Apologia Biology (3rd edition) Module 6
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Genetics
The science that studies how characteristics get passed from parent to offspring.

Genetic factors
The general guideline of traits determined by a person's DNA.
environmental factors
Those "nonbiological" factors that are involved in a person's surroundings such as the nature of the person's parents, the person's friends, and the person's behavioral choices.

Spiritual factors
The factors in a person's life that are determined by the quality of his or her relationship with God.

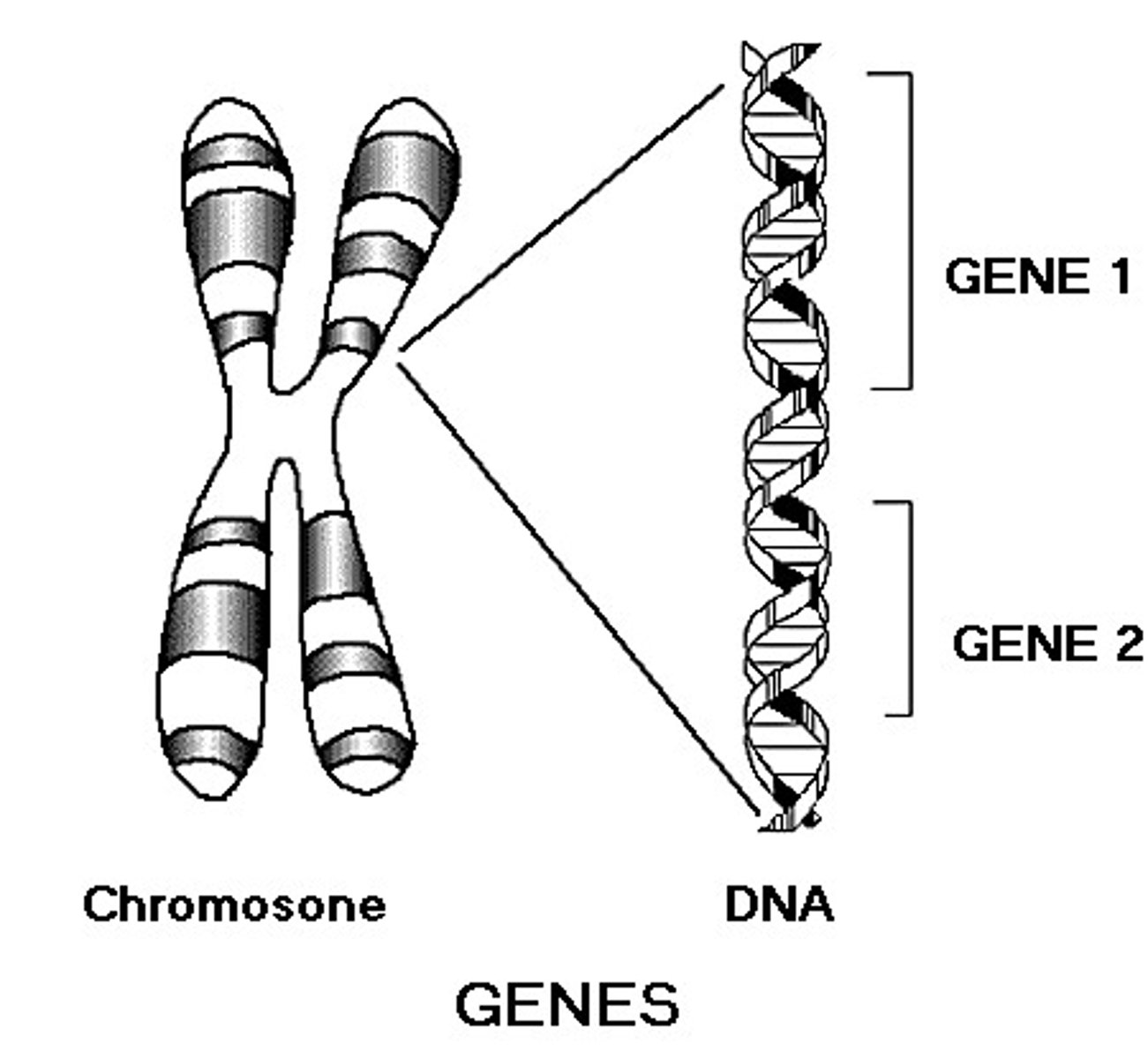
Gene
basic unit of heredity; a section of DNA that contains the code to produce a protein or a portion of a protein, thereby causing a trait
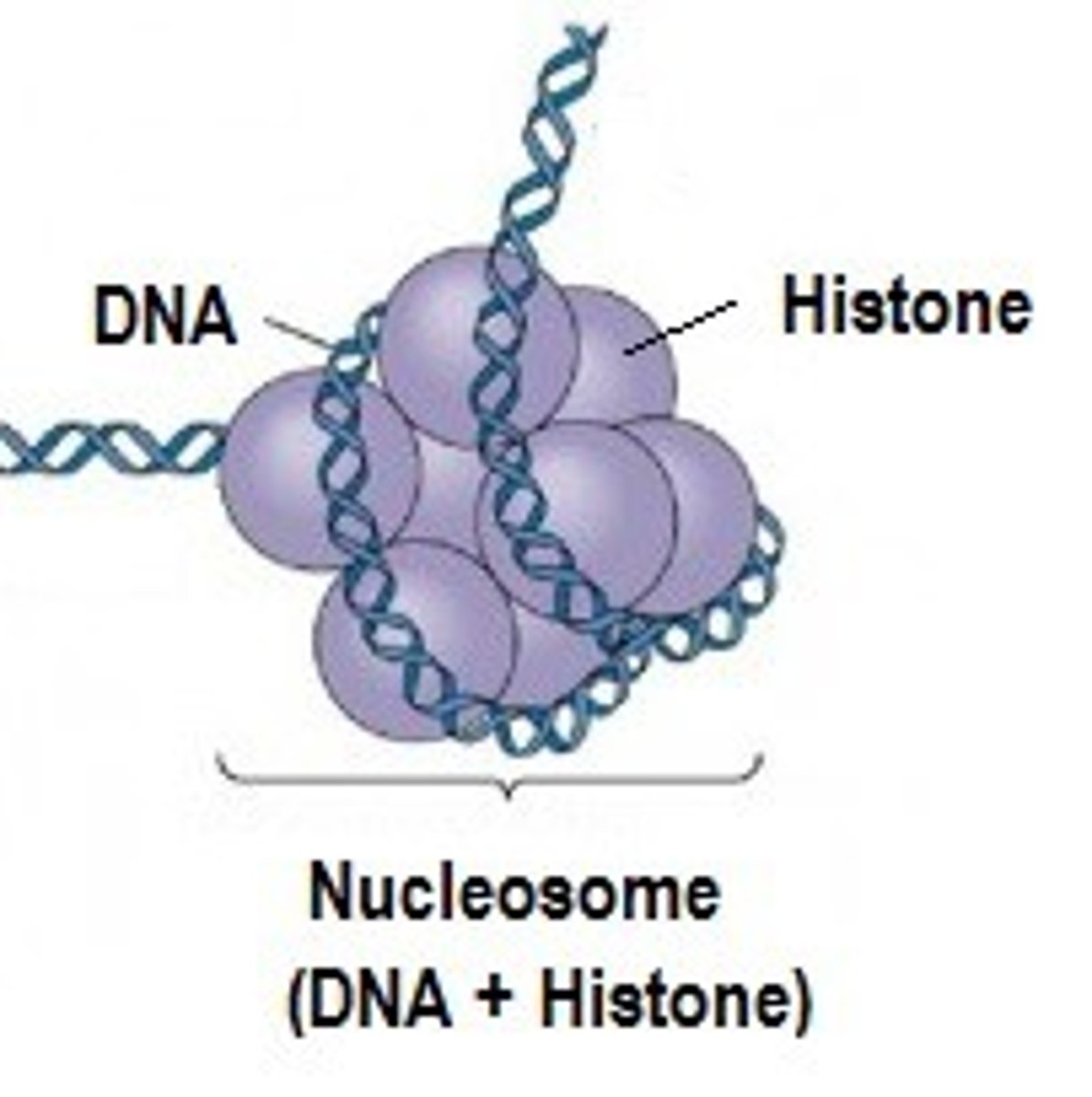
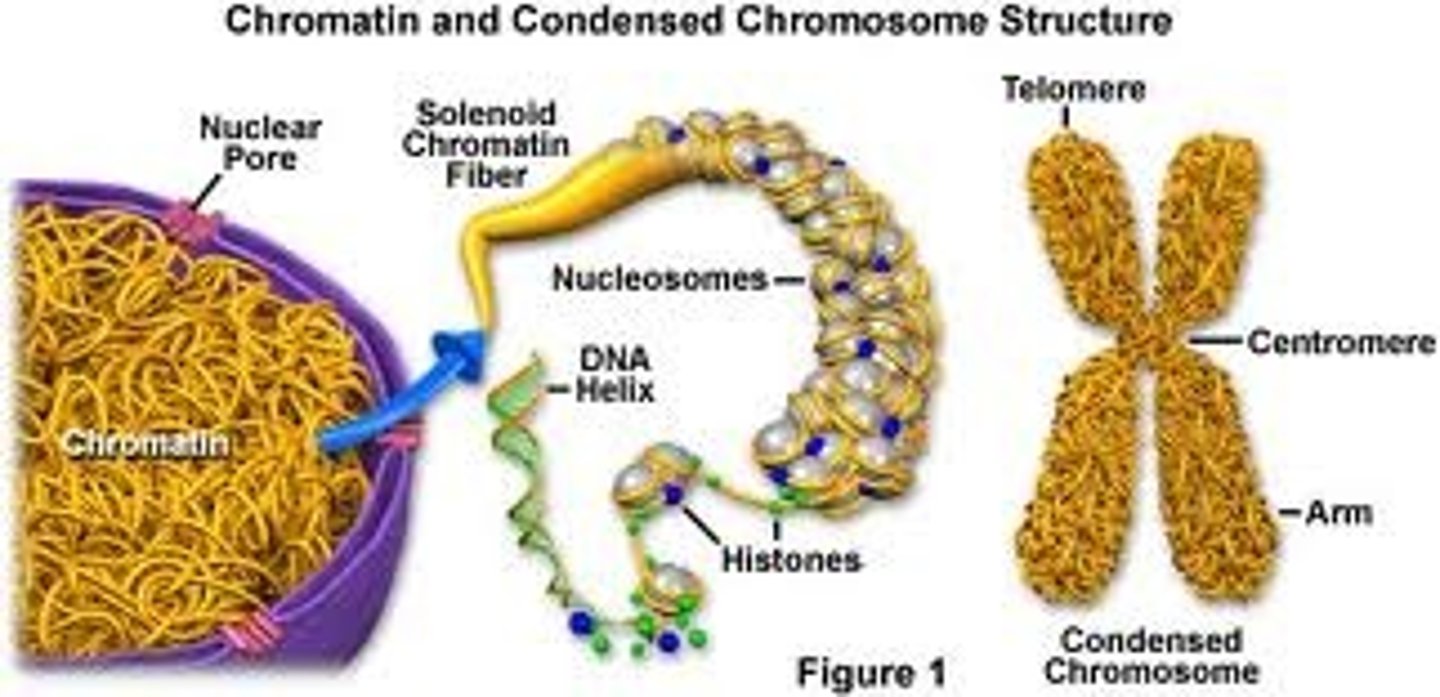
Histones
