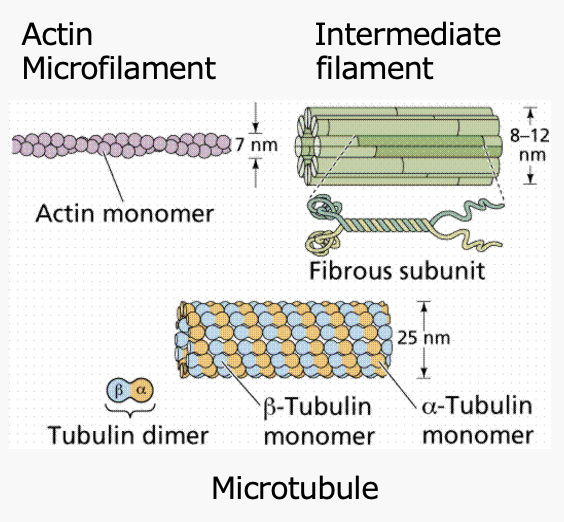
actin microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
differ in size & function
hundreds of cytoskeleton-associated proteins regulate distribution & behavior of cytoskeletal proteins
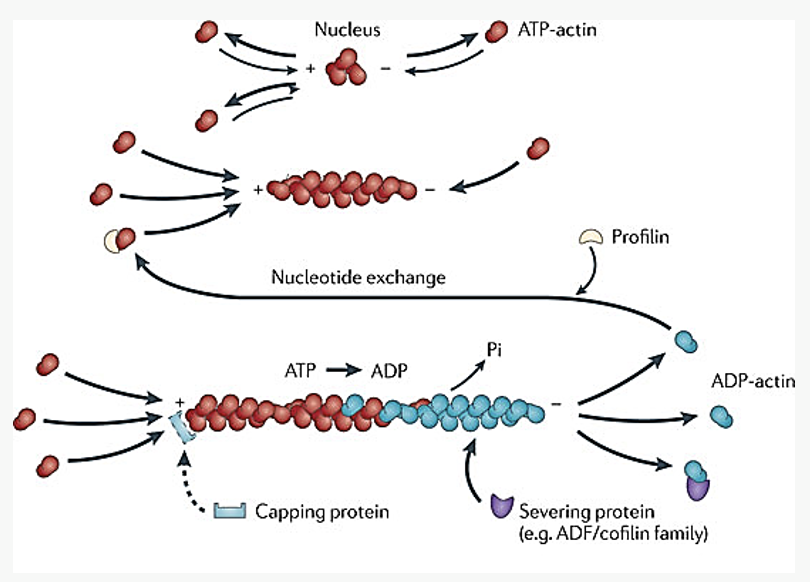
Actin filaments
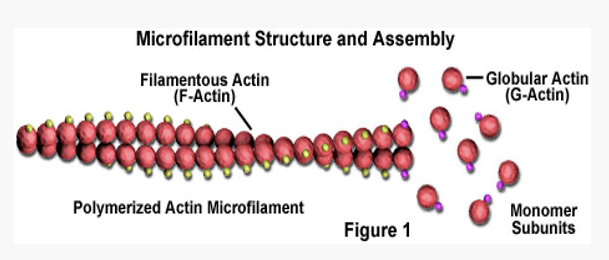
Thinnest component of cytoskeleton
Made of globular actin monomers
Each with ATP binding site
Polymerize into a microfilament (6-8 nm)
Two strings of beads twisted together
Monomers oriented in one direction producing polarity
“Plus end” and a “minus” end
Dynamic structures
“Plus” end is fast growing
“Minus” end is slow growing
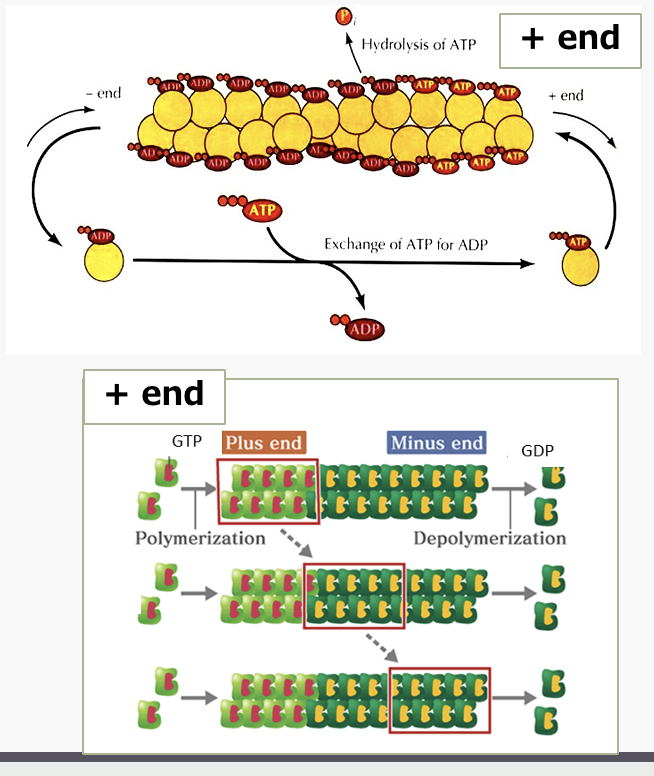
Microtubules
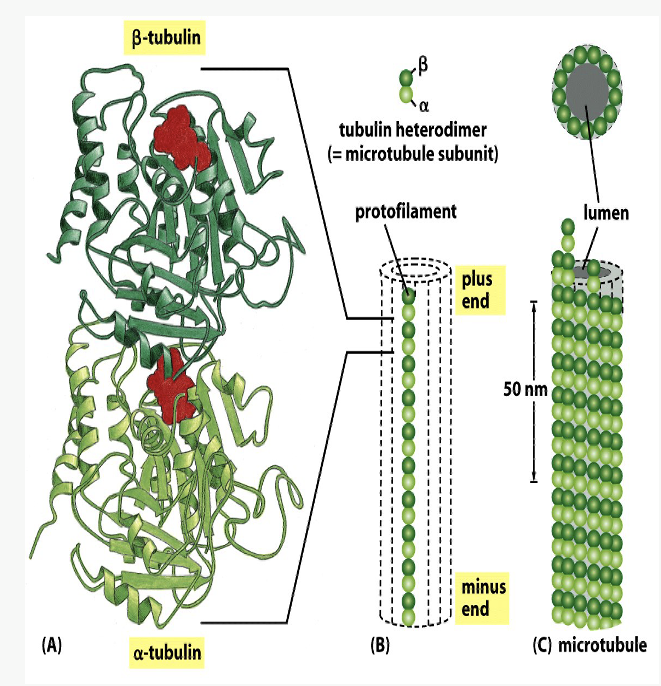
hollow, non-branching cylinders
Heterodimer made of alternating globular tubulin molecules
Alpha tubulin at “minus” end
Beta tubulin at “plus” end
Each beta-tubulin globule is bound to GTP
Each microtubule made of 13 parallel protofilaments
§Dynamic structures
“Plus” end is growing
“Minus” end is non-growing
nucleation site
Both actin filaments and microtubules grow from a _______ _____
Nucleation site
a cellular location or protein complex where the formation of new filaments, like actin and microtubules, is initiated.
