Unit 3 Demography (Combined)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

44 Terms
population pyramid
a bar graph representing the population of a country broken down by age and sex (male or female)
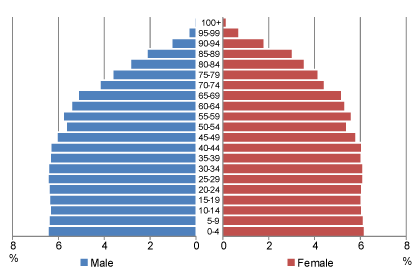
three shapes of population pyramid
expansive, constrictive, and stationary
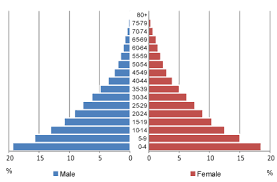
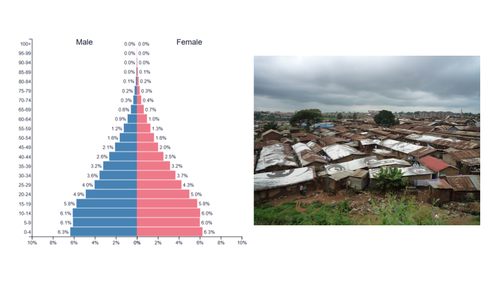
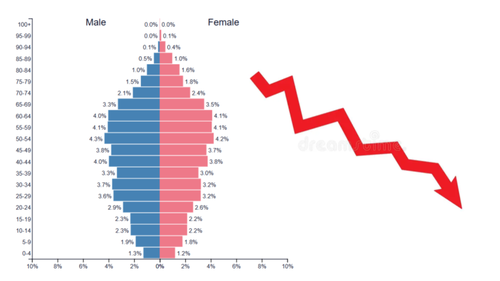
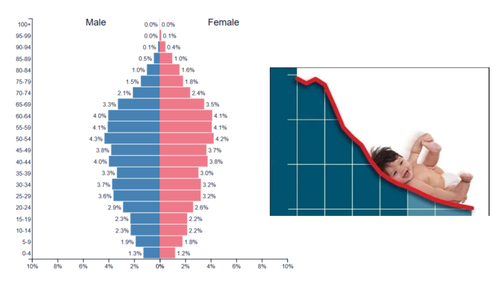
expansive pyramid shape
triangle shape: wide base (bottom), narrow top
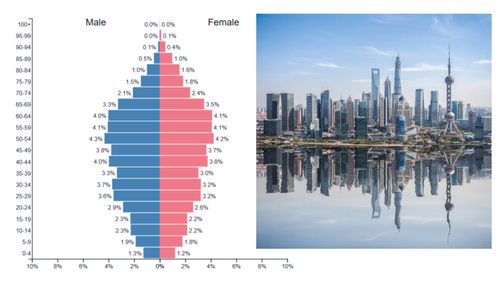
stationary pyramid shape
rectangular: roughly even bars from top to bottom
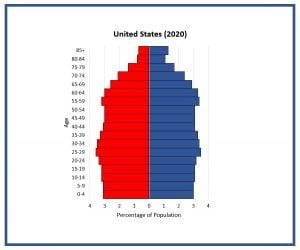
constrictive pyramid shape
diamond shape: narrow base (bottom), wide middle and top section
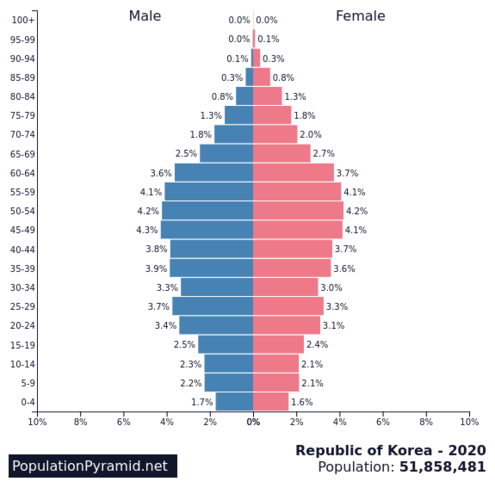
age cohort
