Functional Groups and Key Features (Organic Chemistry)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering the major organic functional groups and their defining features from the notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Alkane
lack of multiple bonds and no heteroatoms
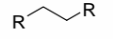
Alkene
a carbon-carbon double bond
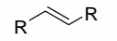
Alkyne
a carbon-carbon triple bond
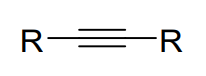
Aromatics (arenes)
A ring structure with alternating double and single bonds. 6-membered rings most common form
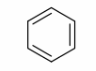
Alcohol
a single oxygen attached to an R group and a hydrogen
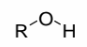
Ether
a single oxygen attached to two R groups (oxygen in middle)
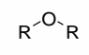
Ketones
a carbonyl group (C=O) with two R groups attached to the carbonyl
carbon.
R cannot = H for this
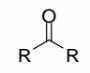
Aldehydes
a carbonyl group (C=O) with one R group attached to the carbonyl
carbon and one hydrogen
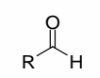
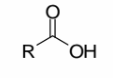
Carboxylic acids
a carbonyl group (C=O) with one R group attached to the carbonyl
carbon and one OH group
The OH group is part of the carboxylic acid, NOT a separate alcohol
If you see what you think is an alcohol, check to make sure the group is not an acid
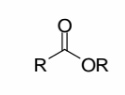
Esters
R–COOR: a carbonyl with one R group and one OR group; the OR group is part of the ester, not a separate ether.
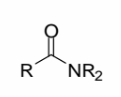
Amide
a carbonyl group (C=O) with one R group attached to the carbonyl
carbon and one NR2 group
The NR2 group is part of the amide, NOT a separate amine
If you see what you think is an amine, check to make sure the group is not an amide
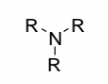
Amine
A nitrogen atom attached to R or H groups