(2 monomers bind weakly; 3 form a more stable group)
Binding of subunits causes hydrolysis of ATP (actin) or GTP (microtubules), which decreases strength of binding – dynamic instability
ADP/GDP molecule dissociates from minus end
Where is actin’s nucleation site most often found?
plasma membrane
Where are microtubules’ nucleation site most often found?
Microtubule organizing centers (MOC)
cytosolic proteins
_____ _____ can stabilize or destabilize actin filaments & microtubules
Some bind actin monomers or tubulin dimers
Prevent binding to filaments/tubules
Maintains reserve pool of monomers
Capping protein – stabilizes plus end of filament
Another protein severs the filament
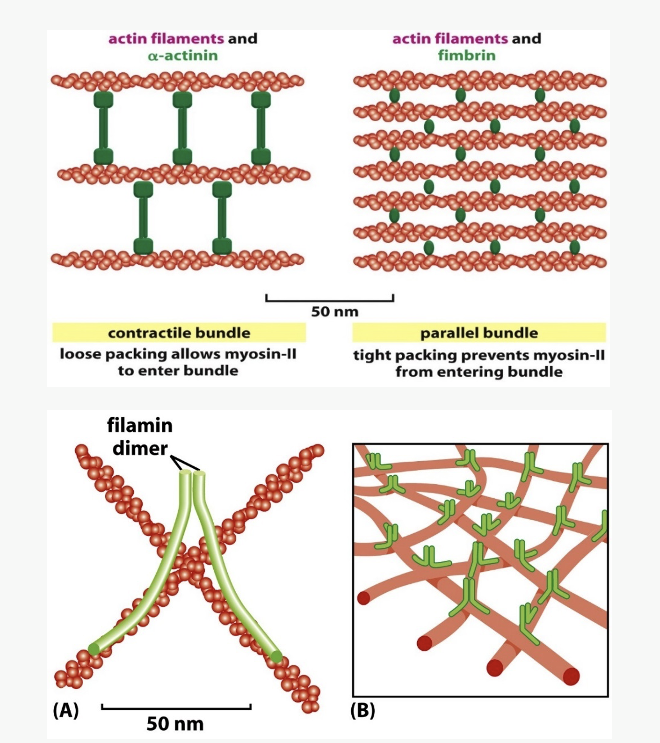
Bundling proteins
_____ _____ can provide stronger, stable actin structures
some promote nucleation at plasma membrane
some cross-link into parallel arrays
some bundle actin filaments at an angle to produce a web-like network
nucleus
Shape and number of actin filaments and microtubules is regulated by the ____ by altering the number of regulatory proteins
What are the functions of actin filament?
Maintains cell shape & anchors membrane proteins
Can provide either flexible or stable support
Motility
Scaffold for myosin (motor protein) in muscle cells
Cellular locomotion of other cells