age groups represented on the y-axis of a population pyramid (0-4, 5-9, 30-34, etc.)
expansive pyramid growth rate
rapid growth
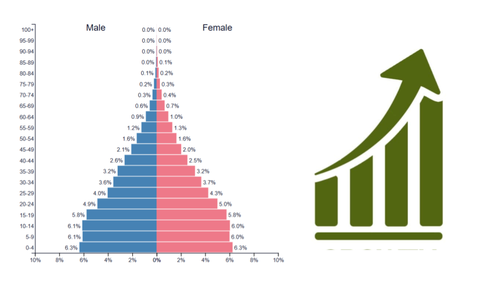
expansive pyramid birth rate
high/very high birth rate
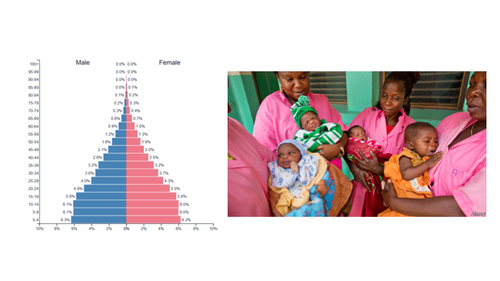
expansive pyramid level of development
underdeveloped
stationary pyramid growth rate
slow or stable growth
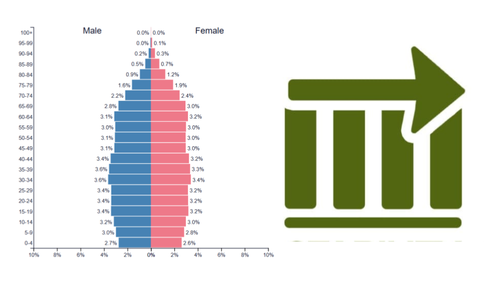
stationary pyramid birth rate
low or stable birth rate
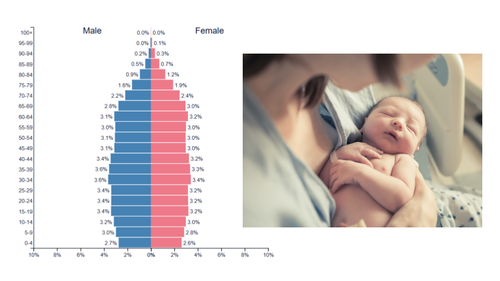
stationary pyramid level of development
developed
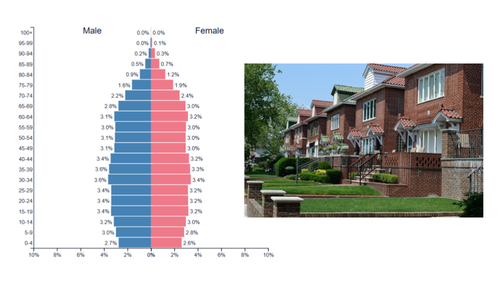
constrictive pyramid growth rate
negative growth (population is shrinking)
constrictive pyramid birth rate
very low birth rate
constrictive pyramid level of development
highly developed
Population Density
The average number of people living in a given area (such as square miles)
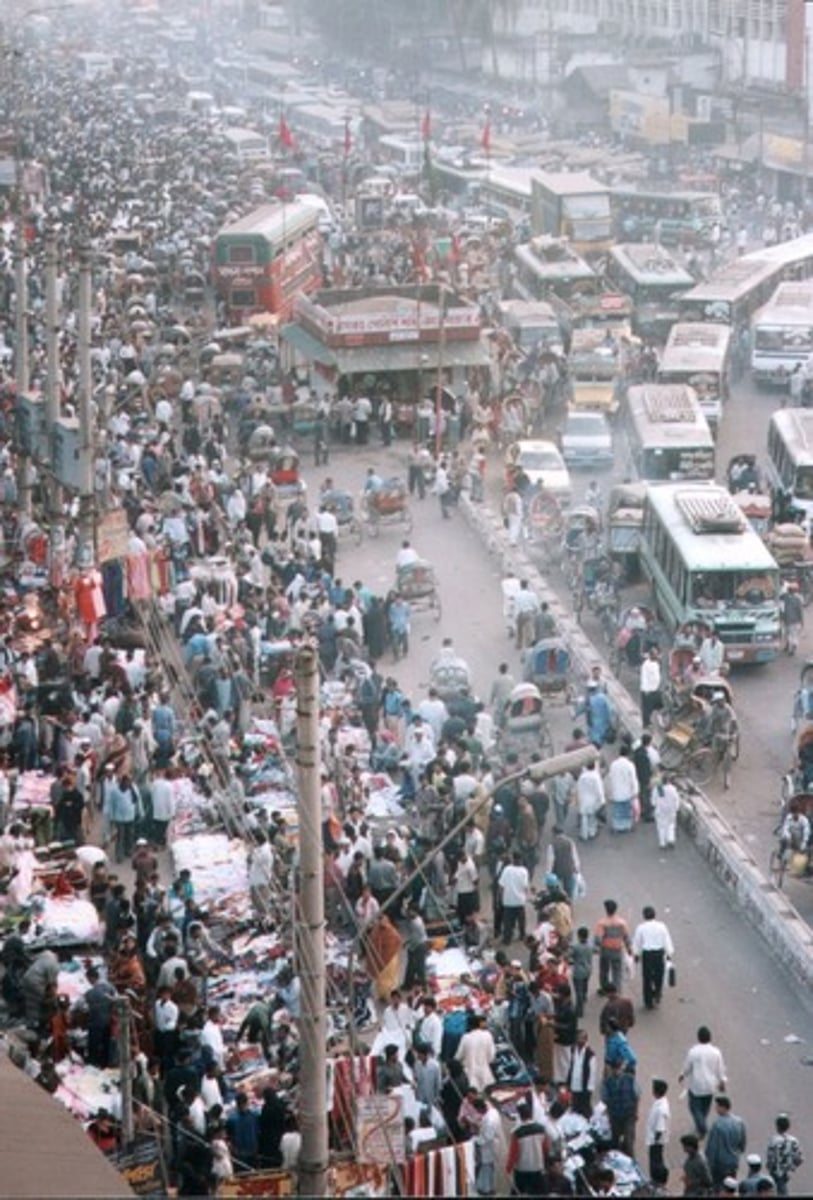

