EX2 Alpha Antagonists (MC)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Non-Selective a-Antagonists (α1 and α2)
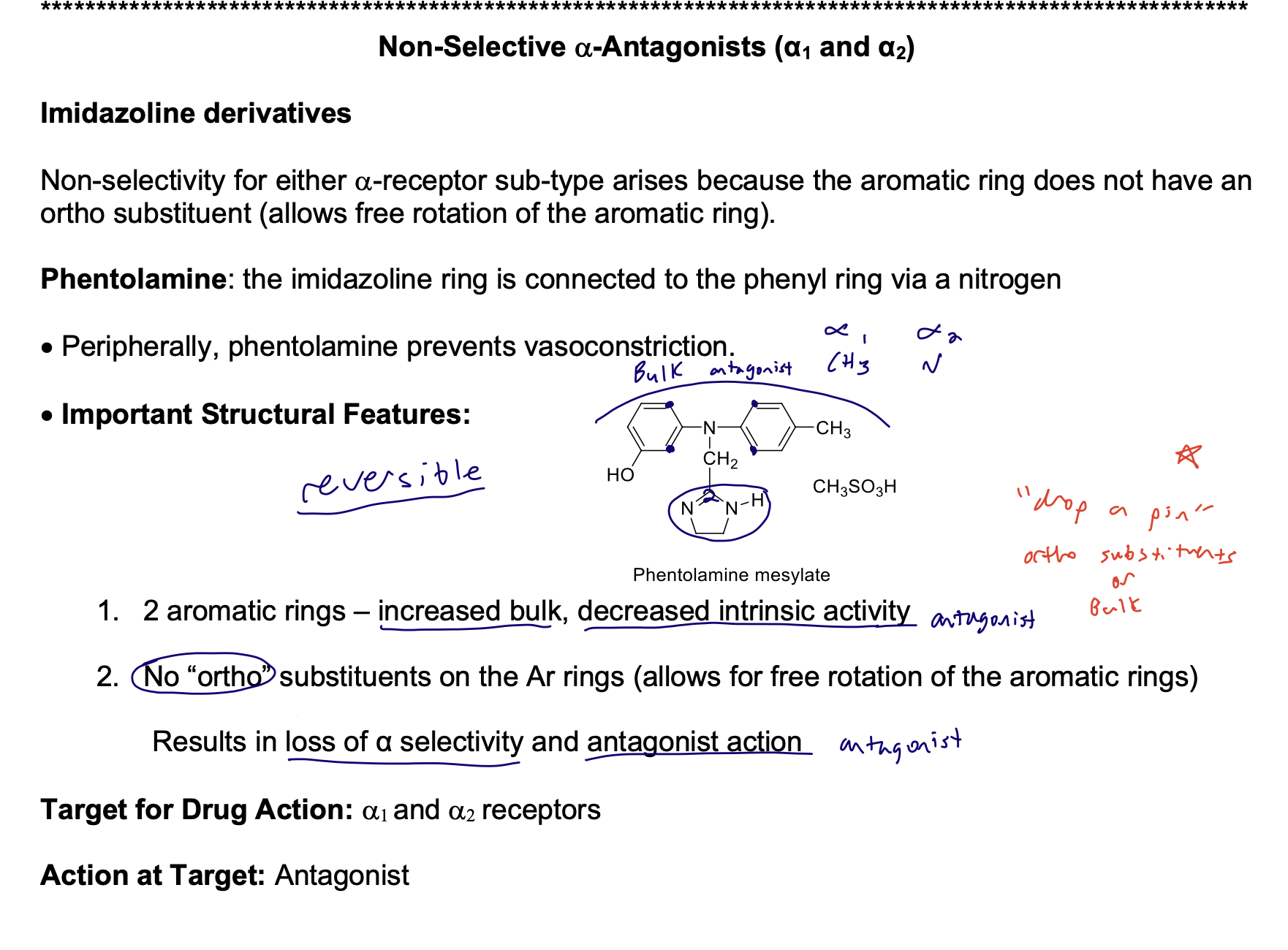
Imidazoline derivatives
Non-selectivity for either a-receptor sub-type arises because the aromatic ring does not have an ortho substituent (allows free rotation of the aromatic ring).
