BIOL 300: Genes Can Be Identified Discussion
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
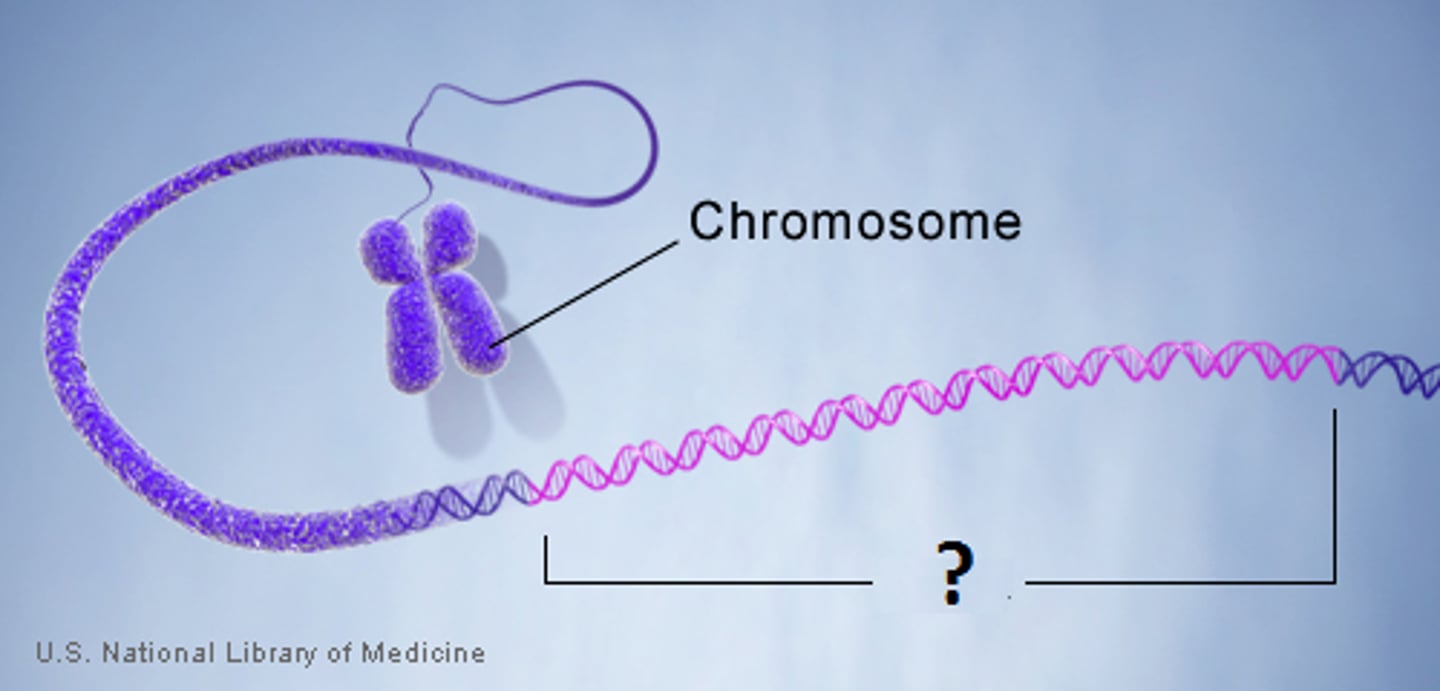
Gene
A region of DNA that gives rise to an RNA transcript
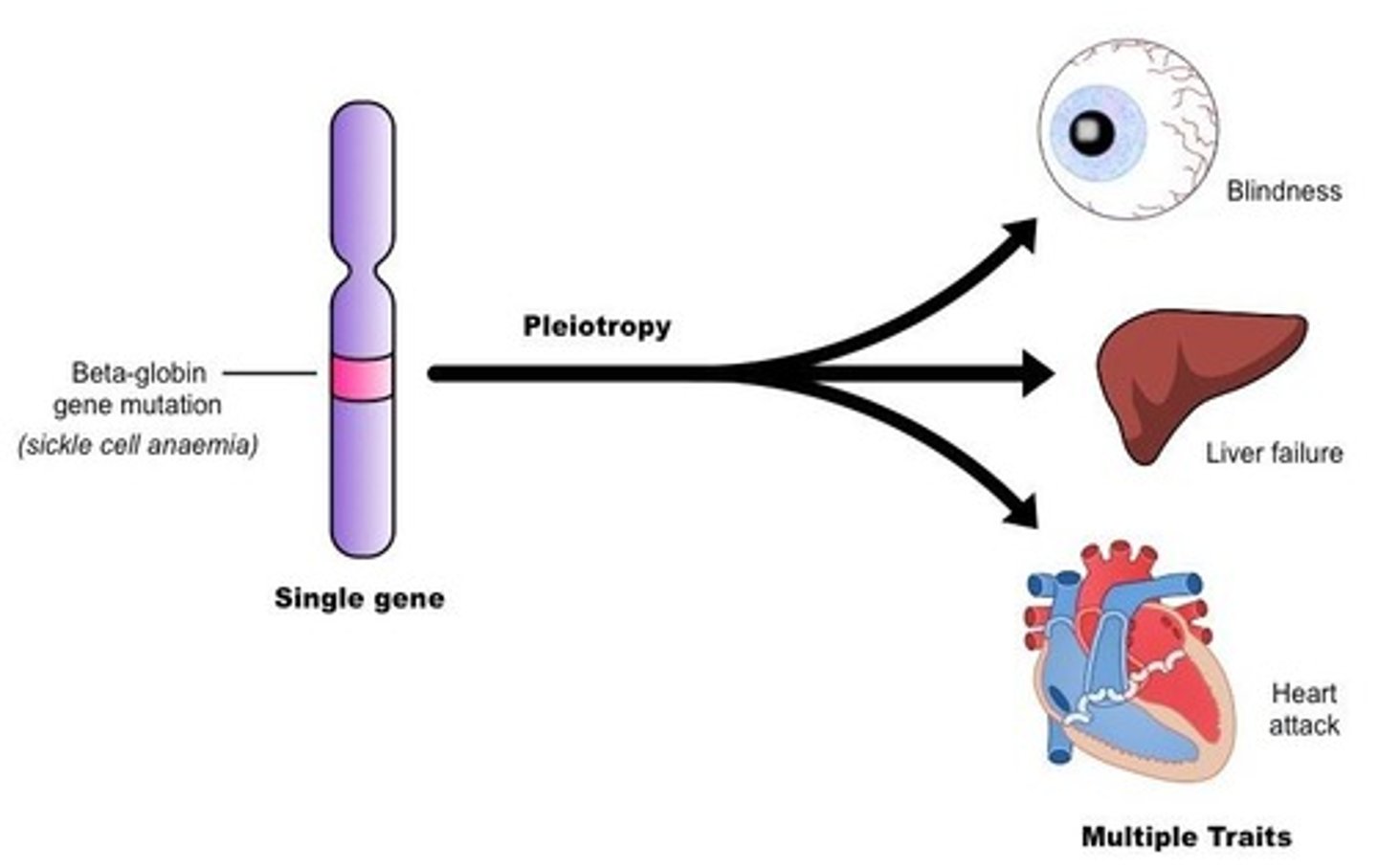
Pleiotropic Genes
Genes that are involved in more than one function
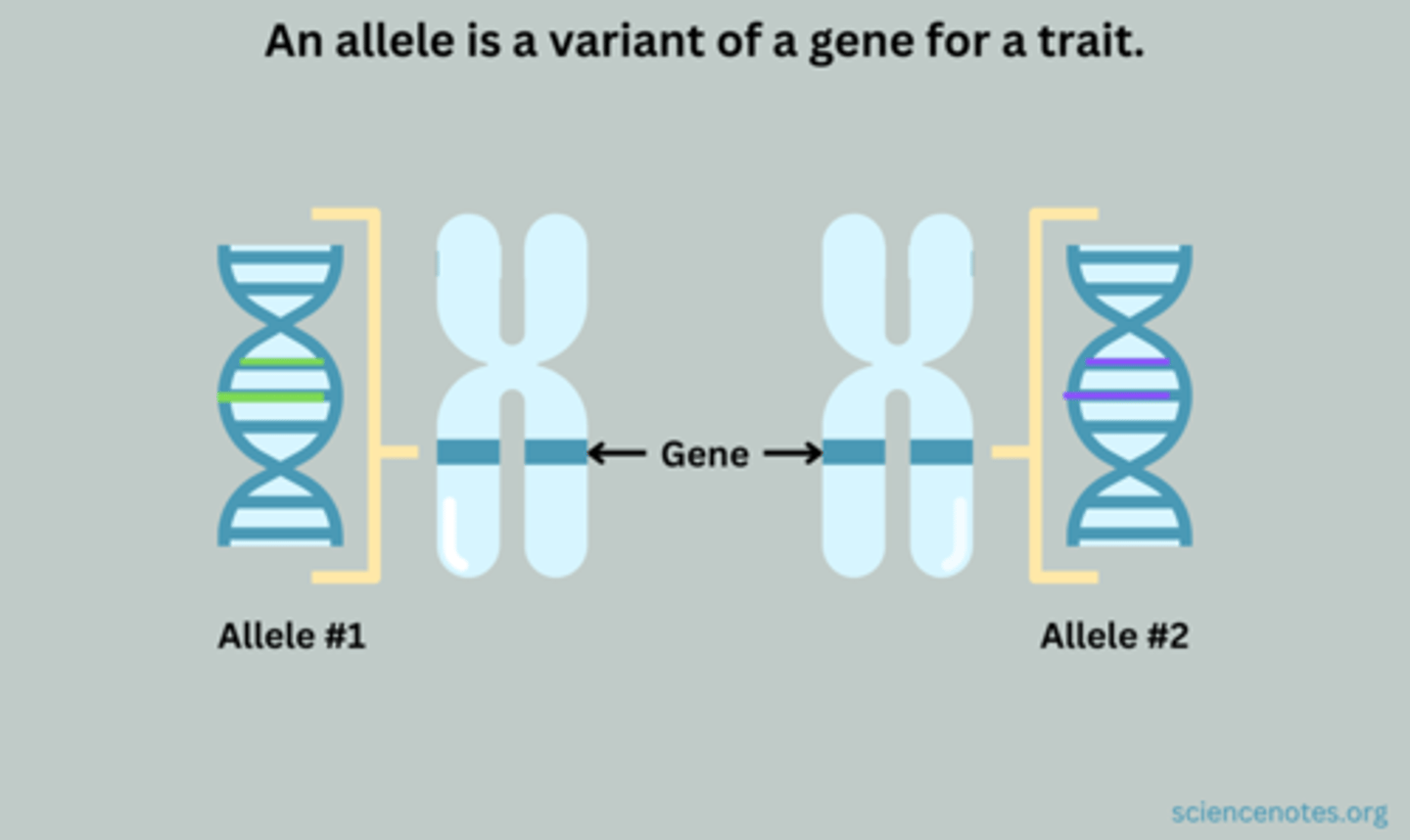
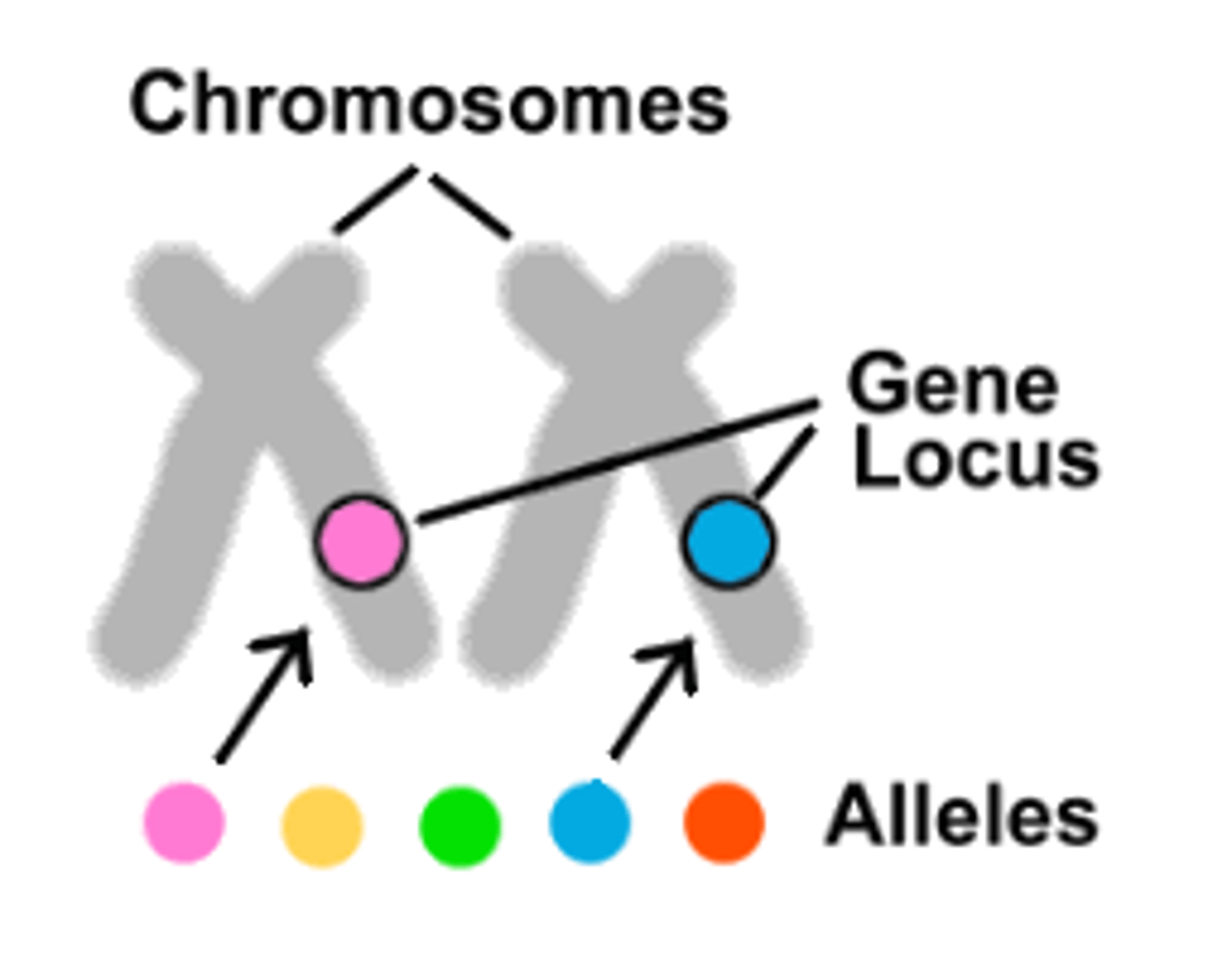
Allele
a specific DNA sequence of a gene that encodes for a protein or RNA
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are the same size, centromere position, and contain the same genes in the same order, though alleles may differ