certain proteins that act as spools that wind up small stretches of DNA
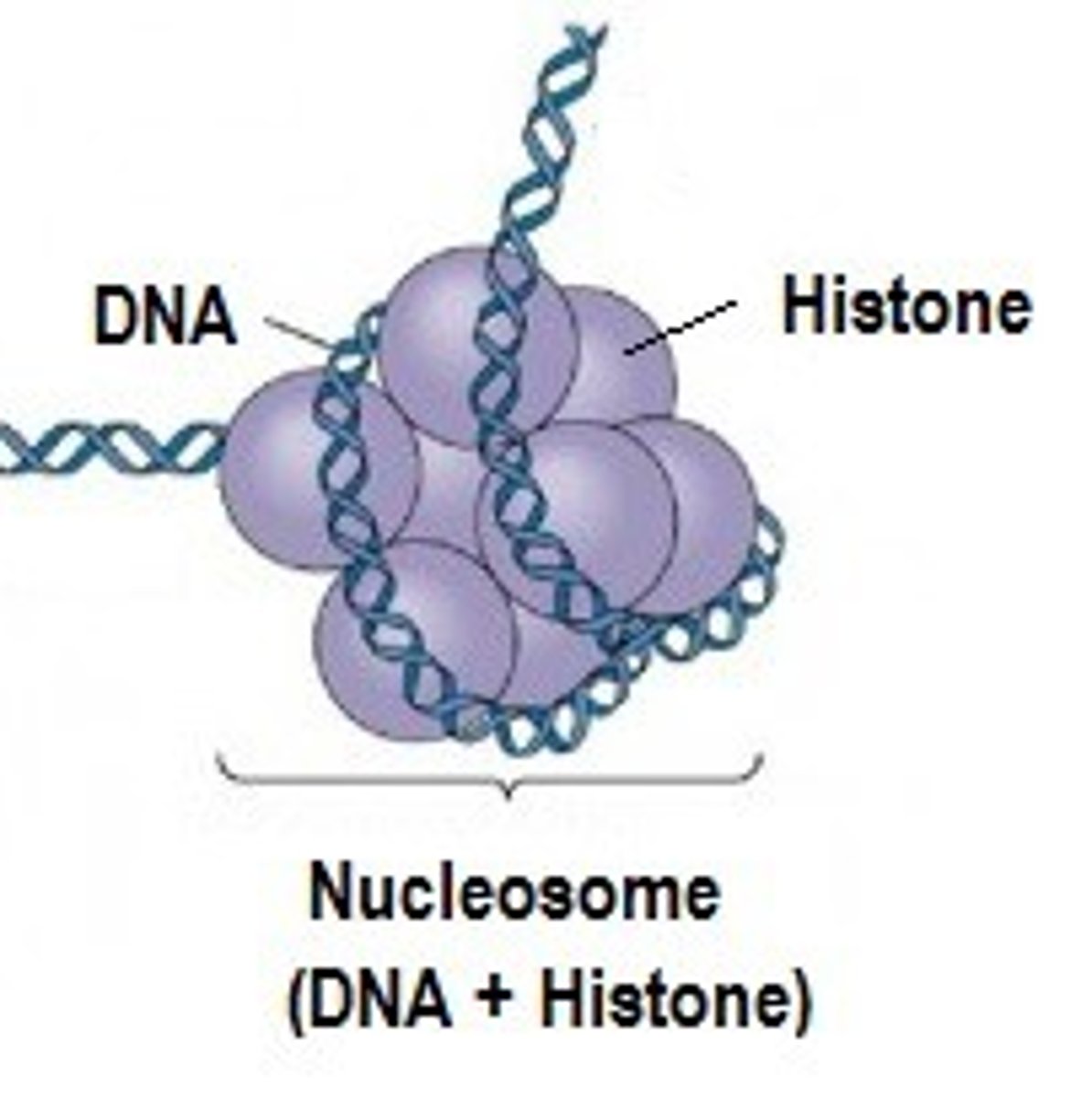
Nucleosomes
Bead-like structures formed by histones and DNA
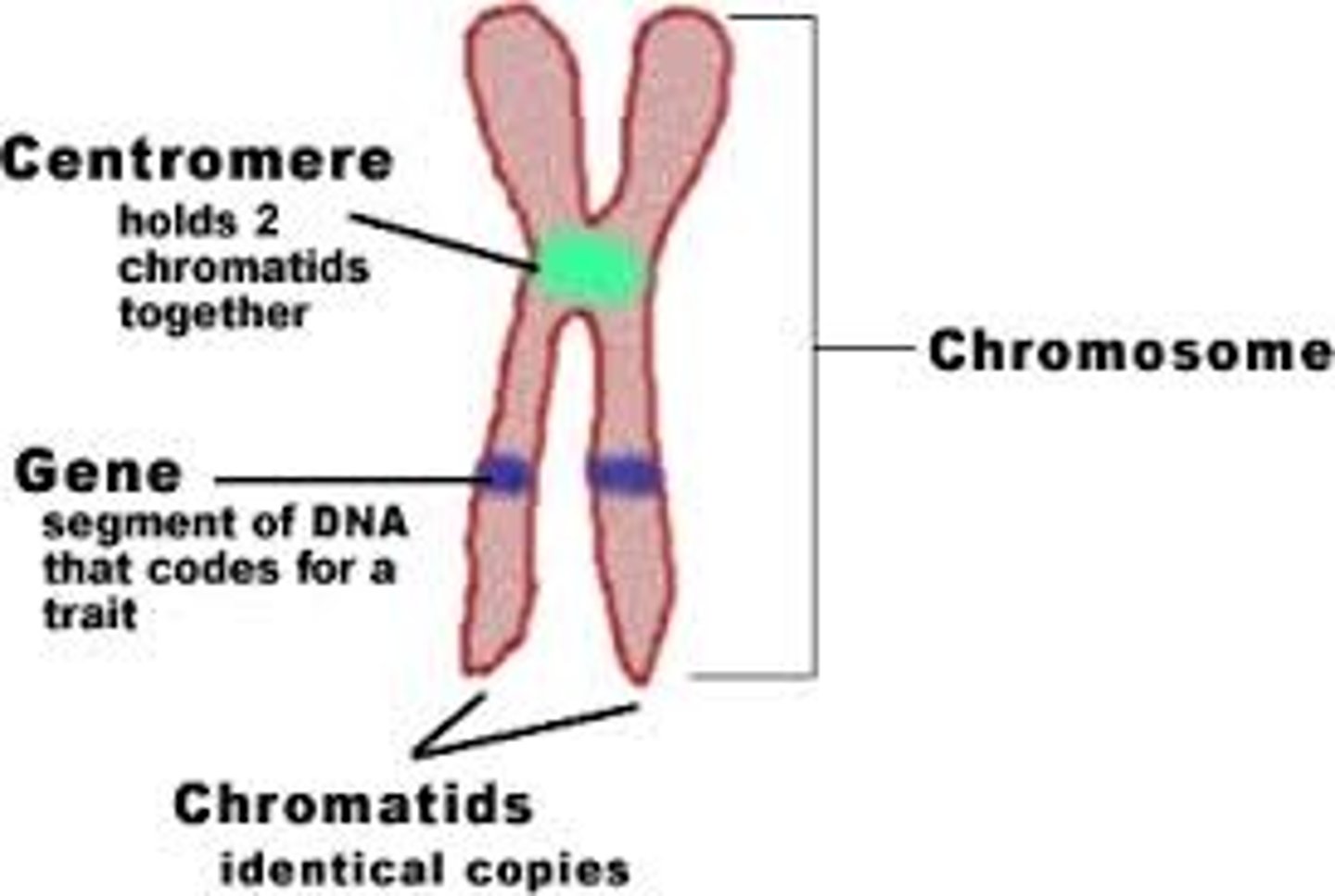
Chromosome
condensed threads of chromatin found in the nucleus of the cell
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
condensed chromosome
small possible package a chromosome forms when ready to reproduction
DNA replication
process by which two identical DNA molecules are produced from one original DNA molecule
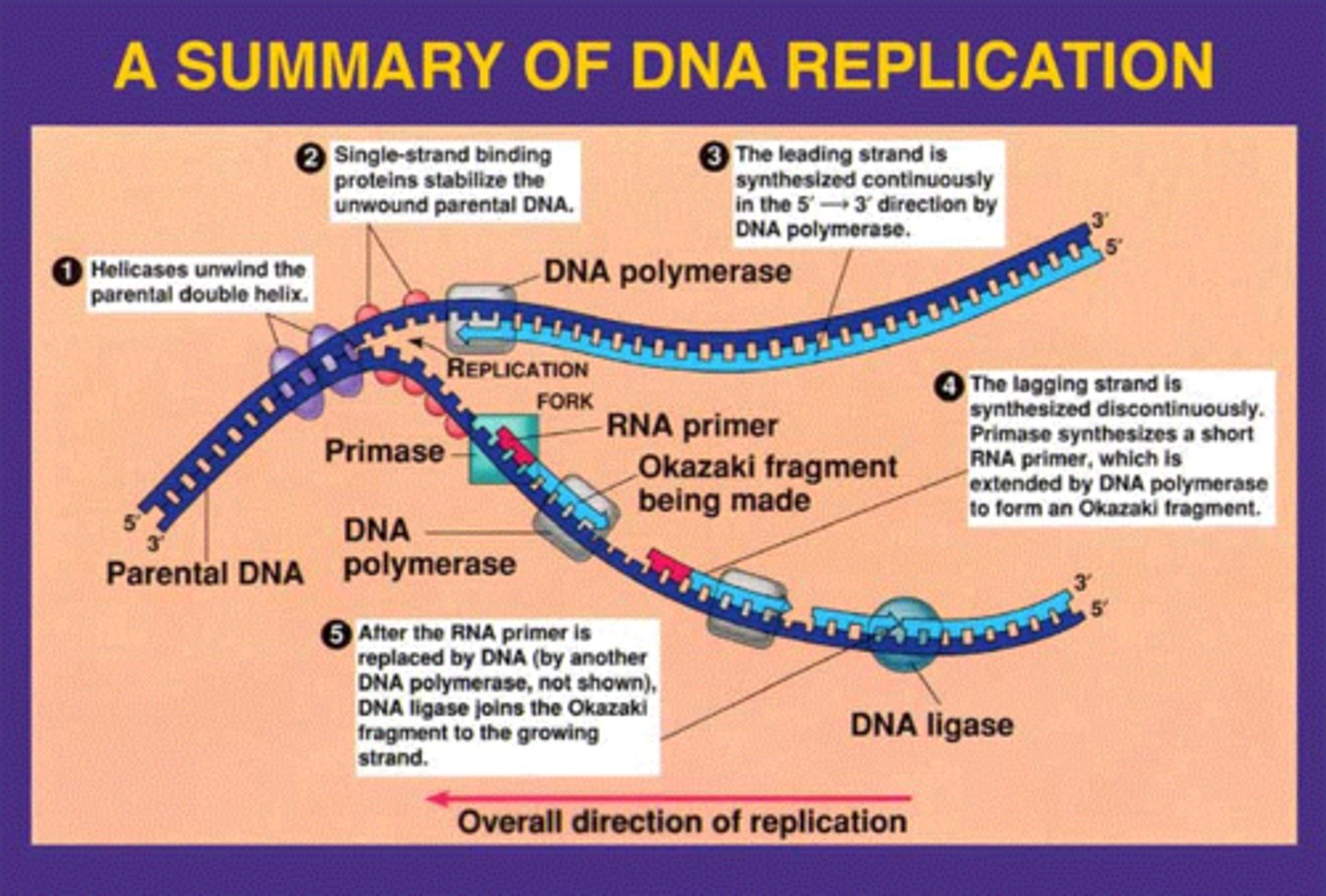
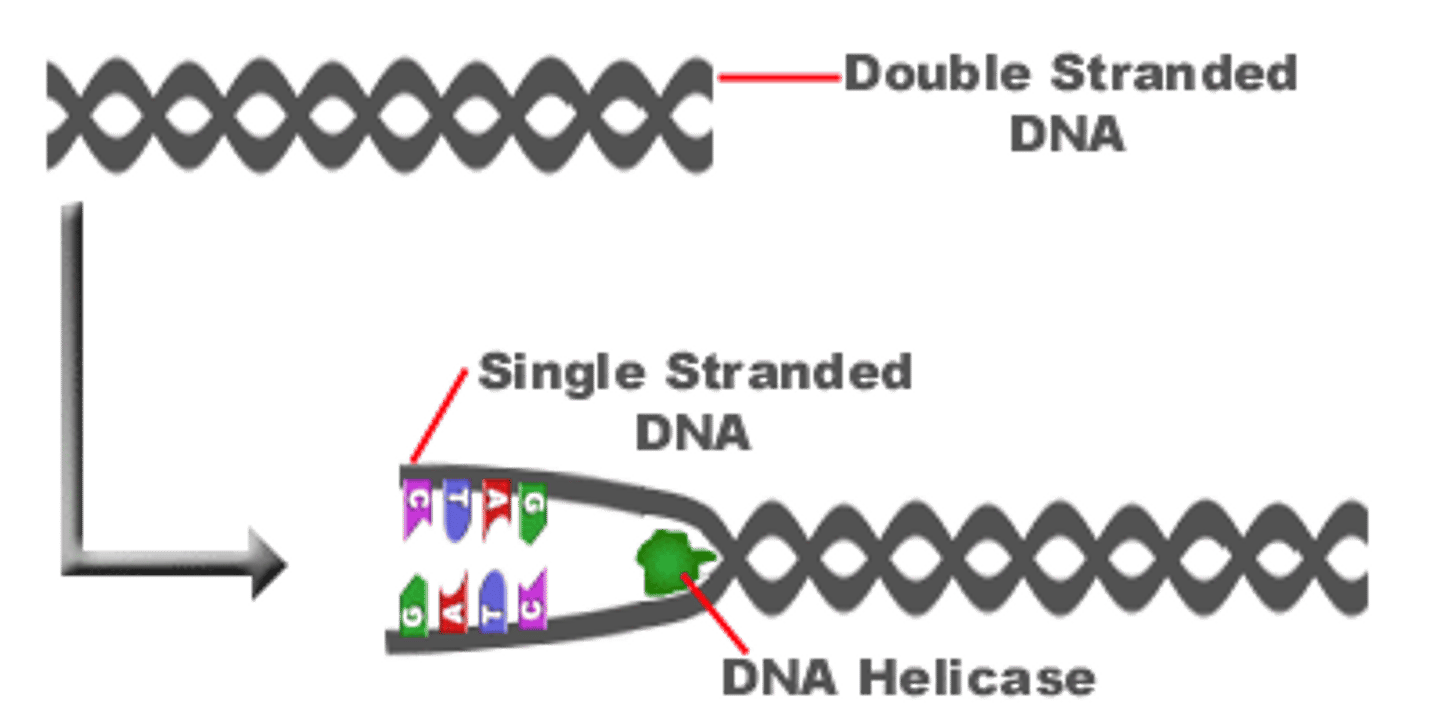
Helicase
An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases holding the two strands of DNA together
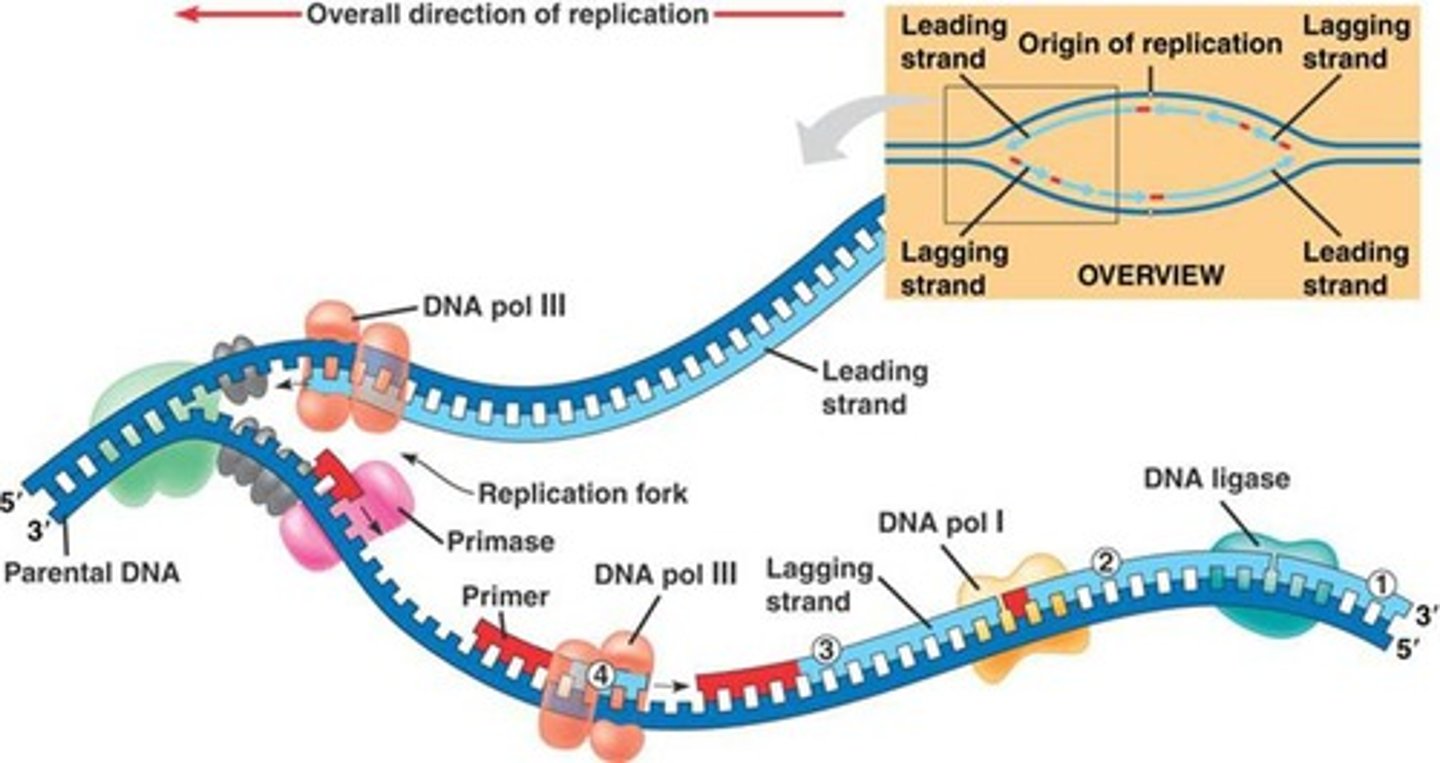
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides forming binds between the sugars and phosphates of the backbone