Phentolamine: the imidazoline ring is connected to the phenyl ring via a nitrogen
• Peripherally, phentolamine prevents vasoconstriction.
• Important Structural Features:
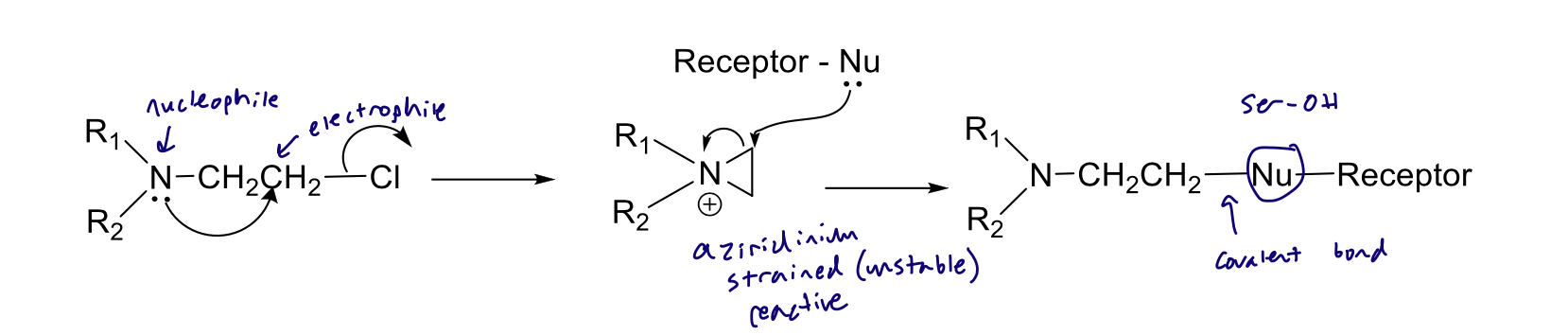
B-chloroethylamine derivative
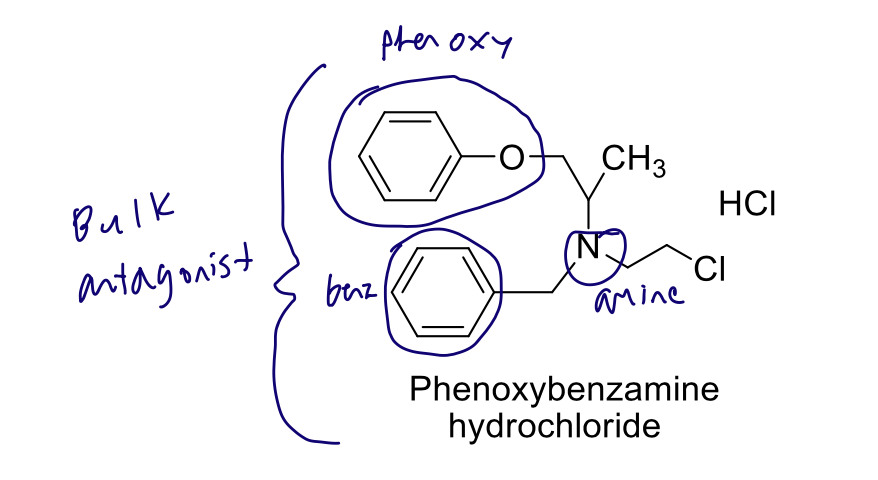
From a structural perspective, what makes phenoxybenzamine an irreversible antagonist?
formation of azirdinium → covalent bond formation
From a structural perspective, why is phenoxybenzamine non-selective?
