Bio-the muscular system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the two main mechanisms used to produce ATP?
aerobic respiration
anaerobic fermentation
ex. both processes are used throughout the body
Aerobic respiration
uses oxygen to create ATP
yields 26-32 ATP per glucose
requires usage of mitochondria
ex. not used during intense exercises when the body can’t deliver enough oxygen
ex. running and swimming are types of aerobic exercise
Anaerobic fermentation
no usage of oxygen
yields 2 ATP per glucose
excess glucose is converted to lactate
ex. used during short and intense exercises
Axon terminal
bulbous swelling at the end of a nerve fiber, separated by the synaptic cleft
ex. contains the synaptic vesicles
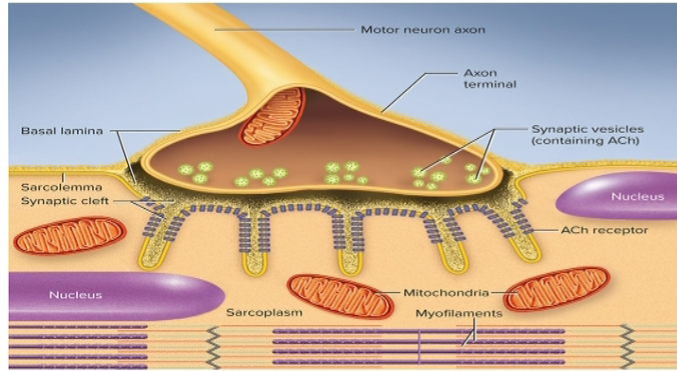
Neuromuscular junction
where a nerve fiber meets a muscle fiber
Synaptic vesicles
sacs in the synaptic knob that contain the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
the neurotransmitter that is released by the nerve fiber in synaptic vesicles that bind to ACh receptors on the muscle fiber, stimulating muscle contraction
ex. ACh = contraction; no ACh = no contraction
Acetylcholinesterase
enzyme found on muscle fiber and synaptic cleft that breaks down excess ACh to stop muscle stimulation
What are the five functions of the muscular system?
movement
stability
control of openings and passages
heat generation
glycemic control
What are the different types of myofilaments?
thick filaments
thin filaments
Thin filament
half as wide as thick filaments
made of intertwined strands of protein actin
also contains tropomyosin and troponin proteins
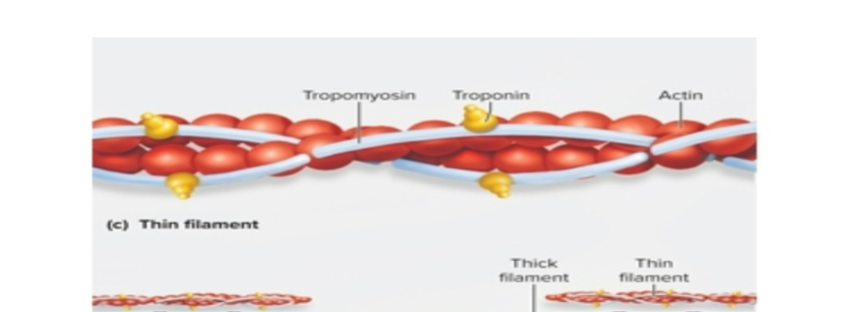
Actin
protein strands on thin filaments than contain myosin binding active sites or depressions
Troponin
protein on thin filaments that attracts calcium (Ca)
Tropomyosin
thread-like structures found on thin filaments that prevents myosin from reaching actin
How does myosin end up reaching actin?