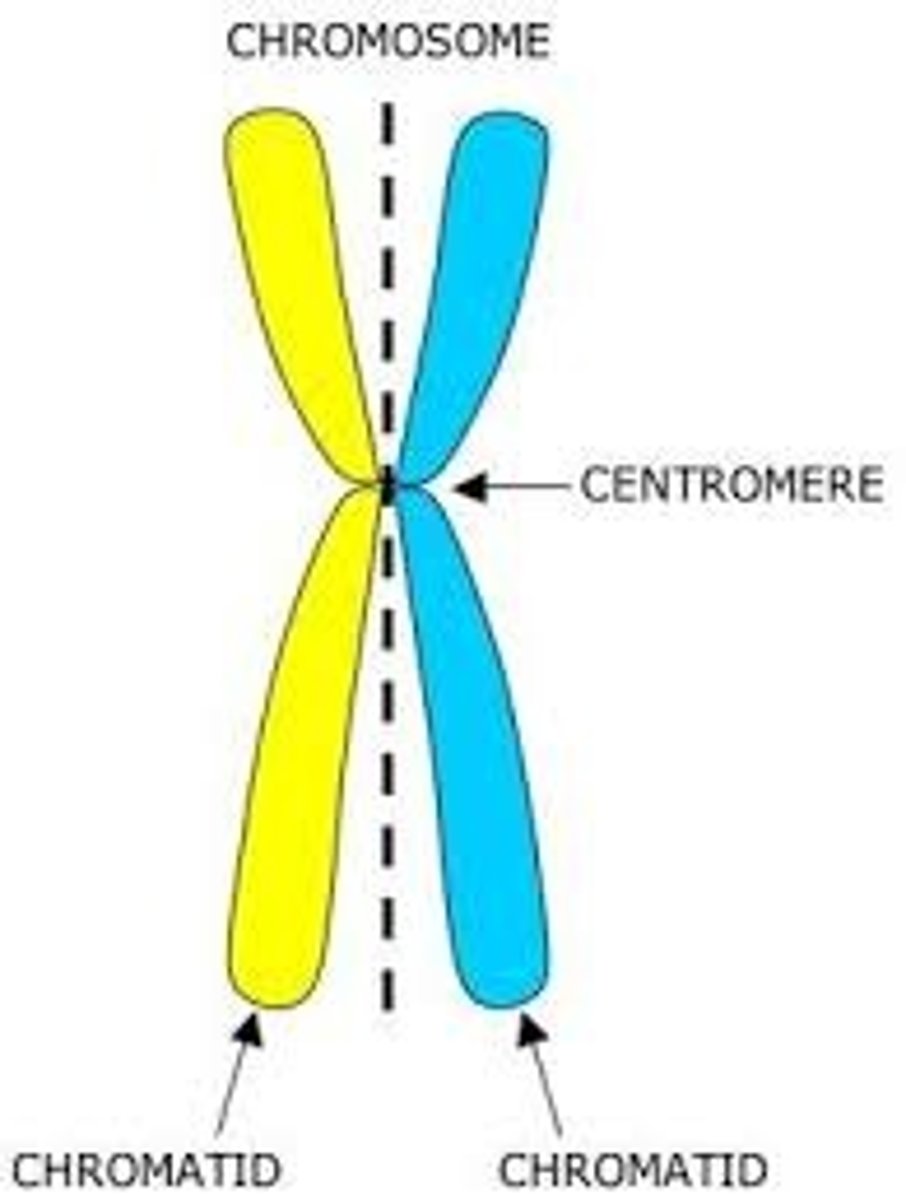
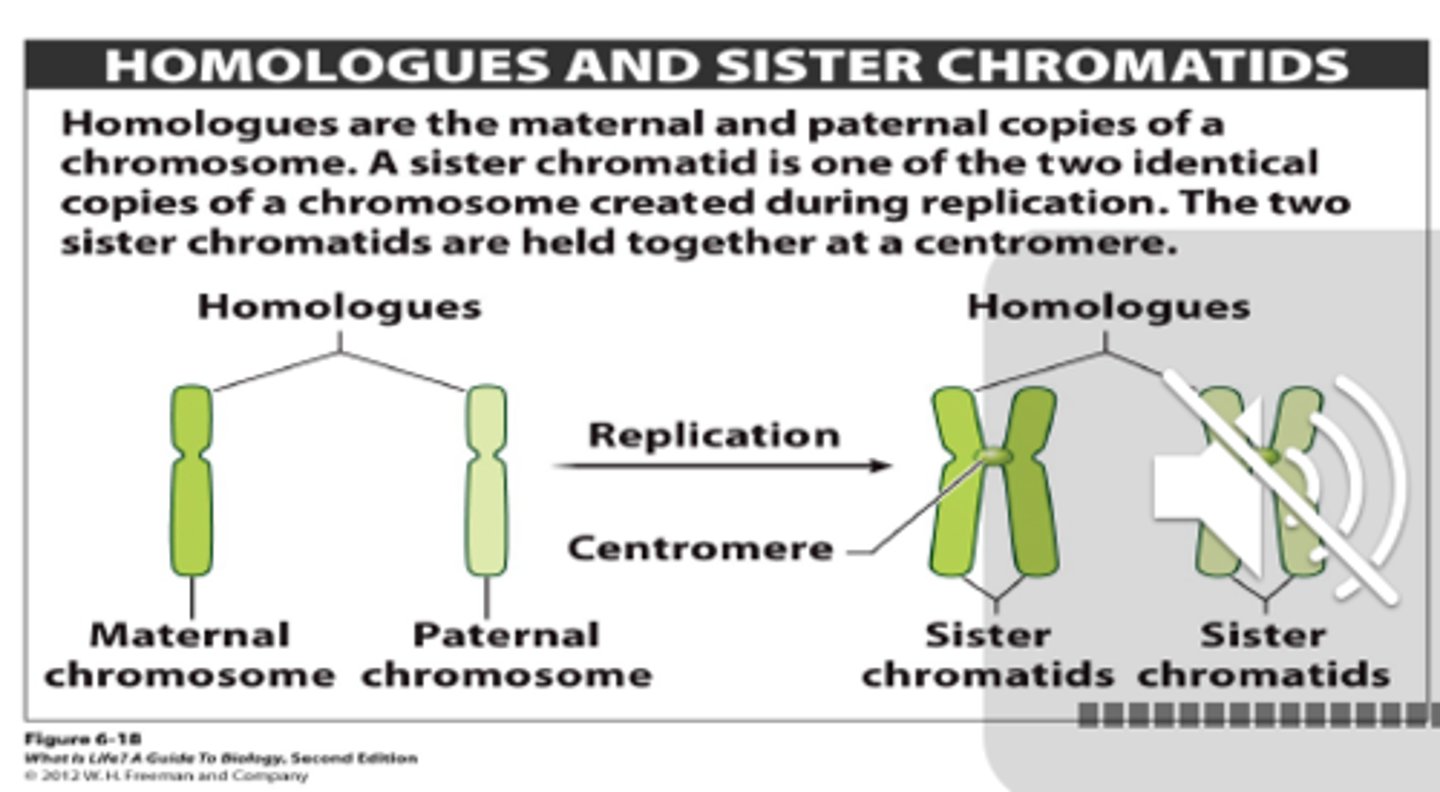
Centromere
Area where the identical strands of chromatin of a chromosome are attached
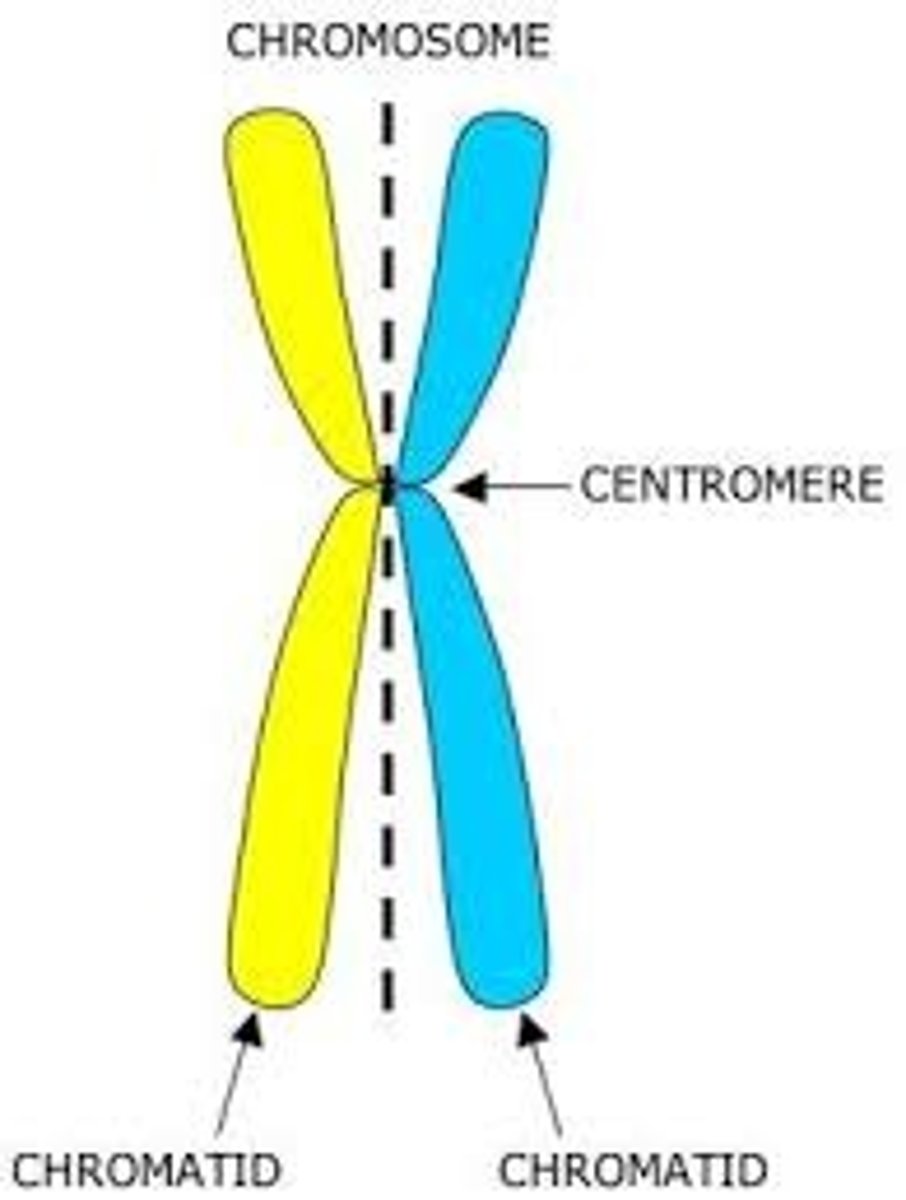
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
RNA polymerase
enzyme aiding in bonding the sugar of one RNA nucleotide to the phosphate of the next RNA nucleotide
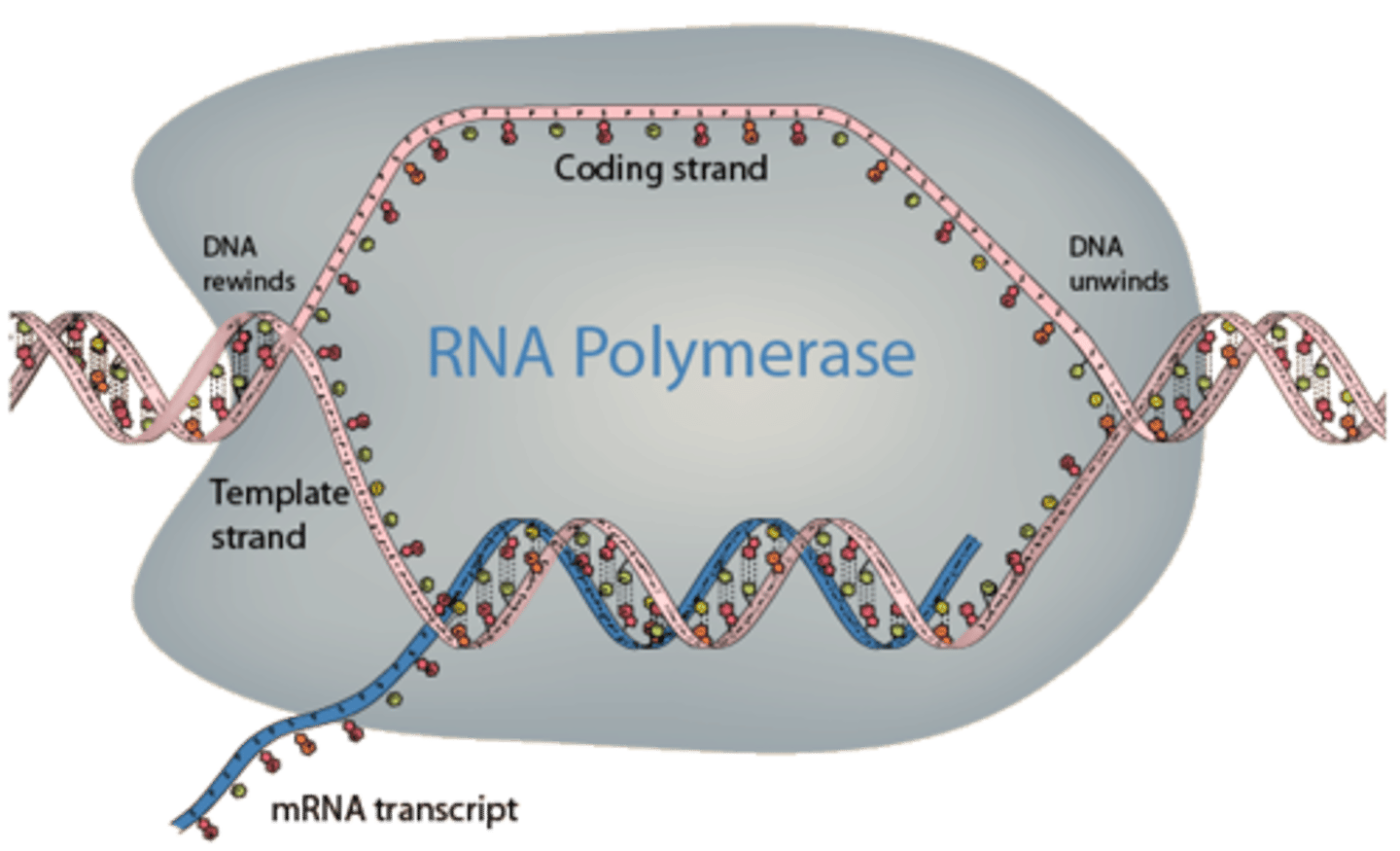
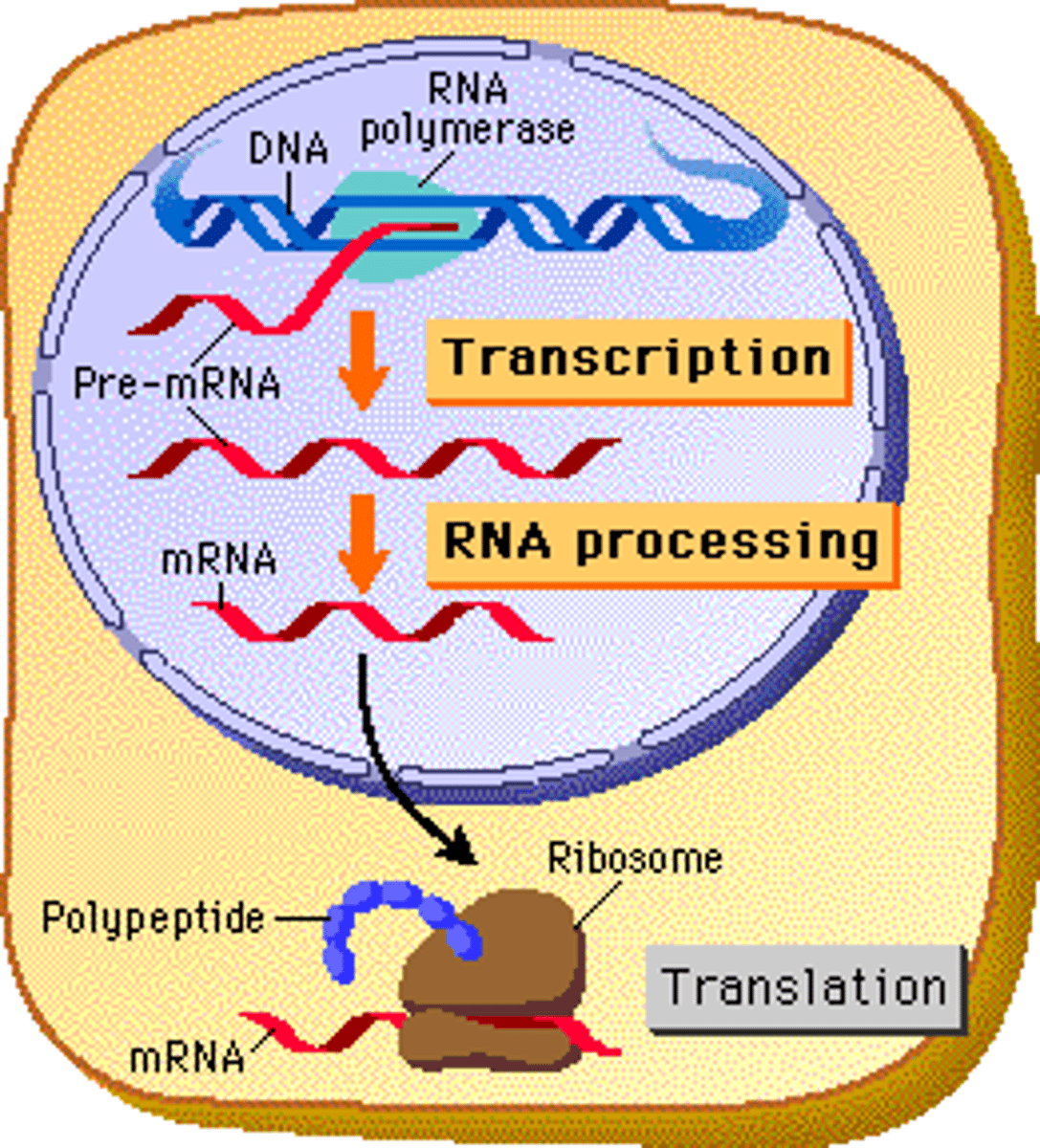
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
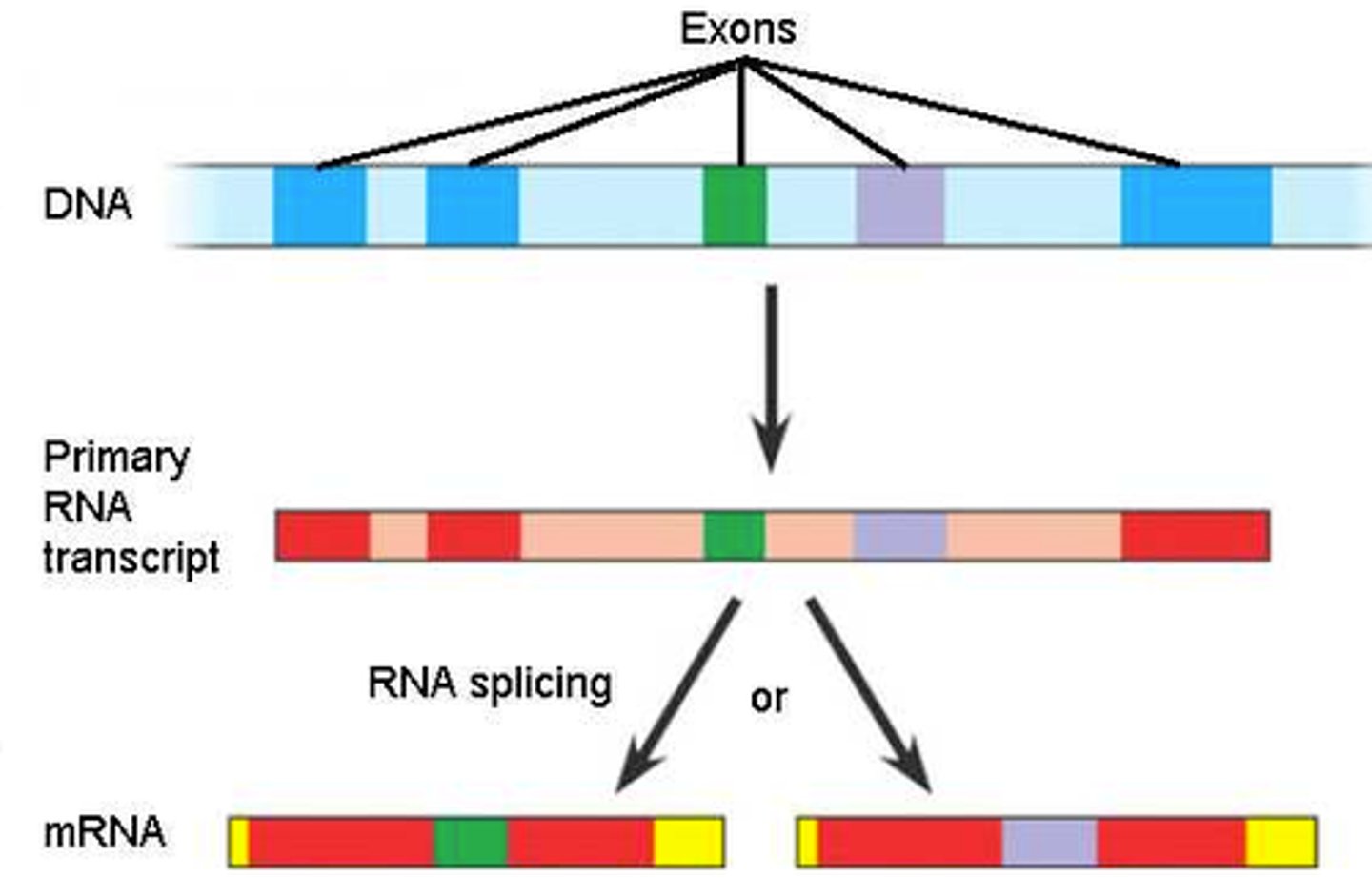
Exons
Coding segments of eukaryotic DNA.
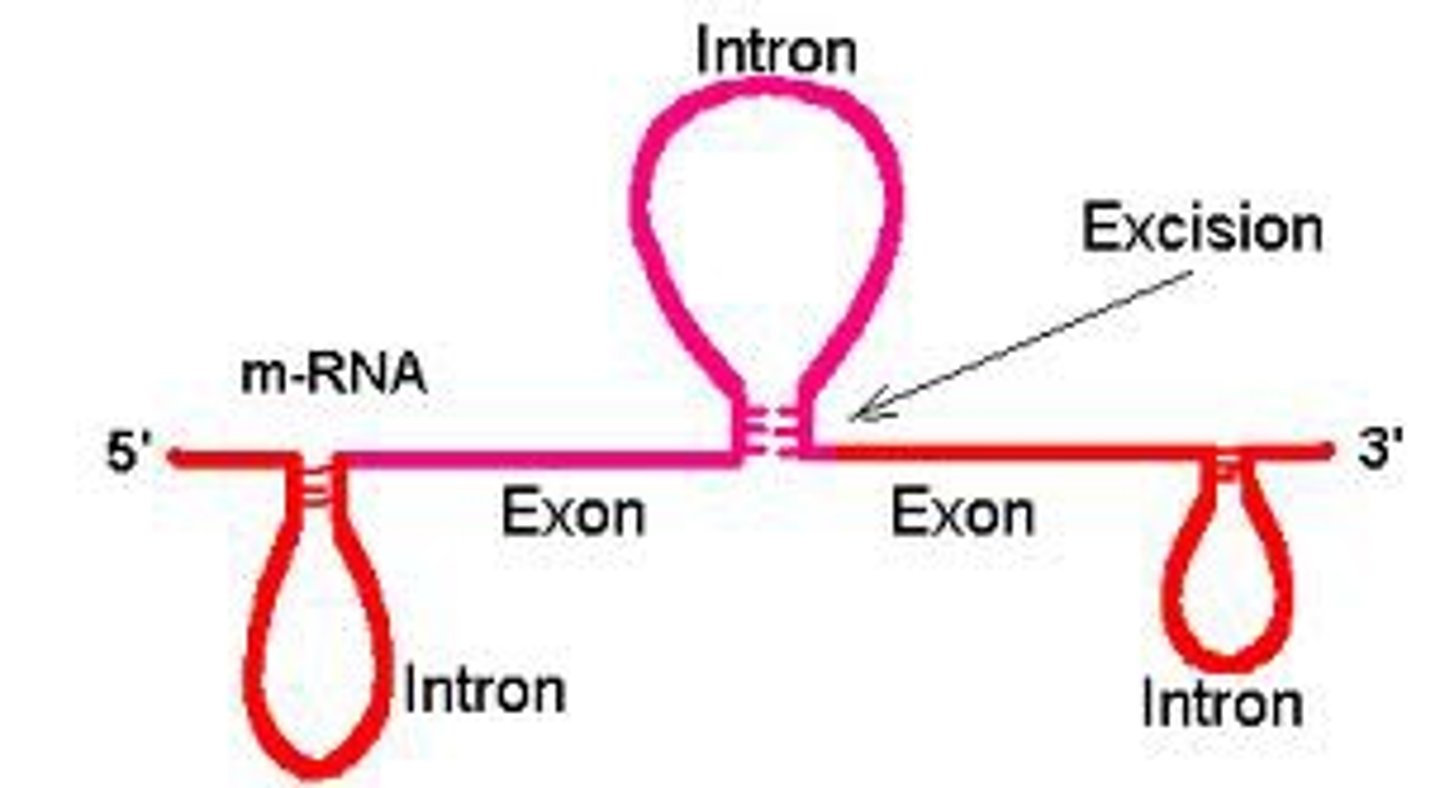
Introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
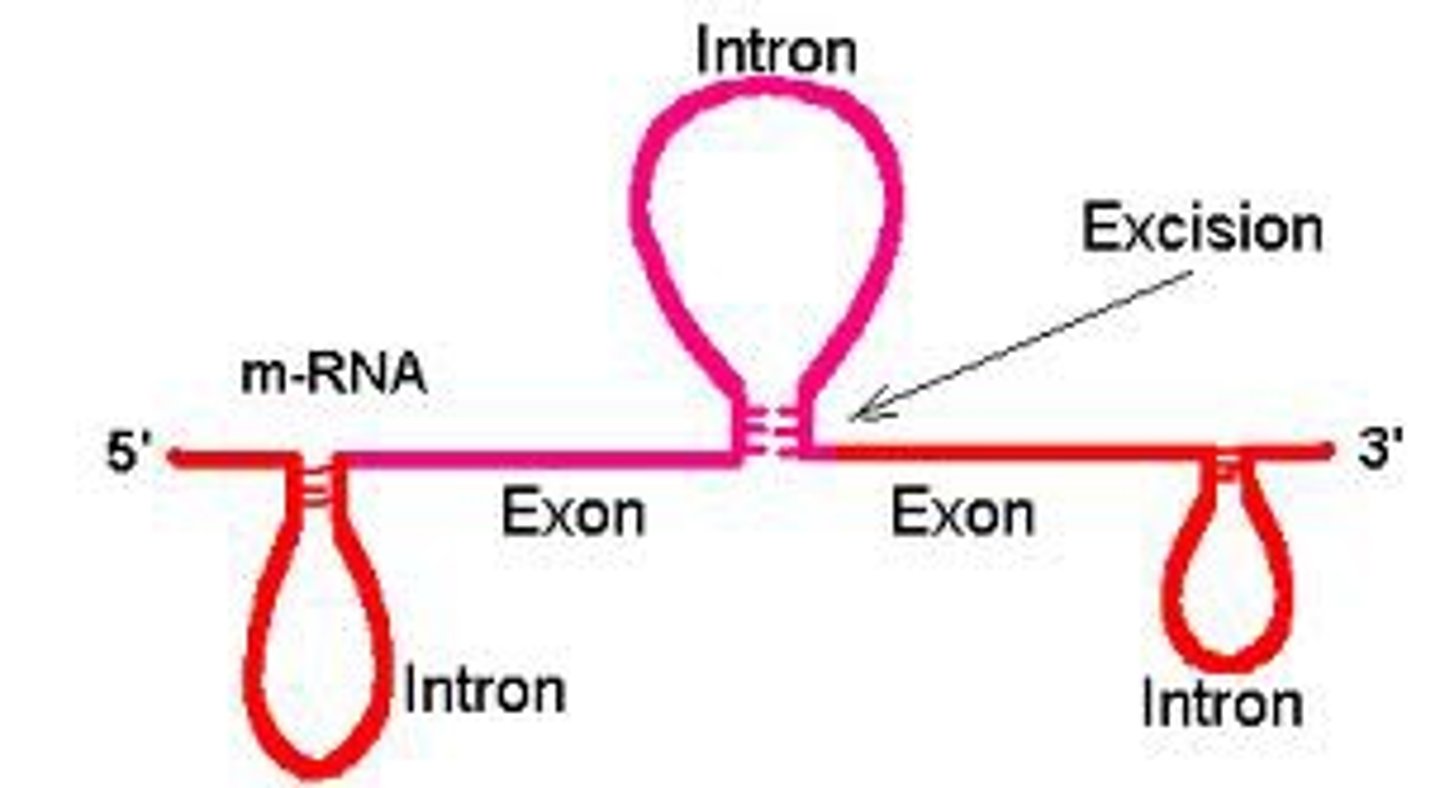
RNA splicing
Process by which the introns are removed from RNA transcripts and the remaining exons are joined together.
