Chapter 4 Quiz Review Ultrasound Procedures
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
The space between the right lobe of the liver and the anterior right kidney and colic flexure is:
•pouch of Douglas.
•Morison's pouch.
•peritoneal recess.
•rectouterine space.
Morison's pouch
The pancreas is located in which abdominal region?
•Right lumbar
•Left iliac
•Epigastric
•Hypogastric
Epigastric
The clinical significance of peritoneal recesses is:
•fluid and infection may accumulate in the recesses.
•organs may be displaced into the recesses.
•gallstones may collect in the recesses.
•hydronephrosis may accumulate in the recesses.
fluid and infection may accumulate in the recesses.
Which one of the following structures divides the pelvic peritoneal space into the anterior and posterior pouches?
•Bladder
•Rectum
•Uterus
•Ovaries
Uterus
The epiploic foramen is the opening between the:
•right and left crus.
•greater and lesser curvature.
•greater and lesser sac.
•inferior and superior inguinal canal.
greater and lesser sac.
An oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall is termed the:
•rectus sheath.
•internal oblique muscle.
•inguinal canal.
•external oblique muscle.
inguinal canal
Vital signs, which are medical measurements to ascertain how the body is functioning, may include all of the following except:
•blood pressure.
•pulse.
•pulmonary function tests.
•temperature.
pulmonary function tests
The membrane that covers an internal organ is known as the:
•mesothelium.
•visceral peritoneum.
•greater omentum.
•parietal peritoneum.
visceral peritoneum
All of the following muscles make up the muscular “sling” in the inferior boundary of the true pelvis except the:
•coccygeus.
•puborectalis.
•levator ani.
•iliacus.
iliacus
The linea alba is found in the:
•abdominal wall.
•external oblique muscle.
•median arcuate ligament.
•crus of the diaphragm.
abdominal wall
Which plane passes through the neck of the pancreas and hilum of the kidneys?
•Subcostal
•Intertubercular
•Midinguinal
•Transpyloric
Transpyloric
Which muscle is not related to the anterior abdominal wall?
•Rectus abdominis
•External oblique
•Quadratus lumborum
•Transversus
Quadratus lumborum
Which kidney sits lower, the right or left?
right
What does the aorta bifurcate into?
left common iliac and right common iliac arteries
________________ is the Dome-shaped muscle that separates the thorax from the abdominal cavity
diaphragm
What is another name for the rectouterine pouch?
pouch of douglas
List the organs that are located in the retroperitoneum:
•Urinary bladder
•Aorta
•Inferior vena cava
•Uterus
•Descending colon
•Adrenal glands
•Kidneys
•Ureters
•Duodenum
•Pancreas
•Ascending colon
The accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum is known as _____________.
ascites
Retroperitoneal organs and vascular structures remain posterior to the cavity and are covered _____________________ with peritoneum.
anteriorly
_____________ is a two-layered fold of peritoneum.
It attaches part of the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall.
mesentary
______________ is peritoneum that is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach and hangs down similar to an apron in the space between the small intestine and the anterior abdominal wall
greater omentum
The arrangement of the ascending and descending colon, the attachments of the transverse mesocolon, and the mesentery of the small intestine to the posterior abdominal wall result in the formation of four______________ _____________.
parabolic gutters
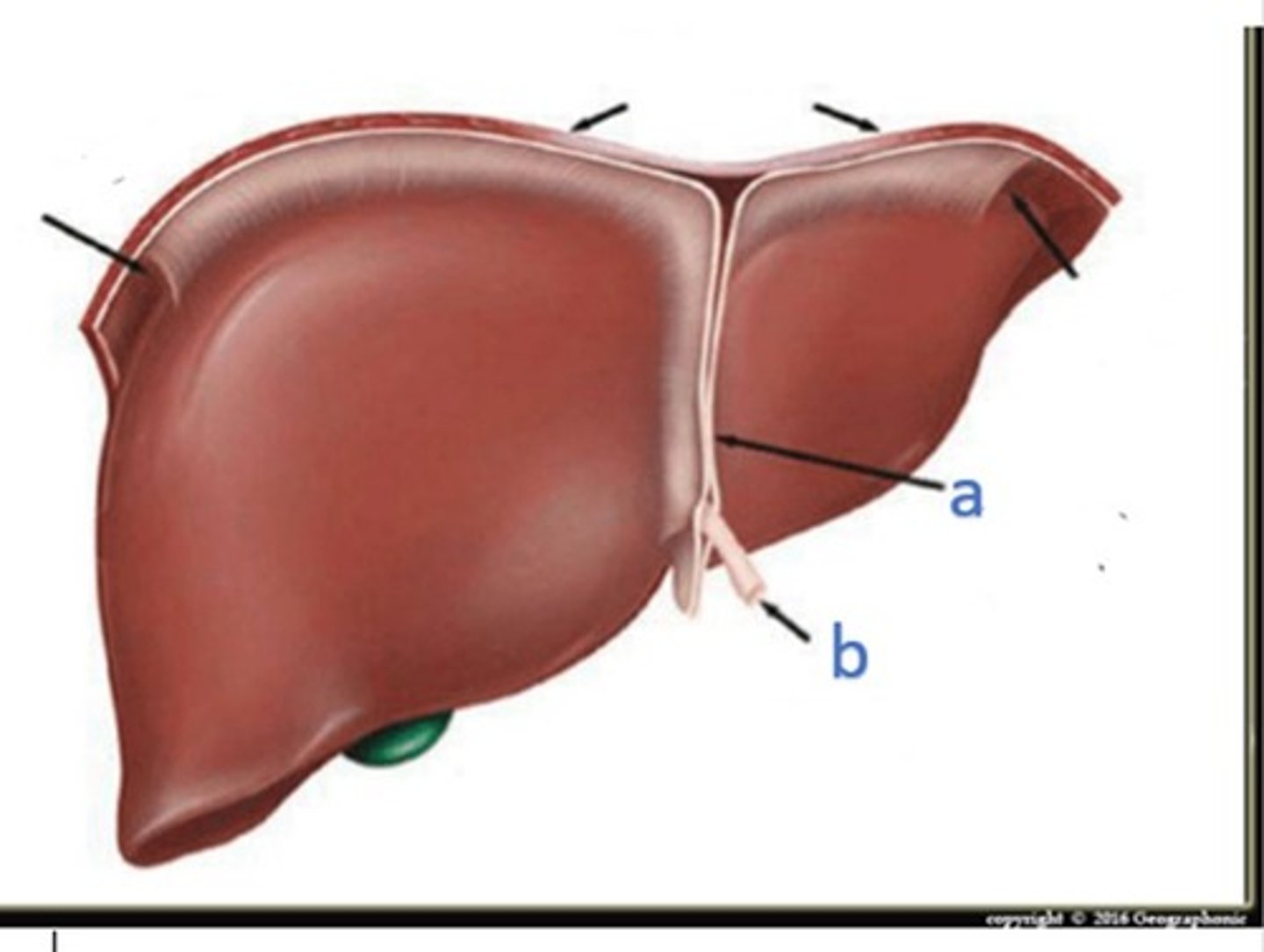
a. falciform ligament
b. ligamentum teres
what ligaments are represented by a and b?