NSG 2000- Exam #2
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Chain of infection
a chain of necessary pieces needed for an infection to occur and includes the following links:
1. infectious agent
2. reservoir
3. portal of exit
4. mode of transmission
5. portal of entry
6. susceptible host
Infectious agent
something that contains bacteria, fungi, virus, parasite, or prion
Reservior
the habitat of the infectious agent; a location where it can live, grow, and reproduce itself or replicate
Portal of exit
the means by which the infectious agent can leave the reservior
Modes of transmission
the moving of bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and prions from place to place; these are contact, droplet, and airborne
Portal of entry
any body orifice, such as ears, nose, mouth, or even the skin, and provides a place for the infectious agent to replicate or for toxin to act; include invasive lines and devices
Susceptible host
required for the infectious agent to take hold and become a reservoir for infection; not everyone who is exposed to an infectious agent will get ill; some people never exhibit manifestations at all but can becomes colonized (temporarily or permanently) with the infectious agent
Virulent
how effective the infectious agent is at causing illness
Factors that increase host susceptibility
1. age
2. underlying disease
3. HIV/AIDS
4. malignancy
5. transplants
6. medications
7. surgical procedures
8. radiation therapy
9. indwelling devices
Direct contact transmission
occurs when microorganisms are directly moved from an infected person to another person, rather than through a contaminated object or person
Indirect contact transmission
occurs when microorganisms are directly moved from the infected person to another person with having a contaminated object or person between these two
Droplet transmission
occurs when droplets from the respiratory tract of a client travel through the air and into the mucosa of a host; include:
1. norovirus
2. rhinovirus
3. covid
4. influenza
5. pertussis
Airborne transmission
occurs when small particulates move into the airspace of another person; include:
1. tuberculosis
2. rubeola (measles)
3. varicella (chickenpox)
Vehicle transmission
transmission of infectious agents to various individuals through a common source, such as contaminated food or water
Vector-borne transmission
transmission of infectious agents through animals, such as an insect or a rodent
Nonspecific immunity
comprised of neutrophils and macrophages and their work at phagocytes
Phagocytes
eat-and-destroy microorganisms, thereby helping to protect the body from harm
Specific immunity
the work of antibodies (immunoglobins) and lymphocytes
Inflammatory response
natural defense of the body when injured, when foreign substances are present, or when infectious agents attack
Infectious triggers
1. viruses
2. bacteria
3. other microorganisms
Noninfectious triggers
1. physical: burns, frostbite, injury, foreign bodies, trauma, radiation
2. chemical: glucose, fatty acids, toxins, alcohol, irritants (e.g. fluoride, nickel)
3. biological: damaged cells
4. psychological: excitment
Manifestations of swelling
1. heat
2. redness
3. swelling
4. pain
5. loss of function (potentially)
Stages of infection
1. incubation
2. prodromal
3. acute illness
4. period of decline
5. period of convalescence
Incubation
first stage of infection in which the client might not feel ill or have visible manifestations
Prodromal
second stage of infection when client begins having initial manifestations as the infectious agent replicates
Acute illness
third stage of infection where manifestations of a specific infectious disease process are obvious; most severe stage
Period of decline
fourth stage of infection when manifestations begin to wane as the number of infectious disease decreases
Period of convalescence
fifth/last stage of the infection when the client returns to normal or a "new normal" state of health
Local infections
infections confined to one area of the body
Systemic infections
start as local infections and then transmit into the bloodstream to infect the entire body system
Antiseptic agents
1. alcohols
2. chlorhexidine
3. chlorine
4. chloroxylenol
5. hexachlorophene
6. iodine/iodophors
7. quaternary ammonium compounds
8. triclosan
Medical asepsis
cleaning technique practices that reduce the presence of disease-causing microorganisms on surfaces
Surgical asepsis
cleaning techniques that ensures the sterility of items that will come in contact with the client, through use of equipment such as sterile gloves, in order to prevent pathogen transfer to the client
Sterilization
cleaning instruments so that all microorganisms, including bacterial spores are eradicated
Sterile field
created to assure that the smallest number of microorganisms possible are present; used for procedures where surgical asepsis is indicated
Disinfection
cleans instruments so that almost all microorganisms are eradicated but not all; high level and low level
Standard precautions (universal precautions)
infection prevention practices that apply to all clients, whether or not they are known to have an infectious agent
Contact precautions
precautions used when a client has an infectious agent that can be transmitted by direct or indirect contact with body secretions; requires a minimum of gown and gloves prior to client interactions; patient must be in private room or cohort with same organism
Droplet precautions
precautions used when a client has an infectious agent that can be transmitted by large particles over close distance; requires donning a mask when entering the client room or coming into close contact with a client; patient must be in private room or cohort
Airborne precautions
precautions used when a client has an infectious agent that can be transmitted through the air and should don an N95 mask or a high-level respirator when entering the room of a client; patient must be in private negative air pressure room and cannot cohort!