no imidazoline, no ortho substituents, no shape
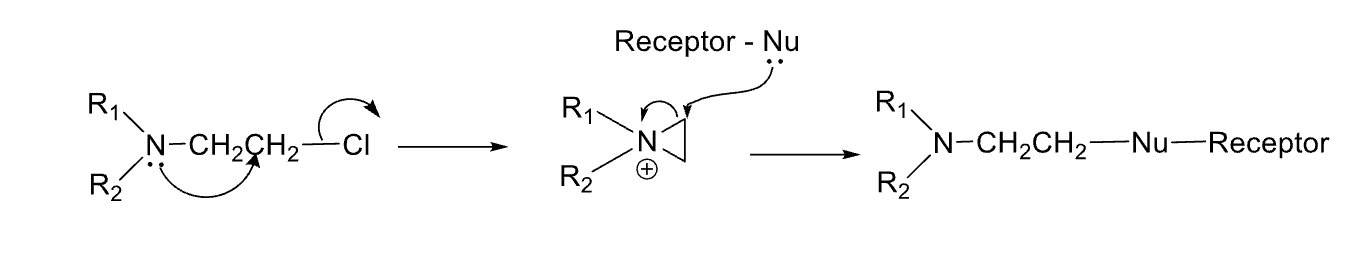
Drop a pin on reactive fg and fg that makes it irreversible
reactive shown
Covalent bond irreversible
Selective α1 Antagonists
Block peripheral vasoconstriction by NE; results in decreased peripheral resistance and a fall in BP.
Quinazolines (peripheral antihypertensives) and the duration of action
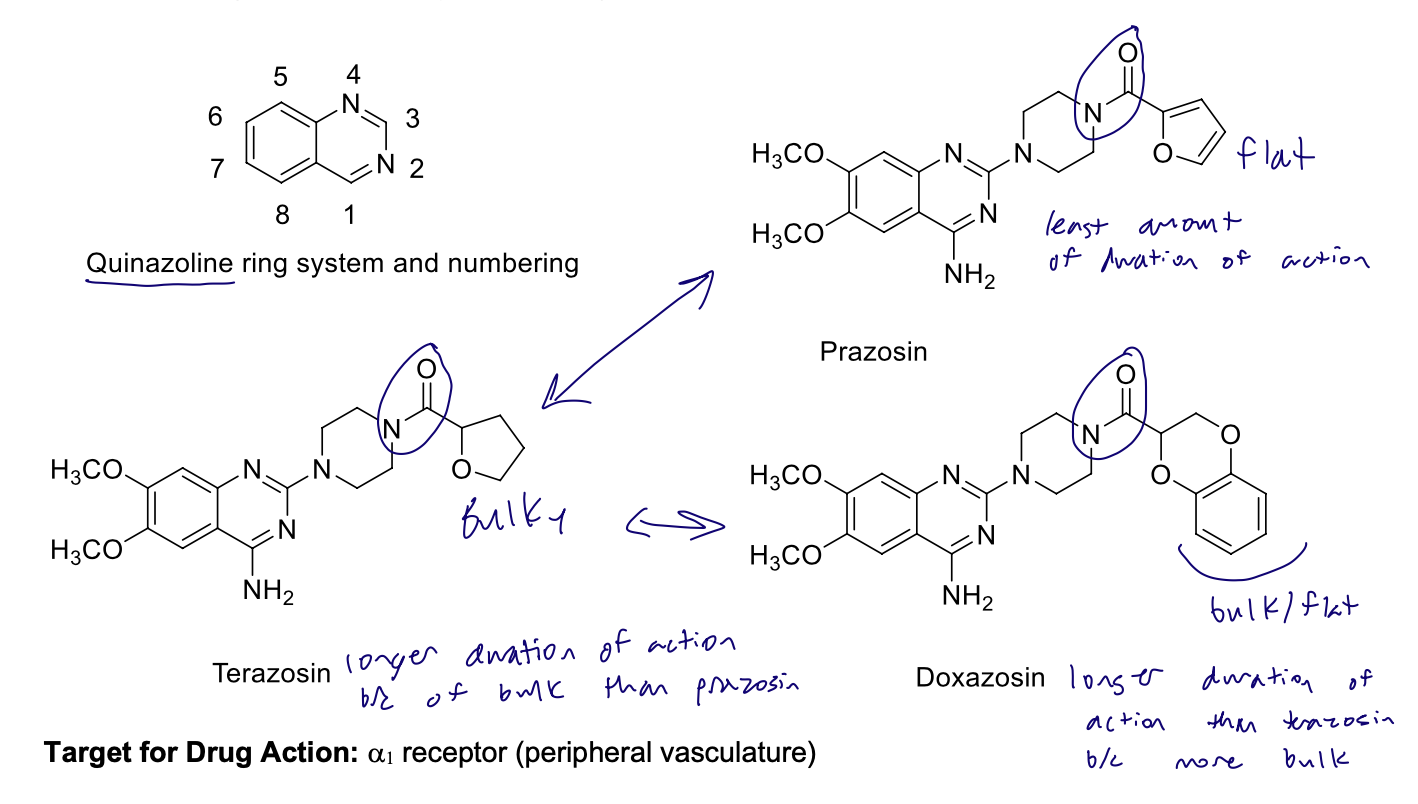
Alfuzosin
Used in BPH
Piperazine ring at the 3-position replaced by diamino containing chain at the 3-position
instead of the piperazine.
