BIOL 3000 Epigenetics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Monozygotic offspring
Identical twins, sharing placenta
Dizygotic offspring
Fraternal twins, being of separate placentas
Genome
The genetic material of an organism
Epigenome
Record of the chemical changes to the DNA and histone proteins of an organism
What is erased during the first days post fertilization?
Epigenetic tags from mom and dad’s chromosomes
Imprinted genes
When epigenetic tags are not erased from mom and dad’s chromosomes during the first days of post fertilization
Role of imprinted genes
Transfer epigenetic information rather than just DNA sequence information to offspring
As the embryo develops,
Cell specialization occurs; each cell type specializes with epigenetic tags. These tags either activate or silence specific genes which lead to further specialization
Age 0, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Nothing yet
Age 3, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Environmental factors
Age 12, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Diet
Age 16, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Physical activity
Age 21, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Toxins
Age 40, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
Stress
Age 75, genetic tags in a pair of twins can be affected by what?
The cumulation of environmental factors, diet, physical activity, toxins, and stress
What are very different as each twin reaches full adulthood?
Epigenome patterns
Epigenetic effect of methylation
DNA methylase/DNA methyltransferase is added to cytosine to make 5-methylcytosine
This alters the gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself
DNA methylation role
Usually inhibits the transcription of eukaryotic genes, especially in the region of the promoter
Many eukaryotic genes contain CpG Islands near their promoter regions
CpG Islands
Sequences of DNA typically 1000-2000 nucleotides long containing lots of CG repeats
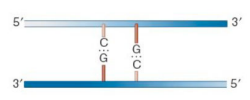
Unmethylated
No strands of DNA are methylated
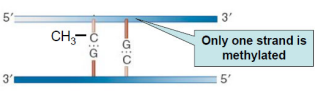
Hemimethylated
One strand is methylated
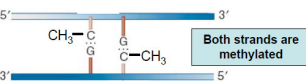
Fully methylated
Both strands are methylated
How does epigenetic control occur?
DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling: Post-transcriptional modification or methylation of DNA
The gene is “switched on” in DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling when:
The chromatin is active (open) and has unmethylated cytosines and acetylated histones
The gene is “switched off” in DNA methylation and chromatin remodeling when:
The chromatin is silent (condensed) and has methylated cytosines and deacetylated histones
Housekeeping genes
Tend to be constitutively expressed in most cell types
CpG Islands are usually unmethylated
Tissue Specific Genes
Gene expression is regulated by methylation at CpG Islands
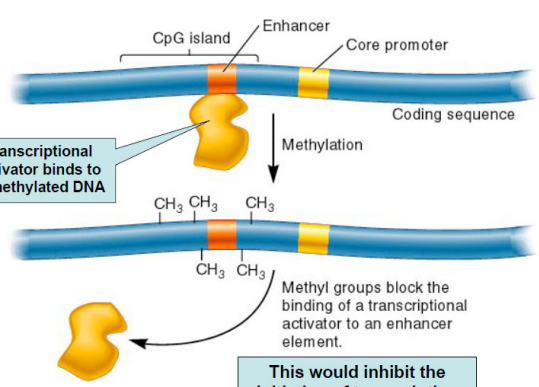
Block Transcription Factor Binding
The transcriptional activator bind to the unmethylated DNA, which then inhibits the initiation of transcription.
The methyl groups block the binding of a transcriptional activator to an enhancer element
Induction of heterochromatin (chromatin compacting)
Methyl-CpG binding proteins binds to the methylated CpG island
This protein then recruits proteins, like histone deacetylase, which converts the chromatin to a closed conformation
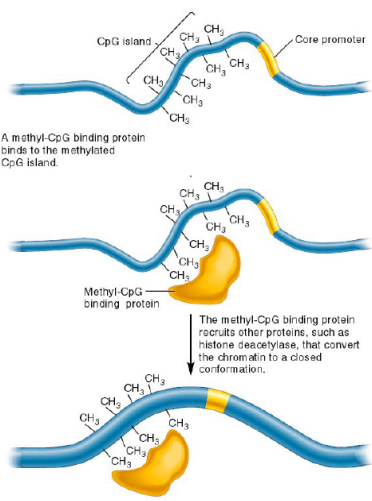
Gene silencing
Decreasing acetylation (HDAC) allows gene silencing
Increasing methylation (HMT) allows gene silencing
Example of epigenetics
Calico cats
One of the several genes encoding coat color is located on the X-Chromosome XB (orange) Xb (black). Orange is dominant to black
Lyonization
The inactivation of one random X chromosome so as not to produce twice the gene product
Barr Body
The supercoiled X chromosome (chromatin condensation)
Epigenetics and nutrition
Food contains nutrients like Folic acid and B complex vitamins which are methyl donating nutrients; these help regulate gene expression
Summary of Agouti Mice experiment
The Agouti gene is a gene that influences the coat color in mammals.
A healthy brown mouse briefly had the Agouti mRNA during development, then it was silenced for the rest of life (methylated).
An obese yellow mouse made the Agouti mRNA continuously throughout life, a constitutively active Agouti gene. It has yellow fur.
They took the F1 generation of an obese yellow mouse and fed it foods rich in methyl groups during pregnancy. This resulted in mostly brown healthy offspring, while a normal diet of the yellow mouse led to a mostly yellow unhealthy offspring.
Epigenetic memory
Methylation protection extends beyond the F1 offspring into the next generation, as shown in the Agouti mice
Can we change the epigenetic profiles of specific genes?
Cancer cells have lower levels of methylation than healthy cells, which allows the activation of genes promoting cell growth. It initiates checks on cell growth genes and programmed cell death pathways.
Epigenetics and behavior
A decrease in protein synthesis in depressed patients and a decrease in transcription in AD patients, which are both regulated by methylation.
Studied the increased level of methylation in suicide victims, and there was a correlation with an increase in methylated CpG sites in suicidal victims
Also found that epigenetic markers left in victims of child abuse.