World War I - Key People/Key Terms/Major Ideas (2025)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Archduke Francis (Franz) Ferdinand
Heir to the throne of Austria Hungary; assassinated by Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian Serb.; sparked WWI
Black Hand
Serbian nationalist/terrorist group responsible for the assassination of Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand which resulted in the start of World War I.
Kaiser William II
German King while Germany was being unified with the help of Otto Von Bismark.
Czar Nicholas II
Czar of Russia during WWI, Last Czar of Russia.
Woodrow Wilson
After World War I, this United States president sought to reduce the risk of war by writing the Fourteen Points that influenced the creation of the League of Nations.
David Lloyd George
Britain's prime minister at the end of World War I whose goal was to make the Germans pay for the other countries' staggering war losses.
Vladimir Lenin
Russian founder of the Bolsheviks and leader of the Russian Revolution and first head of the USSR (1870-1924).
Militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war
Alliance System
A formal agreement between two or more nations or powers to cooperate and come to one another's defense
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.
Assassination
the killing of Archduke Franz Ferdinand was blamed for igniting WWI
Powder Keg of Europe
The Balkan's called this because of the strong nationalism leading up to WWI
Triple Alliance
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy
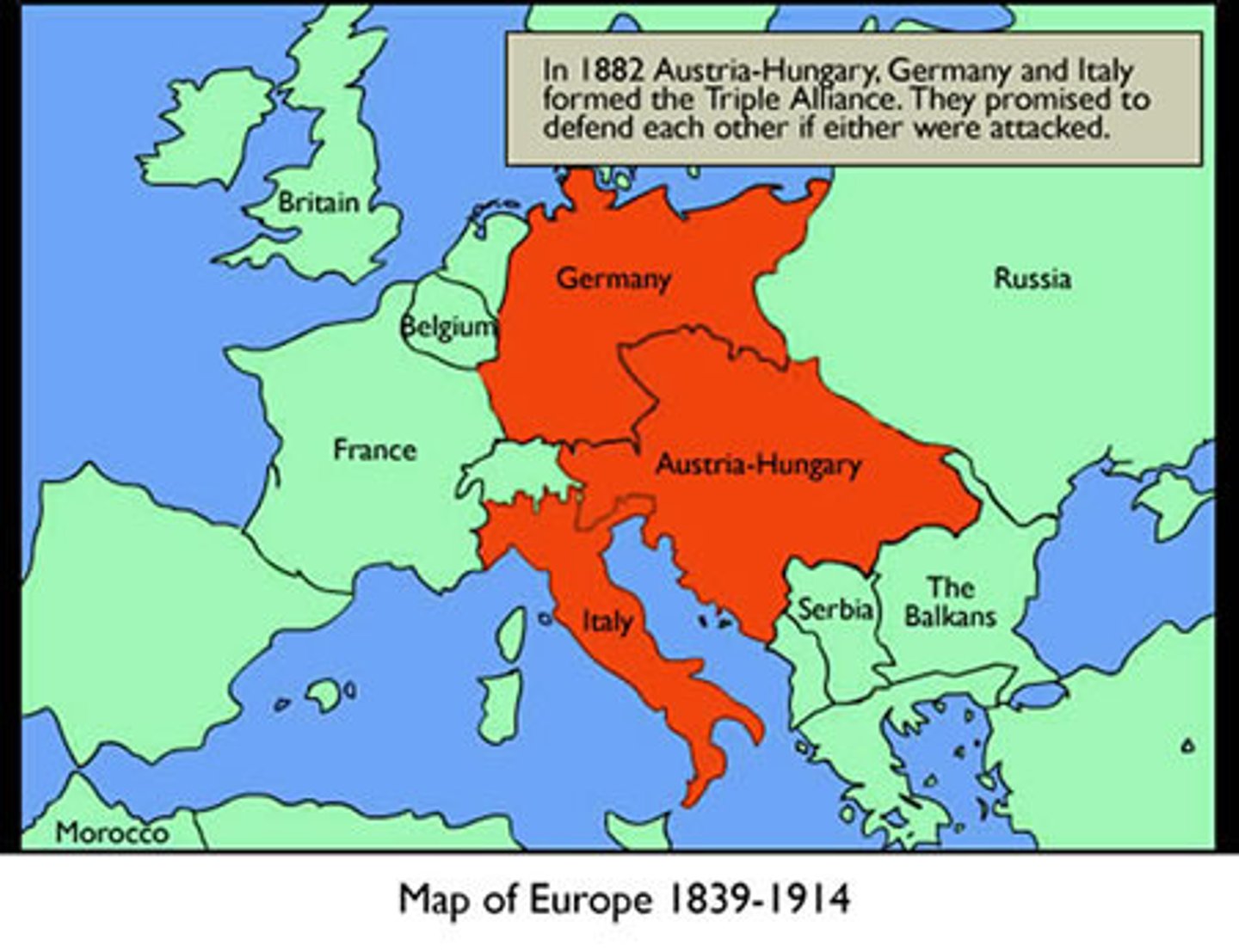
Triple Entente
Great Britain, France, Russia

Central Powers
Austria-Hungary, Germany, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria
Allied Powers
Great Britain, France, Russia
Eastern and Western Fronts
Eastern Front: Russia vs Germany
Western Front: France vs. Belgium
Military Stalemate
A deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other. Neither the allies or Germans were gaining any ground
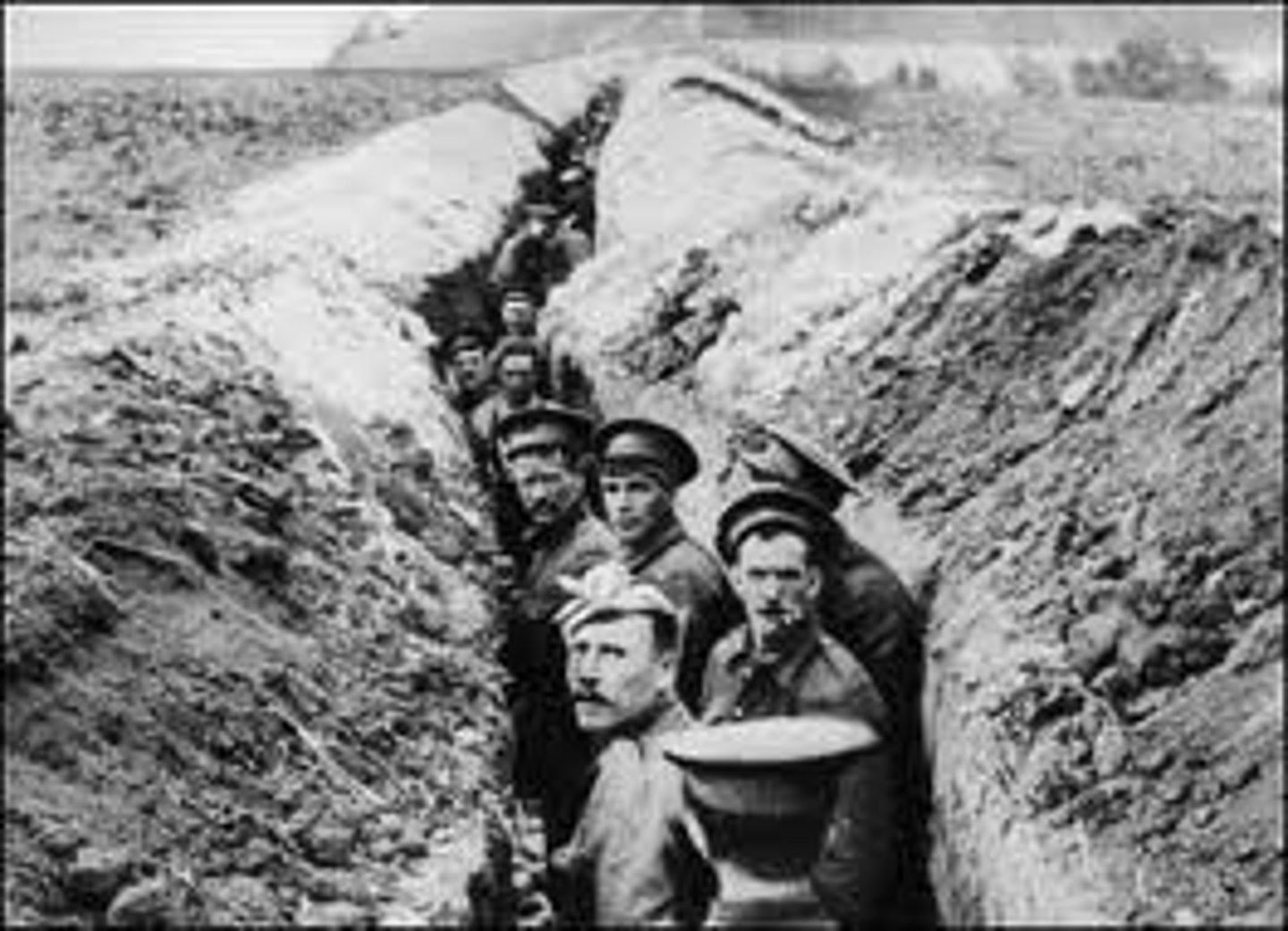
Trench Warefare
A new technique- it defended a position by fighting the from the protection of deep ditches.

Total War
A conflict in which the participating countries devote all their resources to the war effort
Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.

Armenian Genocide
Extermination of the Armenian population by the Ottoman Empire during World War I, resulting in the deaths of approximately 1.5 million Armenians.
“Peace, Land, and Bread”
Communist Revolution Slogan in Russia during WWI
Bolshevik Revolution (Communist Revolution in Russia)
The 1917 uprising led by the Bolshevik Party that overthrew the Provisional Government and established a communist regime in Russia.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