Movement of vesicles
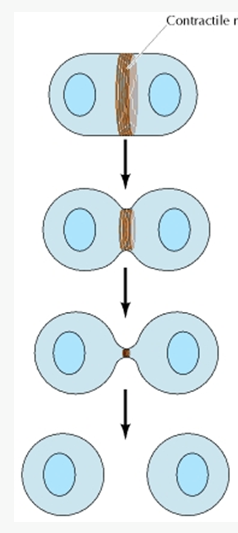
Cytokinesis after completion of mitosis
Myosin needed for contraction of ring
Actin bundles
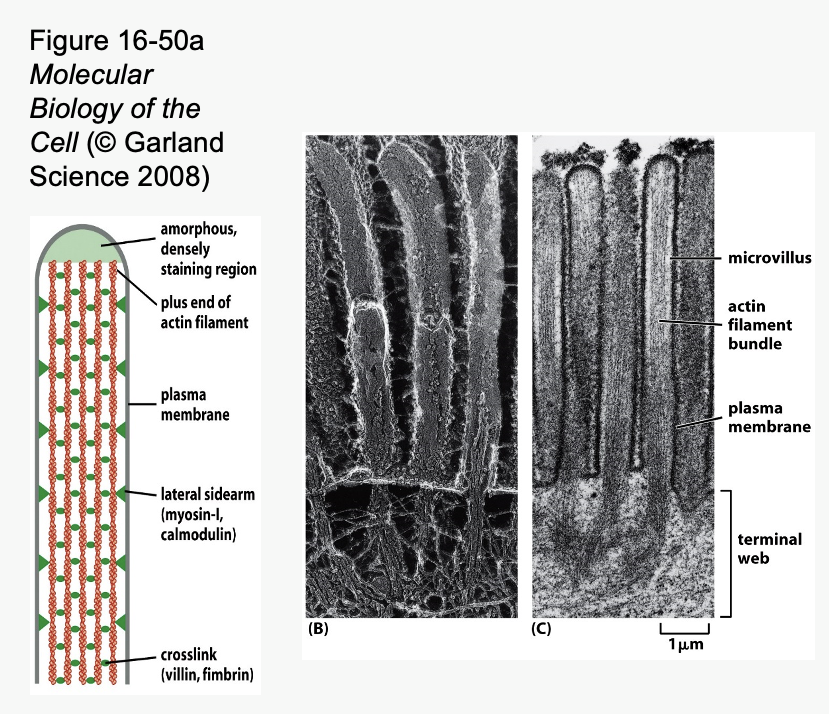
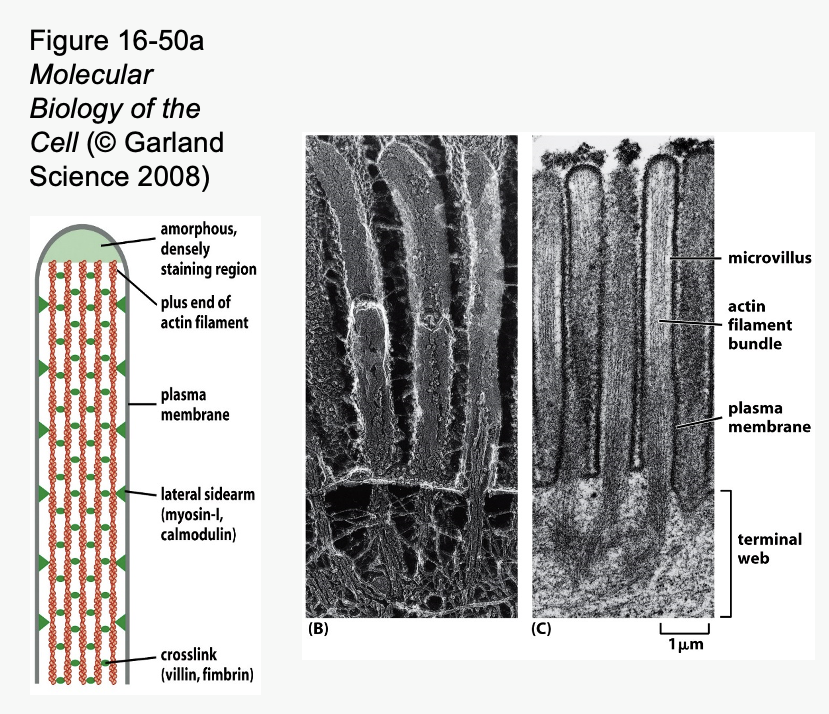
___ _____ in core of microvilli help them to remain upright
Microvilli are cell membrane projections that increase surface area
Particularly well developed in cells that absorb things
– Intestine
– Kidney
Microvilli are supported by stable bundles of actin filaments
Actin bundles are anchored to terminal web of actin at base of microvilli
Microvilli
cell membrane projections that increase surface area
Particularly well developed in cells that absorb things
– Intestine
– Kidney
are supported by stable bundles of actin filaments
myosin
____ produces cellular contraction by sliding actin filaments in opposite directions
Several types of myosin motor proteins
1-2 heads & a tail
Head repetitively binds and releases actin filament in a swinging motion, moving down filament
Hydrolyze ATP in process
Myosin can pull a vesicle along an actin filament
Myosin pulls 2 actin filaments toward each other to facilitate cell movement
1 anchored to back of cell
1 anchored further forward in cell
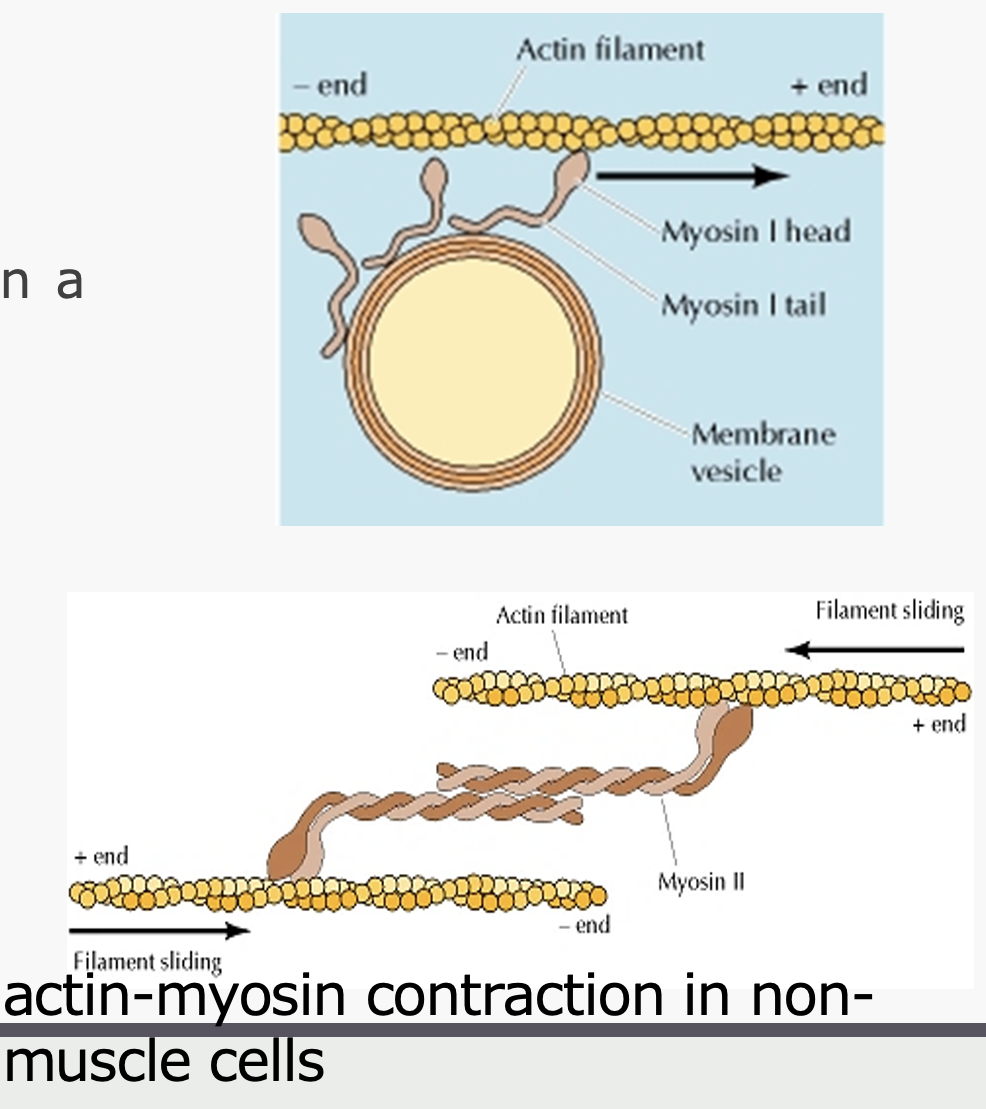
What are the functions of microtubules?
