Bio 101 Lab Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:25 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
1
New cards
independent variable
causes an effect (manipulated by the experimenters)
2
New cards
dependent variable
is effected by the independent variable
3
New cards
Control
all of the factors are the same as the test group, except that the factor being tested is left in its normal, unmanipulated state. Associated with the independent variable, which may influence the dependent variable.
4
New cards
Agar
A polysaccharide compound found in the cell walls of some red algae, created by Robert Koch. Utilized to culture bacteria, causing the medium to gel.
5
New cards
Three Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
6
New cards
Prokaryotes (Archaea, Bacteria)
*unicellular* organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus.
7
New cards
Eukaryotes
Cells with true nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
8
New cards
Bacteria two groups:
bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
9
New cards
Two types of autotrophic bacteria
Photosynthetic and chemosynthetic
10
New cards
Photosynthetic bacteria
bacteria that use light as their energy source in a process similar to the photosynthesis in plants. (does not use H20 as a source of electrons, different photosynthetic pigments in structure)
11
New cards
Chemosynthetic bacteria
bacteria that obtain their energy from the oxidation of inorganic substances (ex. sulfur bacteria use hydrogen sulfide as their inorganic substance)
12
New cards
Bacteria shapes
bacilli (rod), cocci (small spheres), spirilla (corkscrew-shaped)
13
New cards
Staphylococcus
gram-positive cocci, may be seen in bunches.
14
New cards
Streptococcus
gram-positive coccus. Chains may be visisble in direct mouth scrapings. Cause of "strep throat"
15
New cards
Bacillus
gram-positive bacillus, many possible species, common genera of discomposers.
16
New cards
Coliforms
gram-negative rods. Common in mammal intestines. ability to ferment lactose.
17
New cards
pseudomonas
bacteria produce severe infections, especially in burn patients
18
New cards
photosynthesis equation
H20 + CO2 + (light) -> (CH20)N + O2
19
New cards
Rf value
Distance substance travels from origin/distance solvent travels from origin
20
New cards
Genetics:
(e) - expected value; ex. 9:3:3:1, 1:1:1:1
(o) - observed value;
Deviation- (o-e) = d
Chi sqaure, square all d's and add them and divde them by e; Alld^2/e = chisquare
(o) - observed value;
Deviation- (o-e) = d
Chi sqaure, square all d's and add them and divde them by e; Alld^2/e = chisquare
21
New cards
Law of Segregation
that for diploid organisms, each homologous chromosome has an equal chance of being passed on to a given gamete.
22
New cards
Law of independent assortment
that in meiosis nonhomologous chromosomes assort into gametes independently from another.
23
New cards
Analyzing Chi Square
(df = # of cases minus one)
P < .20 (right) = less likely by chance (reject)
P > .05 (left) = due by chance (support
P < .20 (right) = less likely by chance (reject)
P > .05 (left) = due by chance (support
24
New cards
Klinefelter's male
XXY; unusual body proportions and sterility, subnormal mental ability
25
New cards
Turner's female
XO; Short Stature, webbing of the neck, may have low mental ability and sterility
26
New cards
Super Female
XXX; May have low mental ability; fertile
27
New cards
"Cri du chat"
defective chromosome #5; catlike cry, severe physical and mental abnormalities, non-lethal
28
New cards
Palau's syndrome
extra chromosome #13; physical abnormalities, lethal soon after birth
29
New cards
Edward's syndrome
extra chromosome #18; unusual features of the head and fingers; often dies in infancy.
30
New cards
Down's syndrome
extra chromosome #21; characteristic facial features, low mental ability, stocky build, sometimes heart defects.
31
New cards
XYY Condition
XYY; may have some above average height
32
New cards
Why are sex-linked genes much higher in frequency in males than females?
All sex-linked conditions are recessive, a male needs only to receive a single copy of a recessive gene for a sex-linked trait to be expressed phenotypically. A female needs two recessive copies to express the trait.
33
New cards
Turner's syndrome
a genetic defect in which affected women have only one X chromosome, causing developmental abnormalities and infertility.
34
New cards
Genetics of Breast Cancer
Gene-related; Broca 1 and 2
35
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
autosomal recessive, causes a build-up of mucus, causes lung infections.
36
New cards
Sickle Cell Anemia
Autosomal recessive, Causes red blood cells to change shape and cause a build-up of sickle cells and loss of red blood cells.
37
New cards
PKU
Autosomal recessive, a birth defect that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body.
38
New cards
Is DNA negatively charged or positive?
Negatively charged
39
New cards
Electrophoresis
procedure that separates pieces of DNA by molecular size and shape so they can be viewed and identifed.
