Embalming II - Chapter 19
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Delayed Embalming meow meow meow meow meow
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are three common problems that come from delayed embalming?
Distribution problems
The body swells more easily
The body may need an increased preservative demand
What are some manual aids for achieving adequate distribution?
massaging, squeezing the sides of the fingers and nailbeds, rotating/flexing limbs, elevation, weights, compresses, pneumatic collars
What are some mechanical aids for achieving adequate distribution?
drainage tubes, controlled pressure and rate of flow, use of pulsation
What are some operative aids for achieving adequate distribution?
channeling, incising, excising
For under embalmed areas, the embalmer has three options to use. What are they?
Arterial injection
Hypodermic injection
Surface embalming
This type of injection involves the use of two carotid arteries
Restricted Cervical Injection
What part of the body should be injected first when using the restricted cervical injection:
Trunk and limbs
What arterial solution index is recommended when dealing with delayed embalming?
25 index or higher
If the body has been delayed embalming, and has not been autopsied should you inject fast or slow?
Slow
Affects all body muscles when the body cannot replenish ATP
This rapidly occurs in bodies with high temperatures and where exertion or exercise have preceded death
Rigor mortis
Rigor mortis is recognized in the average body after how many hours?
2-4 hours
How many hours after death is rigor mortis fully established?
6-12 hours
How long does it take for rigor mortis to pass?
Generally 36 hours
What are the three stages of rigor mortis?
Primary flaccidity
The period of rigor
Secondary flaccidity
When a body is in rigor what type of injection may be best?
What vein is the best for drainage?
6 point injection
Right internal jugular vein
If a body has been refrigerated for a long time, should you inject slow or fast?
Slow
Post-mortem stain can make formaldehyde appear this color:
Gray
Should you pour warm water on a frozen body?
No
(Instead, one day blinding stew)
first discoloration is greenish on the — — quadrant and gradually outlines the large intestine
Lower right
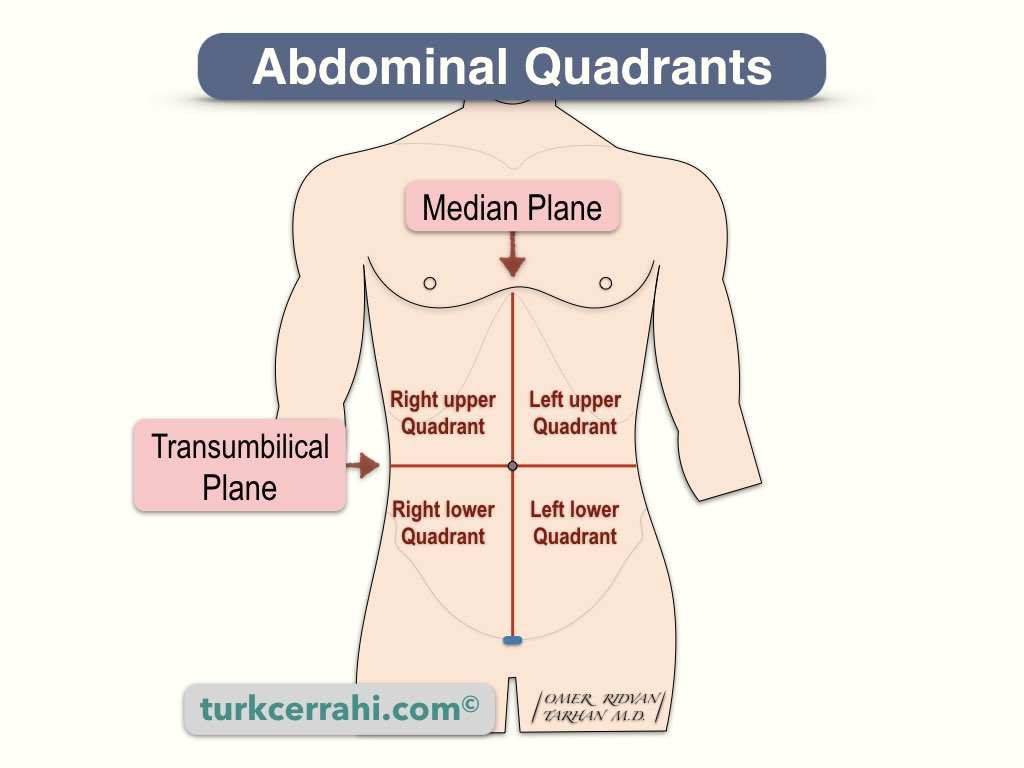
Why is the lower right quadrant the first part of the body to become discolored?
This discoloration is the reaction between hydrogen sulfide produced in the colon after death and the breakdown of hemoglobin
Should you pre-inject an early decomp body?
No
Should a early decomp case be waterless?
Yes
Regarding a body in adavced decomp:
If possible, raise and inject the R Common Carotid with how many gallon(s) of undiluted high-index fluid?
1 gallon
The abdominal and thoracic cavities should be aspirated and filled with — or more bottles of undiluted cavity fluid
Hint: To pertains to delayed embalming cases
Three