Treaty in which Russia lost substantial territory to the Germans. This ended Russian participation in the war (1918).
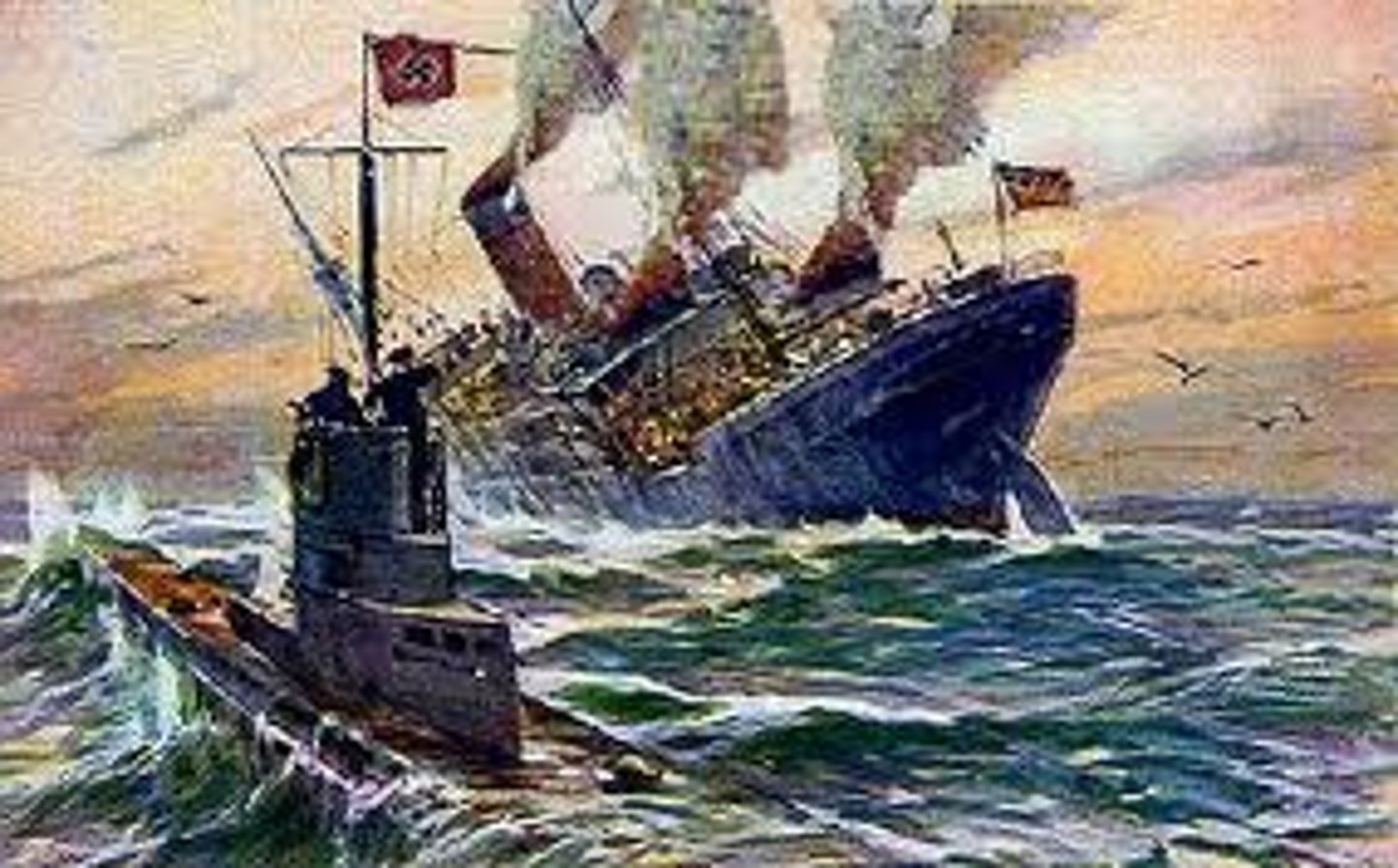
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare
A policy that the Germans announced on January 1917 which stated that their submarines would sink any ship in the British waters

Zimmerman Telegram
A telegram Germany Sent to Mexico to convince Mexico to attack the U.S.
Wilson's "Fourteen Points"
This is the plan for post-World War I outlined by President Wilson in 1918. This plan called for self-determination.
Treaty of Versailles
the treaty imposed on Germany by the Allied powers in 1920 after the end of World War I which demanded Reparations from the Germans
"War Guilt" Clause
In treaty of Versailles; declared Germany responsible for WWI; ordered Germany to pay reparation to Allied powers
Reparations
Payment for war damages
League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations
Collective Security
A system in which a group of nations acts as one to preserve the peace of all
Self Determination
Concept that ethnicity have the right to govern themselves
Describe the long term causes of WWI (MANIA)
Militarism, Alliances, Nationalism, Imperialism and Assassination
Identify the immediate cause of WWI
Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Explain how the Industrial Revolution led to a deadlier war (i.e. technology)
Rifles, machine guns, tanks and planes were manufactured and now used
Explain how technology led to a military stalemate in WWI
Trench warfare emerged due to the failure of the Schliffen Plan. Barbed wire made it impossible for troops to advance.
Discuss the conditions in the trenches
Muddy, uncomfortable, unsanitary, full of diseases
Why was WWI considered a total war?
the nations involved devoted all their resources to it
Describe the costly effects of WWI
Germany was singled out and had to pay reparations and 10 to 13 million people were killed
Explain why Russia withdrew from WWI in 1917
They had low supplies and because they had a political revolt (Russian Revolution)
Explain why the US entered the war in 1917 after three years of neutrality
-Germany was attacking American ships
-Germany violated international law
- The Zimmerman telegram
Discuss the impact of the US entering the war on the side of the Allies
-Fresh troops boosted morale
- 2 million placed in France 1.3 million fighting at the fronts
How did the Treaty of Versailles impact Germany after WWI?
- Germany paid Reparations.
- Demilitarized their Army.
- Had to give colonies to Allies.
Explain the goals of Wilson's "Fourteen Points"
- Wilson wanted PEACE WITHOUT VICTORY.
- He didn't want to punish Germany for the war because he knew one day that could lead to another war.
Why was the League of Nations considered a weak peace keeping organization?
They did not have a military to enforce the laws they created.