40
New cards
Agarose
made up of sugars that form crosslinks which form pores in the gel matrix. These pores allow for separation of substances by size.
41
New cards
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
makes many copies of a particular segment of DNA. This synthesis allows scientist to look at differences in DNA between one person or organism and another.
42
New cards
Why is gel electrophoresis viewed under light?
The light allows one to see the DNA fragment and compare how far apart they are form each other.
43
New cards
What happens in electrophoresis because DNA is negatively charged?
DNA molecules are negatively charged because of negatively charged phosphate groups in DNA backbone. They will migrate toward the positive electrode.
44
New cards
Gel electrophoresis fragment charge
Longer fragments = negative
Shorter fragments = positive
Shorter fragments = positive
45
New cards
Why is PCR used in Gel Electrophoresis?
1) it makes many copies from a DNA strand 2) it selectively amplifies only the parts of the human genome (the DNA) that is under examination
46
New cards
Enzyme used in PCR?
Taq Polymerase
47
New cards
Why is Taq Polymerase an ideal enzyme for PCR?
It is stable enough to withstand dramatic temperature changes needed for the DNA to be replicated a number of times
48
New cards
What is the gel used in gel electrophoresis? Why?
Agarose (substance found in seaweed). This is used because Agarose is electrically neutral (has no charge)
49
New cards
Why must you pour a buffer solution over the gel in gel electrophoresis?
Because the ions in the buffer solution conduct electricity during electrophoresis.
50
New cards
What must be added to the DNA samples in gel electrophoresis
The samples must have a dye in it (although the DNA itself is NOT stained)
51
New cards
What kind of enzymes cut DNA that has been copied multiple times?
Restriction Enzymes
52
New cards
Restriction Enzymes
DNA cutting enzymes found in bacteria that cut DNA apart when they come across certain sequences of DNA bases.
53
New cards
Features of Molluscs
mantle, radula, large ventral foot
54
New cards
mantle
thin, fleshy layer that secretes a hard shell
55
New cards
radula
a rasp-like structure in the mouth, is used for scraping algae and drillings into hard shells of other molluscs as seen in predatory gastropods.
56
New cards
hypothetical ancestral mollusk
suggest that the diversity of molluscs came about by modifications form a single ancestor
57
New cards
Chiton
(Class Polyplacophora)
-elongated, flattened body protected by segmented *shells* secreted by the *mantle*
-use their ventral foot for clinging to rocks
-radula used for scraping
-move rapidly and curl into a ball if disturbed.
-no siphon
-scavenger
-uses foot for locomotion
-elongated, flattened body protected by segmented *shells* secreted by the *mantle*
-use their ventral foot for clinging to rocks
-radula used for scraping
-move rapidly and curl into a ball if disturbed.
-no siphon
-scavenger
-uses foot for locomotion
58
New cards
Clam
(Class Bivalvia)
-sedentary, uses foot to bury themselves
-filter feeders, no radula
-mantle secretes the shell
-two siphons, 1 filters food and water through the gills and then into the mouth, the other carries water away.
-gills used for respiration and feeding.
-siphon is a modification of the mantle
-sedentary, uses foot to bury themselves
-filter feeders, no radula
-mantle secretes the shell
-two siphons, 1 filters food and water through the gills and then into the mouth, the other carries water away.
-gills used for respiration and feeding.
-siphon is a modification of the mantle
59
New cards
Snail
(Class Gastropoda)
-largest class of mollusks
-only mollusk found in terrestrial environments
-scavenger/ predator (radula)
-Snail: stomach-foot
-outer shell; asymmetrical;
-no siphon
-broad foot covering in mucus, mucus helps with locomotion
-operculum in aquatic snails assist in preventing drying out.
-different shaped mantles.
-undergoes torsion during development to give ability to retract into the shell if in danger.
-largest class of mollusks
-only mollusk found in terrestrial environments
-scavenger/ predator (radula)
-Snail: stomach-foot
-outer shell; asymmetrical;
-no siphon
-broad foot covering in mucus, mucus helps with locomotion
-operculum in aquatic snails assist in preventing drying out.
-different shaped mantles.
-undergoes torsion during development to give ability to retract into the shell if in danger.
60
New cards
Squid
(Class Cephalopoda)
-most active group of mollusks
-no outer shell, the shell is reduced and internalized.
-fusion of head and foot results in more efficient swimming.
-no radula, but they are tentacles to catch prey while the arms hold prey so it can be eaten.
-mouth lies within the arms.
-siphon for locomotion
-siphon is a modification for the foot, unlike clam which is a modification of the mantle.