Airborne infection isolation room
AIIR room; single-client rooms built with special air handling and ventilation to provide a negative pressure; also, a negative pressure room; 6-12 exchanges via HEPA filter per hour
Protective isolation
isolation used during approximately the first 100 days after the transplant; specific engineering and hospital designs that decrease the risk of environmental fungi to the client who had HSCT
Health care-associated infections (HAIs)
infections that are acquired in a health care facility; often preventable; increase length of stay, cost, and mortality; major ones include:
1. central line-associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs)
2. catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs)
3. surgical-site infections (SSIs)
4. ventilator-assisted pneumonias (VAPs)
Infection control bundles
guidelines for practice that are bundles together to prevent HAIs such as CAUTIs, CLABSIs, VAPs, and SSIs; "care bundles"
Multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs)
bacteria that are resistant to one or more classes of existing antimicrobials
Enhanced barrier precautions
nursing home staff must wear gown and gloves to prevent transfer of organisms to themselves or their clothing when engaging in certain client care activities
Closed-glove technique
technique to don sterile gloves using surgical asepsis after the individual has performed a surgical hand scrub and donned a sterile gown; hands are kept inside the sterile gown until gloves are donned
Open-glove technique
technique to don sterile gloves using surgical asepsis; gloves are touched directly with the hands
Abdomen
xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis; divided into 4 quadrants
RUQ
contains the:
1. liver
2. pancreas
3. gallbladder
4. ascending colon
5. some of the kidneys
LUQ
contains the:
1. stomach
2. spleen
3. pancreas
4. transverse colon
5. intestines
LLQ
contains the:
1. small and large intestines
2. left reproductive organs
RLQ
contains the:
1. appendix
2. intestines
3. right reproductive organs
Midlines
contains the:
1. bladder
2. uterus