Functions
Cilia and flagella
Mitotic spindle
Cytostructural support – anchor organelles
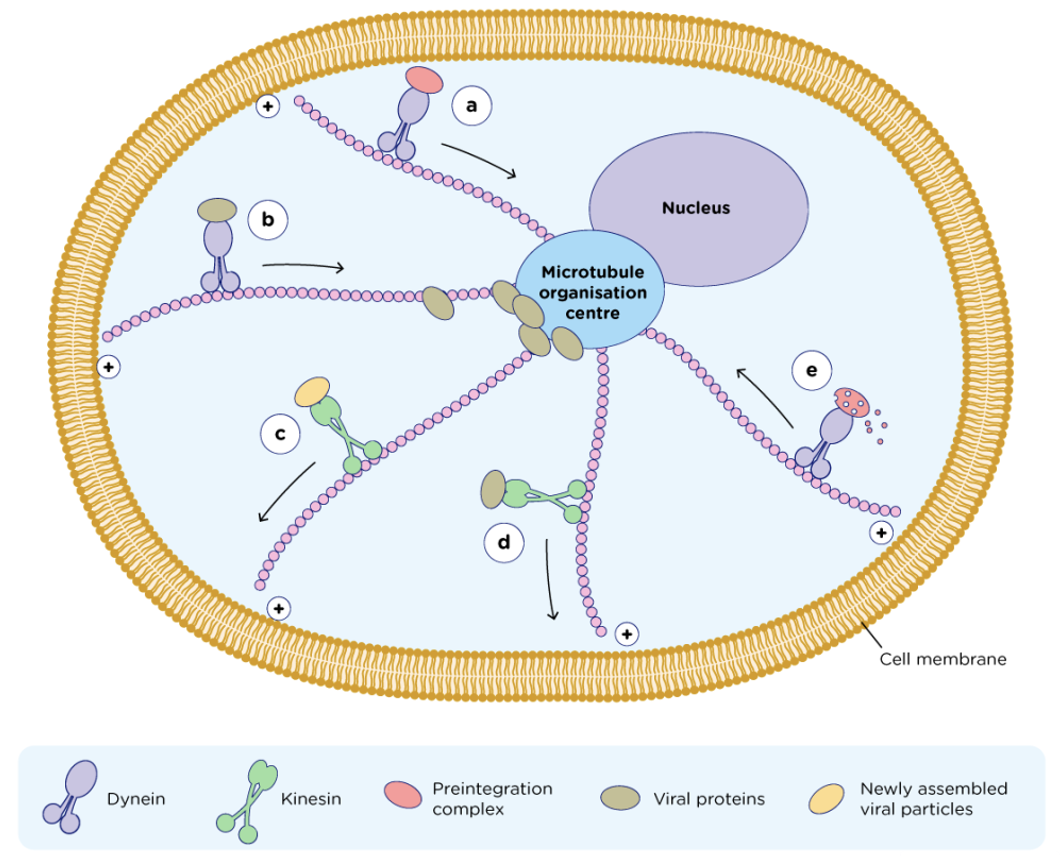
Motor proteins (dynein and kinesin) move vesicles along microtubular “railroad tracks”
Some chemotherapy drugs (e.g. vinblastine) suppress microtubule dynamics
Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOC)
Sites that localize microtubule minus ends
Microtubule nucleation (g-tubulin)
Stabilization & anchoring
Arrangement within cell
Arrangement of microtubules varies with cell type
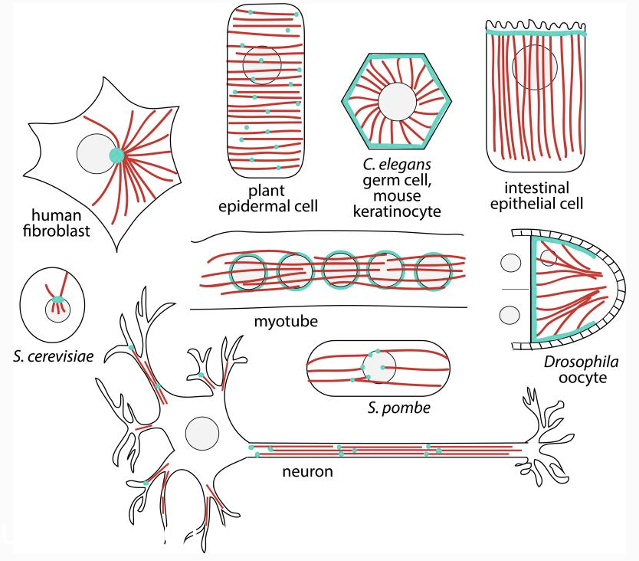
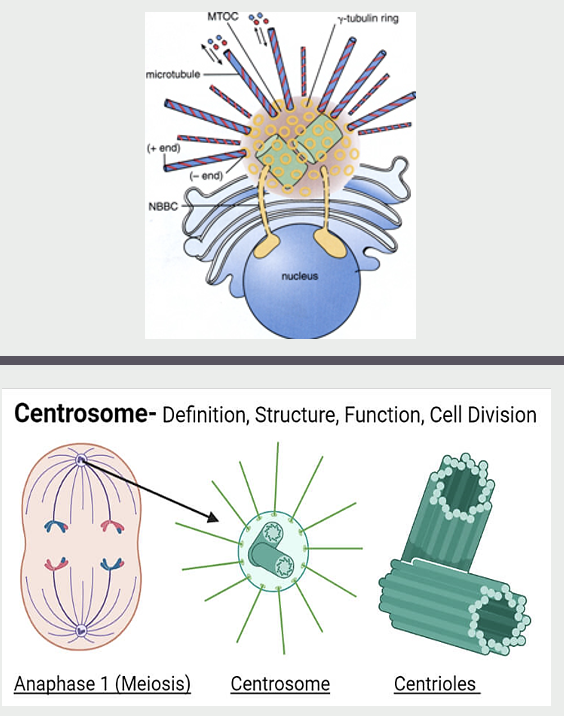
Centrosome
the best studied MTOC (microtubule organizing center)
Used by all cells for generating the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis
During mitosis, duplicated centrosomes serve as poles for mitotic spindle
Centriole contains 2 centrioles surrounded by a matrix of proteins
Short, rod-like, cylinders each built from 9 microtubule triplets.