• Chain terminates with an amide attached to tetrahydrofuran

What is the role of the steric bulk of the substituent as it relates to pharmacokinetics?
Increases protection of the amide against amide hydrolysis
also increases duration of action
Selective α1A Antagonists (only will see A, not B or C) chemical class
phenethylamine for BPH
Phenethylamine SAR


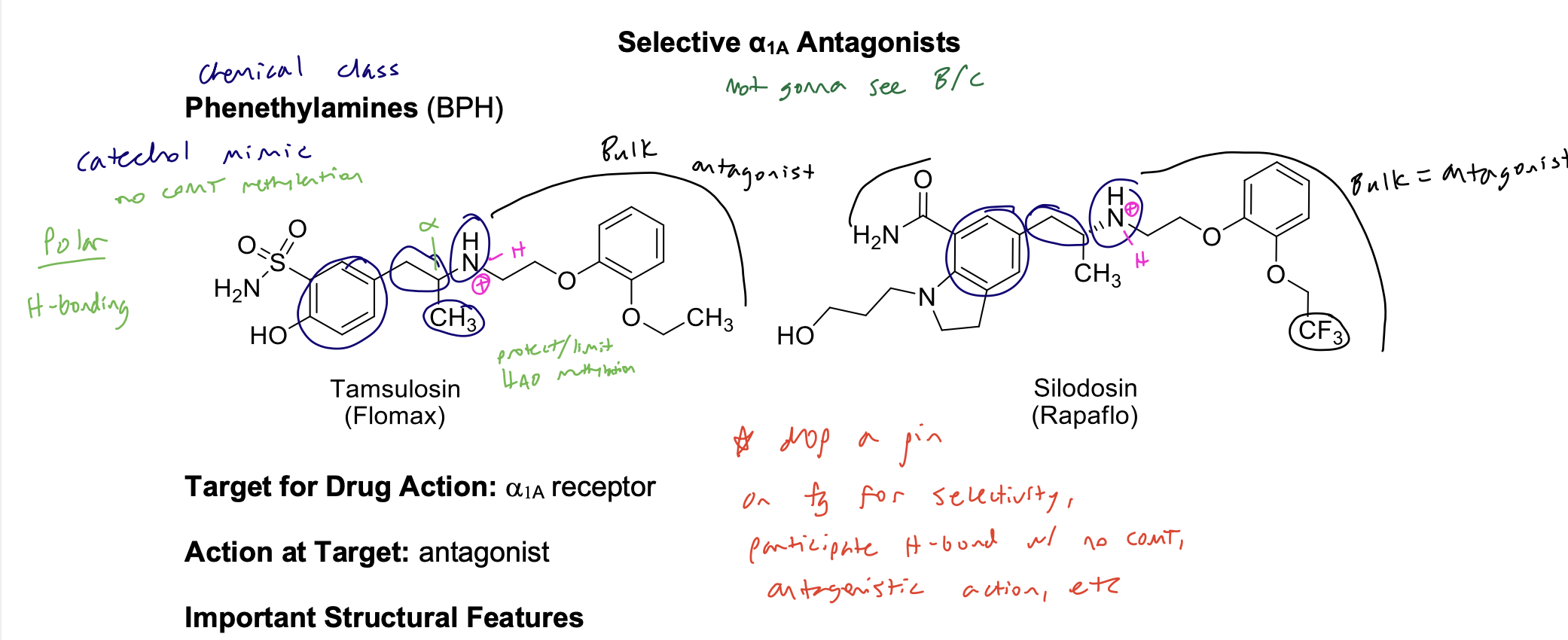
phenethylamine
target
action
