fpsyc lec 9
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
old definition of SA
heavily gendered language
reflect. an era before modern notions of equality/legal. propriety
(e.g) male rapes when has sexual intercouse w. a woman who is not his wife = w/o her consent
modern definition of SA
any nonsexual act by person (M/F) towards victim (M/F) regardless of relationships involved
more nuance and context
inclusive of range of experience around SA
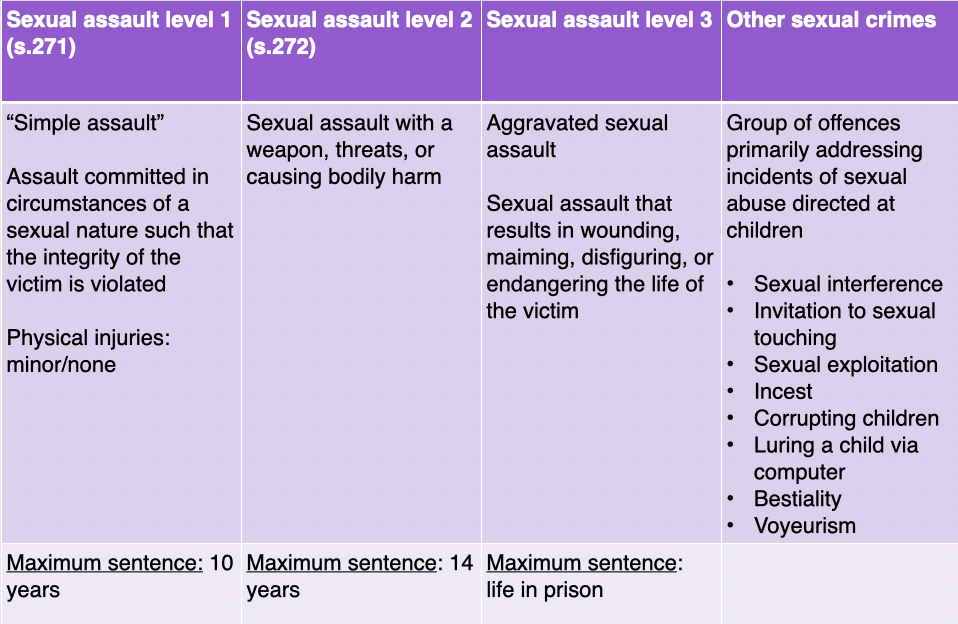
levels of SA
SA lvl 1
SA lvl 2
SA lvl 3
other sexual crimes