triplets
three base sequence on DNA
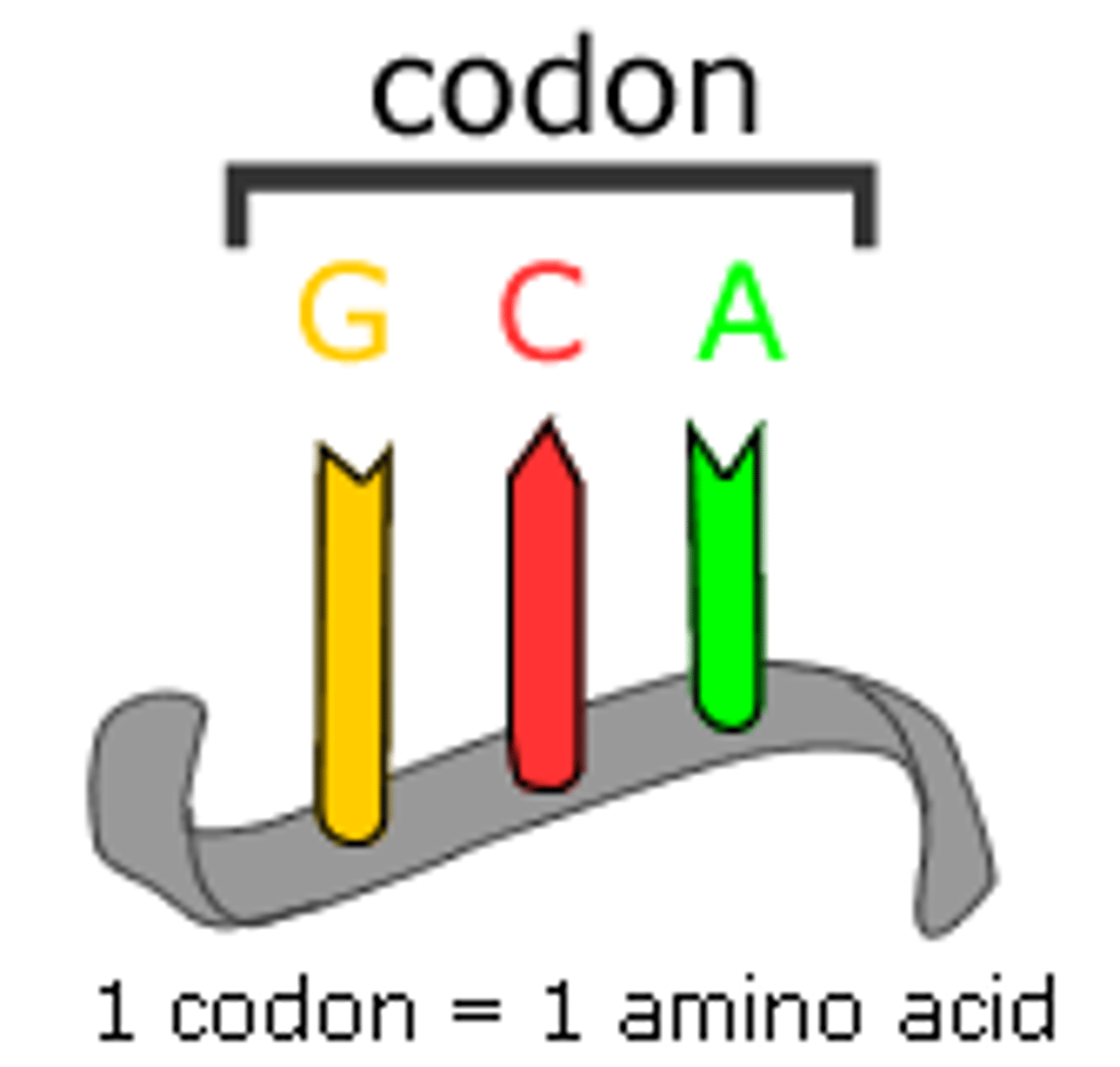
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
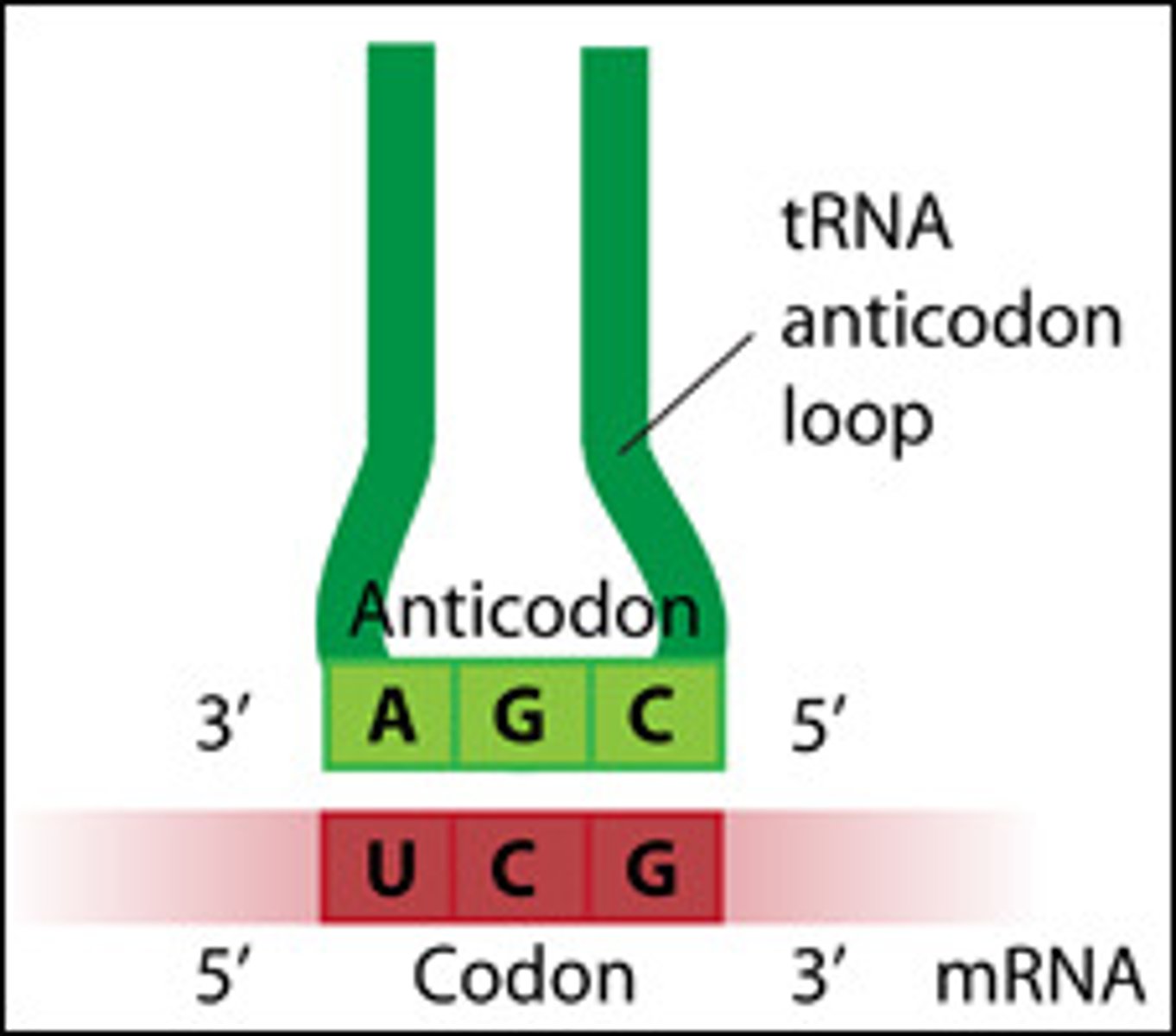
Anticodon
three-base sequence on tRNA
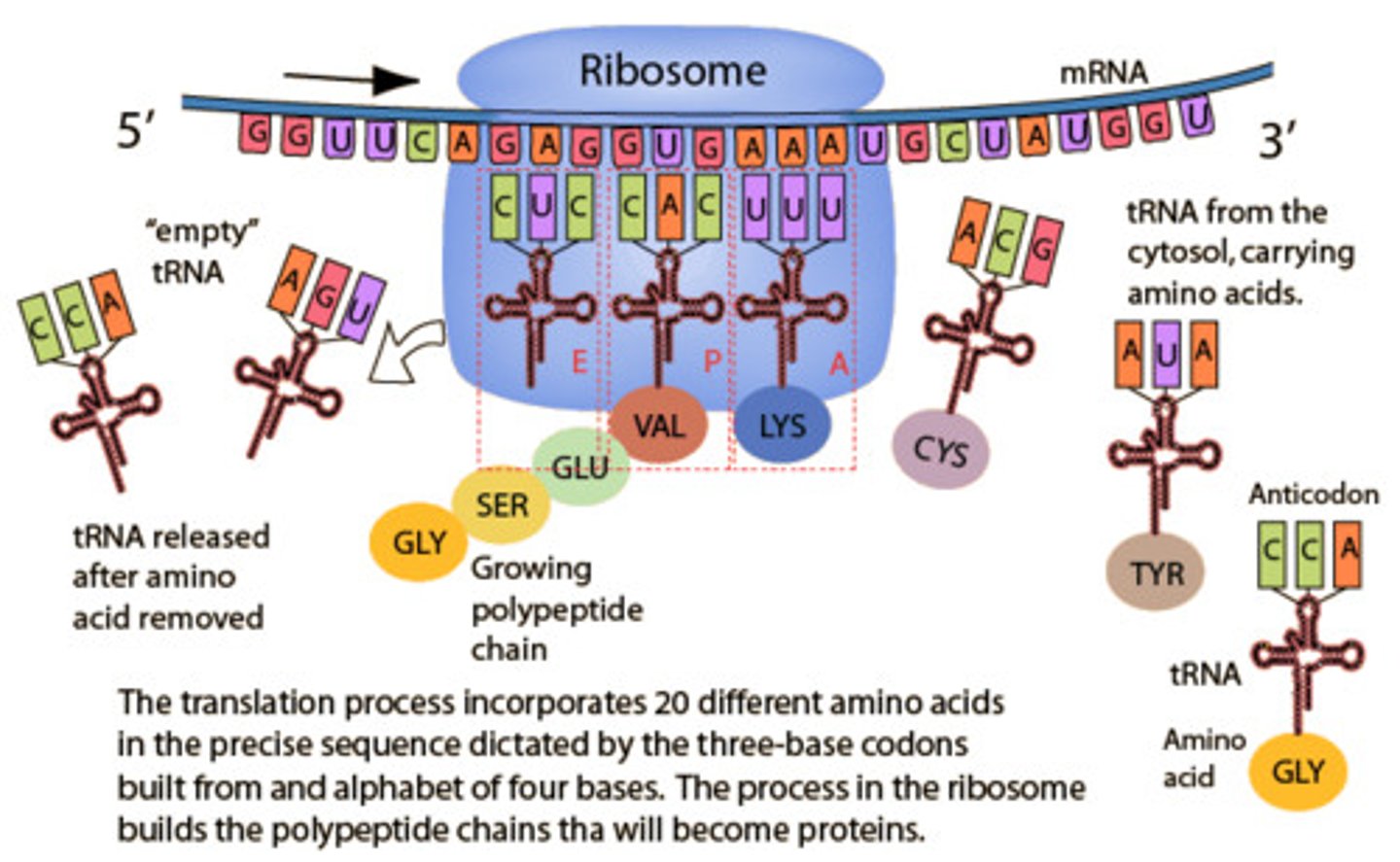
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
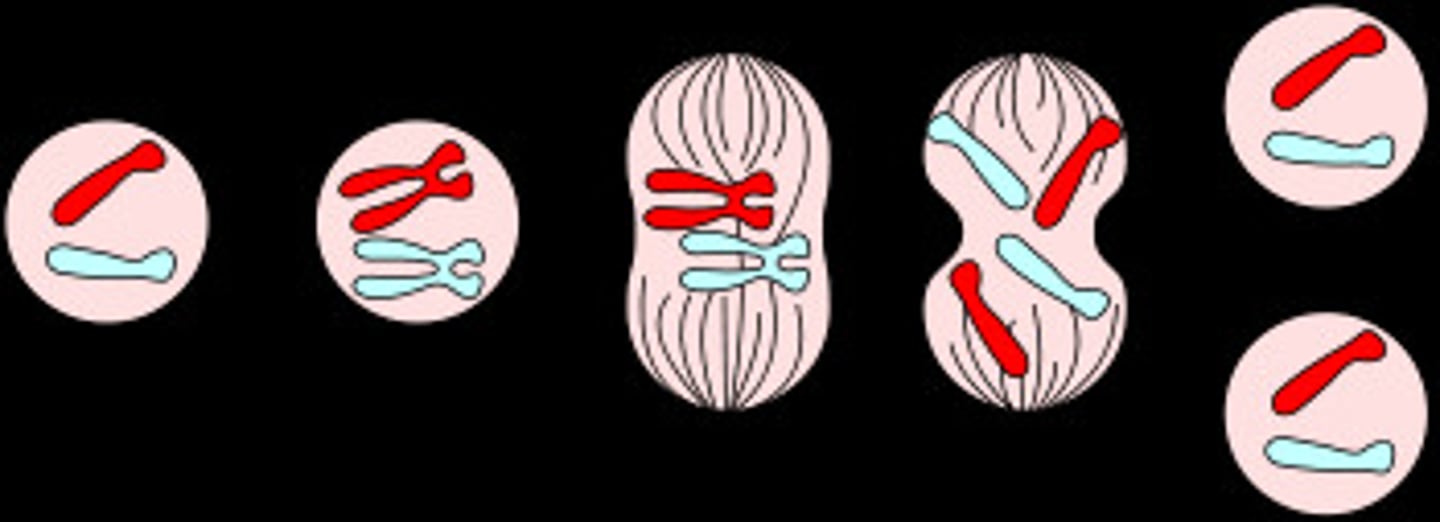
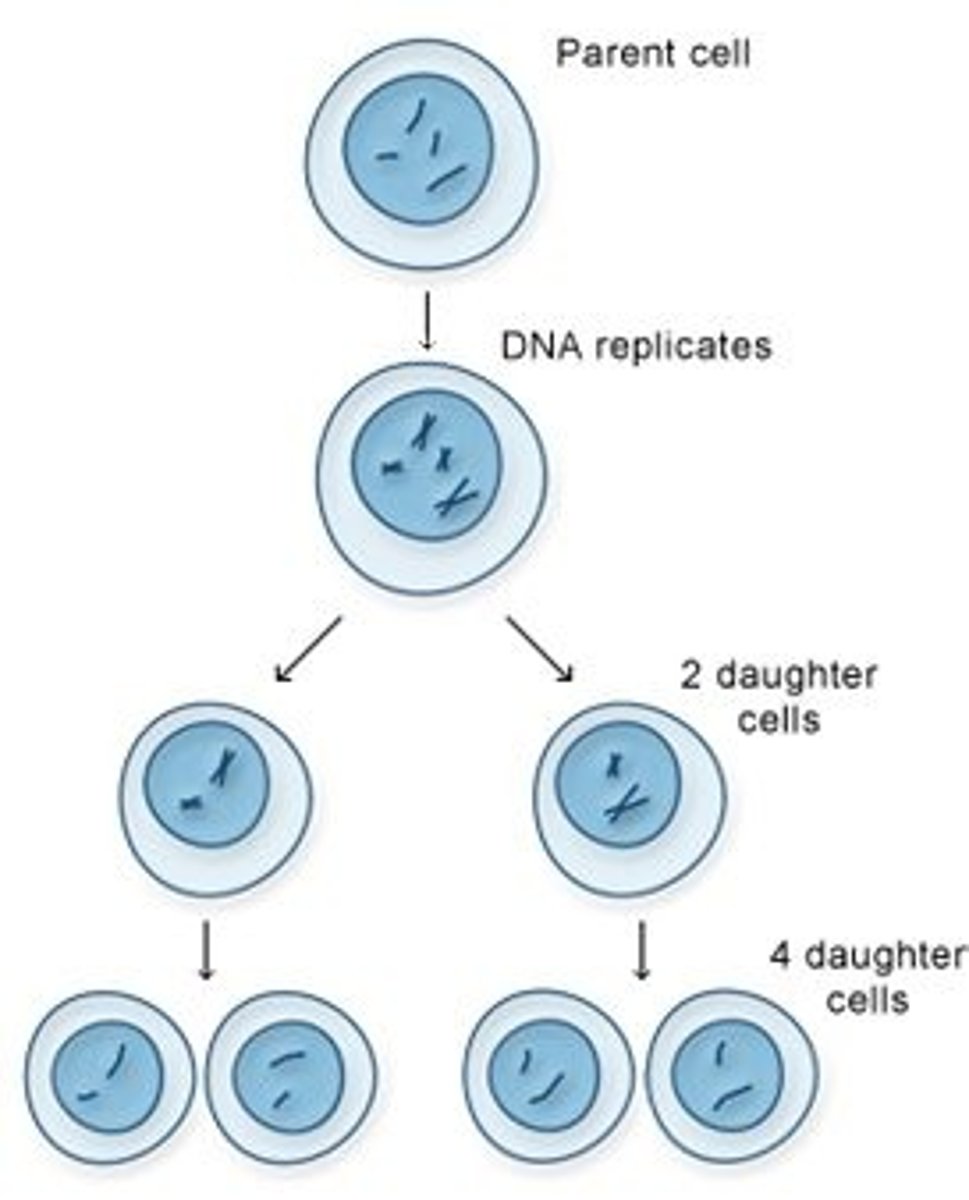
Mitosis
a process of asexual reproduction in eukaryotic cells
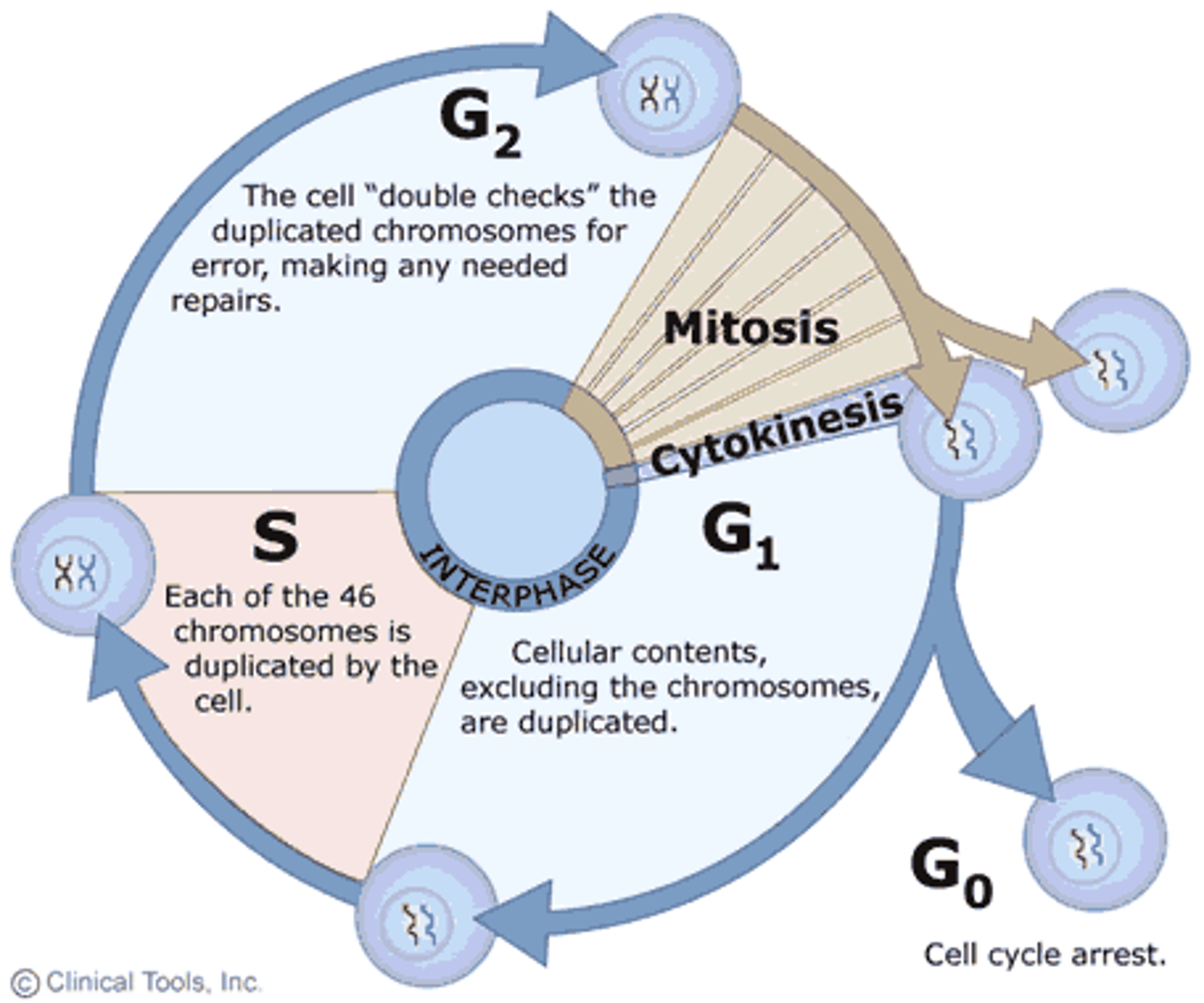
Interphase
The time interval between cellular reproduction.