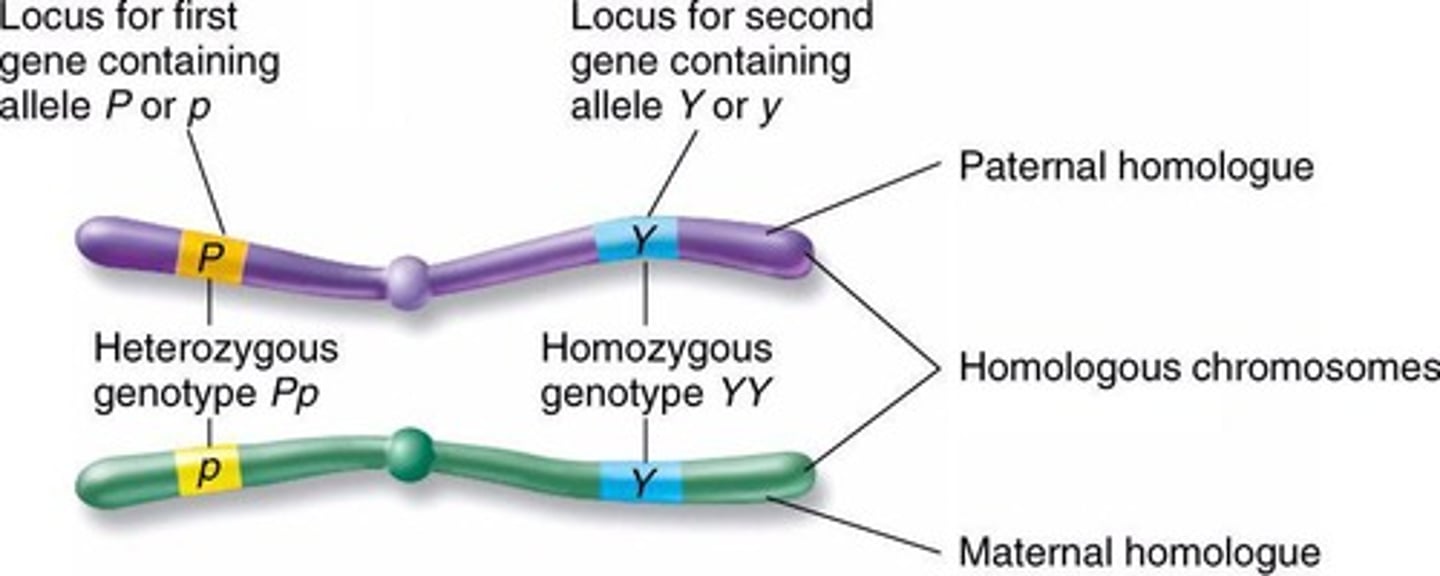
Locus
The region where a gene is located
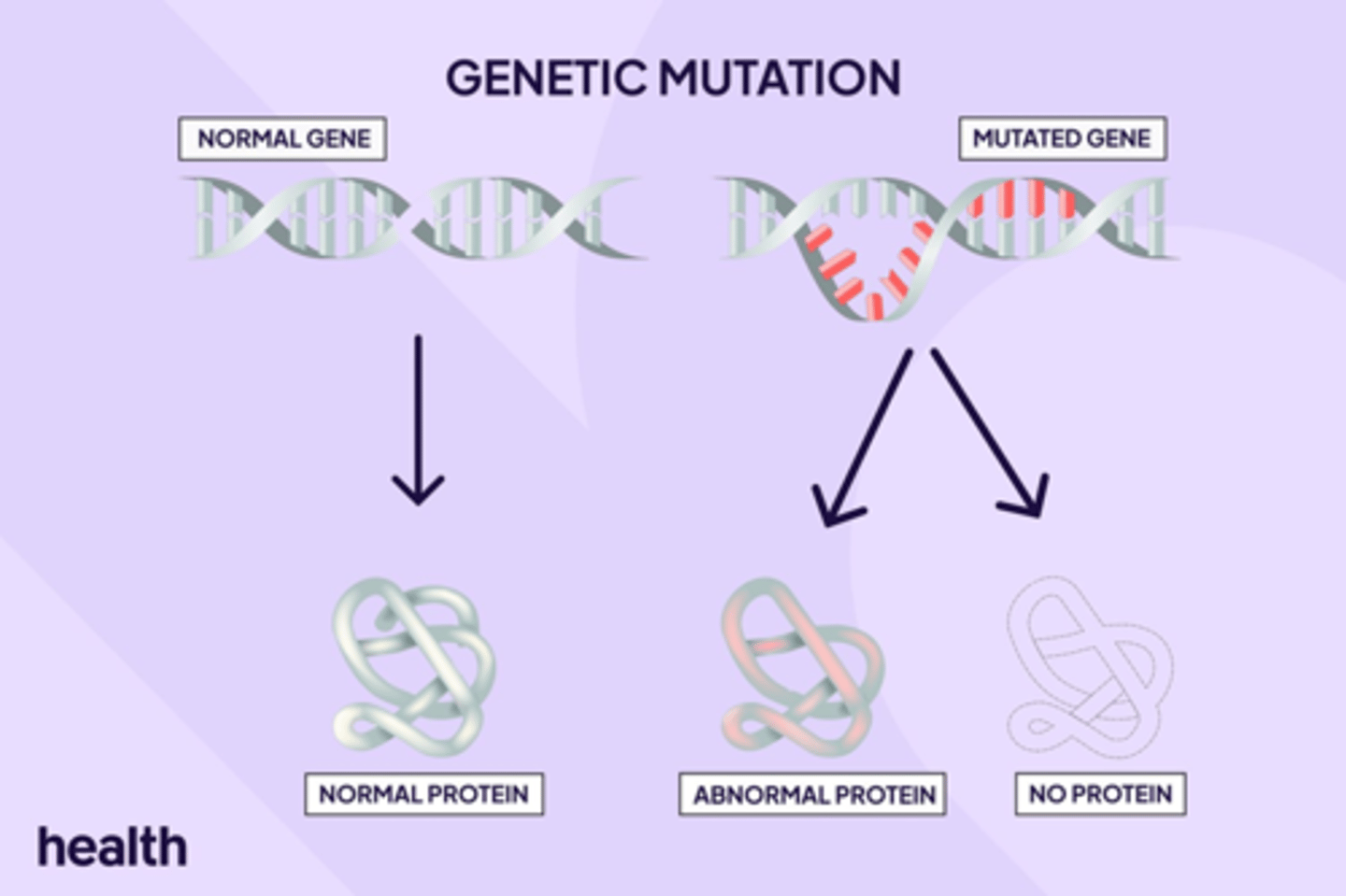
Mutation
A change in the sequence of nitrogenous bases in the DNA
Spontaneous Mutation
Caused by replication error exposure to mutagens, not due to external factors/environment
Single Base Mutation
Substitutions, insertions, deletions

Multiple Base Mutation
chromosomal rearrangements and translocations that affect kilobases or megabases of DNA
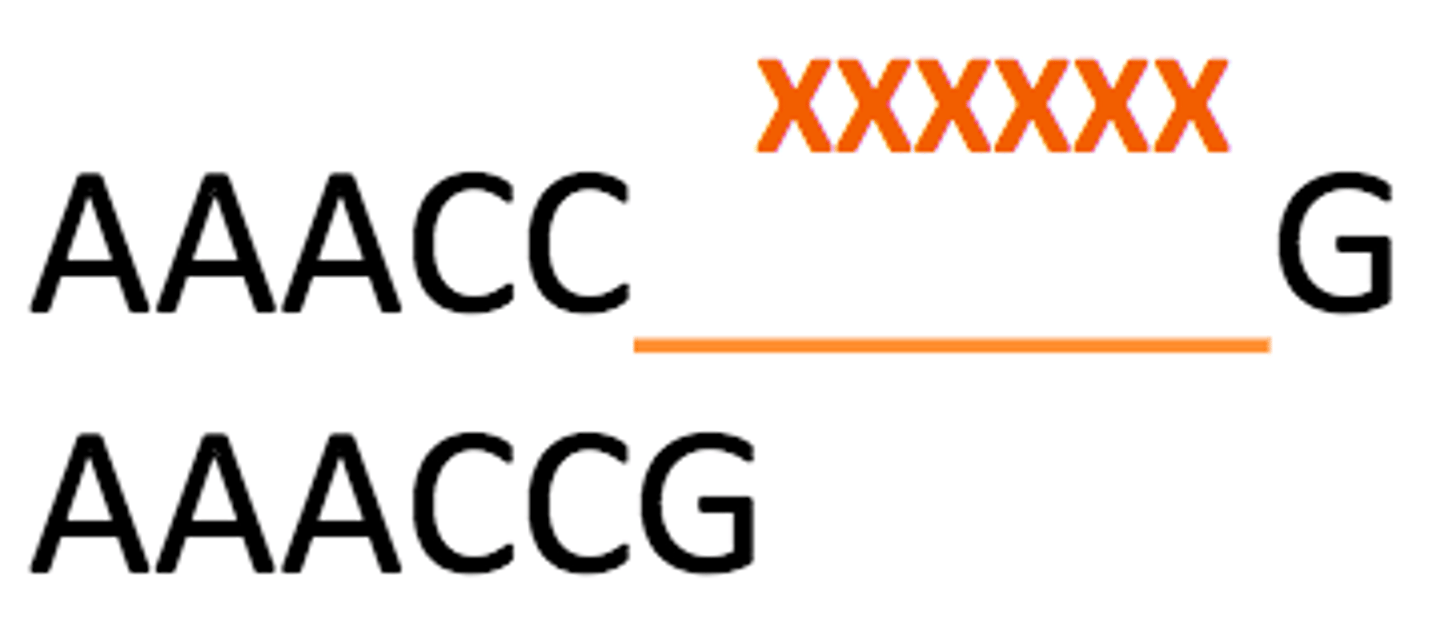