Function is a mystery
Microtubules
Cilia (and flagella) are composed of ______
9 pairs of circularly arranged microtubule doublets
2 central microtubules (9+2)
Linker proteins
Arise from basal body (nucleation site)
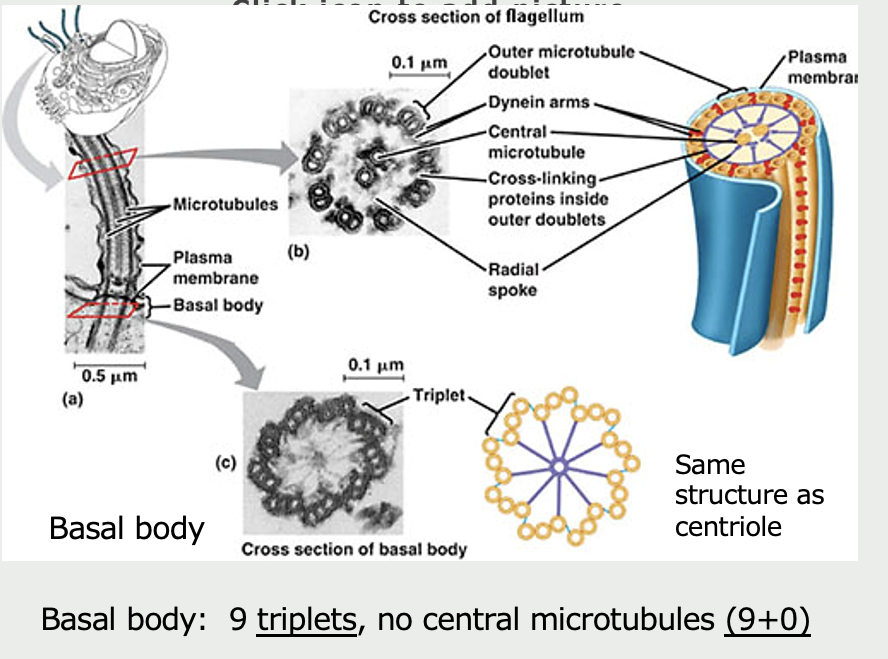
Movement along microtubules are mediated by which motor proteins?
Dynein and kinesin
two globular ATP-binding motor heads and a tail
move only in one direction along microtubule
Dyneins move toward "-” ends (e.g. toward nucleus)
-cause cilia to bend by sliding microtubules past each other
Kinesins move toward “+” ends (away from nucleus)
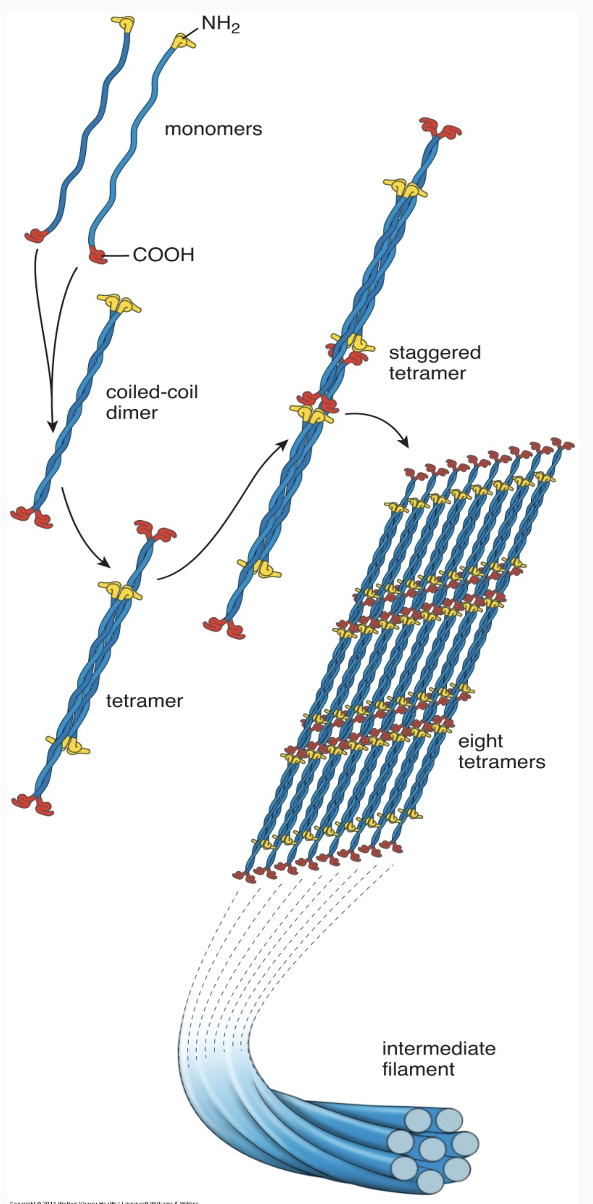
Intermediate Filaments
Structural role
Stable rope-like filaments (8-10 nm)
Unlike most microtubules and actin filaments, they do not typically disappear and re-form (Generally lack dynamic instability)
Exception: Lamins in nucleus disassemble before mitosis
Functions
Maintain cell shape
Cell-cell junctions
Cell-matrix junctions
Cell-cell communication
tissue types
The type of intermediate filament varies by ____ ____
epithelial cells = cytokeratins
mesenchymal cells (connective tissue, muscle) = vimentin & desmin
nerve cells = neurofilaments
nucleus (all cells) = lamins