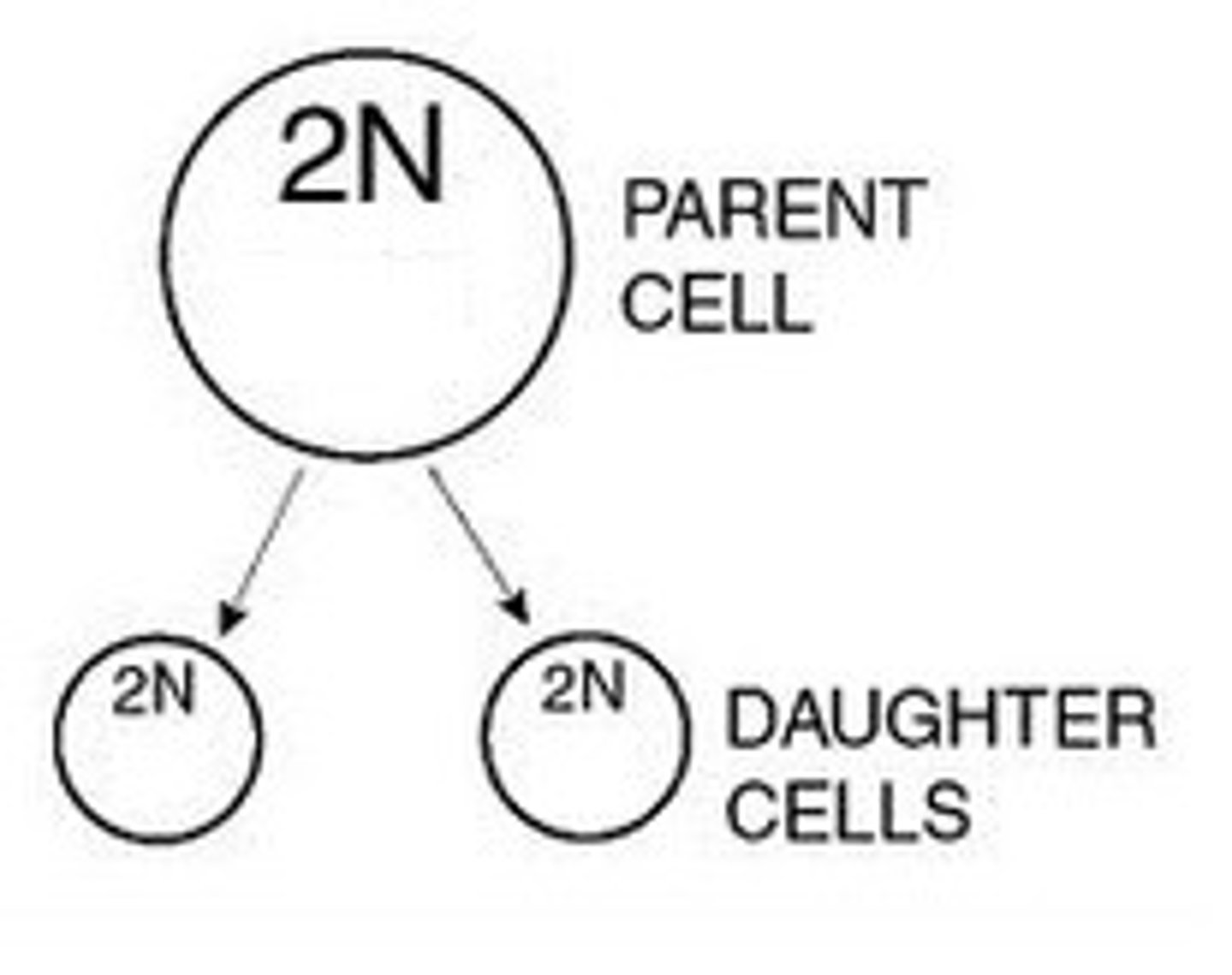
parent cell
original cell before cell division
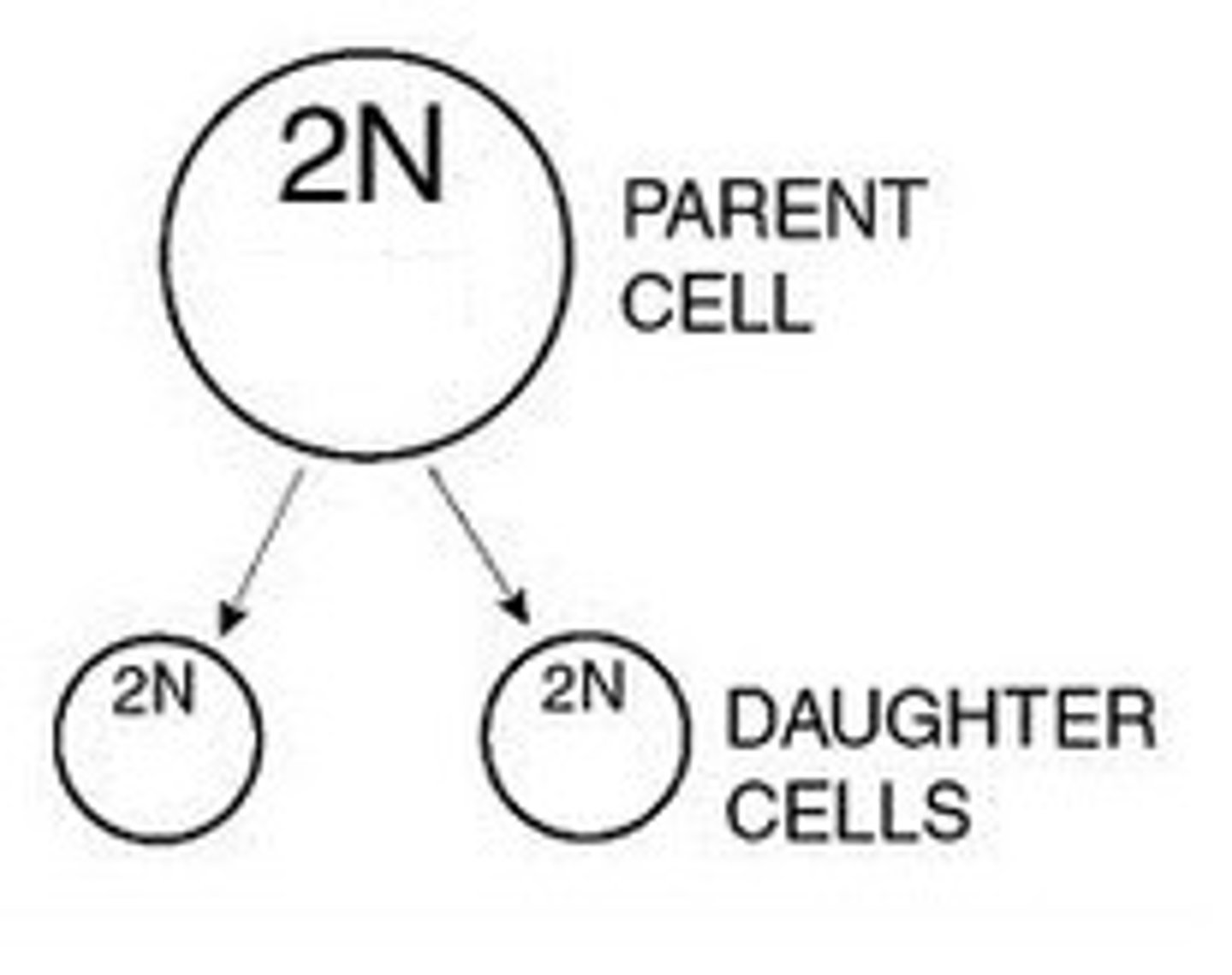
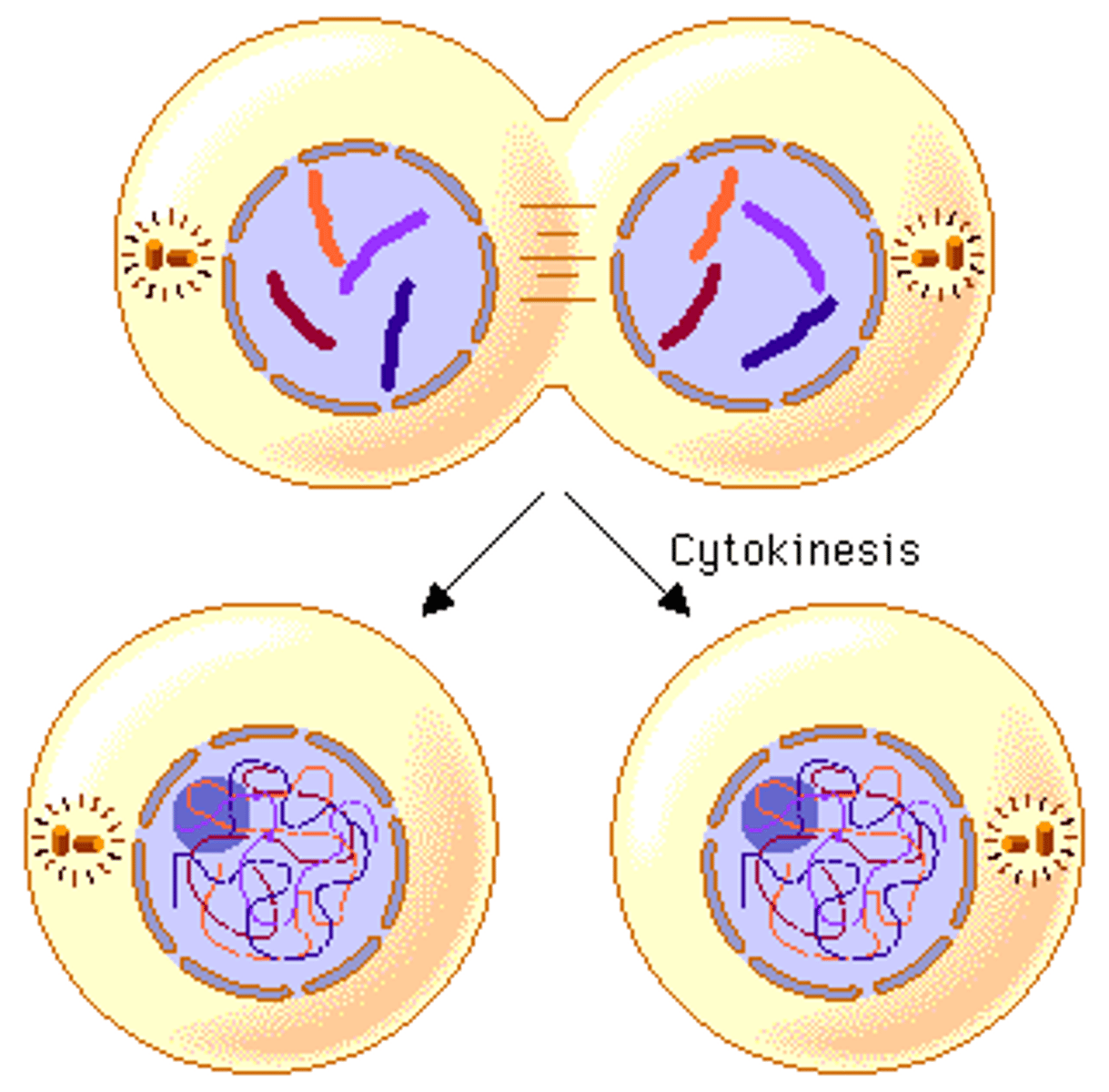
daughter cells
the two new cells that result from mitosis
Cytokinesis
process, usually following mitosis or meiosis, in which the cytoplasm of a cell is divided in two
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus

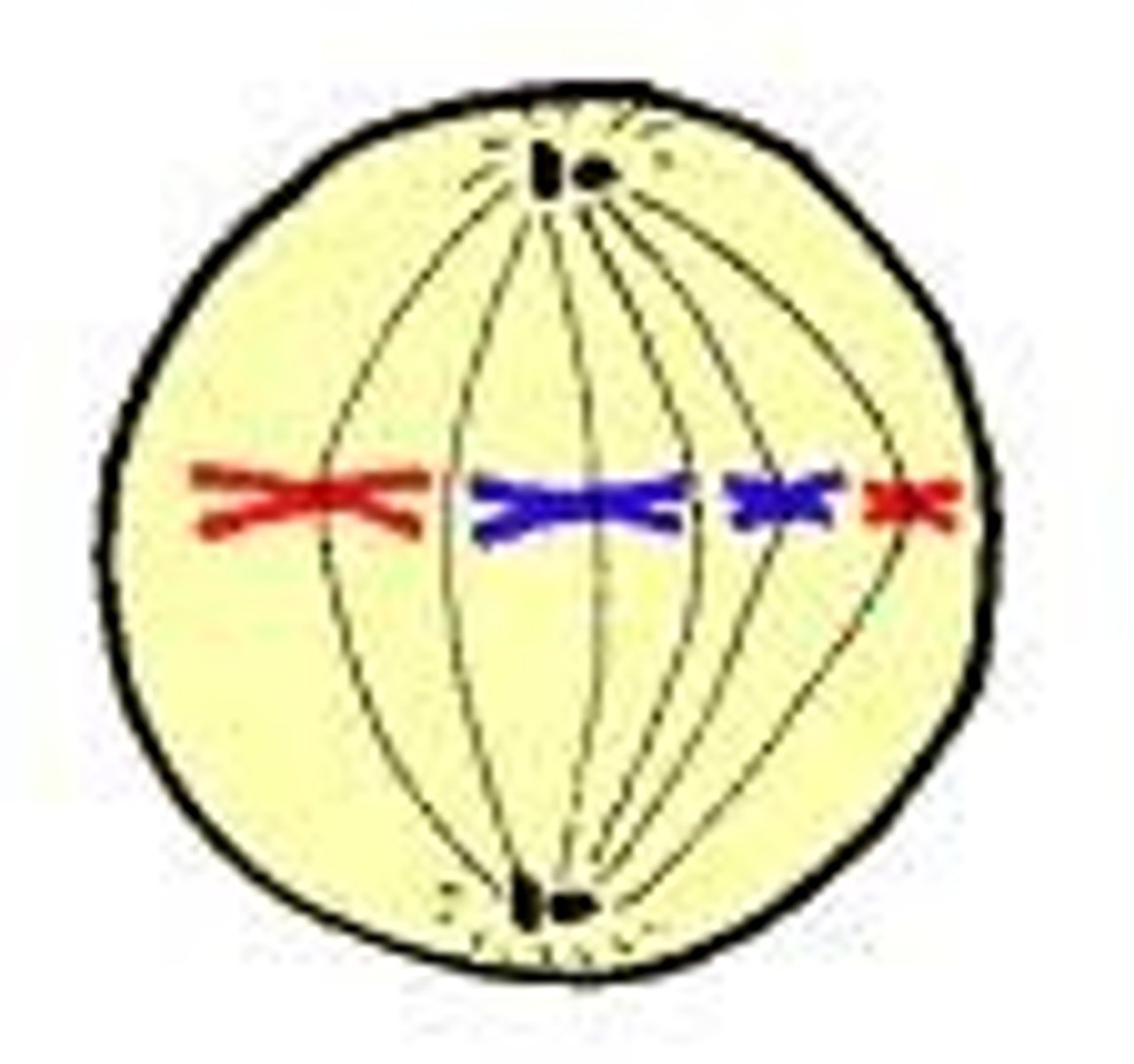
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
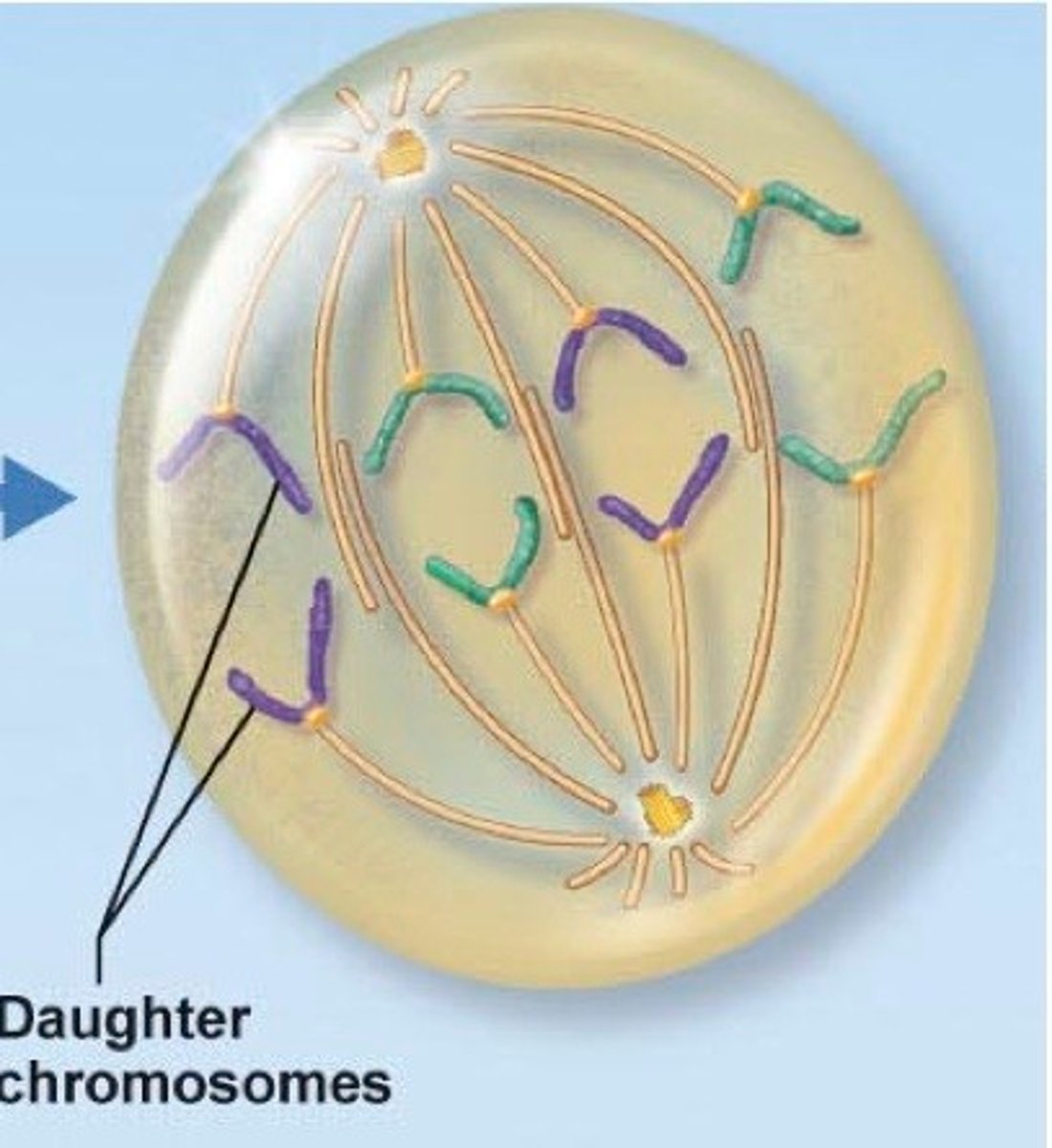
Anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
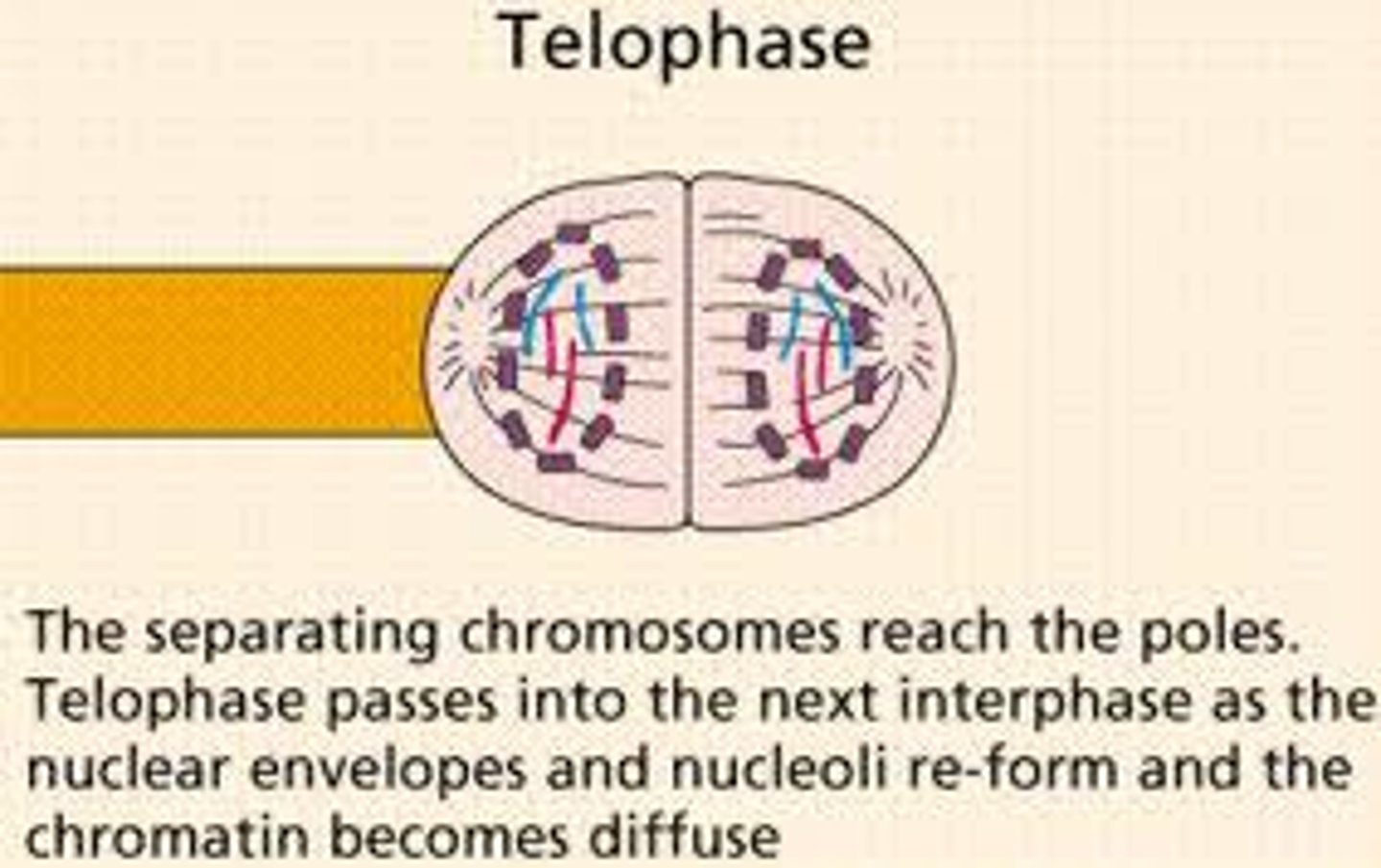
Telophase
After the chromosome seperates, the cell seals off, Final Phase of Mitosis.