Background Level Mutation
the rate at which spontaneous mutations accumulate due to unrepaired changes
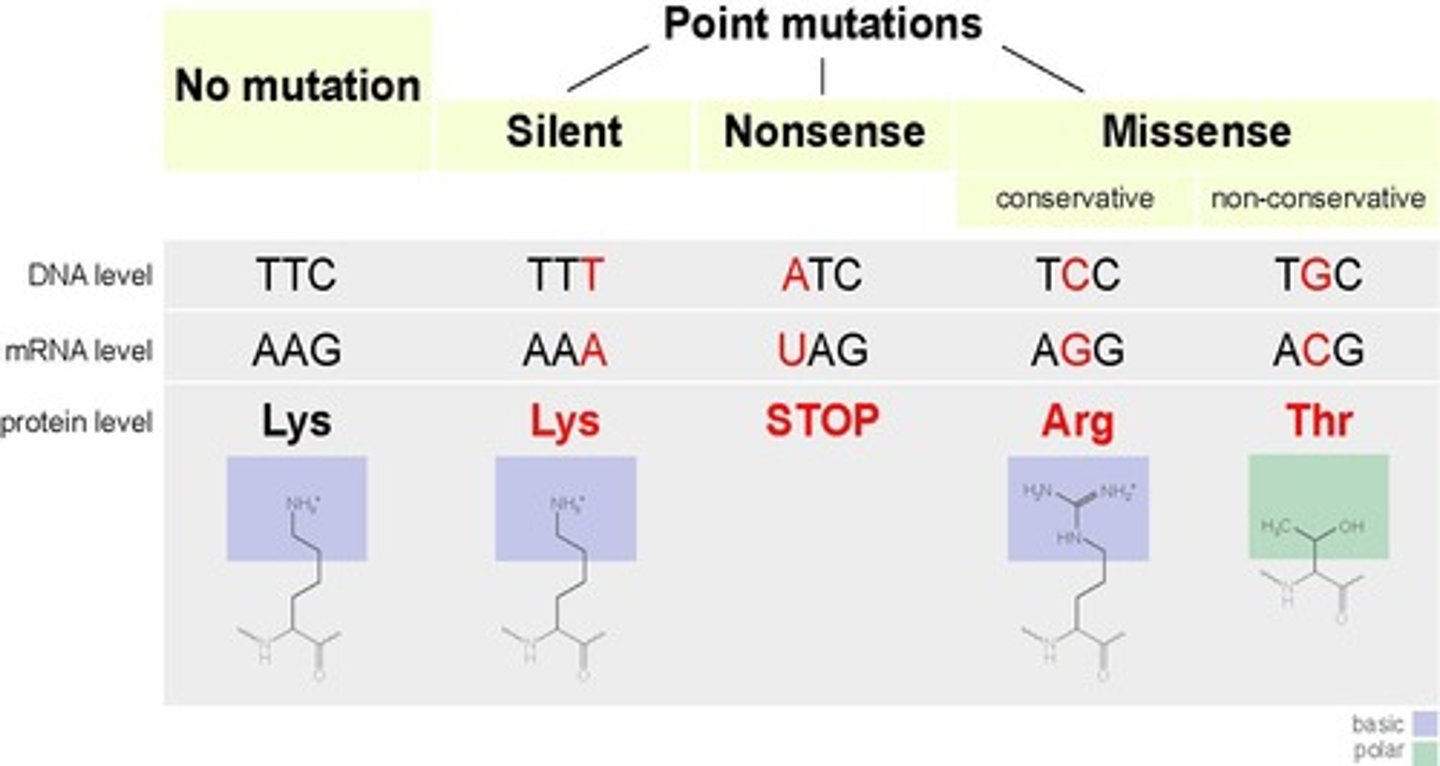
Point Mutation
A change in a single nucleotide base pair
Transitions Point Mutation
mutations that change a purine to another purine or a pyrimidine to another pyrimidine
Transversion Point Mutation
mutations that change a purine to a pyrimidine or vice versa
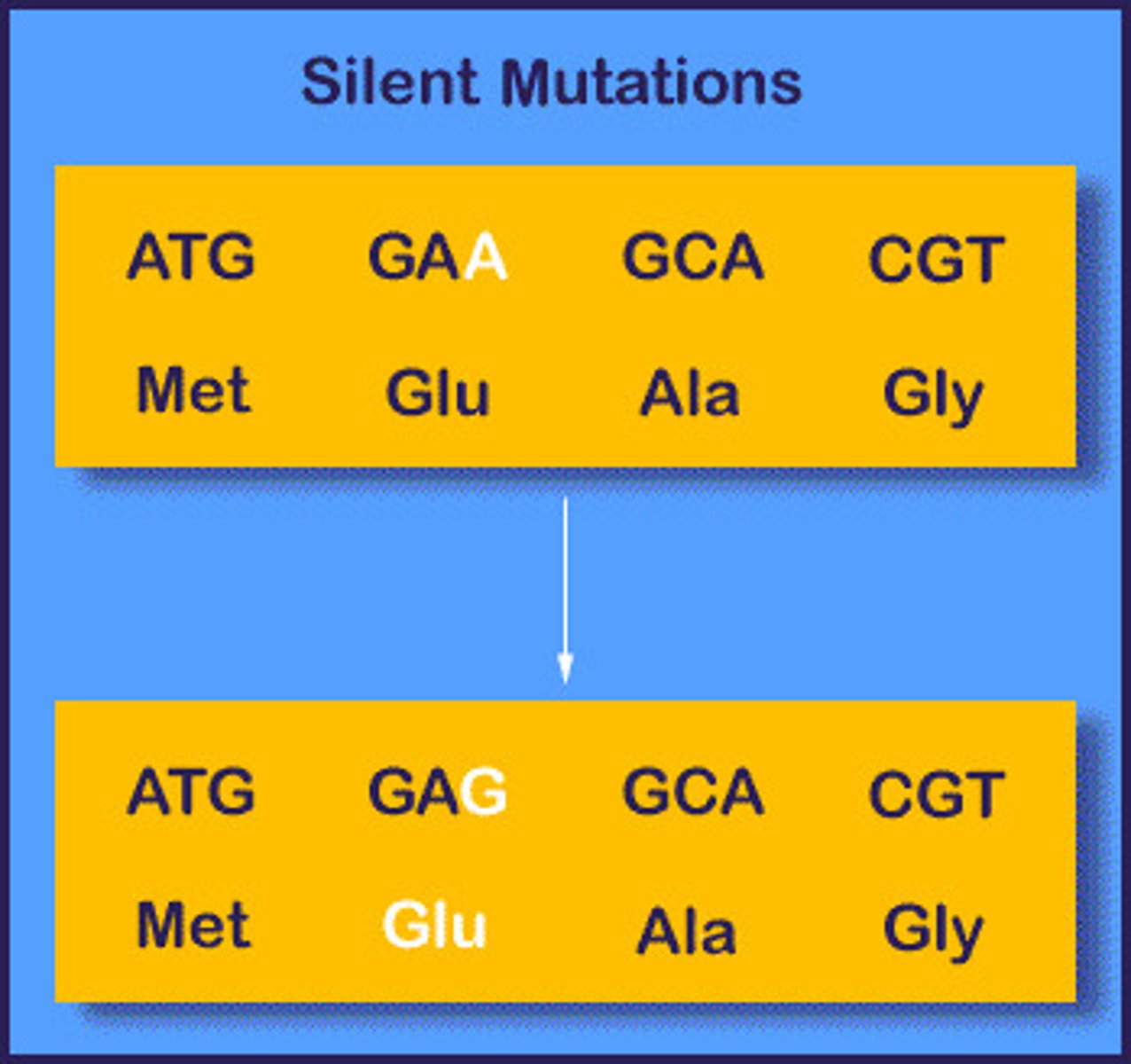
Silent Mutation
A mutation that does not change the amino acid sequence (Same Amino Acid)