after calcium channels open in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, Ca floods the cytosol of the muscle fiber and binds to troponin molecules on thin filament which changes the shape of tropomyosin and reveals the myosin binding active sites of actin
Isometric contraction
contraction of a muscle without a change in length
ex. important in stabilizing joints and maintaining posture
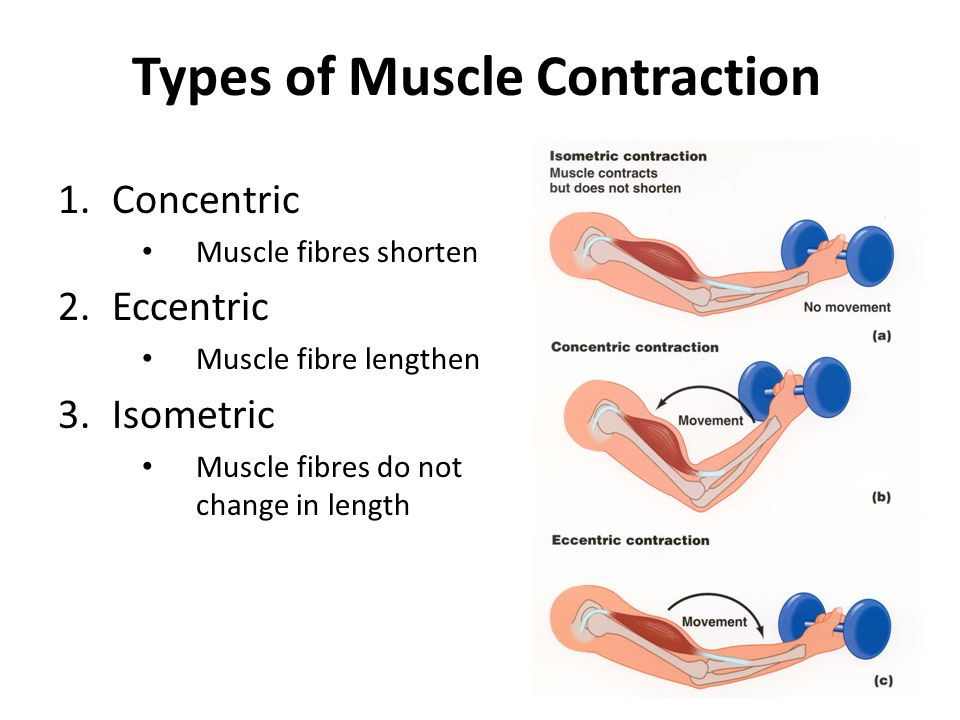
Isotonic contraction
contraction of a muscle with a change in length
two types: concentric and eccentric contraction
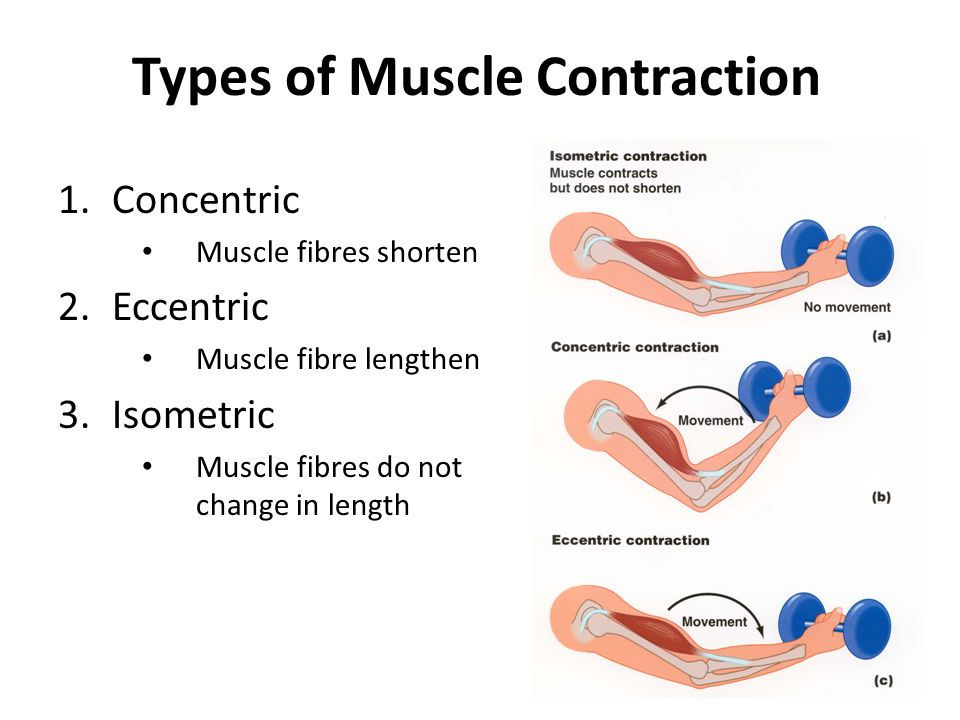
Concentric contraction
muscle shortens as it maintains tension
ex. bicep curls
Eccentric contraction
muscle lengthens as it maintains tension
ex. more likely to cause injury
Endomysium
thin layer enclosing each muscle fiber
allows room for blood capillaries and nerve fibers
Perimysium
layer surrounding bundles of muscle fibers (fascicles)
ex. thicker than the endomysium
Epimysium
layer surrounding the muscle as a whole
Fasciae
fibrous sheets separating muscles from each other that may separate functionally related muscles into compartments
Fascicles
bundles of muscle fibers or nerves
ex. help organize muscle fibers for contraction
Compartment syndrome
when the fasciae binds the muscles
ex. causes problems
Slow twitch (red) muscle fibers
filled with blood vessels
rely on aerobic respiration
long, slow twitches
have good endurance
ex. marathon runners
Fast twitch (white) muscle fibers
have few blood vessels
rely on anaerobic fermentation
fast twitches
fatigue easily
ex. basketball players