Liver, pancreas, gallbladder, ascending colon, and kidneys
organs of the RUQ
Stomach, spleen, pancreas, transverse colon, kidneys, and intestines
organs of the LUQ
Small and large intestines and reproductive organs
organs of the LLQ
Appendix, intestines and reproductive organs
organs of the RLQ
Bladder and uterus
organs in the midline
Referred pain
symptoms do not always occur in the quadrant of the organ of pathology
Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation
order of assessment for abdominal
Tips for abdominal assessments
1. warm up hands
2. have patient empty bladder
3. lay supine or side
4. place pillow under hand and knees
5. identify and assess tender areas last
Hinderances to abdominal examinations
1. clothing
2. surgical incisions and wounds
3. self-consciousness
4. ticklishness
5. cold hands
Peristalsis
bowl/digestion movements
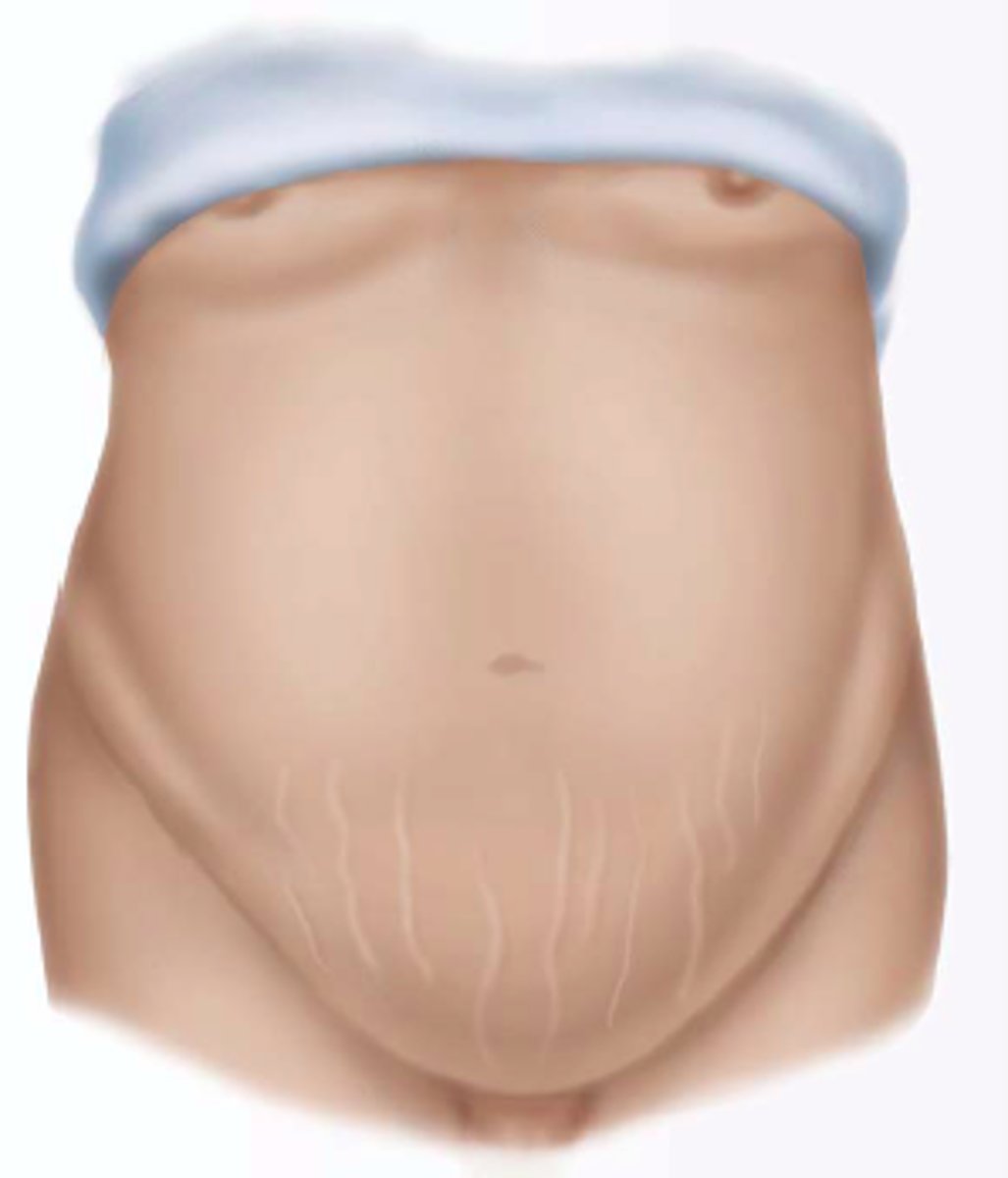
Striae
stretch marks
Cullen sign
ecchymosis; bruising around umbilicus; sign of bleeding in the peritoneal cavity or parancitis
Gray turner