Equatorial plane (metaphase plate)
an imaginary line bisecting the cell where the chromosomes line up
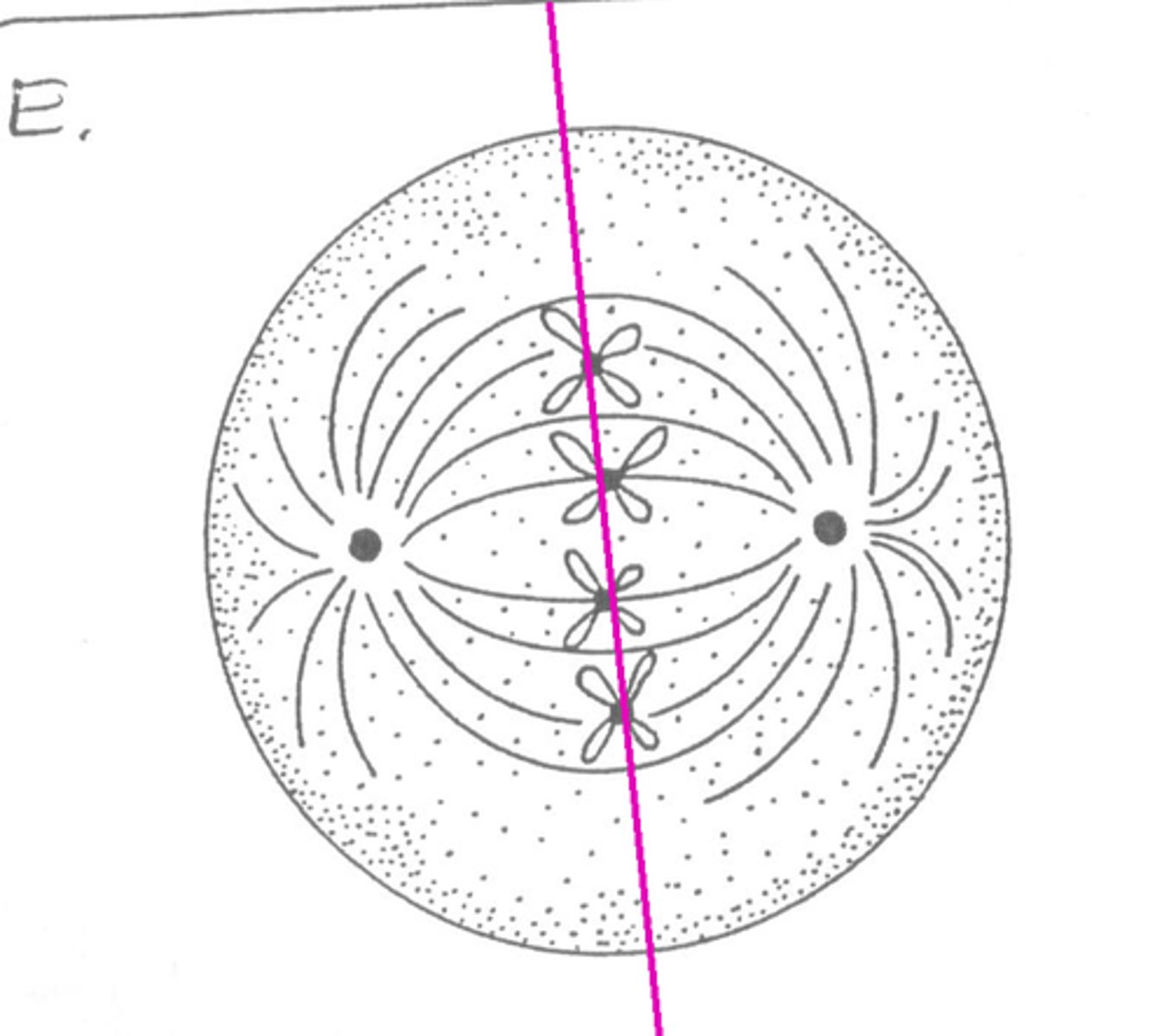
homologous chromosome pairs
Pairs of chromosomes that are similar but not identical
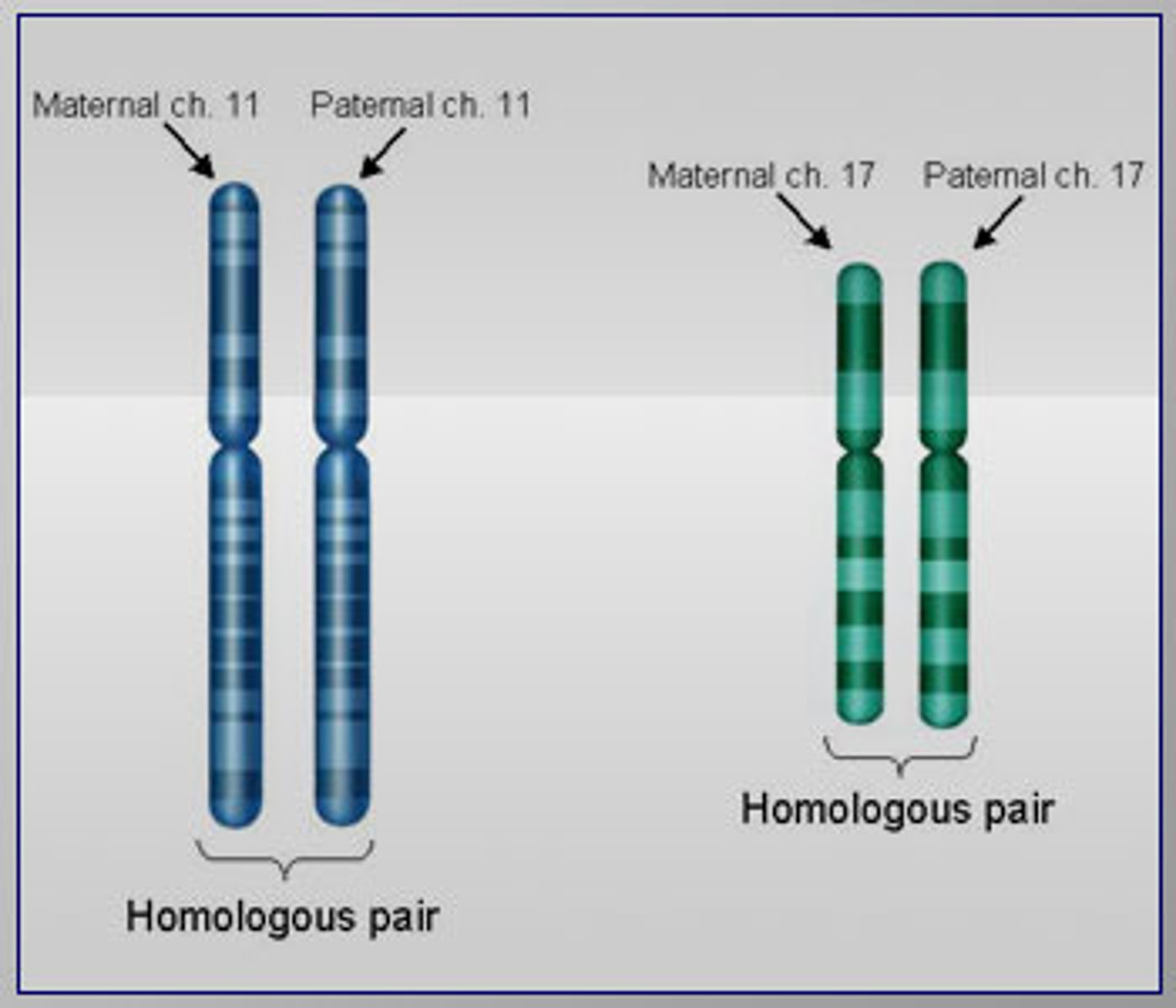
Homologue
One member of a homologous pair of chromosomes
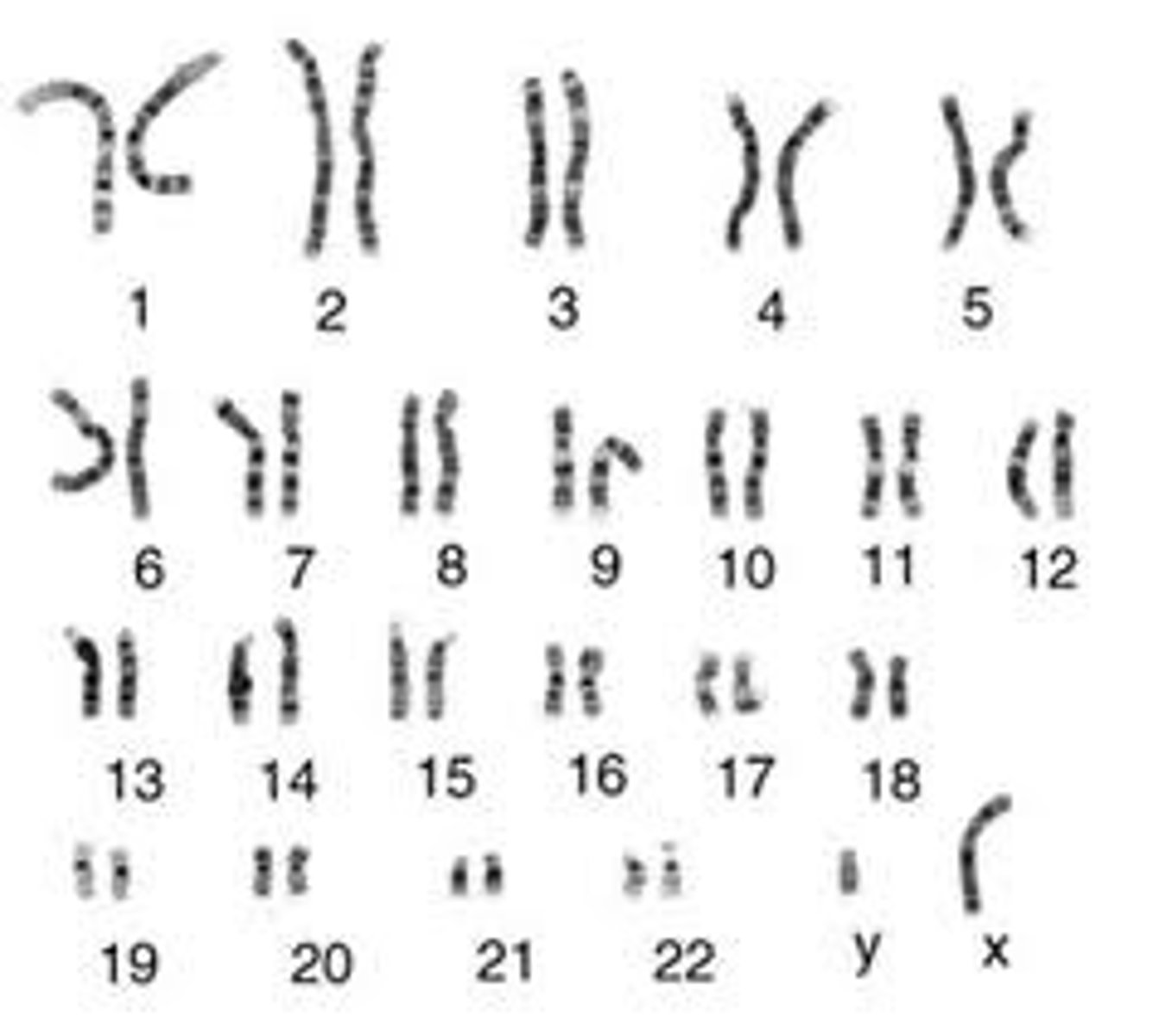
Karotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual
X chromosome
the sex chromosome that is present in both sexes: singly in males and doubly in females
Y chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males
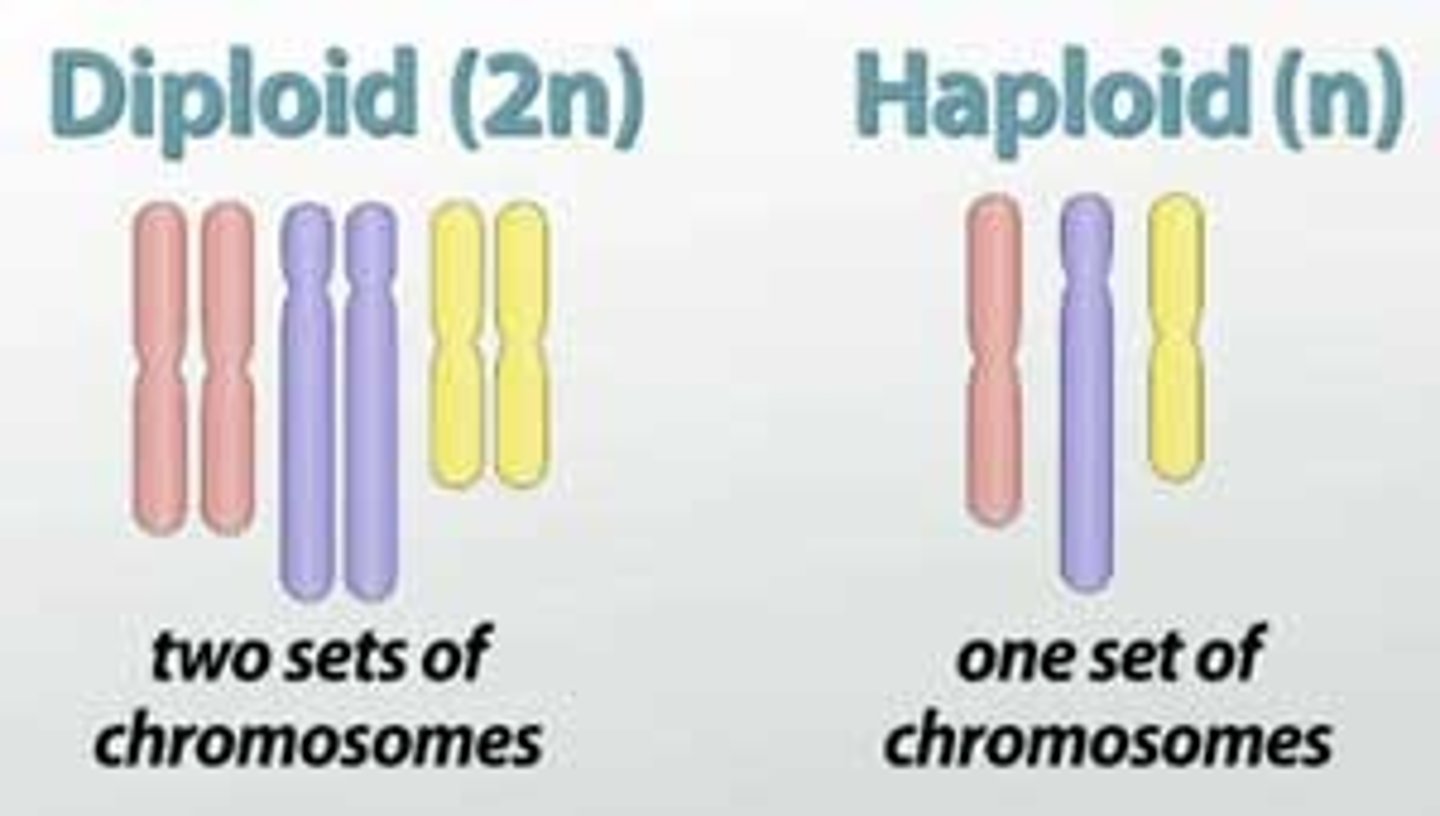
Diploid Cell
A cell with chromosomes that come in homologous pairs or two sets of chromosomes.
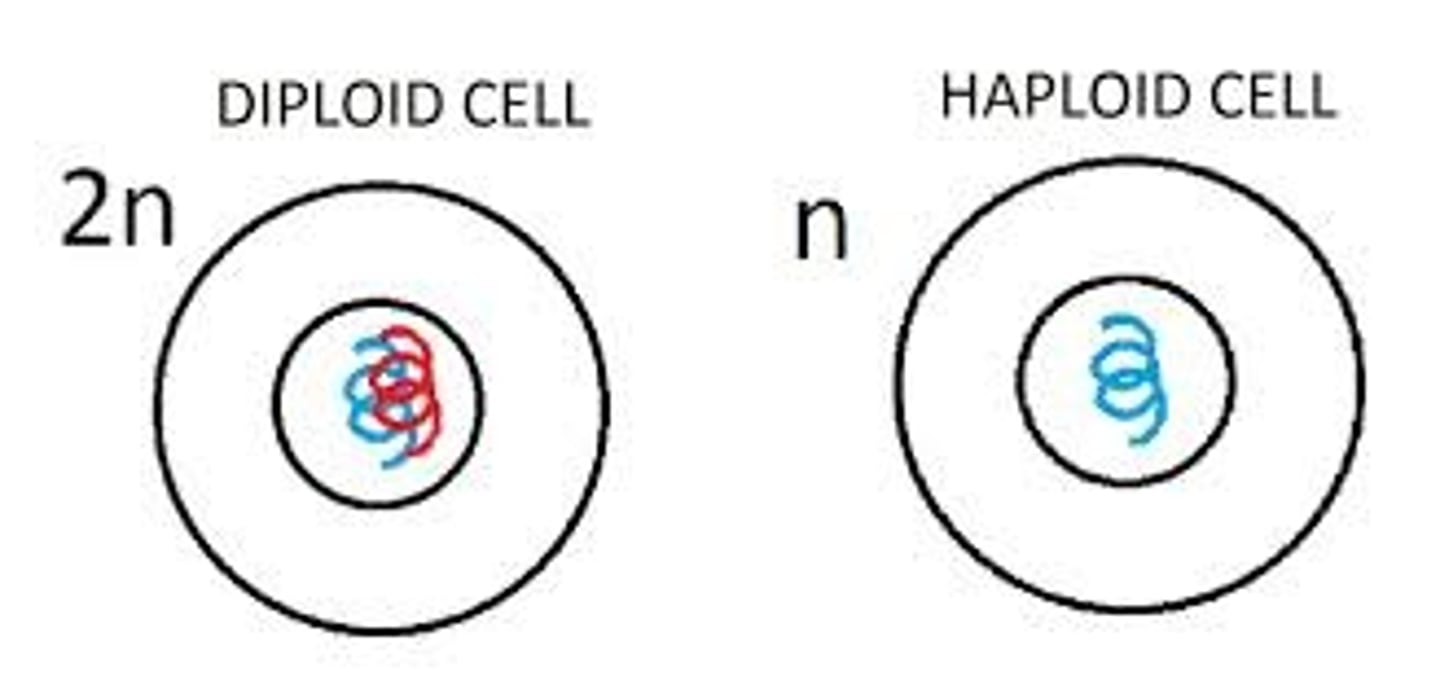
Haploid cell
A cell that has only one representative of each chromosome pair or half the number of chromosomes
diploid number
The total number of chromosomes in a diploid cell.

haploid number
the number of homologous pairs in a diploid cell.
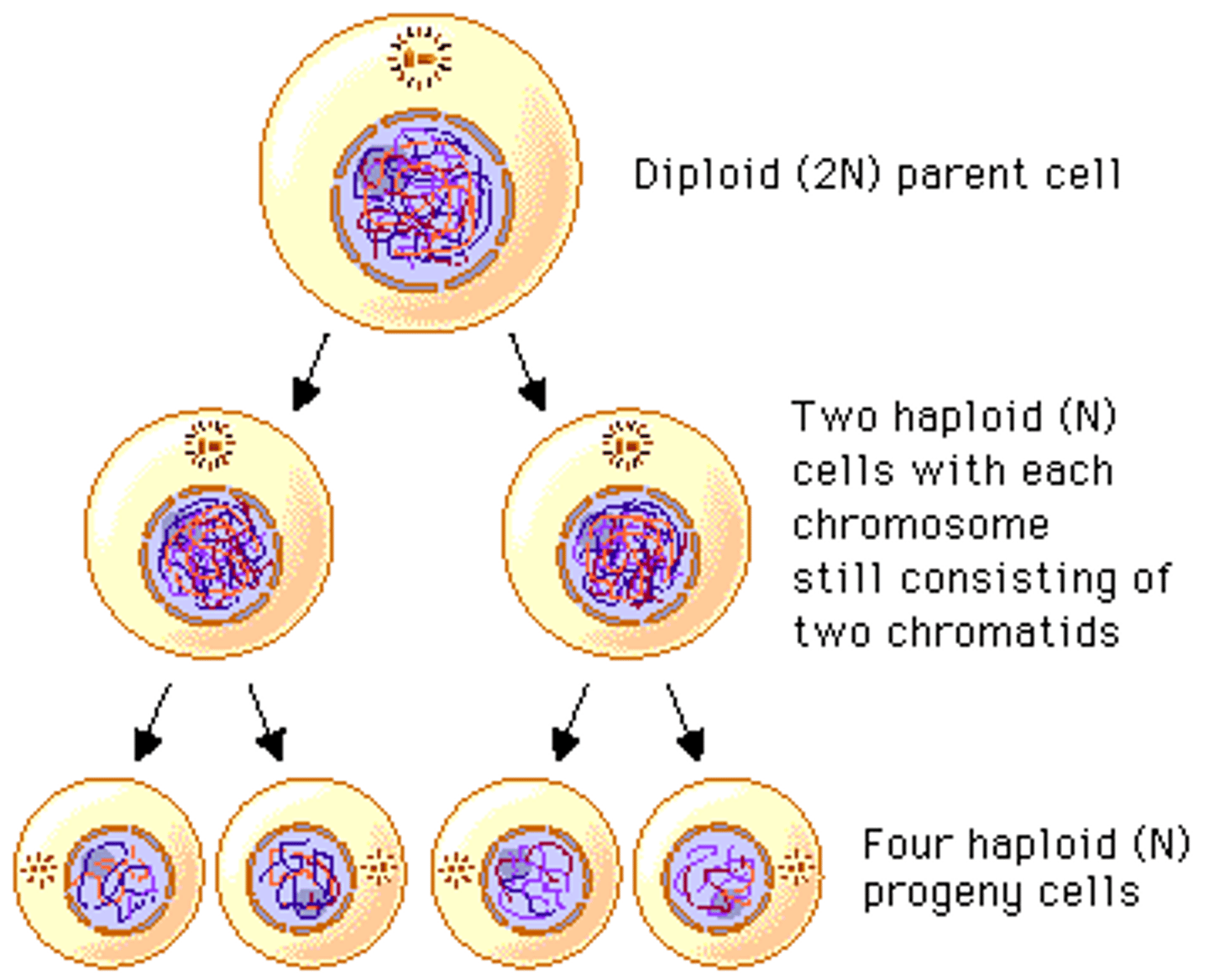
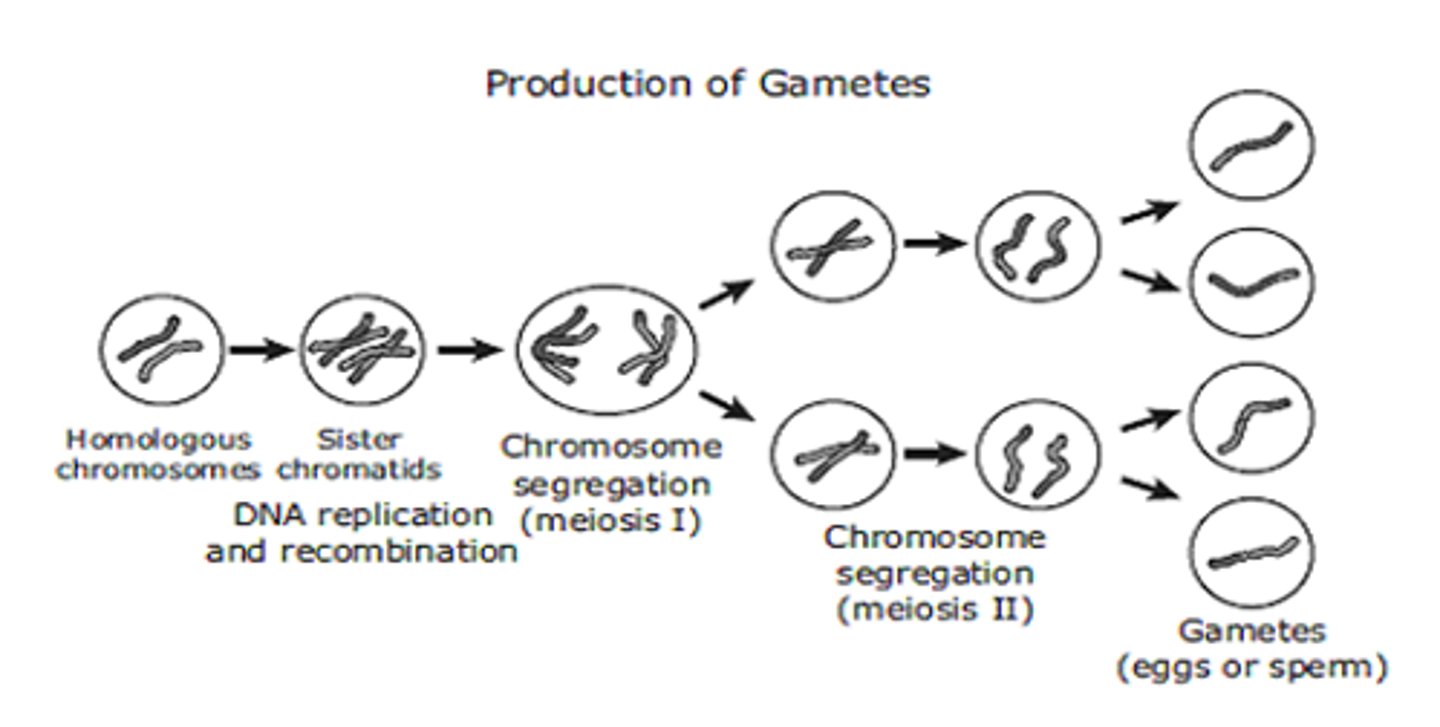
Meiosis
The process by which a diploid (2n) cell forms gametes (n).
