Psy 202 midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:41 AM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
1
New cards
What is intelligence to Sir Francis Galton?
Sensory abilities
2
New cards
What is intelligence to Edwin Boring?
Intelligence is whatever intelligence tests measure
3
New cards
What is intelligence to Alfred Binet?
Higher mental processes
4
New cards
What is general intelligence?
Measure the overall intelligence
5
New cards
What is Specific intelligence?
Measure our special skills and it is unique to each test
6
New cards
What are the 6 components of General intelligence?
1. Visual-spatial processing
2. Quantitative reasoning
3. Knowledge
4. Fluid reasoning
5. Working memory
7
New cards
What is Visual-spatial processing?
helps with puzzles and visual problems
8
New cards
Quantitative reasoning
help with real world problems
9
New cards
Fluid reason
is thinking abstractly, flexibly and fast; use reason to solve/apply rules
10
New cards
Working memory
uses short term memory to attain information for a short period of time to solve
11
New cards
Crystallized *intelligence*
is knowledge you have about the world over time to solve
12
New cards
Fluid intelligence
is knowledge that you gain from learning new things
13
New cards
How does fluid intelligence play along with crystallized *intelligence?*
If we repeat fluid intelligence overtime, it will become crystallized overtime
14
New cards
What is linguistic intelligence?
Speak and write
15
New cards
What is logico-mathematical intelligence?
Use logic and mathematical skills to solve problems
16
New cards
What is spatial intelligence?
Think and reason about objects in three dimensional space
17
New cards
What is musical intelligence?
Perform, understand, and enjoy music
18
New cards
What is bodily-kinesthetics intelligence?
Manipulate the body in sports, dace, or other physical activities
19
New cards
What is interpersonal intelligence?
Understand and interact effectively with others
20
New cards
What is intrapersonal intelligence?
Understand and posses insight into self
21
New cards
What is naturalistic intelligence?
Recognize, identity, and understand animals, plants, and other living things
22
New cards
What is the triarchic model of intelligence?
Analytical, creative, and practical intelligence
23
New cards
Gardner vs. Sternberg
Gardner has 8 intelligence scale and Sternberg is the triarchic model
24
New cards
What is analytical intelligence?
Academic problem solving
25
New cards
What is creative intelligence?
Imaginative and innovative problem solving
26
New cards
What is practical intelligence?
Street smarts and common sense
27
New cards
What is Alfred Binet approach to IQ testing?
Uses mental age to measure IQ; IQ = mental age/ chronological age x 100
28
New cards
What is a problem with Binet IQ testing?
Mental age stays the same at a certain age
29
New cards
What was David Wechlser’s approach to IQ testing?
He uses a scale where everyone at any age has an average score of 100, then adds or subtracts 15 points for every subject testing (like overall IQ, verbal comprehension, etc.)
30
New cards
What is IQ testing today?
Wechsler adult intelligence scale (WAIS)
31
New cards
What is a weakness of WAIS?
Some culture or race are not able to answer some testing because they do not have the experience
32
New cards
What is a culture-fair IQ testing and why?
Raven’s Progressive Matrices; abstract-reasoning items that don’t depend on language
33
New cards
What is the average IQ score?
100
34
New cards
What IQ score is intellectual disability?
35
New cards
What IQ score is gifted?
>130
36
New cards
What is the Flynn effect?
If the person took an IQ test long ago, their IQ test today would be higher than before, due to environmental changes
37
New cards
What environmental influence could change intelligence?
1. Children from larger families
2. Amount of schooling
3. Early intervention programs
4. Poverty
38
New cards
What can females do better than males?
Verbal task and recognizing emotions of other
39
New cards
What can male do better than female?
Spatial reasoning
40
New cards
Who has more variable in IQ score?
Male
41
New cards
What factor explains why IQ difference in race?
Environmental factors
42
New cards
When is the germinal stage?
start - 2 weeks
43
New cards
When is the embryonic stage?
3-8 weeks
44
New cards
When is the fetal stage?
9 weeks - birth
45
New cards
What happens in the germinal period?
Zygote gets implanted
46
New cards
What happens in the embryonic period?
heart starts beating, brain start developing, and body part appears
47
New cards
What happens in the fetal period?
rapid growth of body and brain
48
New cards
When is the most vulnerable stage of prenatal?
embryonic period
49
New cards
What influences prenatal?