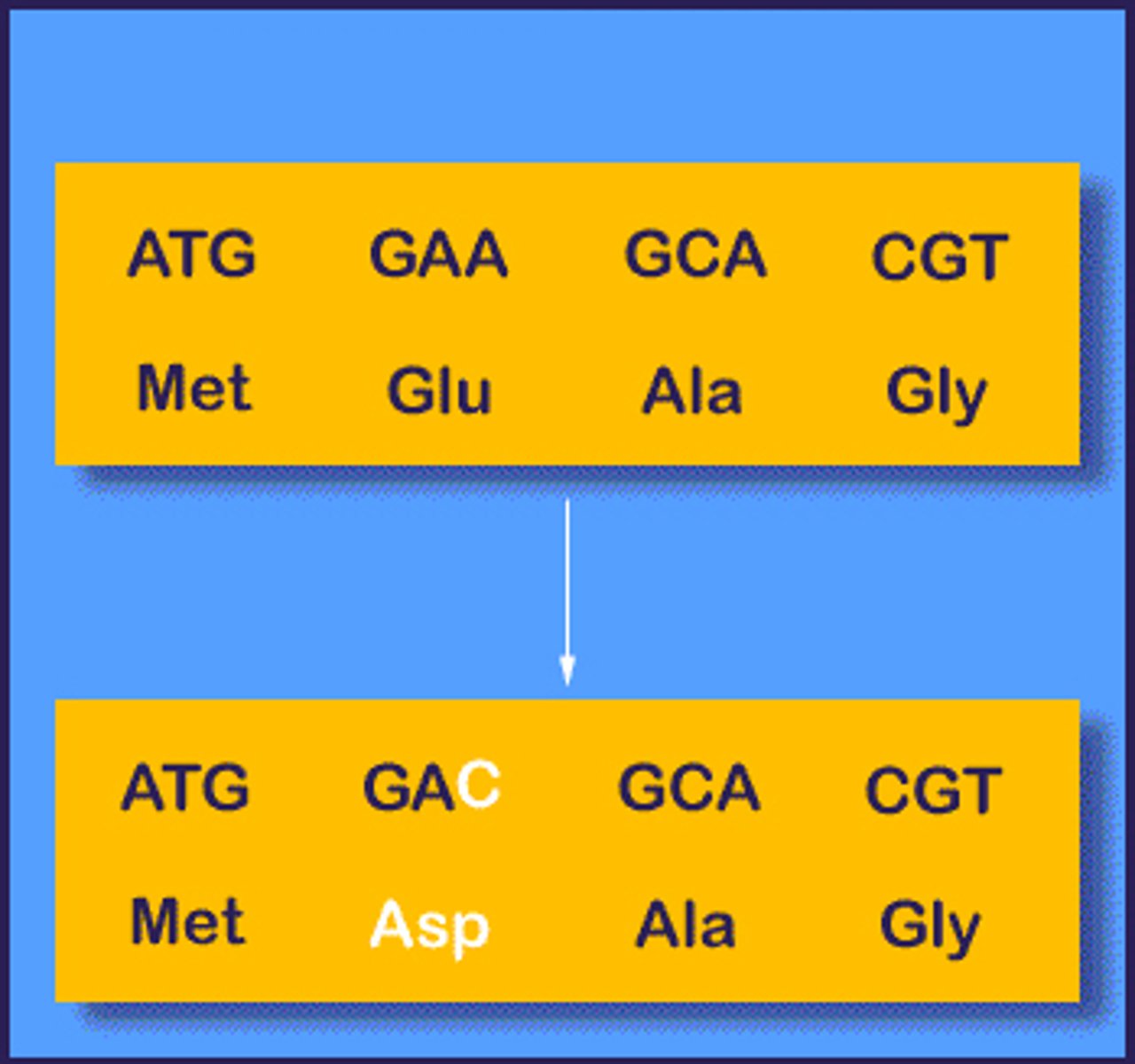
Missense Mutation
A mutation that results in a different amino acid being incorporated into a protein
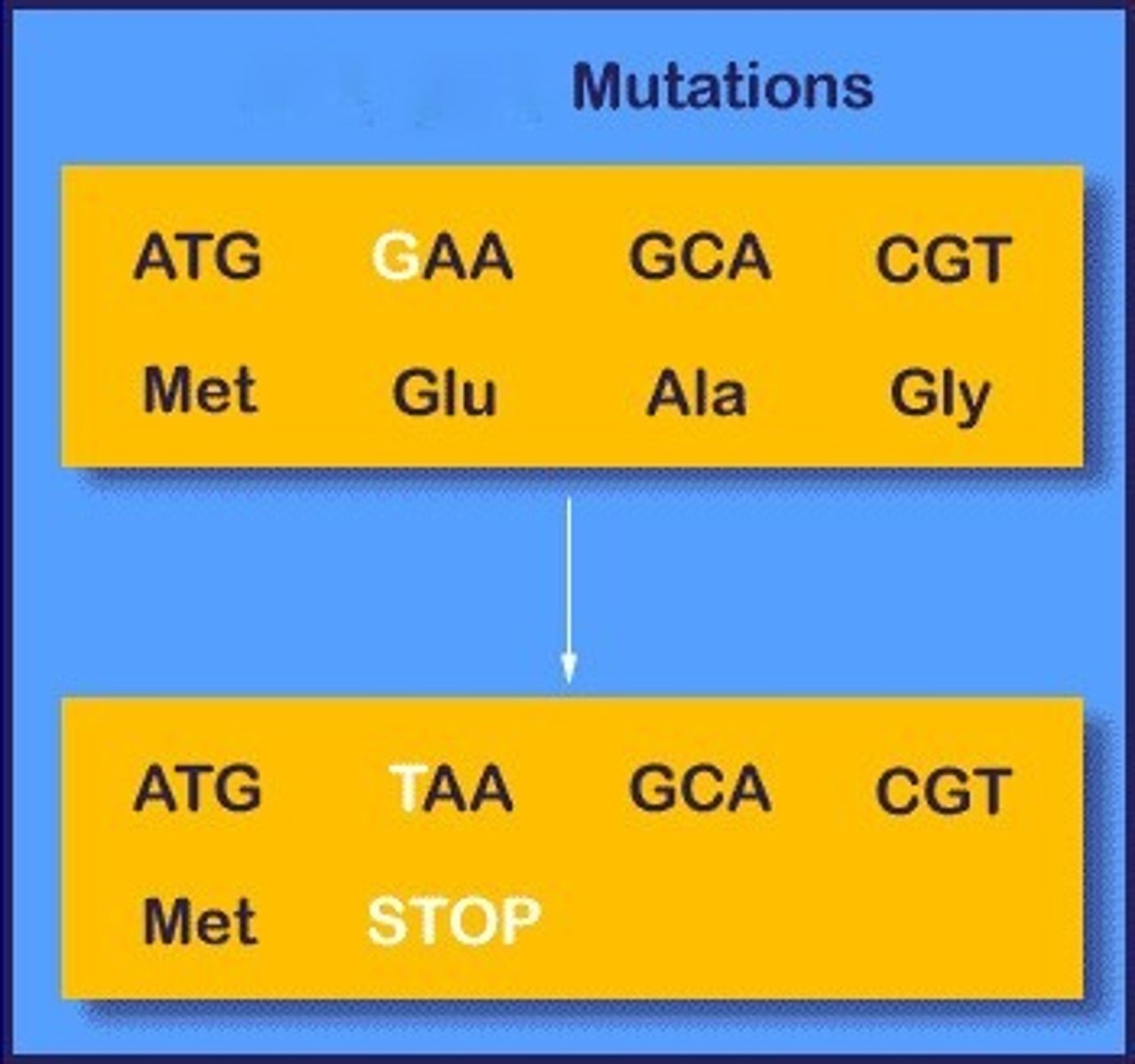
Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that creates a premature stop codon in the protein sequence
Neutral Mutation
A mutation that results in a different amino acid, but one that is chemically similar
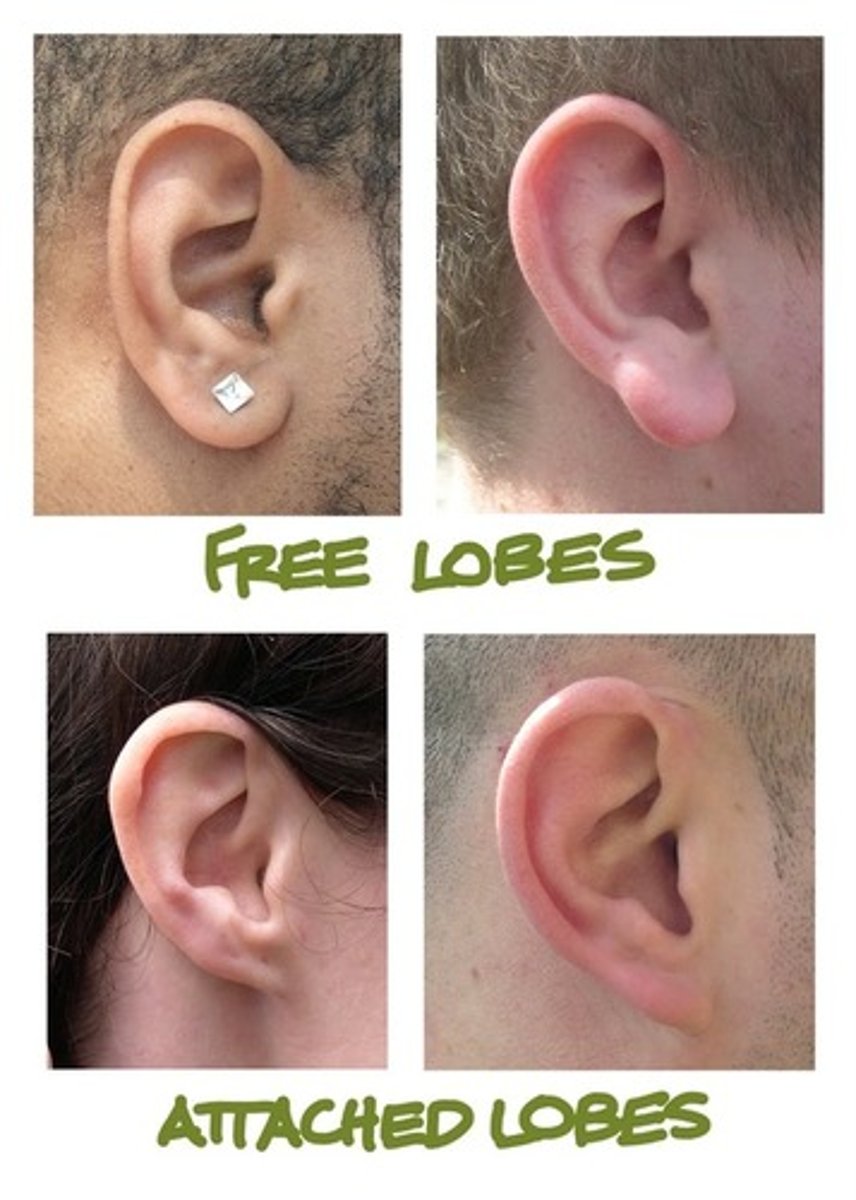
Frameshift Mutation
A mutation that shifts the reading frame of the genetic code, changing the entire sequence downstream