ecchymosis in the flank; sign of bleeding in the peritoneal cavity or parancitis
Gravid
the shape of a pregnant woman's abdomen
Scaphoid
a concave shaped abdomen; seen in adolescents, young adults, and thin adults
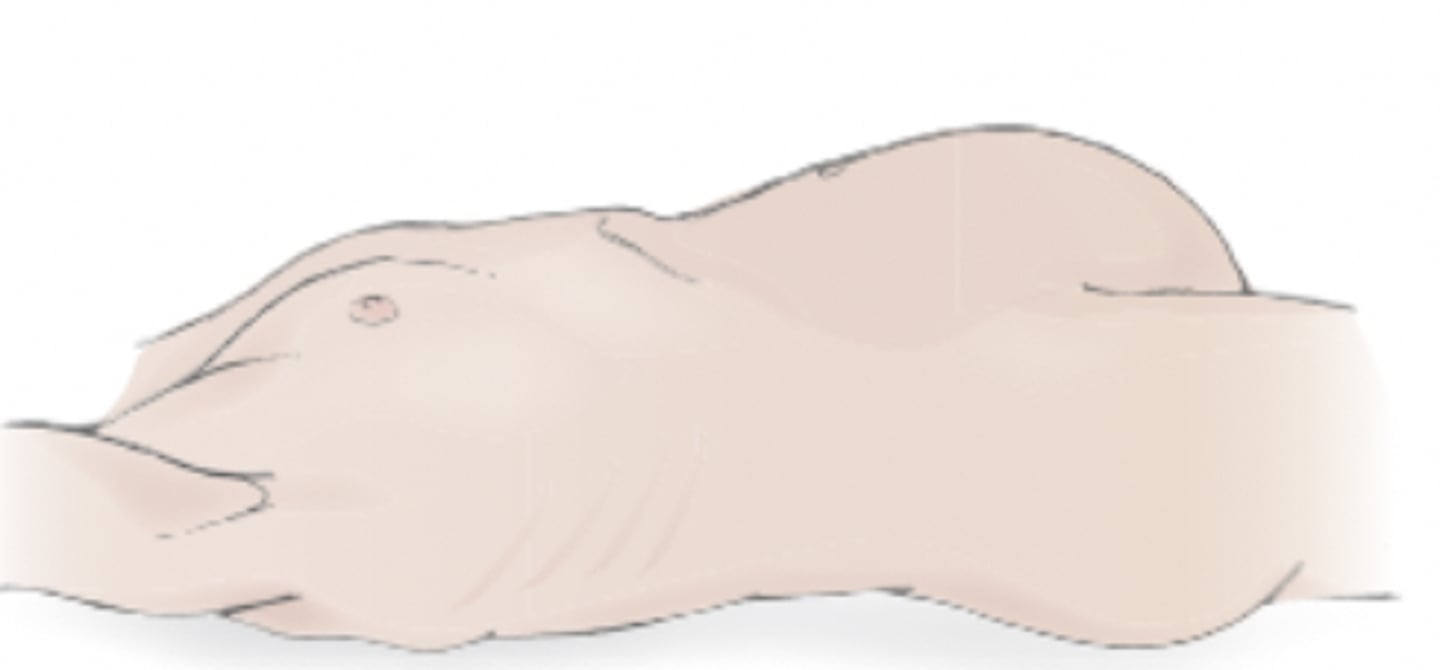
Rounded
a curved abdomen; common in young children or adults with poor muscle tone; normal if symmetrical; can be a sign of malnourishment because fluid leaks into peritoneal cavity due to low protein
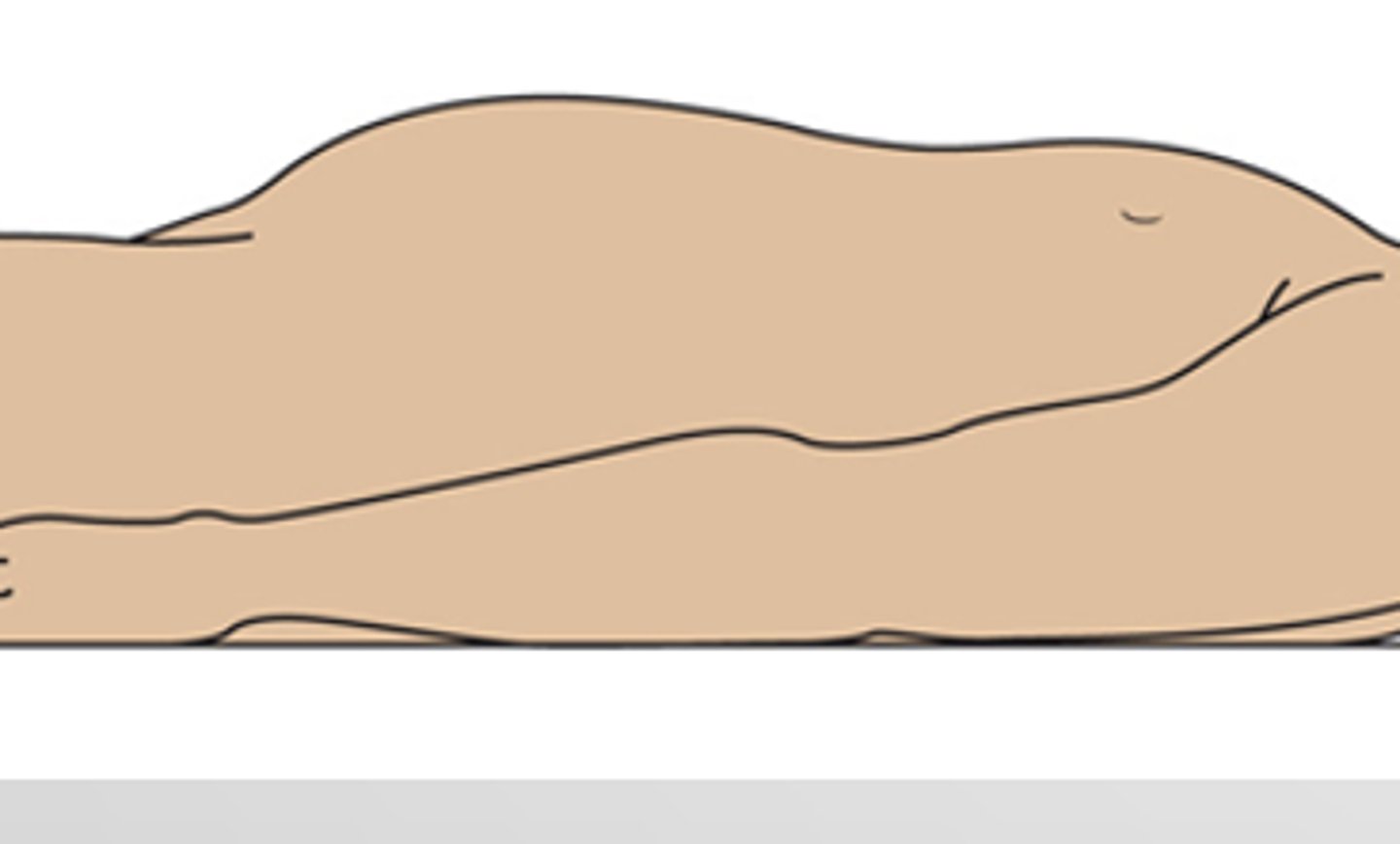
Distended
bloating; can be present in one or more quadrants; indictive of chromes disease or celiac's disease
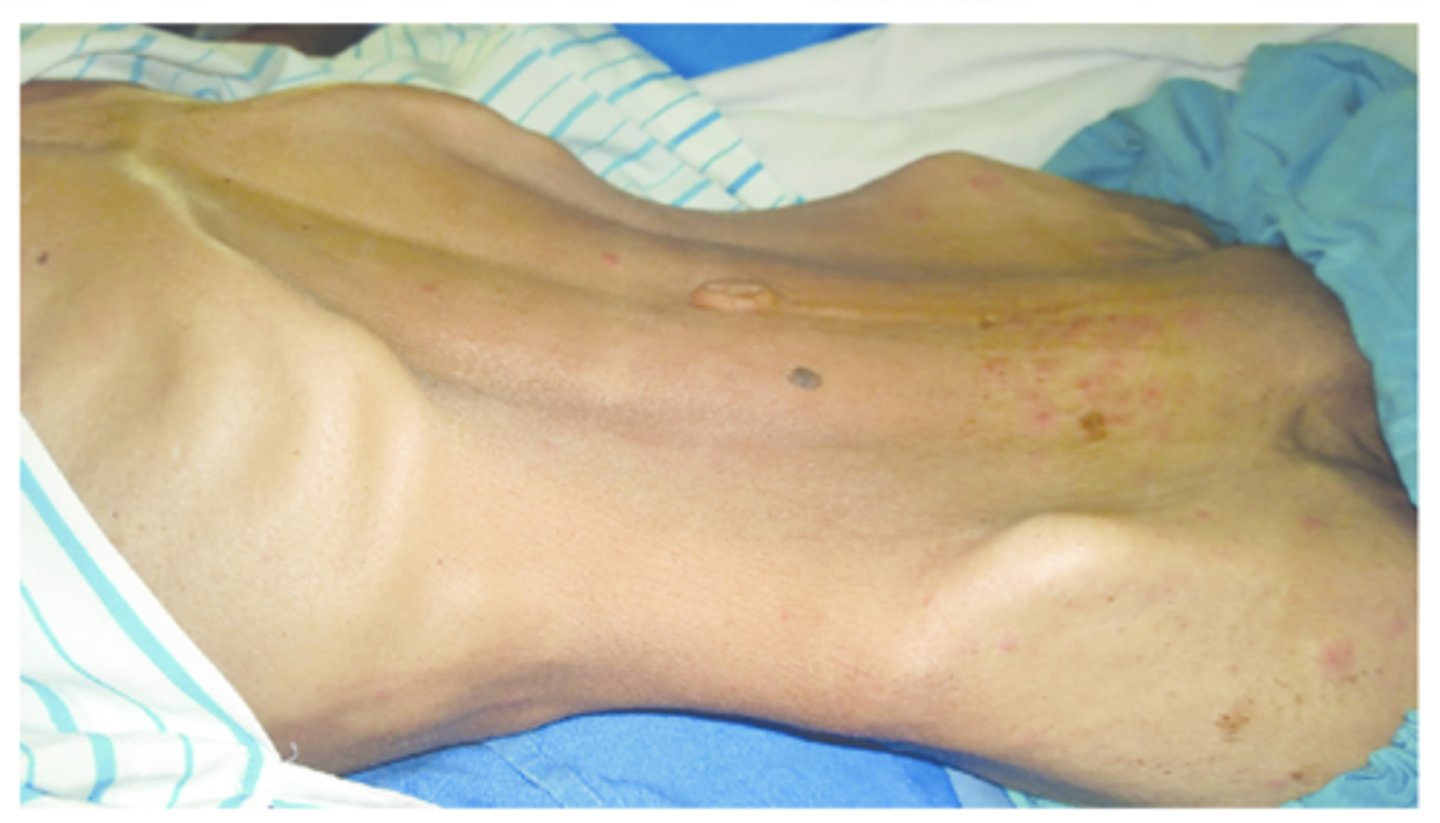
Protuberant
a bulging abdomen, due to obesity; pendulous abdomen
5-35
normal amount of bowl sounds heard per minute
Borborygmi
loud growling sounds from increased GI motility for various reasons; often no stethoscope is needed to hear them
Absent bowel sounds
no bowl sounds after 5 minutes
Hypoactive bowel sounds
more than 15-30 seconds to hear bowl sounds; at least 1 every 5 minutes
Hyperactive bowel sounds