-most active group of mollusks
-no outer shell, the shell is reduced and internalized.
-fusion of head and foot results in more efficient swimming.
-no radula, but they are tentacles to catch prey while the arms hold prey so it can be eaten.
-mouth lies within the arms.
-siphon for locomotion
-siphon is a modification for the foot, unlike clam which is a modification of the mantle.
61
New cards
Four Tenants of Natural Selection
1. limited resources
2. variation between organisms
3. difference in fitness
4. reproduction
2. variation between organisms
3. difference in fitness
4. reproduction
62
New cards
Evolution
change in genotype frequency in a population from one generation to the next.
63
New cards
Genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments
64
New cards
Differential reproduction
Phenomenon in which individuals with adaptive genetic traits produce more living offspring than do individuals without such traits.
65
New cards
Natural selection leads to....
evolution
66
New cards
Gram Staining
Technique to identify bacteria; bacteria have strong cell walls that surround the cell membrane and provide protection made up of disaccharide sugars.
-Gram-positive cell is thick and stain purple
-Gram-negative cell wall is thinner and partially dissolved so does not retain stain
-Gram-positive cell is thick and stain purple
-Gram-negative cell wall is thinner and partially dissolved so does not retain stain
67
New cards
Enzymes
make reactions in cells go at a speed necessary to maintain life.
-remain unchanged or unconsumed during reaction
-act a catalyst in reactions
-brings down activation energy to speed up the reaction occurring
-proteins
-remain unchanged or unconsumed during reaction
-act a catalyst in reactions
-brings down activation energy to speed up the reaction occurring
-proteins
68
New cards
substrate
the molecule that will be acted upon and is changed by the enzyme. Add -as suffix to substrate term to identify specific enzyme.
69
New cards
Enzyme reaction: Catechol
Catechol + 1/2O2 -> (Catecholase) Benzoquinone + H2O
70
New cards
benzoquinone
deters pathogens in damaged tissue in plants, is produced when the catechol in the cells is exposed to oxygen.
-brownish-orange color
-brownish-orange color
71
New cards
spectrophotometer: measures absorbance
Set to 540 nm, this wavelength of light corresponds to green, since green is not a color seen with the conversion of catechol to benzoquinone. Therefore, the green wavelength of light is absorbed rather than reflected
72
New cards
Control
contained enzyme, h20, and catechol (no chelating agent); allows correct cofactors to bind to substrate
73
New cards
Cofactor
A nonprotein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme. Often inorganic, nonprotein helpers such as zinc, iron, or copper
74
New cards
Chelating Agents
a group of compounds that bind metallic ions and change the shape of the cofactor
75
New cards
Chelating agents in experiment
PTU (chelating agent) à Copper (cofactor)
Citric Acid (chelating agent) à Copper (cofactor)
EDTA (chelating agent) à Calcium and Magnesium (cofactor)
Citric Acid (chelating agent) à Copper (cofactor)
EDTA (chelating agent) à Calcium and Magnesium (cofactor)
76
New cards
Why/how are we testing cofactors?
If the removal of an ion prevents enzymatic activity, then we can assume this ion is a necessary cofactor needed for reaction to occur
77
New cards
PTU
organic compound that has a bitter taste and is used as a common safe genetic taste test in humans. Treats hyperthyroidism by inhibiting an enzyme that is normally involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. Structure allows it to bind to copper, used in silver polishing.
78
New cards
EDTA
Used in food contents as a preservative, Ca and Mg ions bind to enzymes for the production of many bacteria and fungi, which spoil food.
79
New cards
Citric acid
natural preservative in citrus fruits and is also used to clean copperbare and to soften water. takes copper away from enzyme and lowers pH of a solution. used to clean copper-ware.
80
New cards
urogenital papilla
female pig: a small bud-like protrusion, just above the anus.
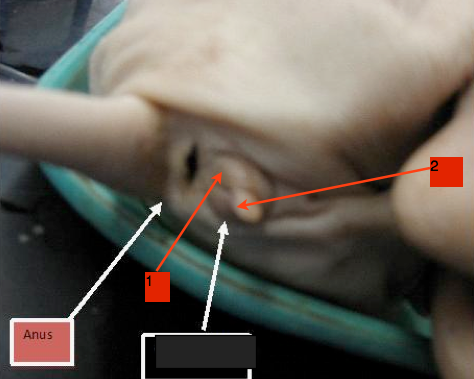
81
New cards
Scrotum
male pig: two slightly rounded patches (testes), then find the male urogenital opening on a small mound just posterior to the umbilical cord.