1. Maternal factors like health, nutrition, age, etc.
2. Teratogens: environmental hazards like drugs, radiation, etc.
50
New cards
When is the central nervous system vulnerable in prenatal stages?
3-12 weeks
51
New cards
When is the heart vulnerable in prenatal stages?
3-6 weeks
52
New cards
When is the ears vulnerable in prenatal stages?
4-12 weeks
53
New cards
When is the eyes vulnerable in prenatal stages?
4-8 weeks
54
New cards
When is the legs vulnerable in prenatal stages?
4-7 weeks
55
New cards
When is the arms vulnerable in prenatal stages?
4-7 weeks
56
New cards
When is the teeth vulnerable in prenatal stages?
6-8 weeks
57
New cards
When is the palate vulnerable in prenatal stages?
6-12 weeks
58
New cards
When is the external genitalia vulnerable in prenatal stages?
7-12 weeks
59
New cards
What could happen if prenatal stages are affected by alcohol consumption?
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
60
New cards
When does the brain reach adult size?
Reaches 75% of adult size by 2 years
61
New cards
What dies with age?
Neurons
62
New cards
What is dementia?
an umbrella from brain disease
63
New cards
What is alzheimer disease?
The cortex and hippocampus is damaged, which affects thinking, planning, and remembering
64
New cards
What was Piaget’s theory of development?
Constructivist: children construct knowledge by themselves
65
New cards
What are the 3 Piaget’s theory processes?
Assimilation, accommodation, equilibration
66
New cards
What is assimilation? and an example
translate new information into a form you
already have/understand
ex,. a kid sees a plane and call it birdie
already have/understand
ex,. a kid sees a plane and call it birdie
67
New cards
What is equilibrium? and an example
balance assimilation and accommodation to create stable understanding
ex., a kid is familiar with birds so they think all flying thing is a bird
ex., a kid is familiar with birds so they think all flying thing is a bird
68
New cards
What is accommodation? and an example
When new information does not fit, you need to restructure your “theories”
ex., the kid concludes that planes are not birdies, creates new category for them
ex., the kid concludes that planes are not birdies, creates new category for them
69
New cards
Examples of sensorimotor stage
1. The monkey being in sight then is blocked by a wall and the baby cannot process that it is behind the wall
2. A-not-B Error; the baby believes the item is always in A even if it’s been changed to B
3. Deferred imitation; the baby imitates a move that is shown later on
70
New cards
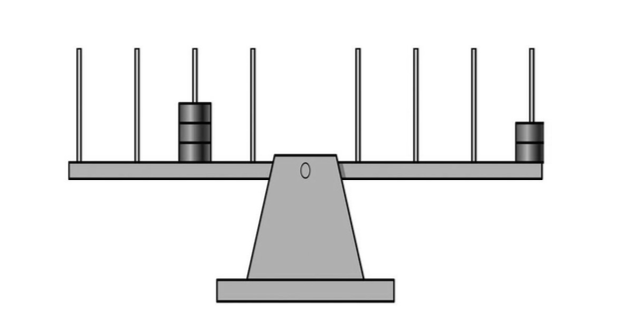
Examples of preoperational stage
1. Use of scale models; using a smaller model to locate the object then searching for the object in the bigger room
2. Egocentrism; the kid thinking his perspective on his side of the mountain view is the same for everyone else
3. Centration; a kid trying to balance at scale and only focusing on the uneven distribution instead of the location of placement
4. Conservation; a kid believes the food on the smaller plate has more food than the big plate
\
71
New cards
What is concrete operational stage?
The kid is starting to understand most concept like conservation
72
New cards
What is Vygotsky view of development?
1. Children are social being, therefore people teach them to help them learn
2. Culture shape their thinking
73
New cards
Example of social referencing
baby sees mom happy so they cross; baby sees mom fearful baby won’t cross
74
New cards
What is the percentage of easy temperament profile?
40%
75
New cards
What is the percentage of difficult temperament profile?
10%
76
New cards
What is the percentage of slow to warm up temperament profile?
15%
77
New cards
What is goodness of fit?
the compatibility of the child’s temperament to an enviroment
ex., for an active child, enroll them in sports, for an inactive child enroll them in inactive activity like chess
ex., for an active child, enroll them in sports, for an inactive child enroll them in inactive activity like chess
78
New cards
What is Bowlby’s attachment theory?