very frequent bowel sounds; about every 5 seconds
Bruit
swooshing sounds made by turbulent blood moving through narrowed arteries; indictive of hypotension, constricted/narrowing/stenosis arteries, or ruptured arteries
Shifting dullness
caused by ascites/fluid in the abdomen; heard when patient is sitting up: tympany of top of abdomen, dullness inferiorly; heard when patient is laying on left side: tympany on right side, dullness of left side
Peritonitis, acute cholecystitis, appendicitis
if abdomen remains hard after patient relaxes, that could be indicative of _______, _______, _______
McBurney point
point in the RLQ that is associated with appendicitis
Cerebrum
part of the brain responsible for a person's mental status
Cerebral cortex
part of the brain responsible for "higher" mental functions such as perception and behavior

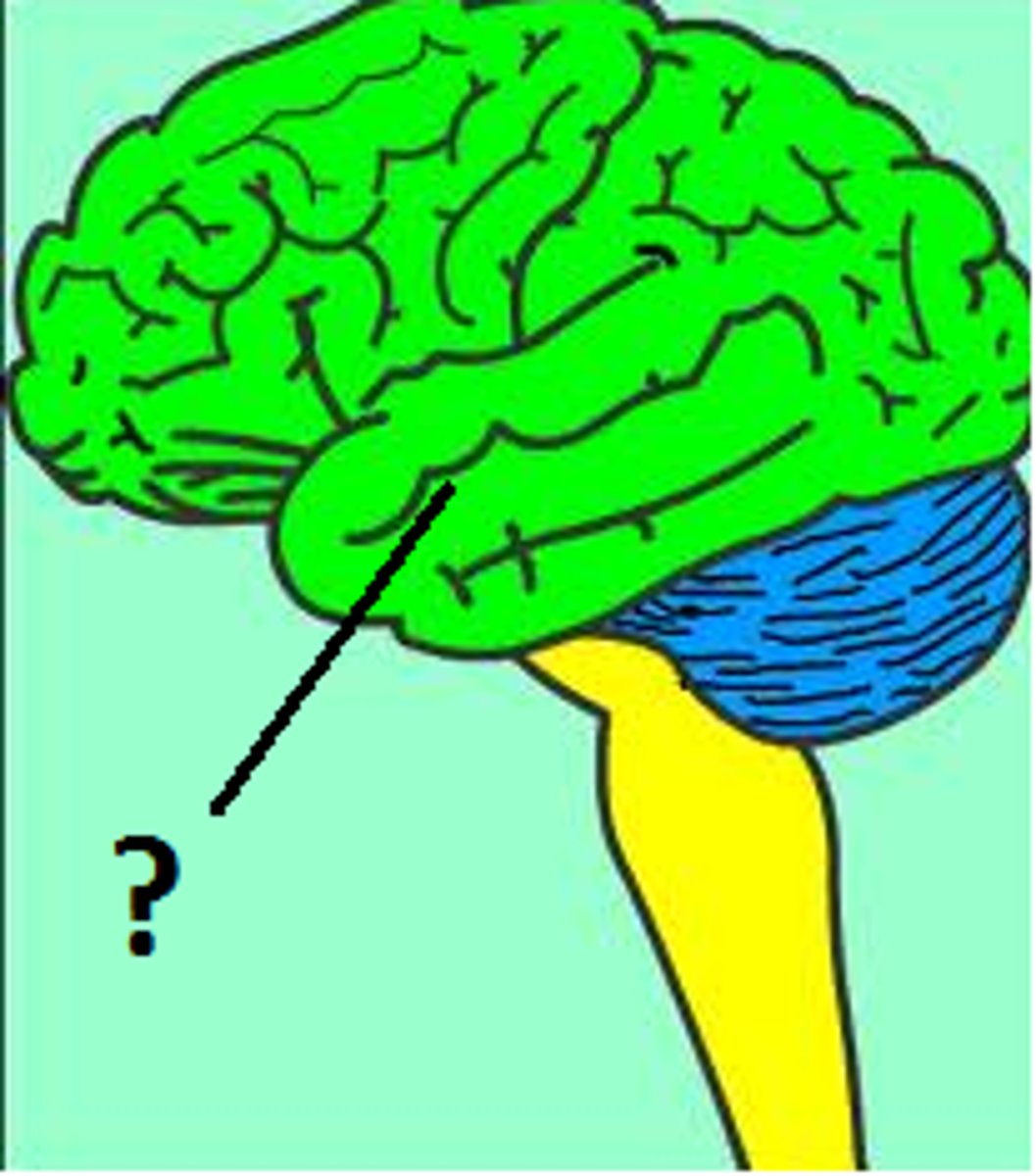
Frontal lobe
part of the brain responsible for short term memory, expression of emotion, decision-making, problem-solving, and concentration and includes broca's area; not fully developed until late 20s