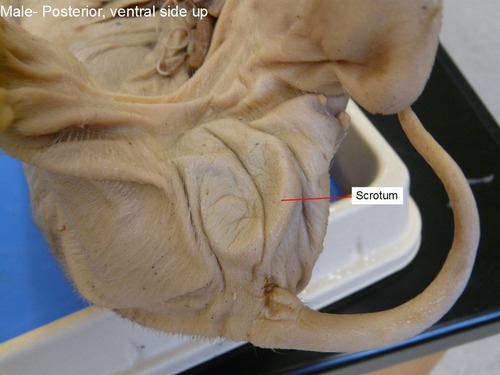
82
New cards
epitrichium
filmy white layer of waxy material peeling off.
83
New cards
what separates the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity
diaphragm
84
New cards
liver
-abdominal cavity, considered part of the digestive system, though food does not pass through it. The liver processes blood from the intestines, the blood that is filled with nurtients and other substances absorbed from the digestive system.
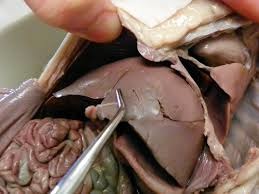
85
New cards
gall bladder
stores bile produced in the liver. one of the components of bile is a by-product of the breakdown of hemoglobin.
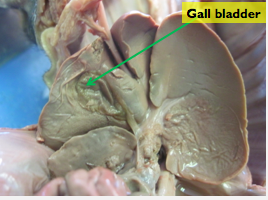
86
New cards
Small intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
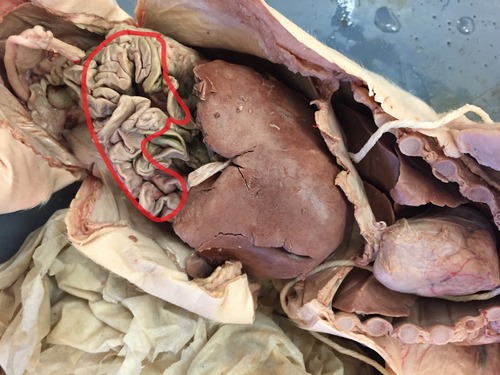
87
New cards
Bile duct
The gal bladder empties its contents into the small intestines using the bile duct. connected the gall bladder and the small intestine
88
New cards
stomach
sac-like organ anterior to the small intestine
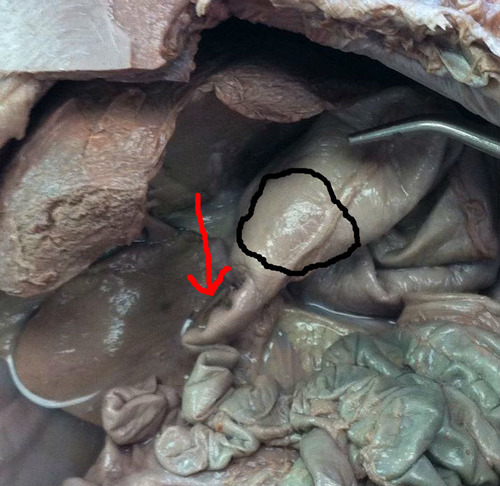
89
New cards
meconium
greenish-black material formed mostly from amiotic fluid and sloughed-off cells, that fills fetal digestive system. (inside stomach)
90
New cards
spleen
part of the immune system; left of stomach, looks like tongue. it is involved in breaking down blood cells.
91
New cards
What is separating the stomach and the small intestine?
the pyloric sphincter, a circular muscle which prevents back flow of contents from the intestine to the stomach.
Ring of smooth muscle fibers around the opening of the stomach into the duodenum
Ring of smooth muscle fibers around the opening of the stomach into the duodenum
92
New cards
What is between the stomach and the duodenum (first loop of the small intestine)?
the pancreas, an organ which has both digestive and endocrine function. white granular organ held in placed by the mesentery membrane.
The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
The first is an exocrine role: to produce digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, which are delivered to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. The second is an endocrine role: to secrete insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to help regulate blood glucose levels.
93
New cards
What is the mesentery membrane part of?
the peritoneum, which lines the body cavity.
94
New cards
Caecum
near large intestine and the anus.
95
New cards
epiglottis
keeps the respiratory and digestive systems separate.
96
New cards
glottis
below the epiglottis is the glottis, the epiglottis is activated during swallowing to cover the glottis which is the opening to the respiratory system.
97
New cards
thoracic cavity
also known as the chest cavity or thorax, surrounds and protects the heart and lungs
98
New cards
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
99
New cards
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathin
100
New cards
large intestine
- About 6 feet long and is composed of the caecum, colon, rectum and anus.