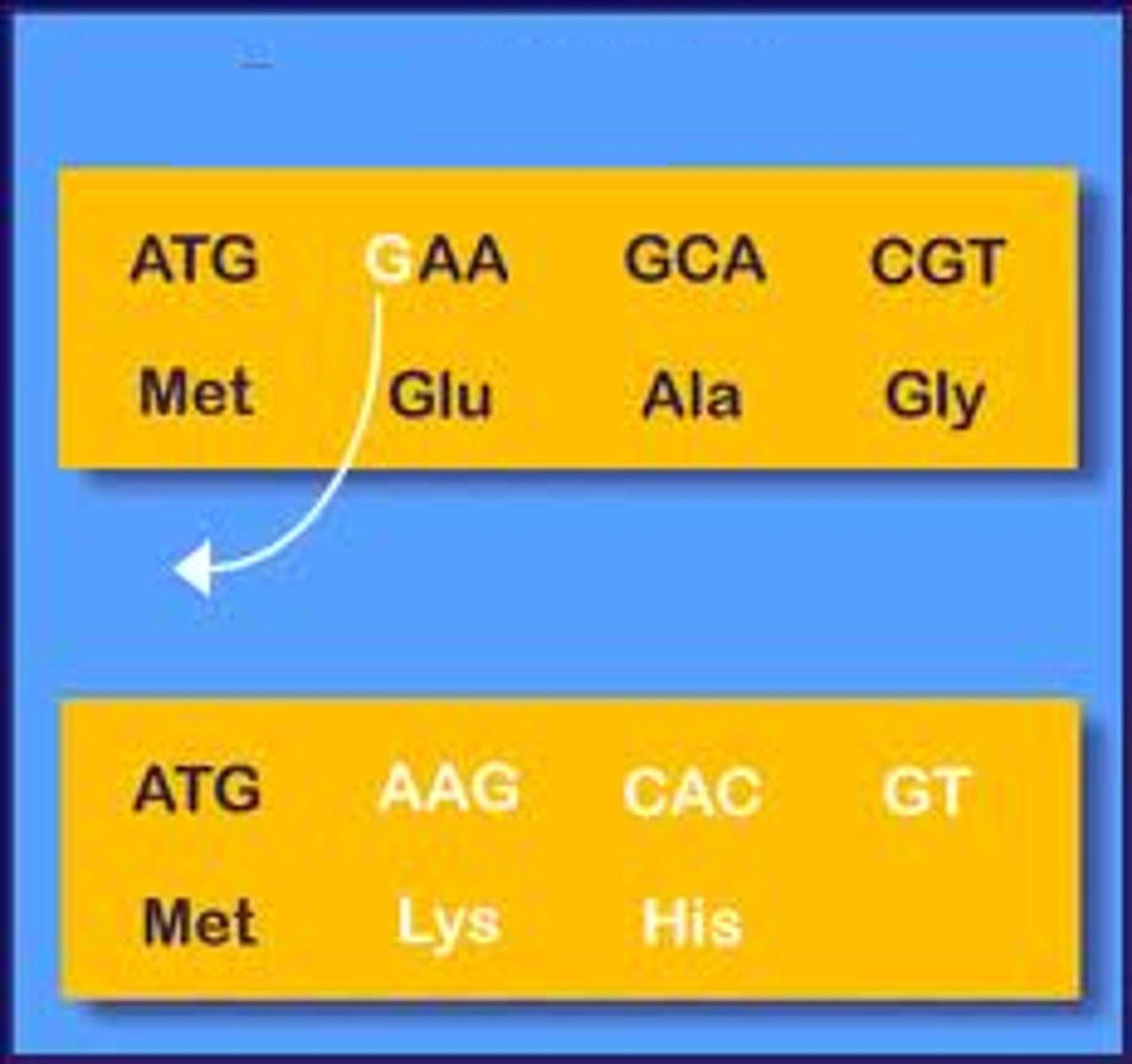
Dominant Allele
An allele whose phenotype is always expressed, even in heterozygous organisms
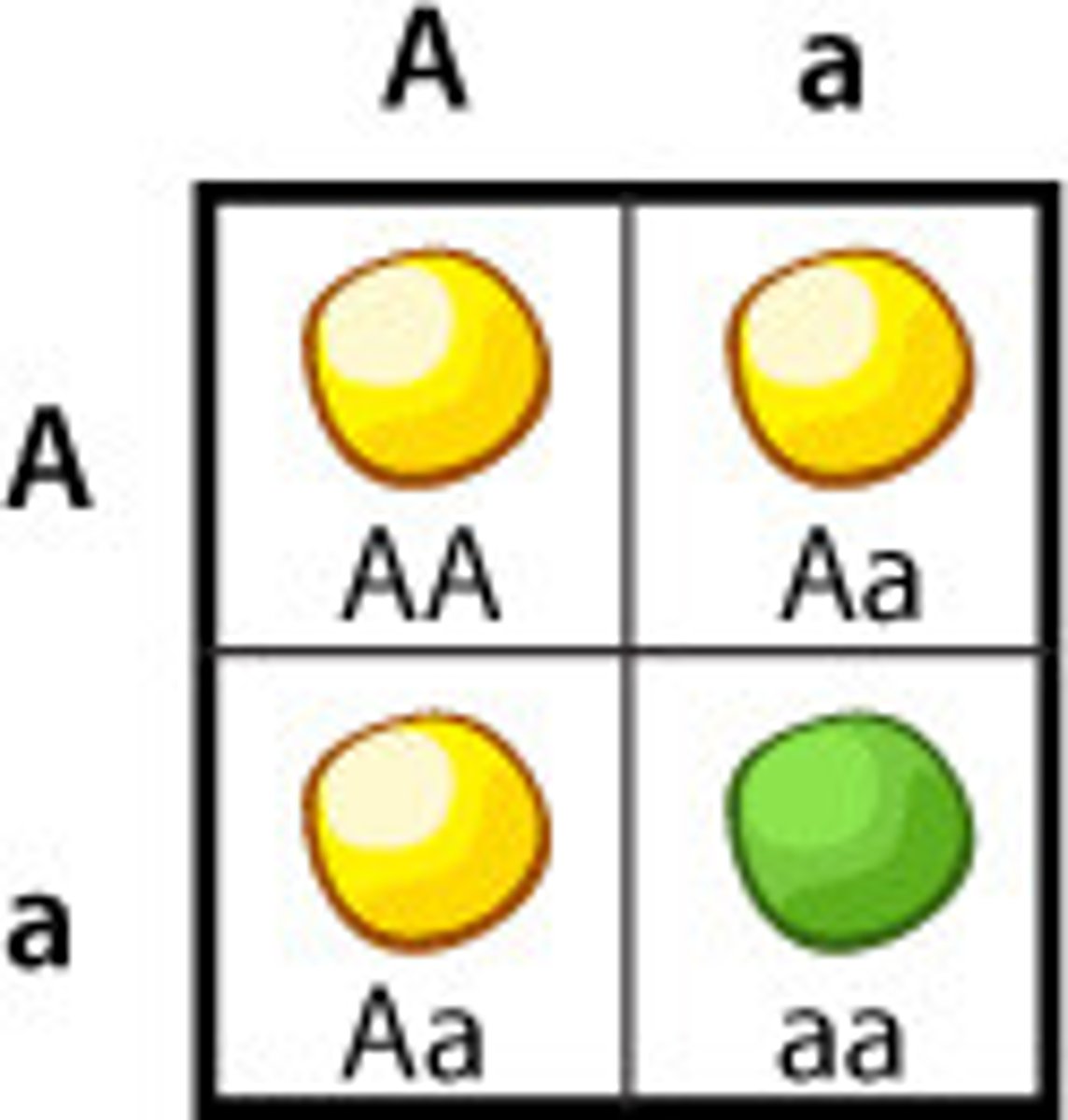
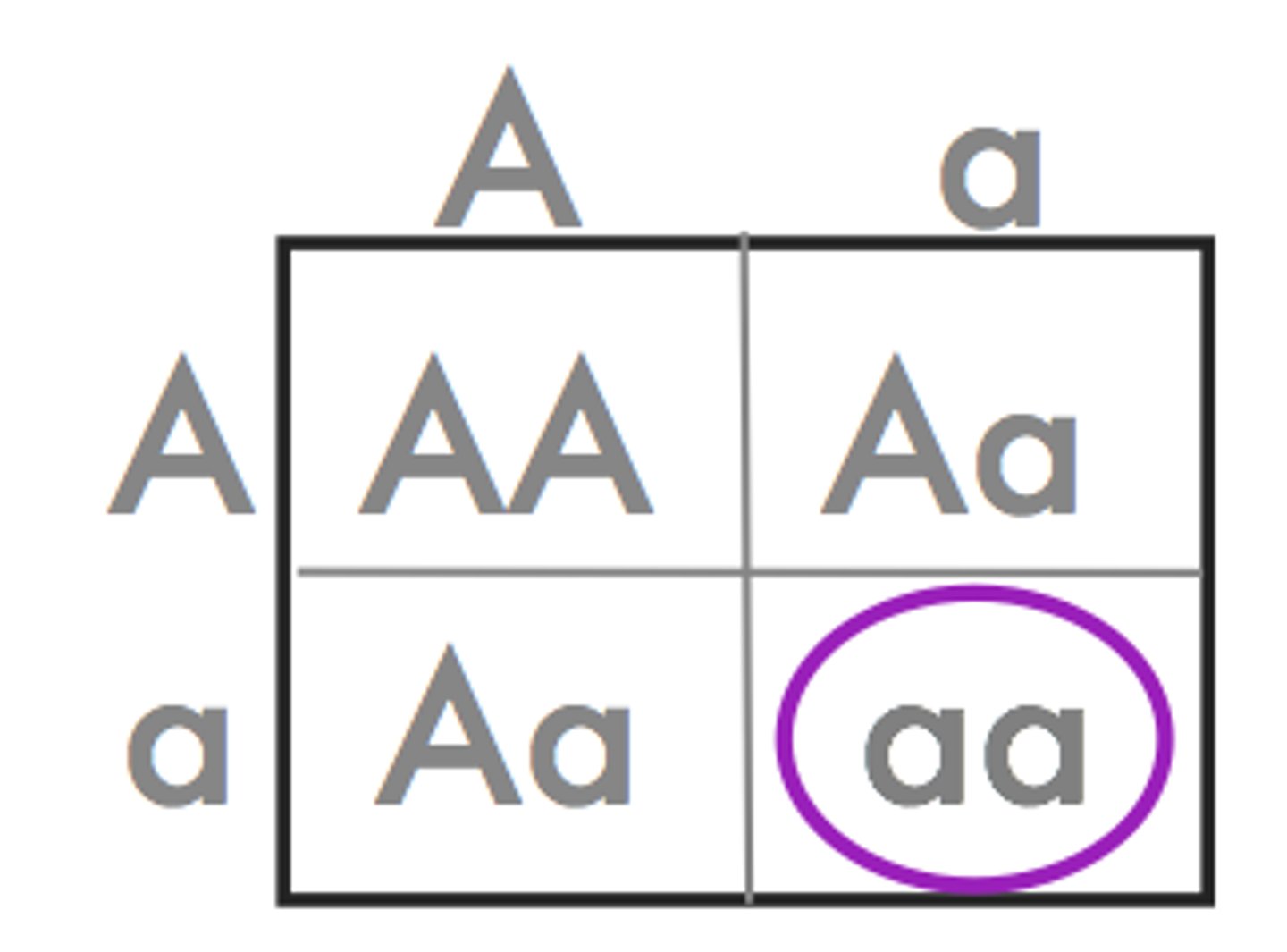
Recessive Allele
an allele whose phenotype is only expressed when two identical copies are present
Wildtype
The phenotype generally found in the natural population, not necessarily dominant
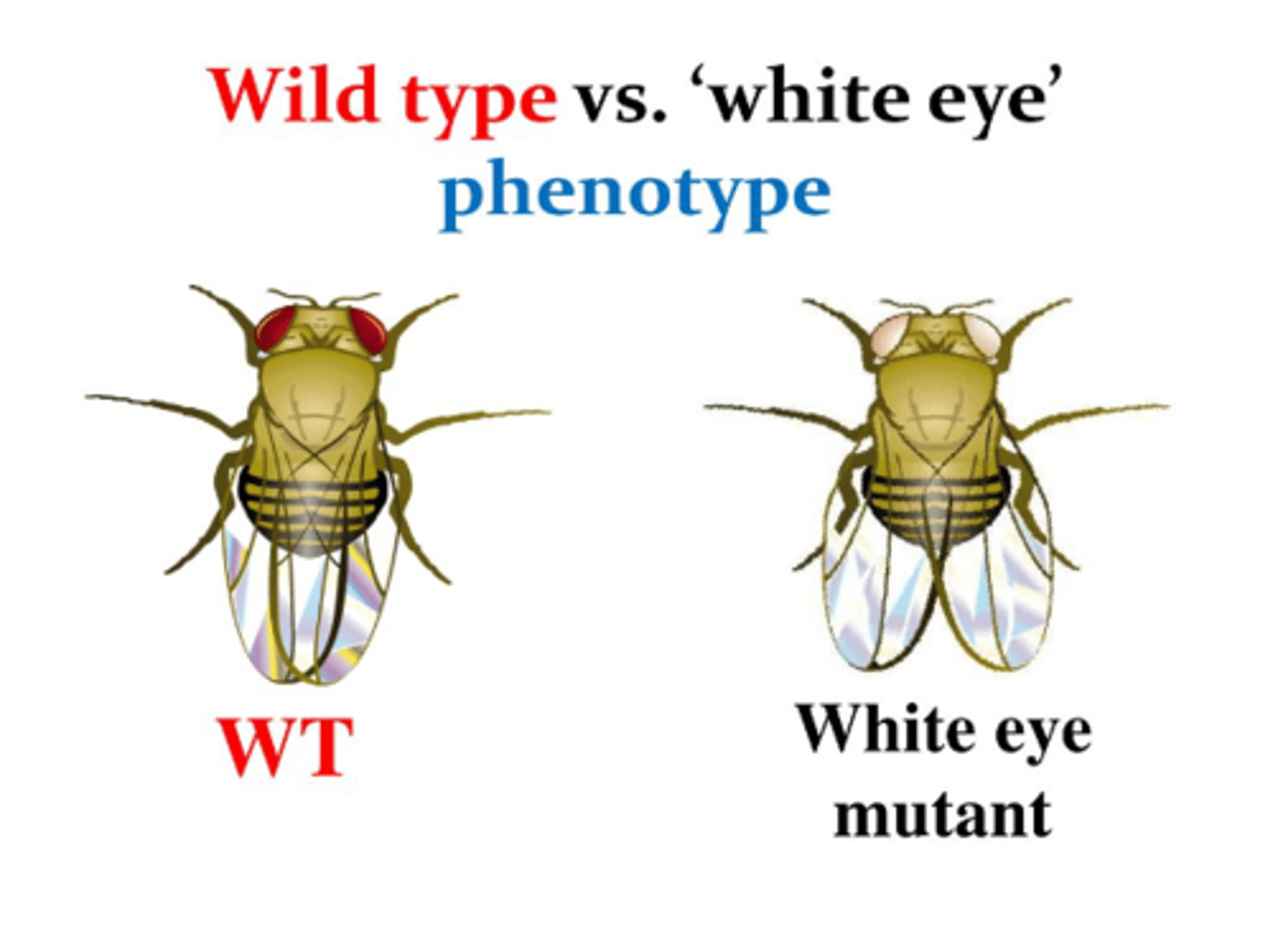
Mutant
Any phenotype different from the natural population

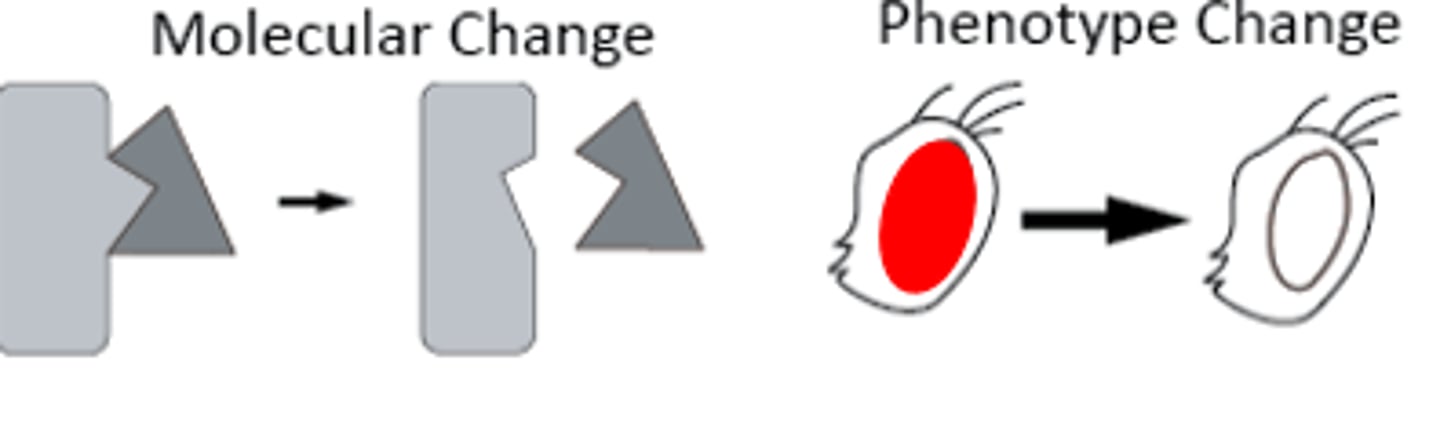
Forward Mutation