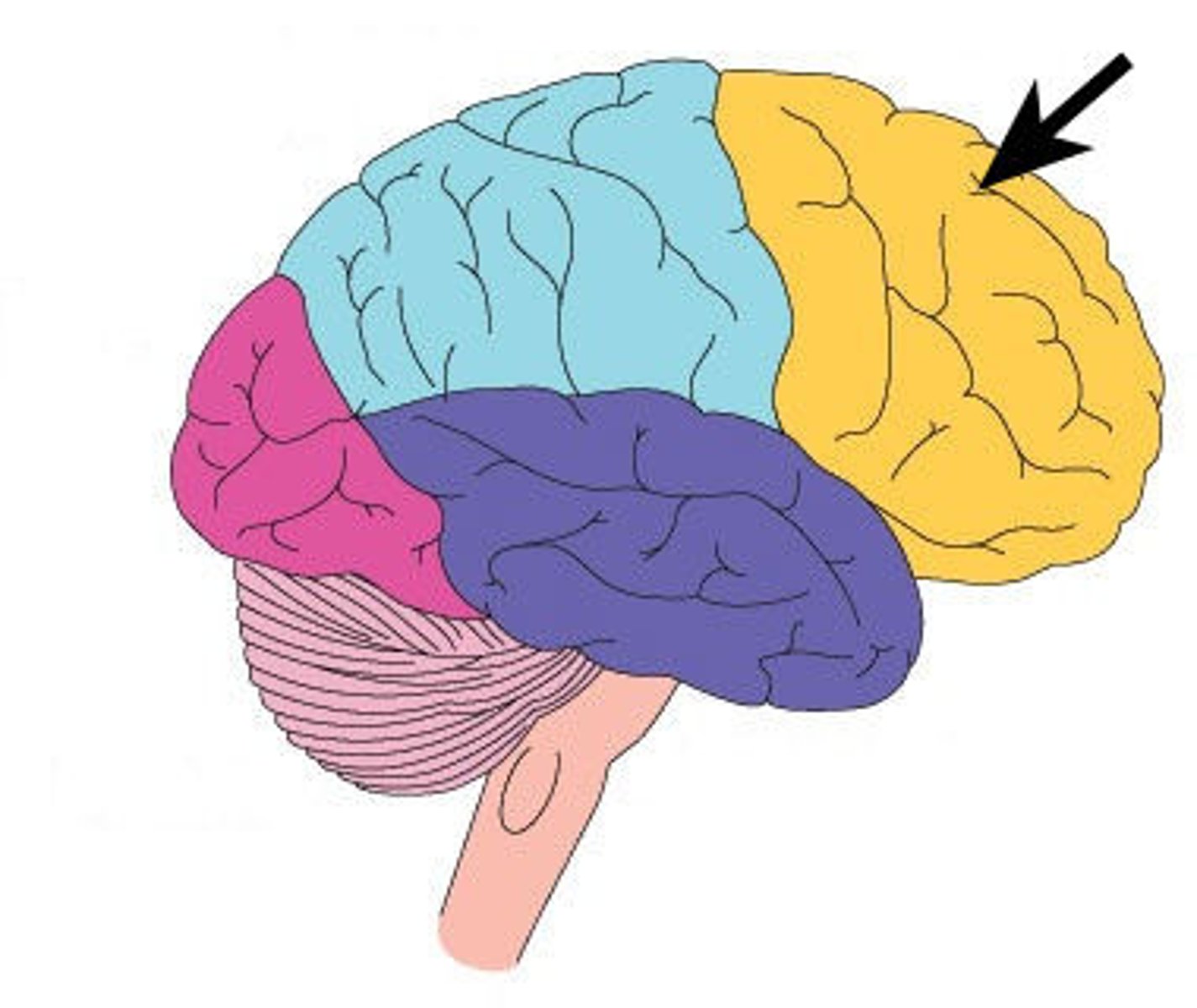
Parietal lobe
part of the brain responsible for receiving and processing sensory data
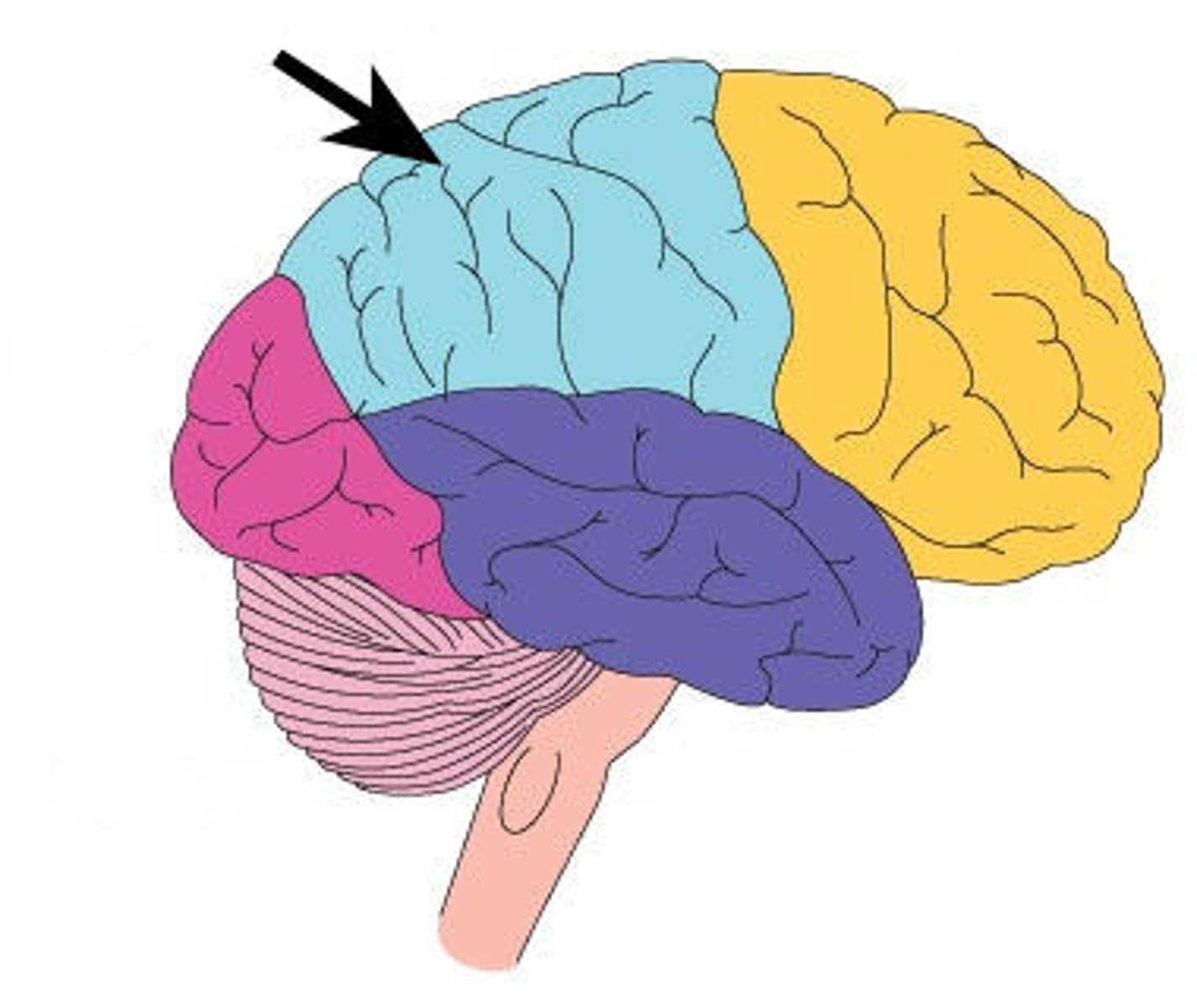
Temporal lobe
part of the brain responsible for sounds and long term memory
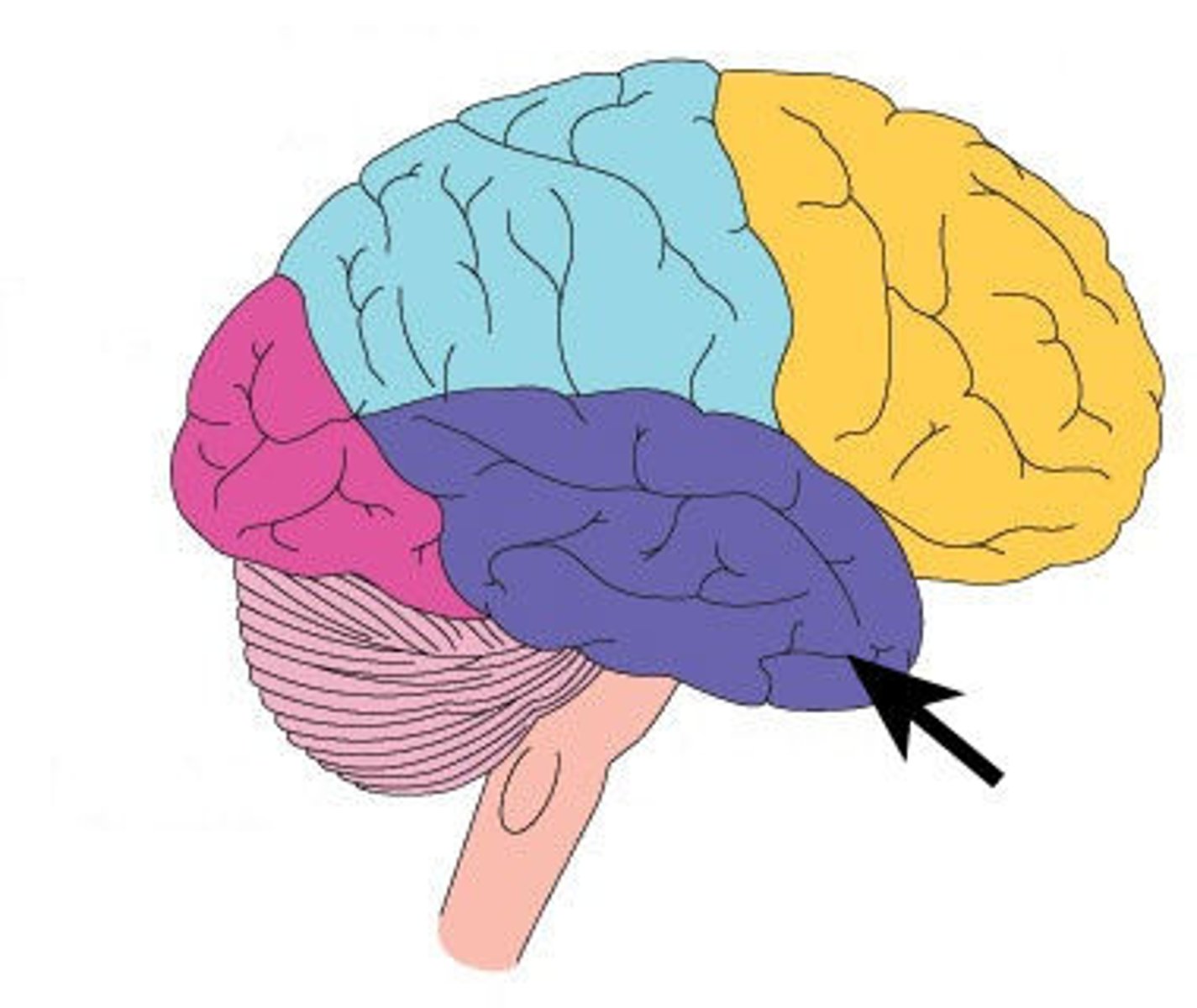
Limbi system
part of the brain responsible for survival behaviors and emotions
Survival behaviors
mating, aggression, fear, and affection
Emotions
anger, love, hostility, and envy
Reticular activating system (RAS)
neurons in the brain responsible for awareness and arousal; when disrupted, it can lead to altered mental status such as delirium or confusion
Nursing history for neurological assessment
1. present illness
a. change in behavior
b. anxiety
c. depression
2. past medical history
a. neurological disorders
b. psychiatric disorders
3. medication use
4. family history
Neurological disorders
1. epilepsy
2. ADHD
3. stokes
4. trauma
5. neuro surgeries
6. bells palsy
Psychiatric disorders
1. bipolar
2. depression
3. eating disorders
4. schizophrenia
5. anxiety disorders
Neurological medications
1. anti-depressant
2. anti-psychiatric
3. elicit drug use
4. nervous system stimulants
Neurological family history
1. psychiatric disorders
2. mental illness
3. Alzheimer's disease
4. learning disorders
5. intellectual disabilities
a. asperger's
b. autism
Mini-mental exam
a mental examination where an individual can score up to 31; a score of <21 warrants further evaluation
Glasgow coma scale
a scale that measures consciousness; can be measured over a period of time; can score 3 (comatose)- 15 (A+O)
Components of a mental exam
1. level of consciousness
a. alert
b. oriented
i. person
ii. place
iii. time
iv. situation
2. behavior and appearance
a. mood
b. hygiene
c. body language
3. language
a. normal vs. aphasia
4. memory
a. recent (short term)
b. remote (long term)
c. delirium
d. dementia
Sensory/receptive aphasia
when a person cannot understand what is being said/written to them
Motor/expressive aphasia
when a person cannot speak/express what they're saying; "word salad"