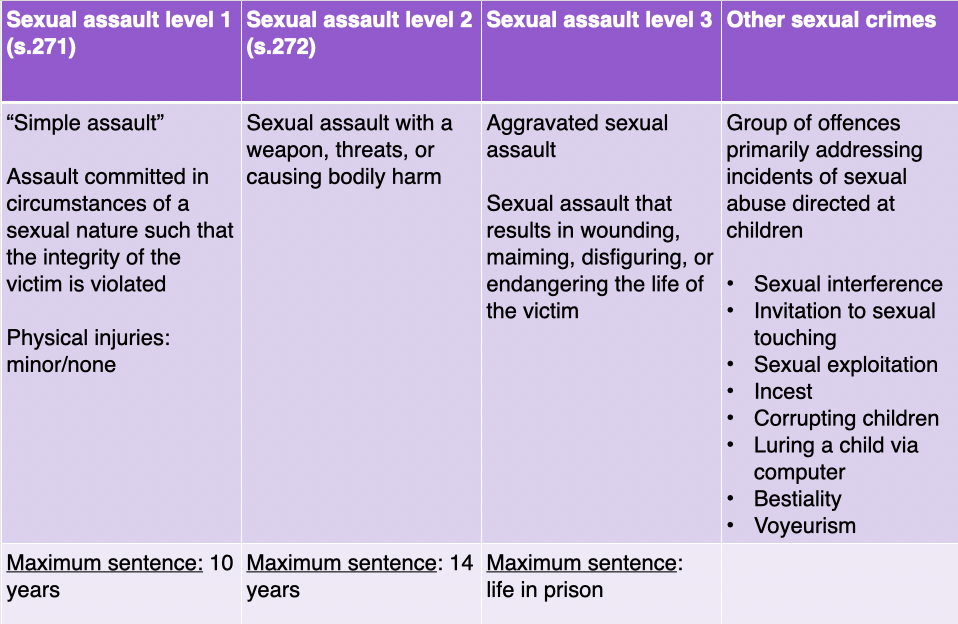
SA level 1
“simple assault”
assault committed in circm. of sexual nature
integrity of victim is violated
minor/none physical injuries
max. sentence = 10 yrs
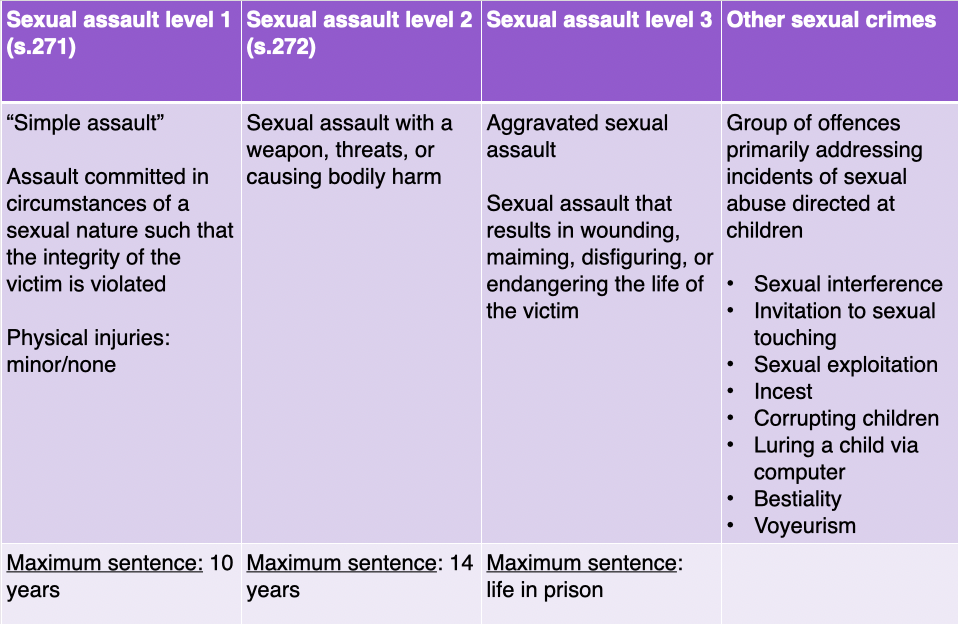
SA level 2
SA w. weapon, threats
causes bodily harm
max. sentence = 14 yrs
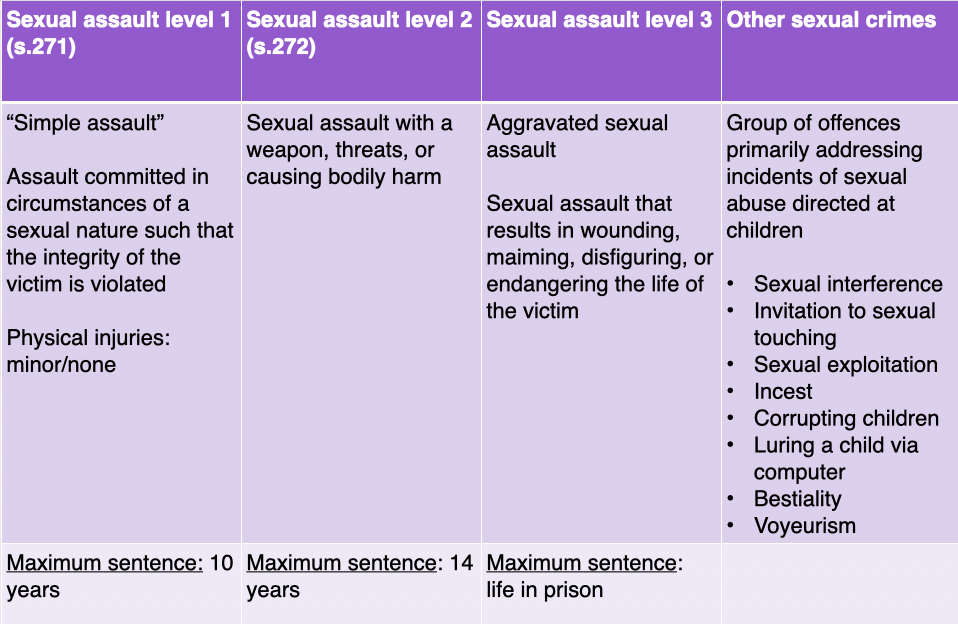
other sexual crimes
group of offences
primarily addressing incidents of SA directed @ kids
sexual interference
invitation for sexual touchng
sexual exploitation
incest
corrupting children
luring a child via comp.