Phases of attachment formation:
1. Asocial phase
2. Indiscriminate attachments
3. Specific attachment
4. Multiple attachments
1. Asocial phase
2. Indiscriminate attachments
3. Specific attachment
4. Multiple attachments
79
New cards
What is the asocial phase?
crying to get needs
80
New cards
What is the indiscriminate attachment?
showing preferences to familiar people by emotions
81
New cards
What is specific attachment?
showing regular caretakers attachment issues when they are not around
82
New cards
What is multiple attachment?
towards other caretakers
83
New cards
What is a secure attachment style?
explores while mother is present, not distress around strangers, upset when mother leaves, happy when mother is back
84
New cards
What is a insecure-avoidant attachment style?
explores without mother, not upset when mother leave and not happy when she returns
85
New cards
What is a **Insecure-Anxious/Resistant** attachment style?
Clings to mother, doesn’t explore, distress around strangers, when mother they return but rejects the contract
86
New cards
What is a **disorganized** attachment style?
A combination of avoidant and resistant traits, usually in high risk families
87
New cards
What is internal working models?
building sense of emoting though relationship with others
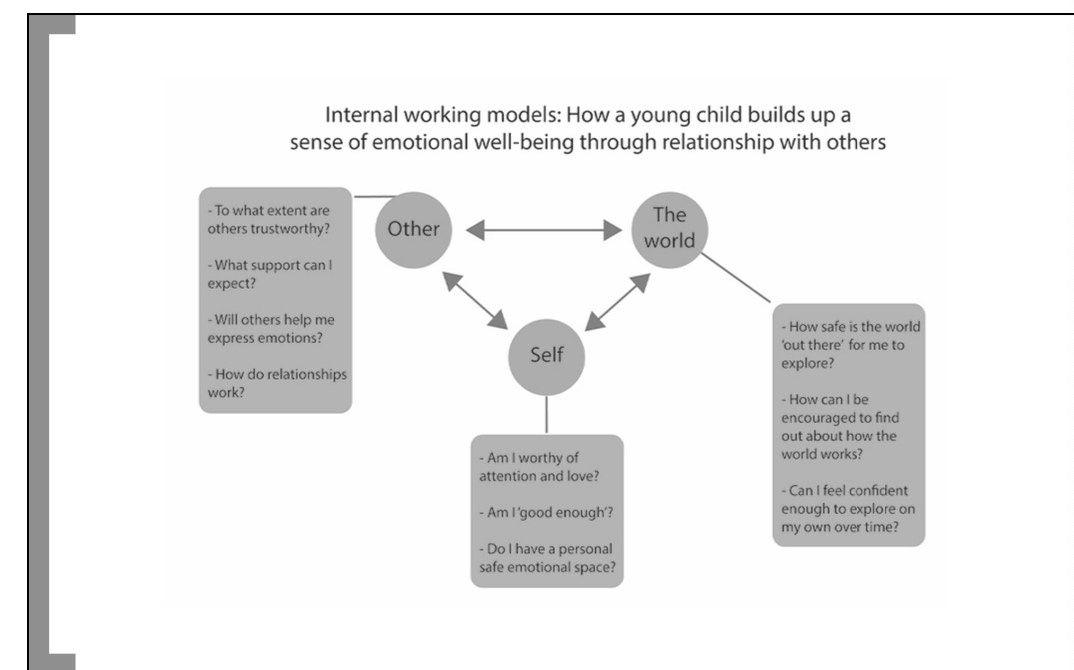
88
New cards
Example of delay of gratification
kid waiting to get double the amount of marshmallow
89
New cards
Does delay of gratification lead to success later in life?
Yes
90
New cards
How can culture affect delay of gratification?
Culture changes the raising of the child which changes their self-control development
91
New cards
What is pre-conventional reasoning?
Moral judgment in terms of reward and punishment
92
New cards
What is conventional reasoning?
Moral judgment in terms of social order, rules, and approval
93
New cards
What is post-conventional reasoning?
Doing what’s right based on your belief
94
New cards
What happens if the limbic system is damged?
damage to the amygdala may result in psychic blindness; not being able to detect other’s emotion
95
New cards
What is the left and right of the frontal lobe?
Left is the positive emotions and right is negative emotions
96
New cards
Example of James-Lange theory
You see a bear, you run, then you fear
97
New cards
Example of Cannon-Bard theory
You see a bear then you run and fear at the same time
98
New cards
Example of **Two-Factor theory**
a bear approaching → running away → assesses the emotion → fear
99
New cards
What are non-verbal expression?
body language, posture, gestures
100
New cards
How does polygraph test work?
measures arousal