Gametes
Haploid cells (n) produced by diploid cells (2n) for the purpose of sexual reproduction
Zygote
The result of sexual reproduction when each parent contributes half of the DNA necessary for the offspring.
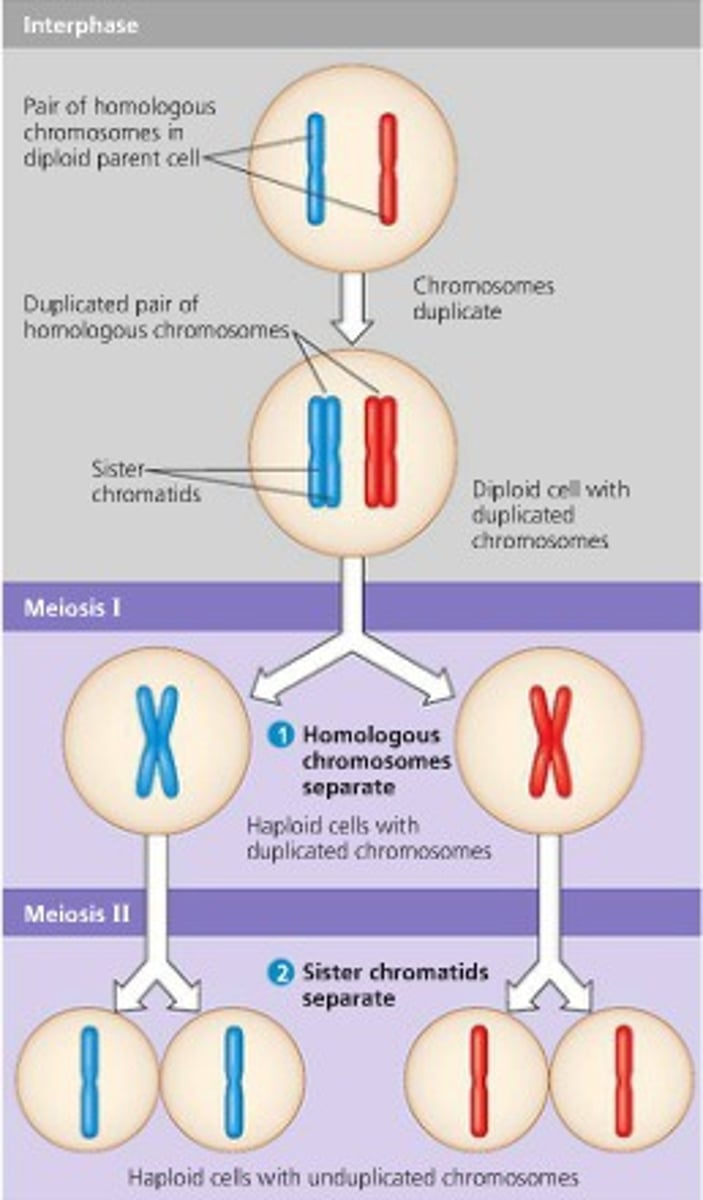
Meiosis I
Diploid cell produces two haploid cells
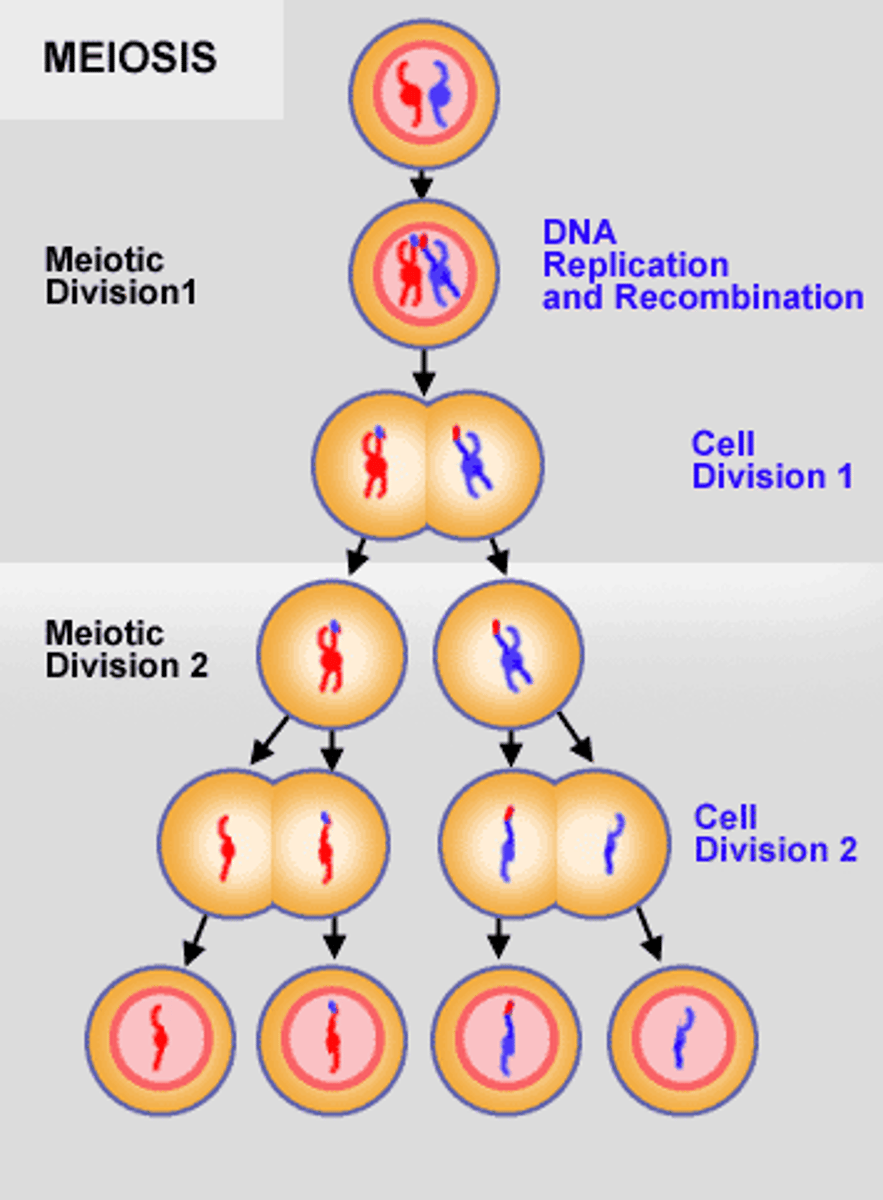
Meoisis II
Two haploid cells divide to form 4 haploid cells
Prophase I (Meiosis)
Centrioles move to opposite sides of cell, mitotic spindle forms, chromatin condenses and forms chromosomes
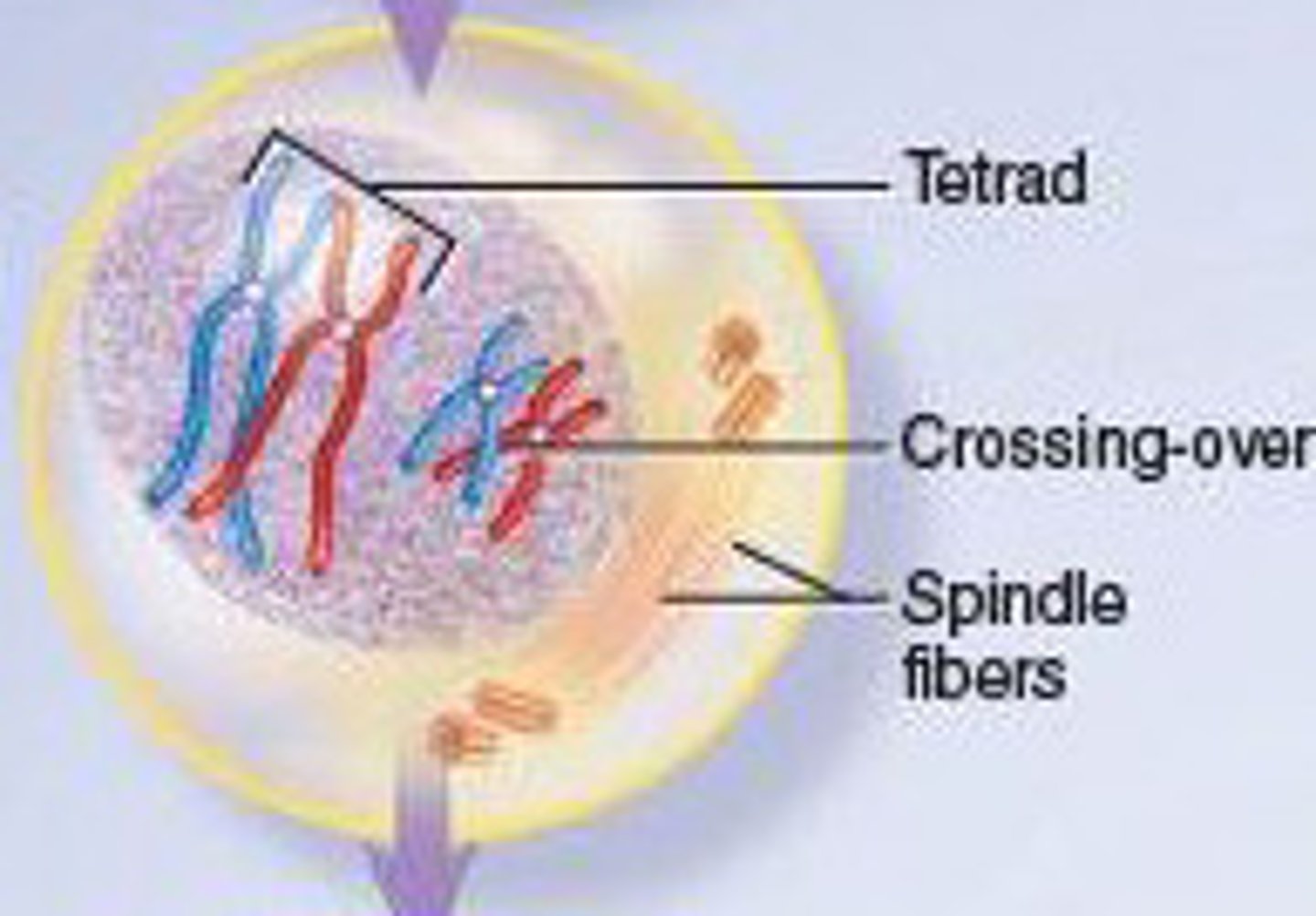
Tetrad
two duplicated homologous chromosomes (four chromatids) , two sister chromatids in each chromosome
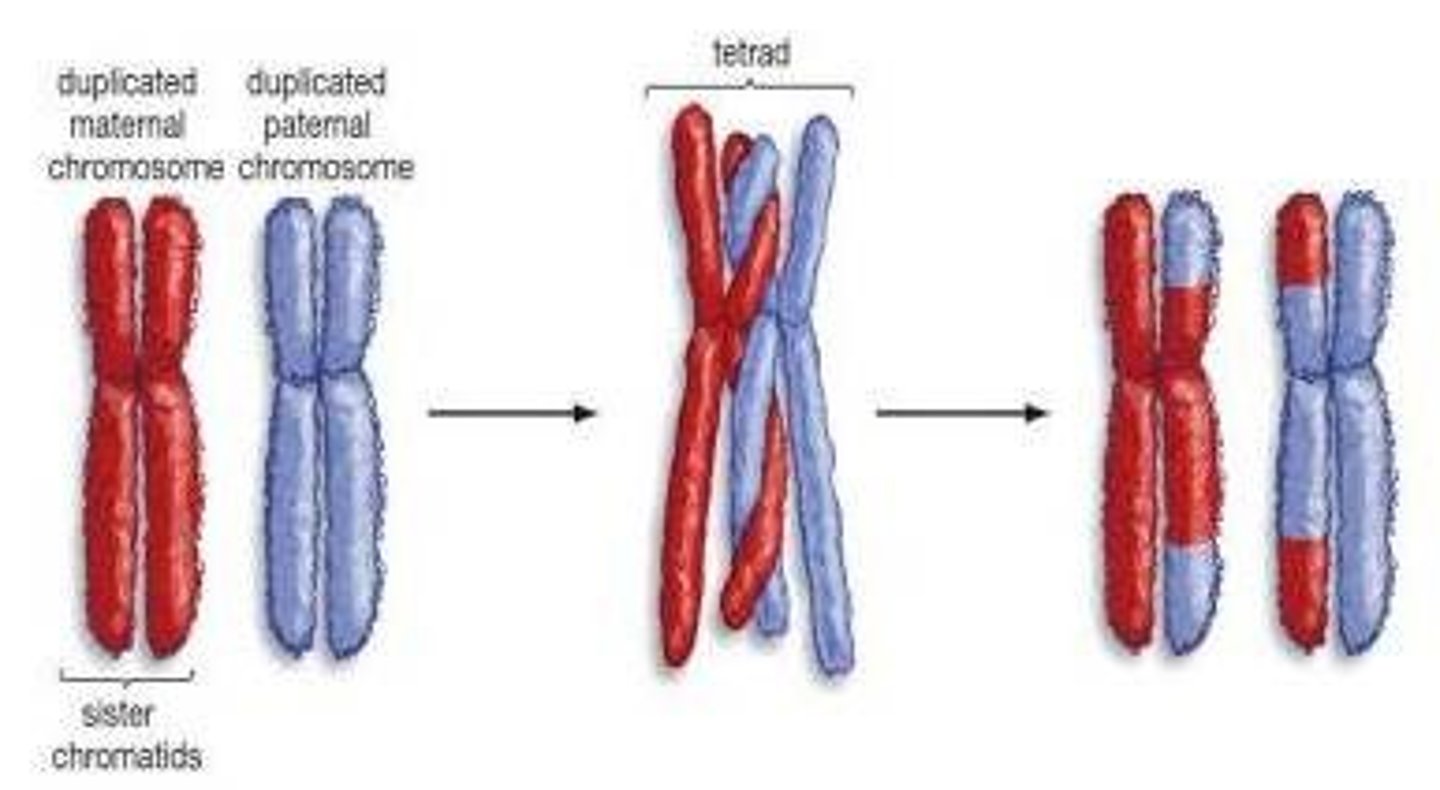
crossing over
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes
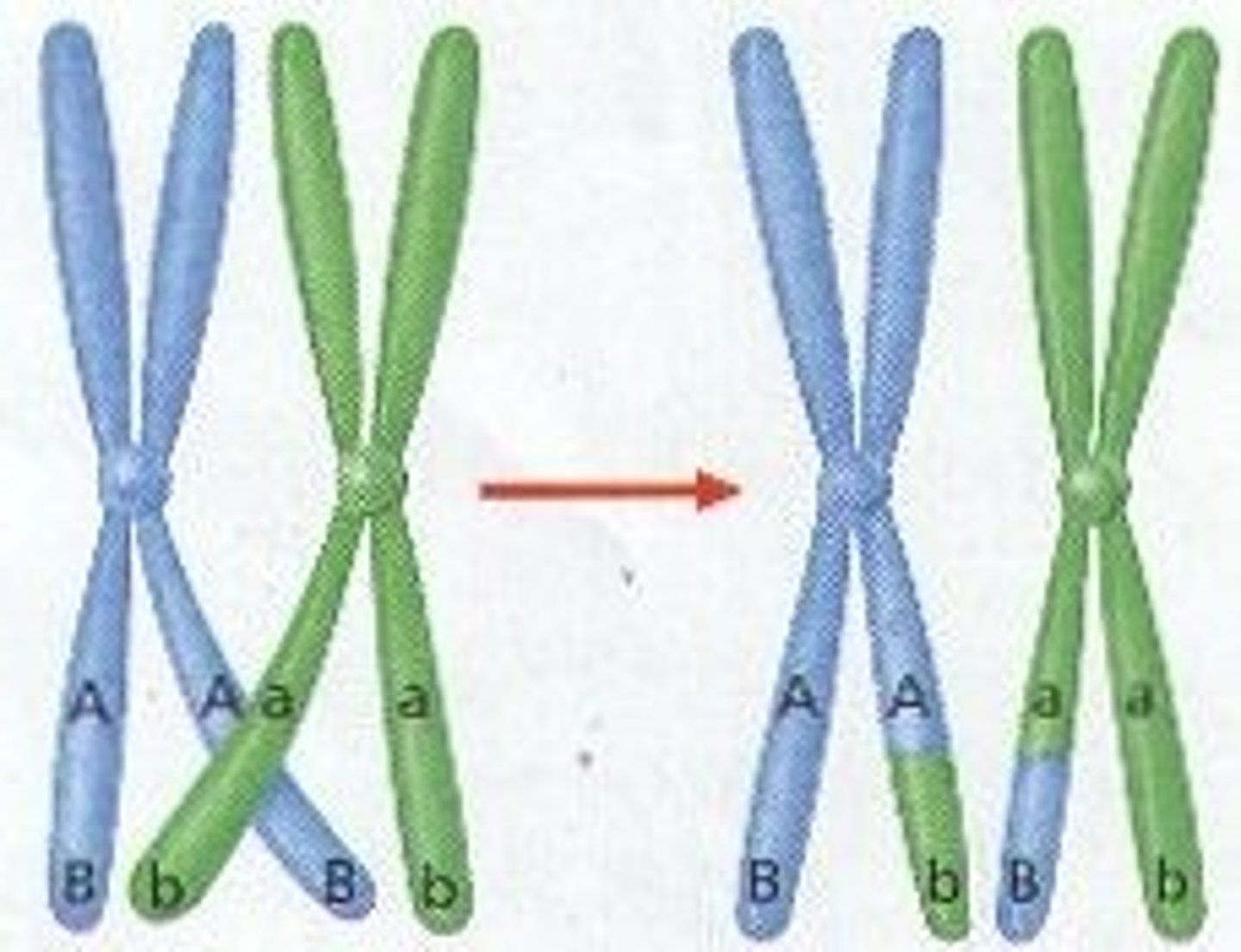
genetic recombination
The regrouping of genes in an offspring that results in a genetic makeup that is different from that of the parents.