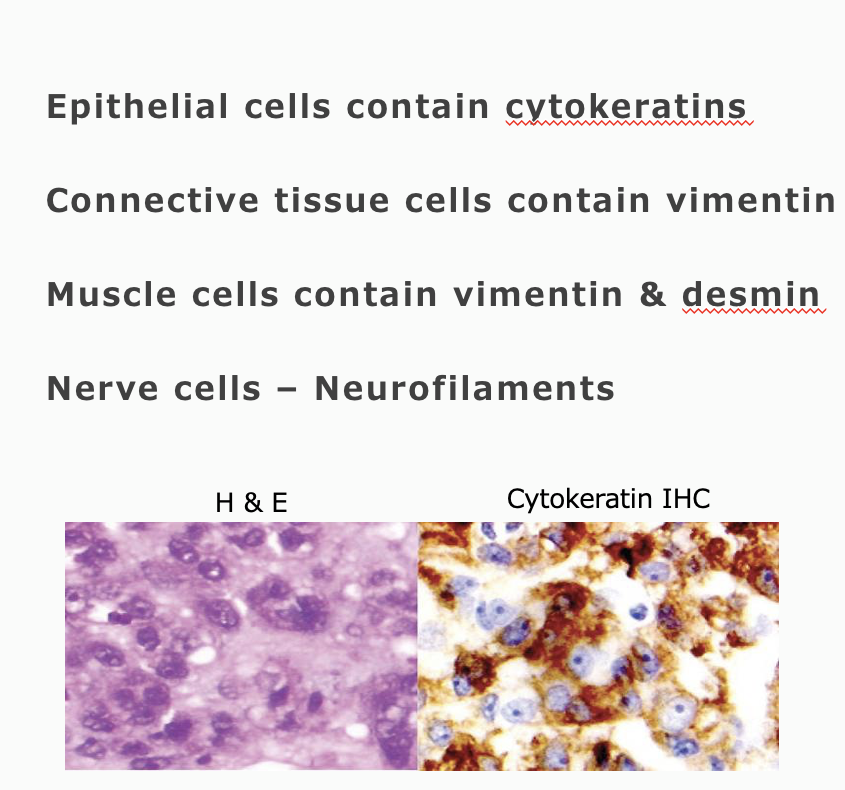
Brown color = presence of cytokeratin = epithelial tumor → carcinoma
Pathologists can often identify a tumor’s tissue of origin by examining how its cells are arranged, but some tumors are too poorly differentiated to determine this by appearance alone. Knowing the origin is important because it influences treatment choices (e.g., radiation for connective tissue tumors, chemotherapy for epithelial tumors). To help identify the tissue type, immunohistochemistry is used: antibodies tagged with peroxidase bind to specific intermediate filaments in the cells. When a substrate is added, peroxidase produces a brown color wherever binding occurs. For example, if cells stain brown with a cytokeratin antibody, the tumor is confirmed to be epithelial in origin, though further tests are needed for a more specific diagnosis.
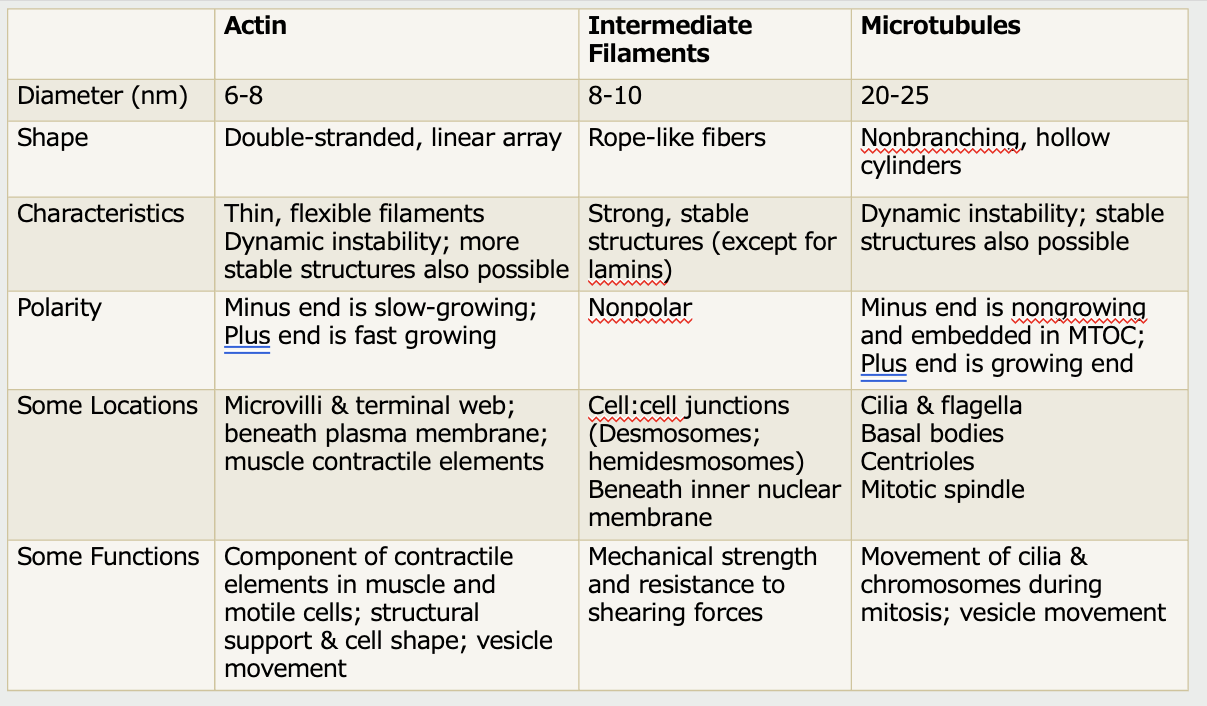
Cytoskeleton Functions (Summary)
Stabilizes plasma membrane & maintains cell shape (A)
Hold cells together (A; I)
Anchor organelles (A; T)
Movement of vesicles (A; T)
Cell movement (A)
Changes during mitosis
–Segregation of chromosomes (T)
–Pinching cell apart into two new cells (A)