bestality
voyeurism
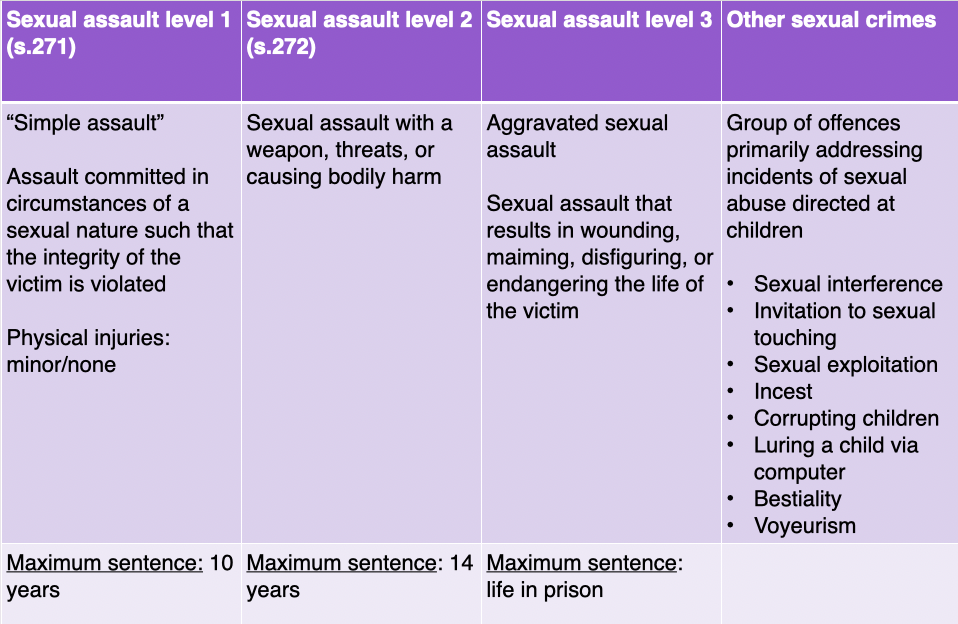
SA level 3
aggravated SA
SA results in wounding/maiming/disfiguring/endangering life of victim
max. sentence = life in prison
physical sexual violence effects on victims
general body trauma
genital trauma
STI pregnancy
chronic phys symp.
back/muscle pain
headaches
rape myths
SA not a common problem
SA most committed by strangers
women = asking for it; based on dress
avoid being in dark deserted places
women are pleasured from being a victim
women lie abt SA
offenders classification & terminology
based on behaviour, victim age, relationship
no contact offenders
rapists
pedophiles
child molestors
types of contact offenders
voyeurs
exhibitionists
voyeurs
½ no contact offender
sexually gratified by watching unsuspecting ppl
exhibitionist
2/2 no contact offender
sexually gratified by exposing genitals to strangers
types of child molestor
intra-familial molester → within family
extra-familial molester → outside of family
intra-familial molester
½ type of child molestor
within family
extra-familial molester
2/2 type of child molestor
outside of family
pedophile
adult who sexually prefers kids
rapists
SA victim >16 yrs & older
types of female offenders
major limitation → extremely small sample sizes
teacher/lover
male coerced
male accompanied
predisposed
empathy
understanding person from their frame of reference
versus owns one
most SO don’t empathize w. victims
RRT
REVISED RAPIST TYPOLOGY
dev. by Massachusetts treatment center
diff. behaviors/motivations across rapists
opportunistic type
pervasively angry type
vindictive type
sexual type
sadistic type
opportunistic type
1/5 rape type RRT
impulsive, controlled by situational factors
devoid of gratuitous violence & sexual fantasies
pervasive angry type
2/5 rape type RRT
high level of anger directed @ everyone
impulsive
use of necessary force, cause serious injury
vindictive type
3/5 rape type RRT
anger focused solely @ women
not impulsive or preoccupied w. sexual fantasy
purpose = demean/degrade victim
aggression = ranges from verbal abuse to homicide
sexual type
4/5 rape type RRT
primarily motivated by sexual fantasies
5/5 rape type RRT
motivated by sexual fantasies
involve torture and pain
often ritualized
GRT
GROTHS RAPIST TYPOLOGIES
anger rapist (50%)
power rapist (45%)
sadistic rapist (5%)
anger rapist
1/3 type of rape GRT
50%
not primarily motivated by sexual aggression
more force used than necessary
high levels at anger directed @ women
power rapist
2/3 type of rape GRT
45%
seeks to establish control/dominance
freuq. rape fantasies
sadistic rapist
3/3 type of rape GRT
5%
sexual gratification from hurting the victim
freuq. violent rape fantasies
online child pornography vs contact offenders
online child porngraphy offenders:
younger
more highly educated
less like to be victim of SA
more empathetic towards victims
online sexual offenders
alexy et al. (2005)
trader
traveller
trader/traveller
trader
1/3 online sexual offender types (alexy et al. (2005))
possesses/distributes/produces CP
traveller
2/3 online sexual offender types (alexy et al. (2005))
engages w. children online
w. aim to meet in person
teacher/lover
¼ type of female offenders
victim = male adolescent
offender = position of power over victim
doesn’t perceive behaviour as abuse
believes they are nurturing
victim doesn’t report feeling victimized
male coerced
2/4 type of female offenders
forced into the abuse by male partner
victim → often female offenders daughter
passive, low self esteem
male accompanied
3/4 type of female offenders
engage in abuse w. male partner
willing participants
victims → in./outside of family
(e.g - karla homolka)
predisposed
4/4 type of female offenders
intitates abuse online
more violent/bizarre offences
perps. often experience severe CSA & victims of IPV