A mutation that adversely affects the wildtype phenotype
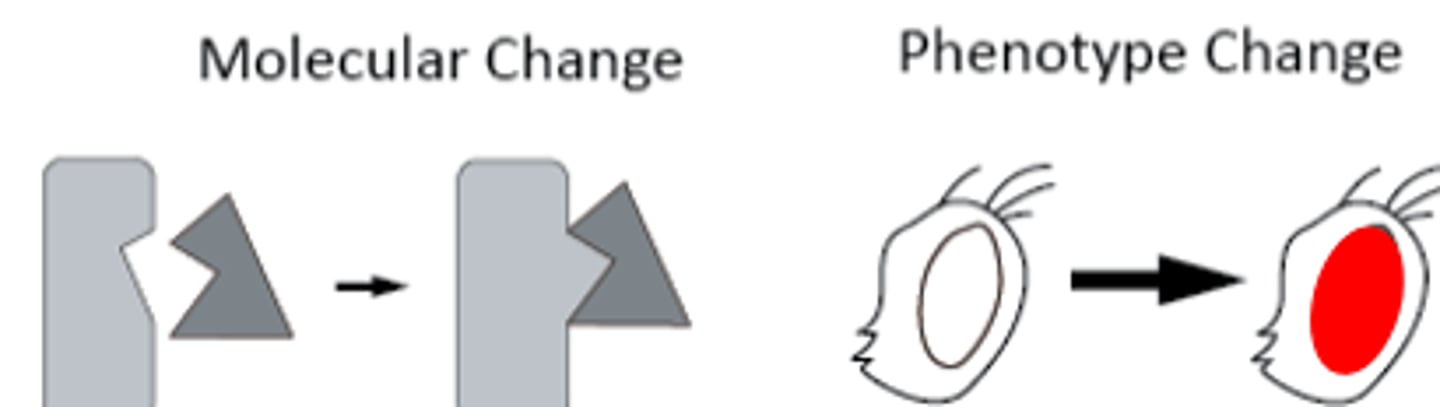
Back Mutation
a mutation that reverts a mutant back to the wildtype phenotype
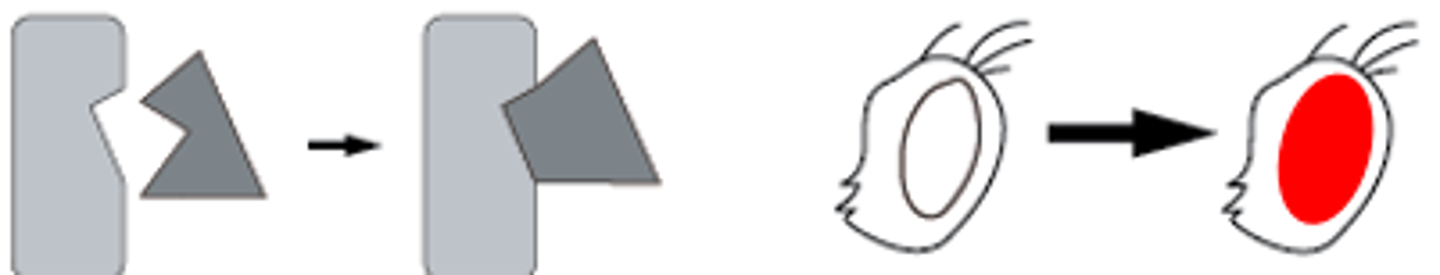
True Reversion
A mutation changes the mutant DNA sequence back to the exact original wildtype
Second-site reversion
A second mutation in the same gene that compensates for the effect of the first mutation

Suppressor Mutation
A second mutation in a different gene that compensates for the primary mutation
Null Mutation