******************************************************
A = actin; I = intermediate filaments; T = microtubules
Pink lines represent actin filaments; Green lines represent microtubules
Motor proteins are needed to move vesicles
Inclusions
_____ are inert, NOT metabolically active
Examples
melanin
lipofuscin (wear and tear pigment)
hemosiderin (iron stores; from hemoglobin breakdown)
glycogen (glucose stores)
lipid
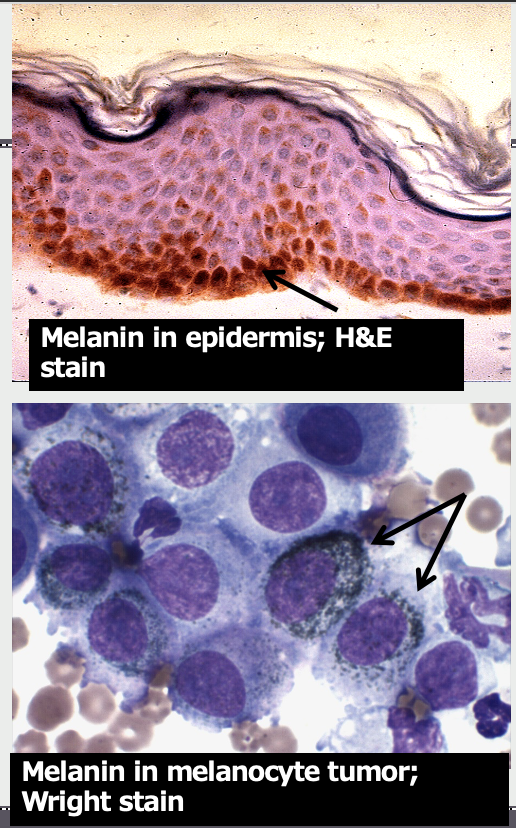
Melanin
____ produced by melanocytes but transported into adjacent epithelial cellls
grossly: brown to black (eumelanin) or yellow-reddish (pheomelanin)
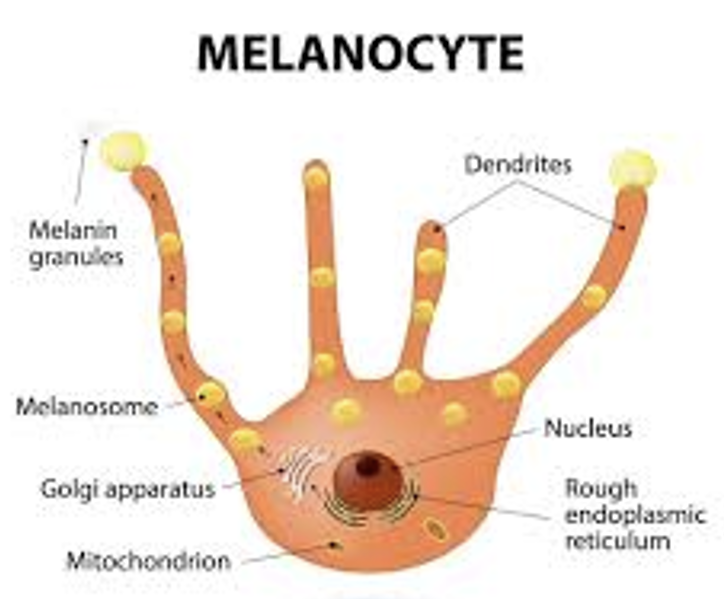
eumelanin
brown to black
pheomelanin
yellow-reddish
What are the functions of melanin
protection against UV radiation, heat, and chemical damage
coat and feather coloration
ink used by many cephalopods
In which normal canine tissues might you find melanin pigment?
hair
lips
skin
eyelids
gums
Microscopic appearance of melanin depends on stain used. In H&E stain, it is a _____ pigment
brown
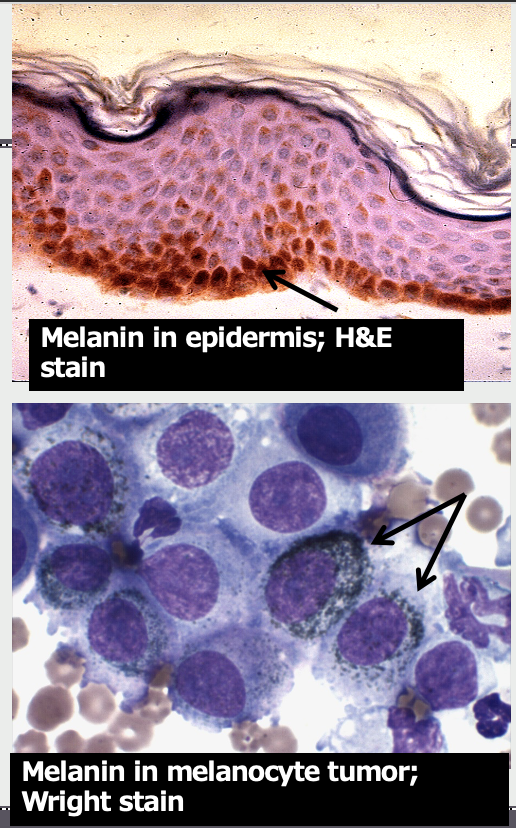
Microscopic appearance of melanin depends on stain used. In a Wright (Romanowsky) stain, it is a _____ pigment
often dark green, green-grey
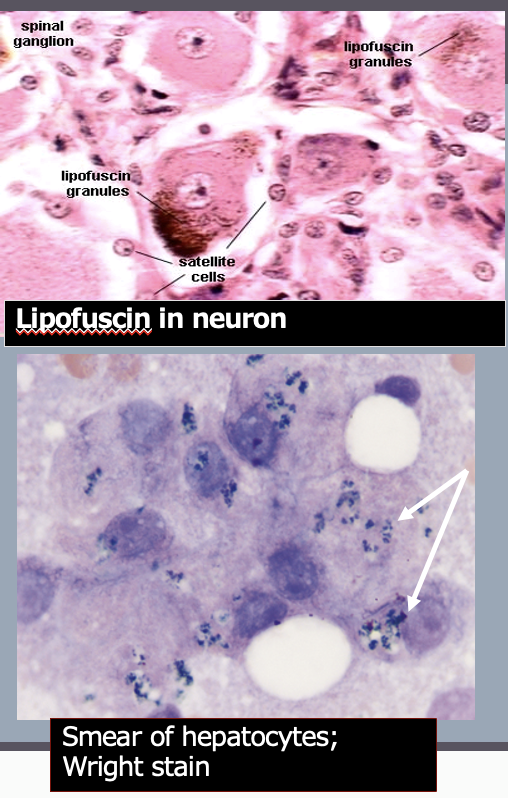
Lipofuscin