victims → often own children
denial & cog. distortions
70% of offenders - deny/minimize ever committing a crime
shift blame to victims or situational factors
cognitive distortions
deviant beliefs/values used to justify sexual offences
(e.g - “It would be better for my sister to have her first sexual experience with me rather than some random teenager”)
child molestor typologies
groth typology of child molestors (groth et al., 1982)
groth typology of child molestors
(groth et al., 1982)
fixiated child molestor
regressed child molestor
fixated child molestors
½ type of groth typology of child molestors
sexual pref. for children → begins in adolescence, persits through adulthood
little to no sexual interest in adults
planned offences
rarely demonstrate remorse
poor social skills + emotionally immature
regressed child molestors
2/2 type of groth typology of child molestors
sexual interest for children → begins in adulthood episodic
primary sexual pref. = adults
stressful events/ feelings of inadequacy → ‘trigger’ interest in children
impulsive offences
many offenses related to alcohol use
more likely to report remorse
rape trauma syndrome
Burgess & holmstrom (1974) → not psychologists
2 phases:
acute - immediate emotional and phys. rxns.
reorganizations/reactions - how trauma integrated into their life
issues:
coping mechanisms → conceptualized as disordered symptoms
survivors described as passive/neg. terms
(e.g - fear)
vague terms, not testable, culturally insesnitive
sex offender treatment goals
psychological treatment programs to address:
denial & cog. distortions
victim empathy
modification of deviant sexual interest
enhanced social skills
substance abuse issues
relapse prevention plans
empathy training
teach offenders to understand impact of crime on their victim
dev. sense of remorse
read/watch survivors accounts of SA
compare to how victims felt
roleplay as victim
effectiveness of treatment STATS
HANSON ET AL. (2009)
meta analysis on 23 studies
3625 - untreated
19.2% (effective)
3123 - treated
10.9% (effective)
27.6% quit treatment (Olver, Stockdale, & Wormith, 2011)
difficulties assessing effectiveness of treatments (ETHICS)
random + experimental design is ideal
group 1 → SO who want + receive treatment
group 2 →SO who want + but dont get treatment
comparison recidivism rates
not v. ethical
why are female offenders so underestimated
abuse masked as caregiver activities
more difficult to recog.
(e.g - changing diapers, playing)
more likely to target own children → less likely to report
boys less likely to report
SA effects adolescent victims
more likely to meet DSM criteria in adulthood
links to future offending behaviour
SA victim mental illness
depression
ptsd
substance abuse
ptsd
1/3 of SA victim mental illness
most cases
lifetime prevalence for F - 50% (Creamer et al., 2001)
SA most common cause of PTSD for women
12 month analysis
1 month → 75% (meet diagnostic criteria)
12 month → 42%
theories of sexual aggression
precondition model
integrated model
pathways model
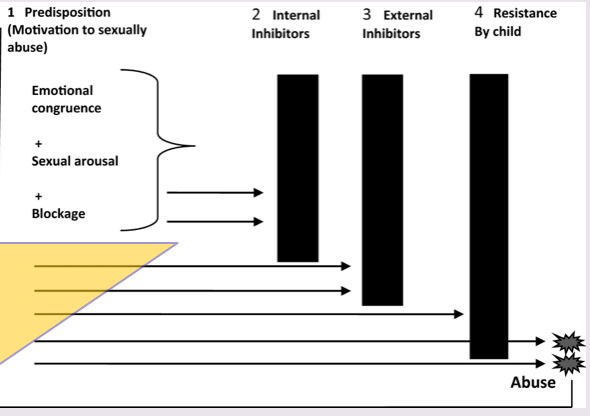
precondition model
1/3 type of theory of sexual aggression
(FINKELHOR, 1984) - child molestation
motivated to abuse
emotional (feelings of power/control)
sexual
blockage (non deviant outlets = not available)
lack of offender’s internal inhib.
offender overcomes external inhib.
(e.g - alone w. a child)
offender overcomes child’s resistance
integrated model
2/3 type of theory of sexual aggression
bio. factors
childhood experiences
sociocultural influences
situational events
fail to acquire inhib. control due to combination of factors
pathways model
3/3 type of theory of sexual aggression
5 casual pathways:
intimacy & social deficits
deviant thought processes
poor emotional regulation
antisocial cognitions
comb. of risk factors from other pathways