a mutation that eliminates the function of the entire polypeptide or a critical domain
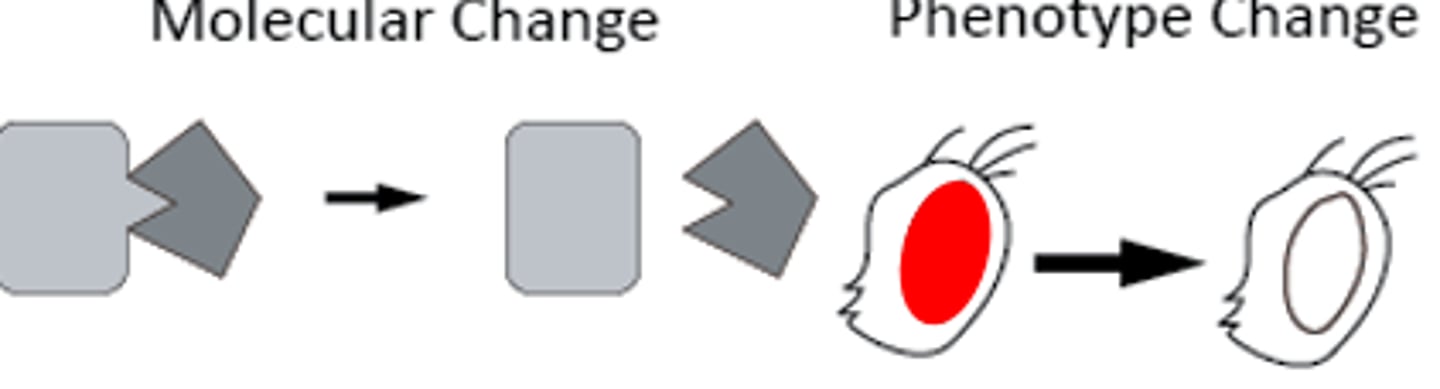
Hypomorphic Mutation
Some activity of the polypeptide is reduced, or less gene product is made

Hypermorphic Mutation
a mutation that results in an overactive polypeptide, producing too much product
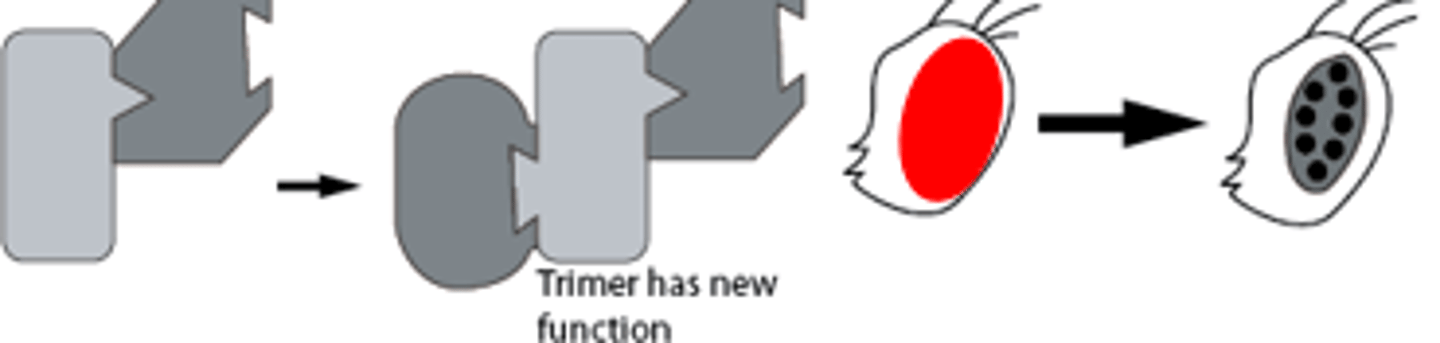
Neomorphic Mutation
New activity is acquired
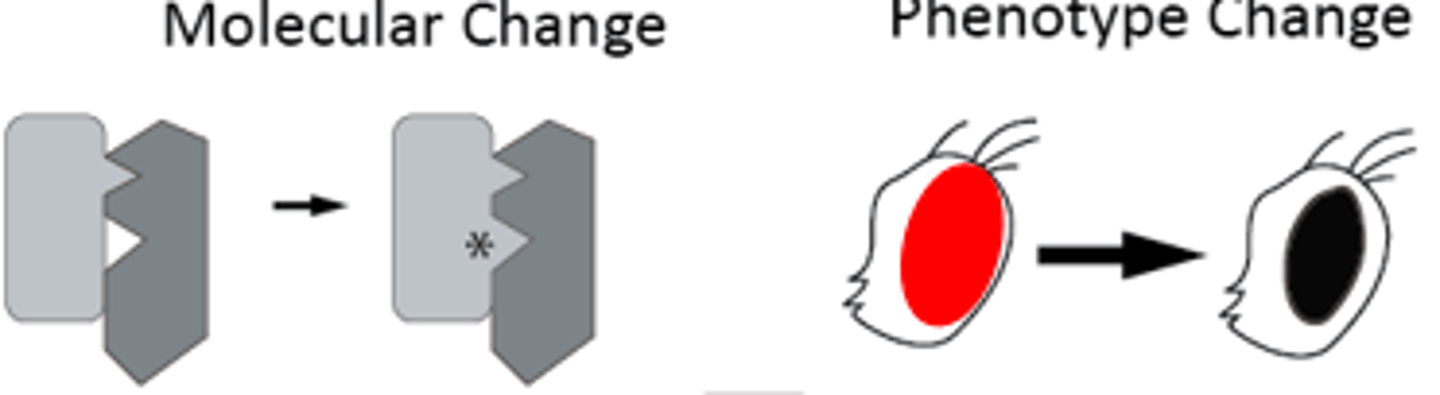
Antimorphic Mutation
The new function is against the old activity

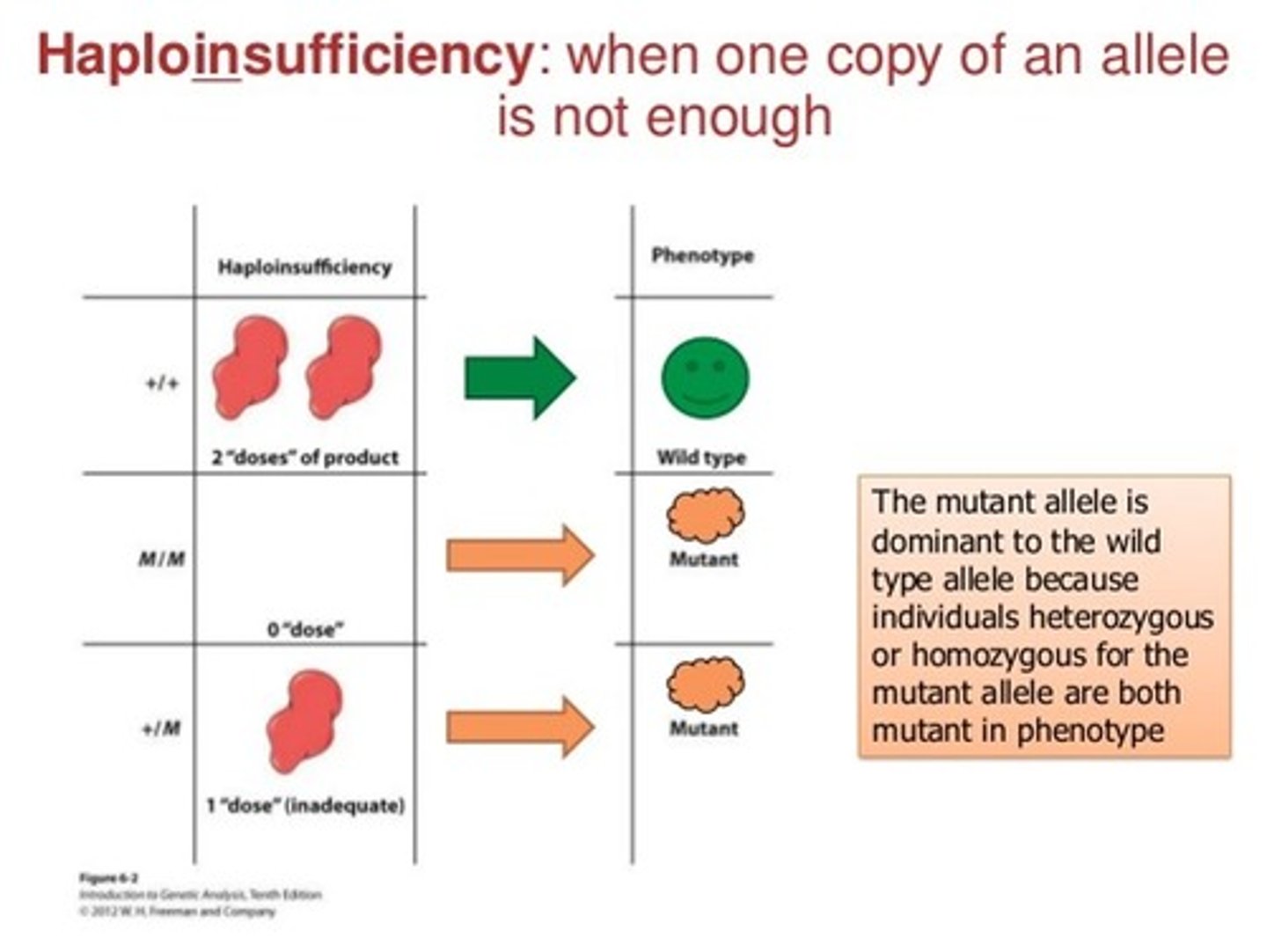
Haploinsufficiency