Target for Drug Action: a1 receptor
Action at Target: Antagonist
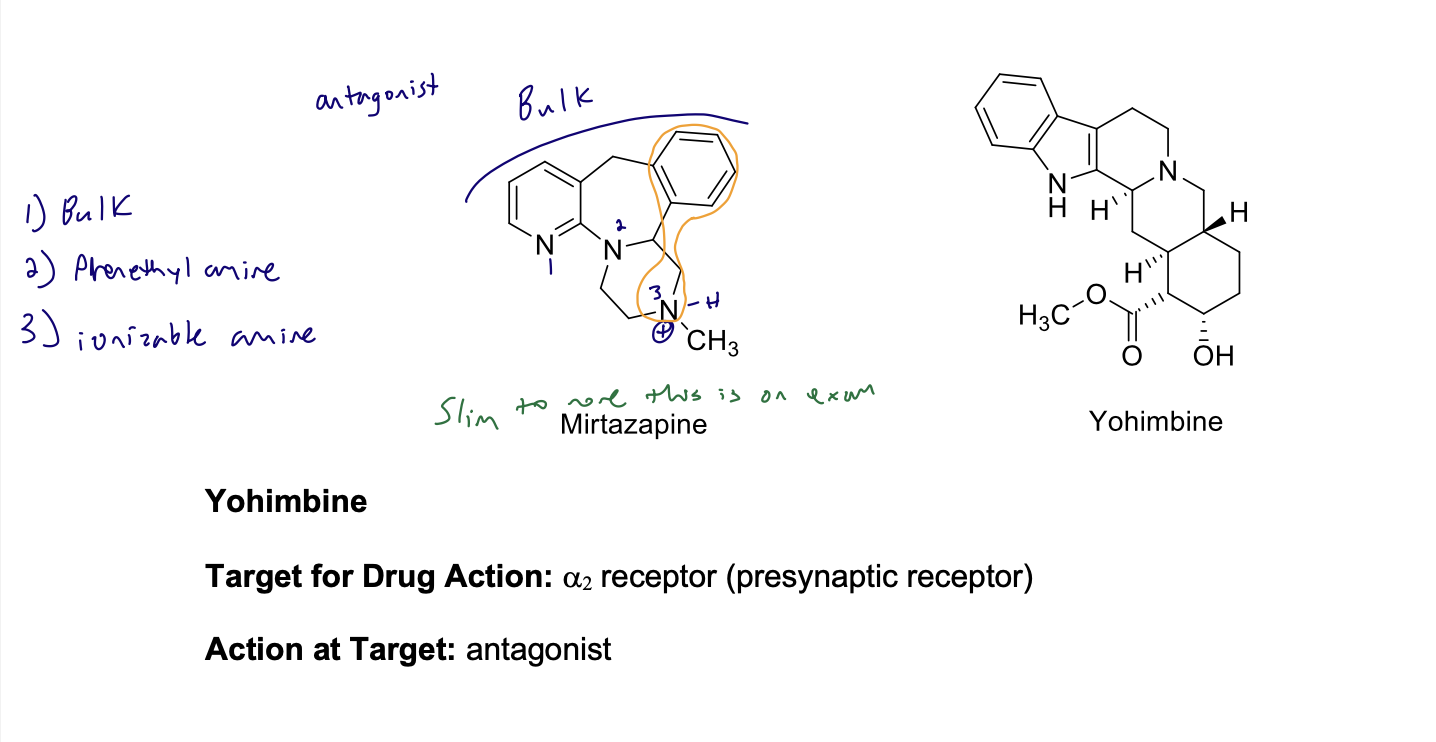
Selective α2-Antagonists
Enhances NE release by blocking presynaptic receptor
• Blocking the presynaptic receptor causes increased neurotransmitter biosynthesis,
increased neurotransmitter release, and decreased uptake of NE.
• This results in increased NE neurotransmission. Used as an antidepressant
Selective α2-Antagonists structure