“wear & tear pigment”
From oxidative breakdown of mitochondria and lysosomal digestion
Common in cells with high metabolic rate
Liver
Neurons
Muscle
Appearance depends on stain used
H&E: Brown pigment
Wright (Romanowsky) stain: dark green
****If they look the same, how do you know if it is melanin or lipofuscin (—> based off of location/what cell is the pigment in? = if epithelium, more than likely it is melanin)
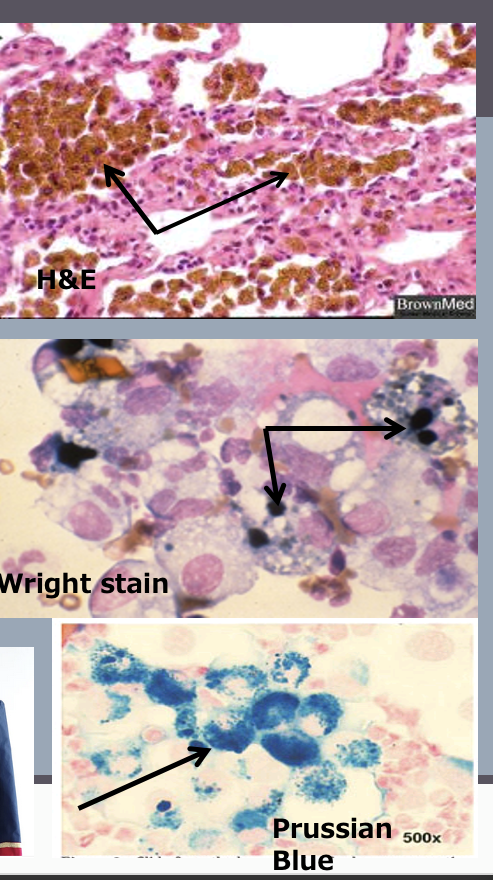
Hemosiderin
iron storage molecule, partly derived from breakdown of RBCs
usually found in macrophages
especially in spleen +/- bone marrow
seen in any tissue after hemorrhage
appearance depends on stain
fixed H&E stain: yellow-brown chunky pigment
cytology smear Wright stain: blue-green
Prussian blue stain can be used to stain the iron turquoise
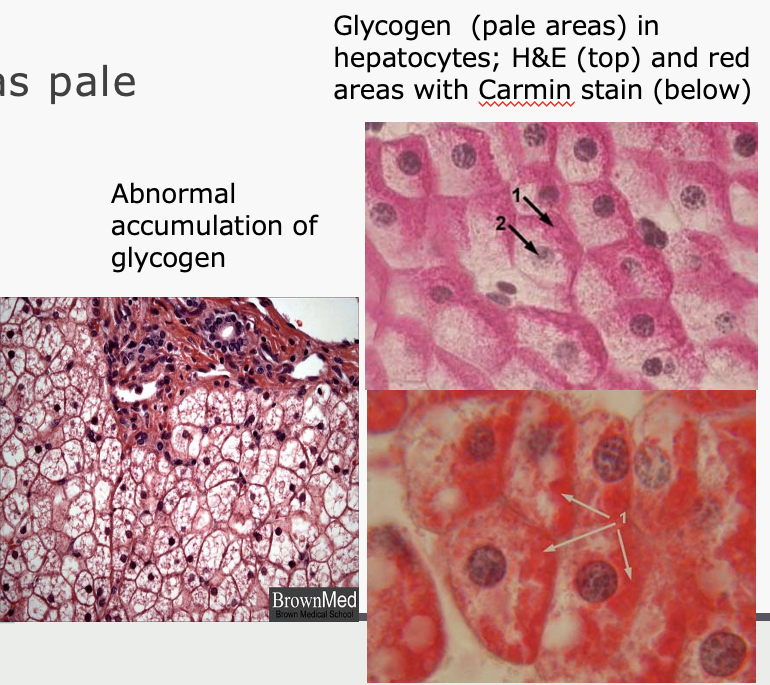
glycogen
storage form of glucose
not stained by H&E (appears as pale areas or vacuoles)
stains for glycogen
Carmin (red) - specific for glycogen
PAS (pink) - stains all carbohydrates
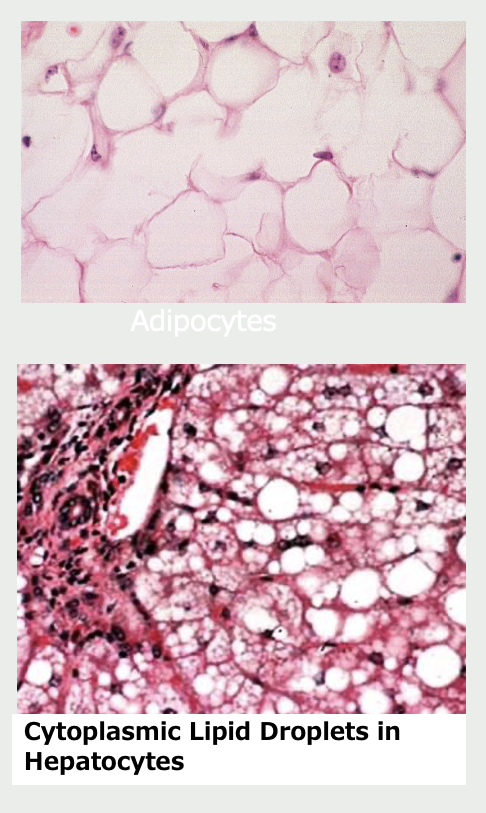
Lipid
fat droplets
found in
adipocytes (fat cells)
steroid hormone producing cells
some types of glands
extracted during processing so appear vacuoles