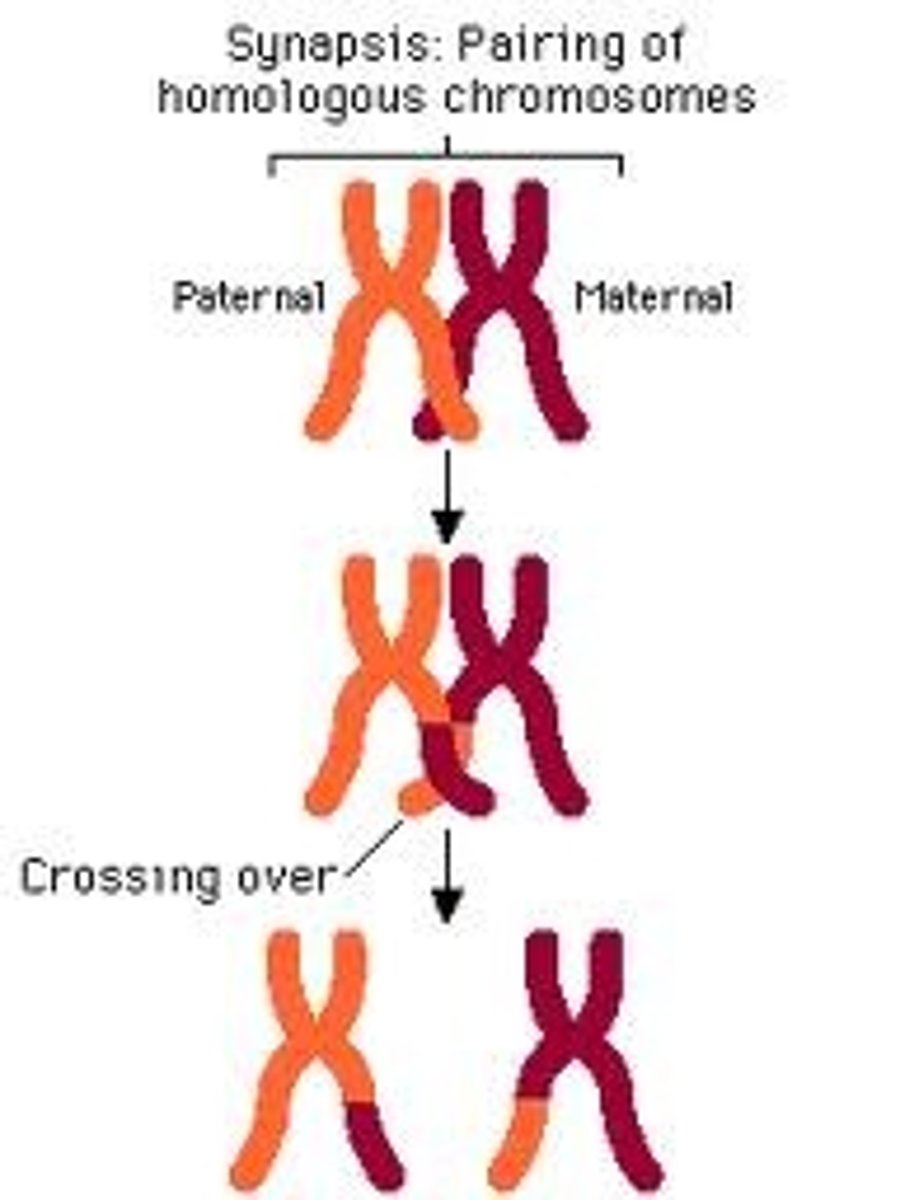
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
homologous pairs (tetrads) align at the equatorial plane and each pair attaches to a separate spindle fiber at the kinetochore

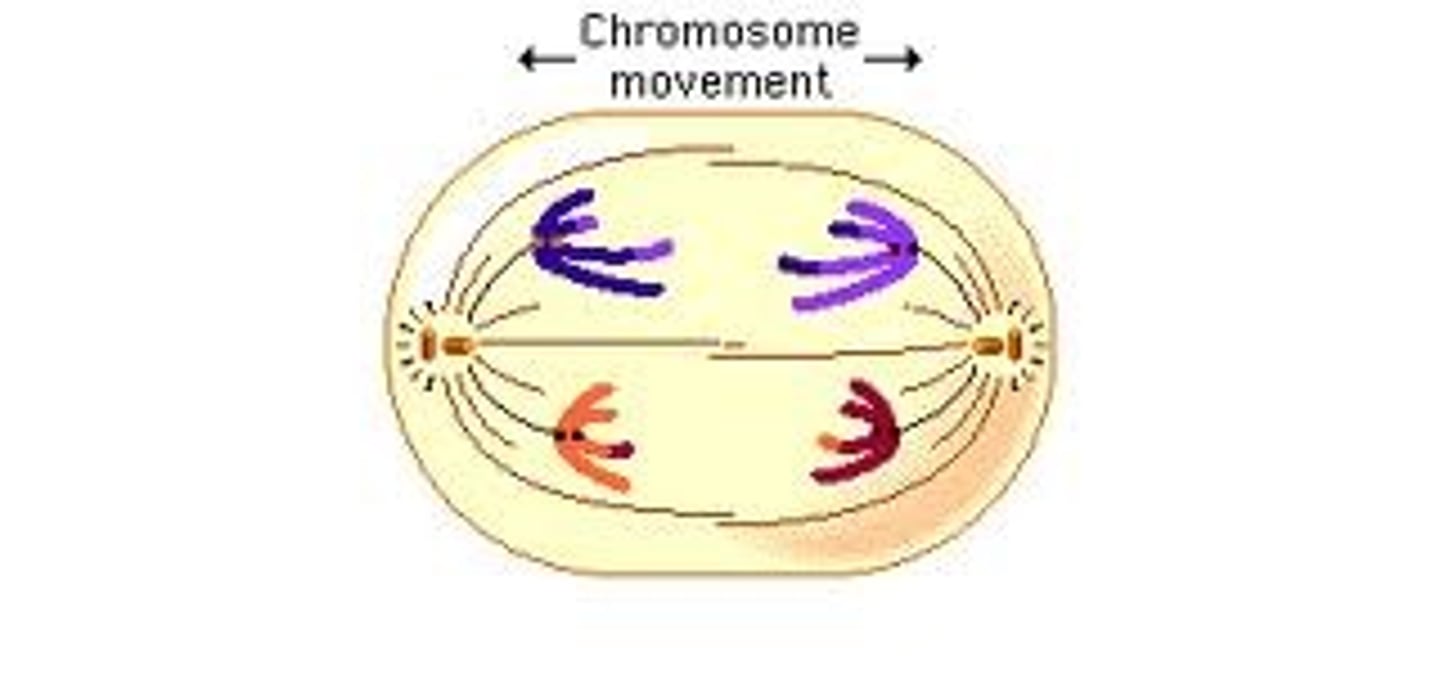
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes separate
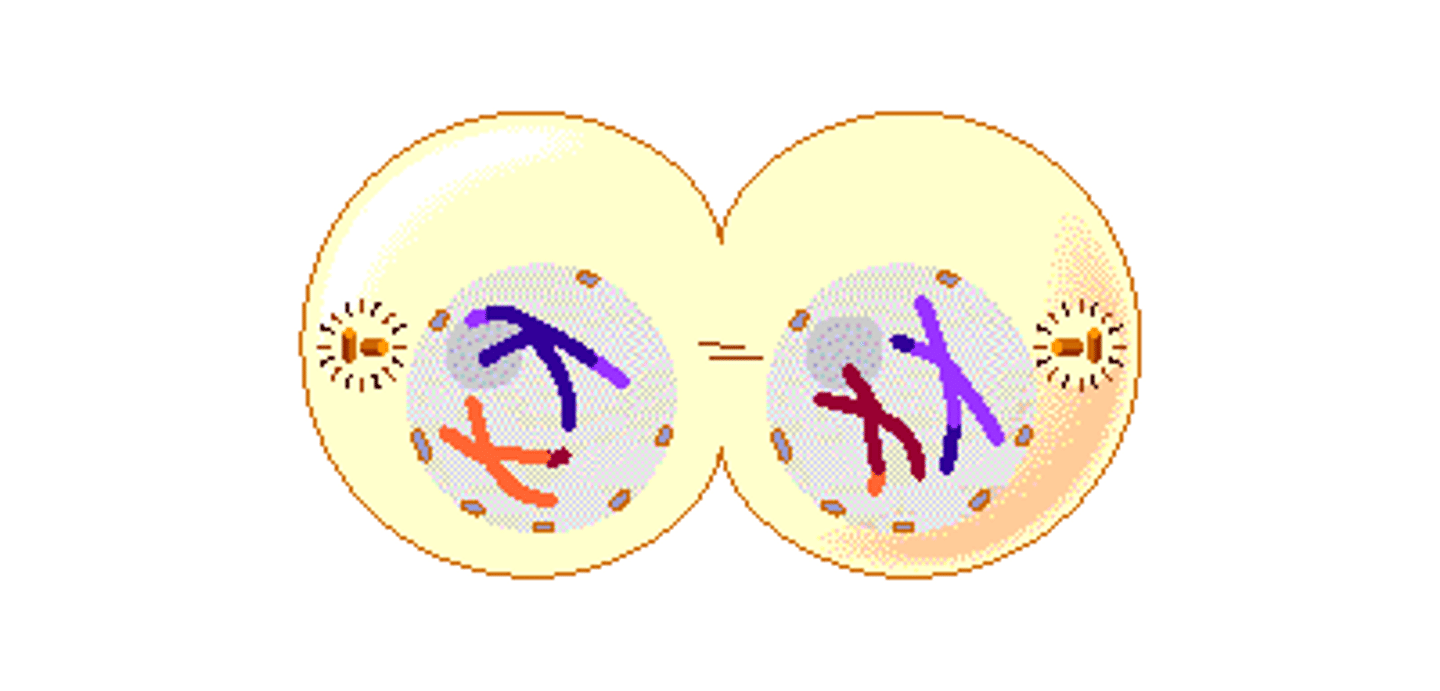
Telophase I (Meiosis)
Cytokinesis occurs, the result are two haploid daughter cells
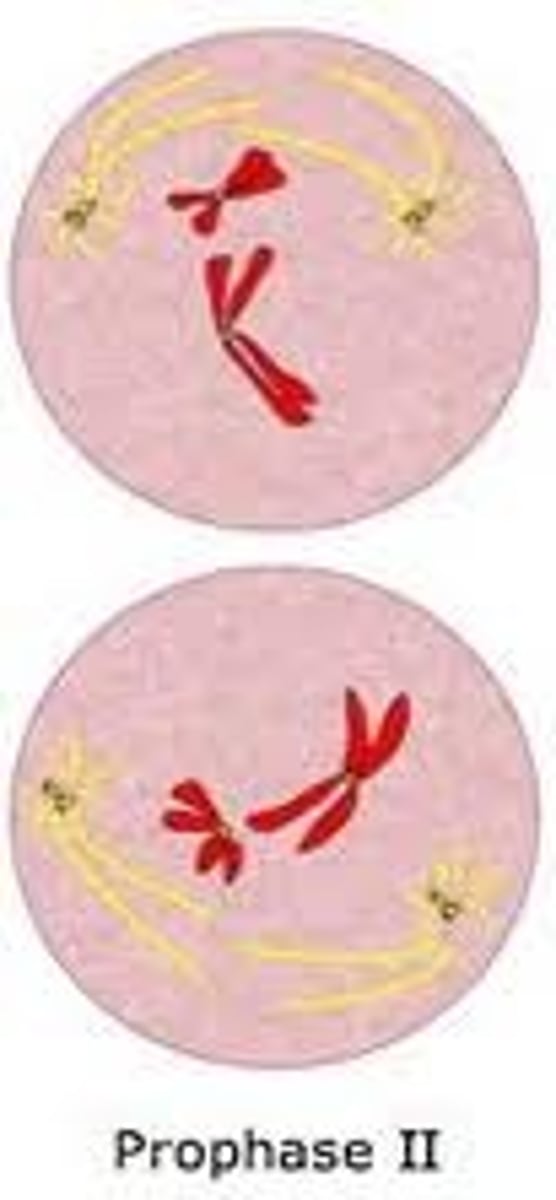
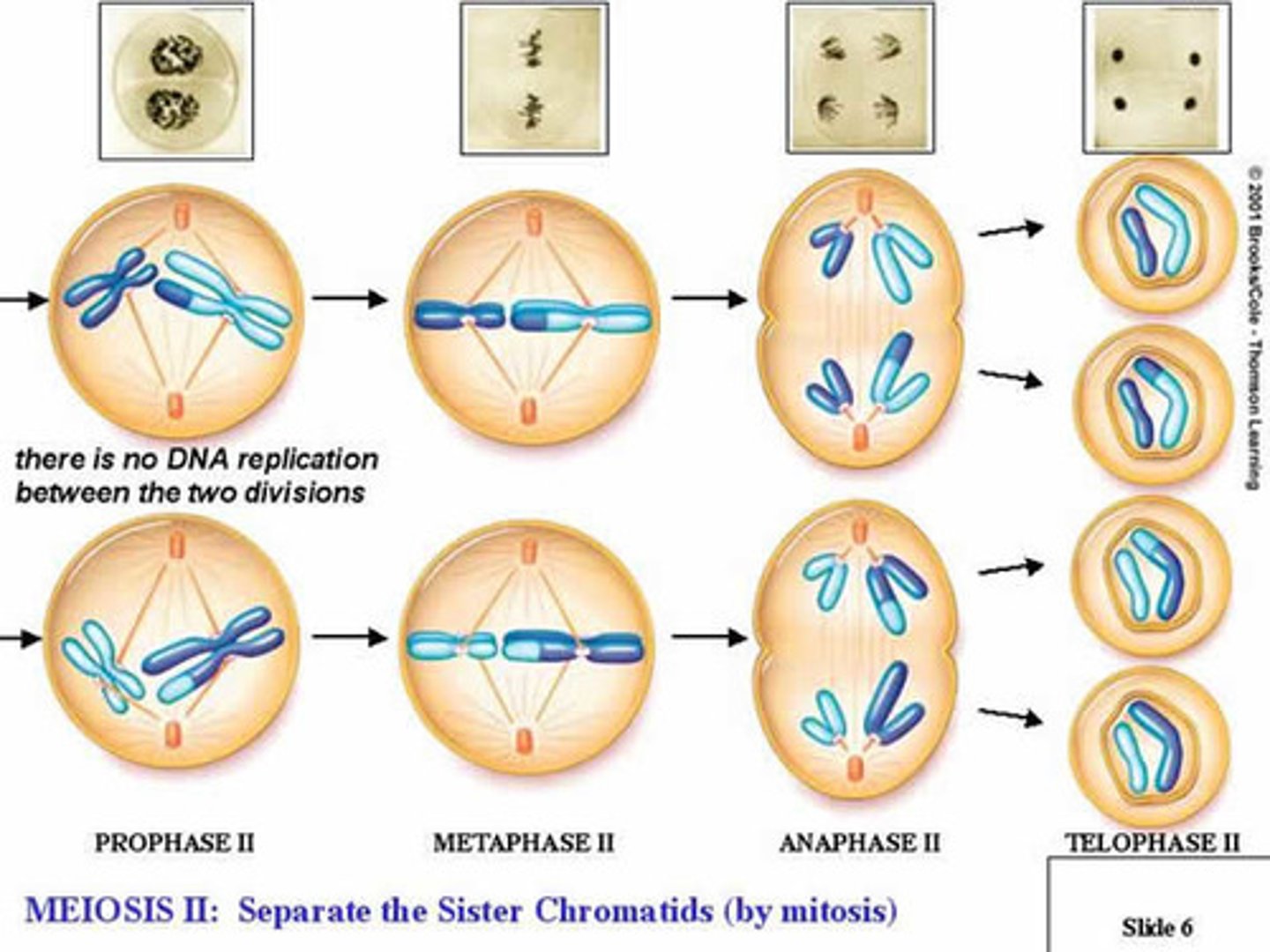
Prophase II (meiosis)
Centrioles duplicate and move to opposite ends of cell, forming spindles, spindles attach to centromerees of chromosomes and move them to middle of cell
Metaphase II (Meiosis)
Spindle fully formed, chromosome in equatorial plane, microtubules attach to sister chromatid at centromere
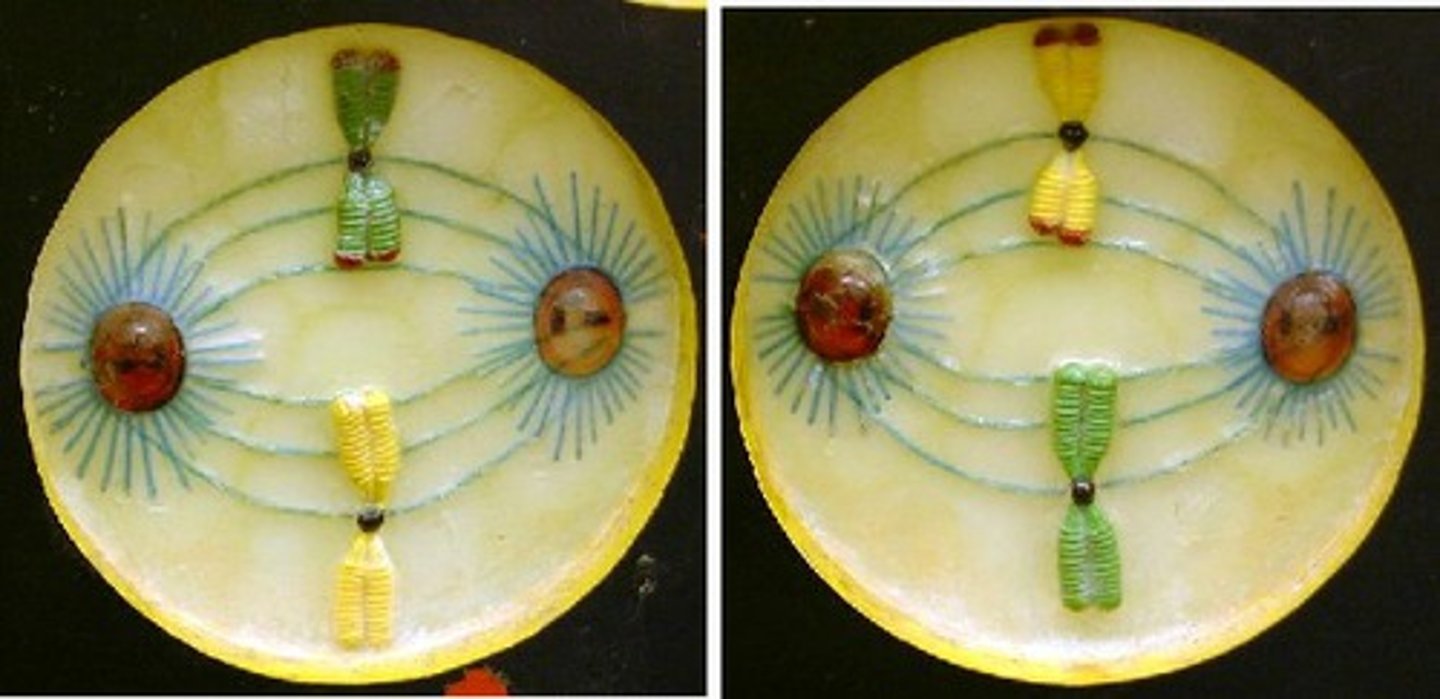

Anaphase II (Meiosis)
Sister chromatids split and head toward opposite poles
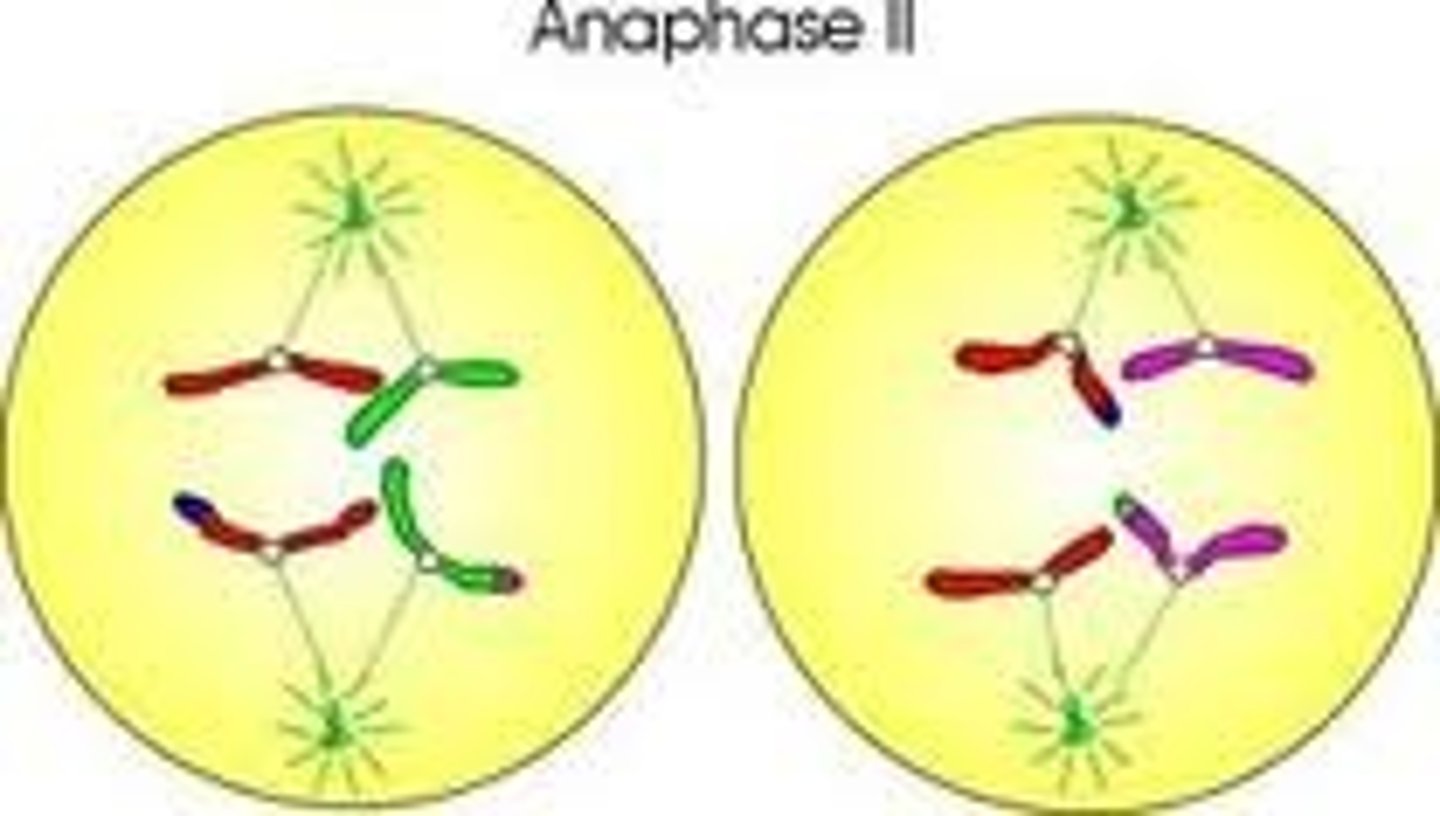
Telophase II (Meiosis)
Cytokinesis occurs, four haploid cells are the result
polar bodies
cells with little more than DNA that are eventually broken down