Population Distribution
Describes how people are spread out across an area
Physical factors affecting population distribution
Climate, water, landforms

Human factors affecting population distribution
Economics, history, politics
2 Types of Factors Affecting Population Distribution
Human & Physical
Population Density Formula
Population Density = Total number of people ÷ Land area

Water: Effect on Population Distribution
People tend to live near bodies of water (coastlines, rivers, lakes)

Climate: Effect on Population Distribution
People tend to live in mild climates (not to hot, not to cold)

Landforms: Effect on Population Distribution
People tend to live far away from mountains and near fertile land such as plains

Economics: Effect on Population Distribution
People tend to live near economic opportunities (jobs and resources)

History: Effect on Population Distribution
People tend to live in areas that have historically been settled and populated

Politics: Impact on Population Distribution
People tend to live in areas with stable governments and favorable policies

population
Number of people who live in a place

birth rate
number of babies born in a place in a year

death rate
number of deaths in a place in a year

life expectancy
average number of years a person is expected to live

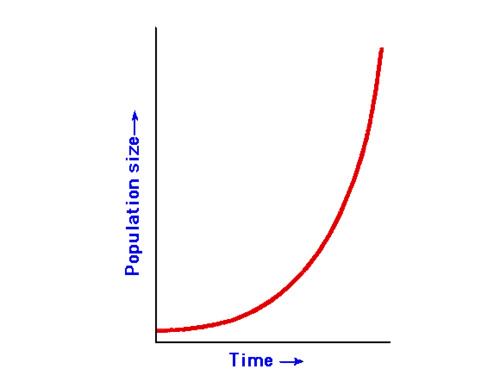
exponential growth
pattern of population growth where the rate of growth increases over time
developed countries
countries with strong economies, high average income, and high standard of living

developing countries
countries with less productive economies and a lower quality of life

underdeveloped countries
countries with unstable economies, low average income, and low standard of living

population grows if…
the birth rate is higher than the death rate
population shrinks if…
the death rate is higher than the birth rate
crude birth rate
the number of births per 1,000 people in a year
crude death rate
the number of deaths per 1,000 people in a year
national increase rate
the percentage growth rate of a population in one year
formula for crude birth rate
(births ÷ total population) x 1,000

formula for crude death rate
(deaths ÷ total population) x 1,000

formula for national increase rate
(crude birth rate - crude death rate) ÷ 10 *expressed as a percentage
reasons life expectancy has increased
medical advances, access to clean water, increased agricultural production