1 copy of WT allele is not enough to express the phenotype = LOF phenotype is expressed
Purpose of Complementation Test
To determine if two mutation of a specific phenotype are in the same gene or different genes.
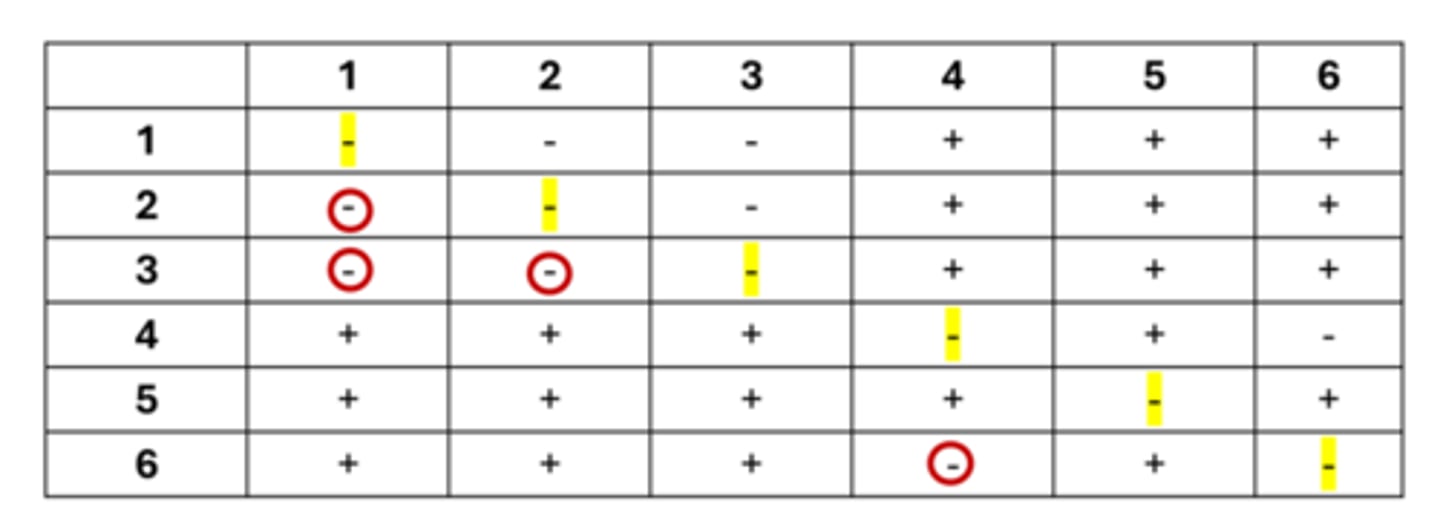
Complements
Progeny looks like the wild type meaning the mutation occurred in two different genes
Fails to complement
Progeny looks mutant meaning the mutations occurred in the same gene.
LOF Mutations
Apomorphic and Hypomorphic Mutations
GOF Mutations
Hypermorphic, Neomorphic, and Antimorphic Mutations