PSY 324 Quiz Questions
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Zhang et al 2013 paper examines behavior in
Humans
In the Zhang et al 2013 paper, all the participants were males.
false, participants were not all male
Zhang et al 2013 paper results show slower times after ball heading on ___ task.
the anti-point
The Zhang et al 2013 paper provides definitive evidence that the cognitive slowing that occurs after soccer playing with ball heading is only a transient effect and not a long-lasting changing or brain injury. True or false
False, this is not only a transient effect and could be long-lasting
the Zhang et al 2013 paper measures sensorimotor and cognitive behavior using:
a tablet
the Zhang et al 2013 paper, data was collected from ____ different participants.
24
Heading a ball in soccer is typically considered a ____ head impact.
subconcussive
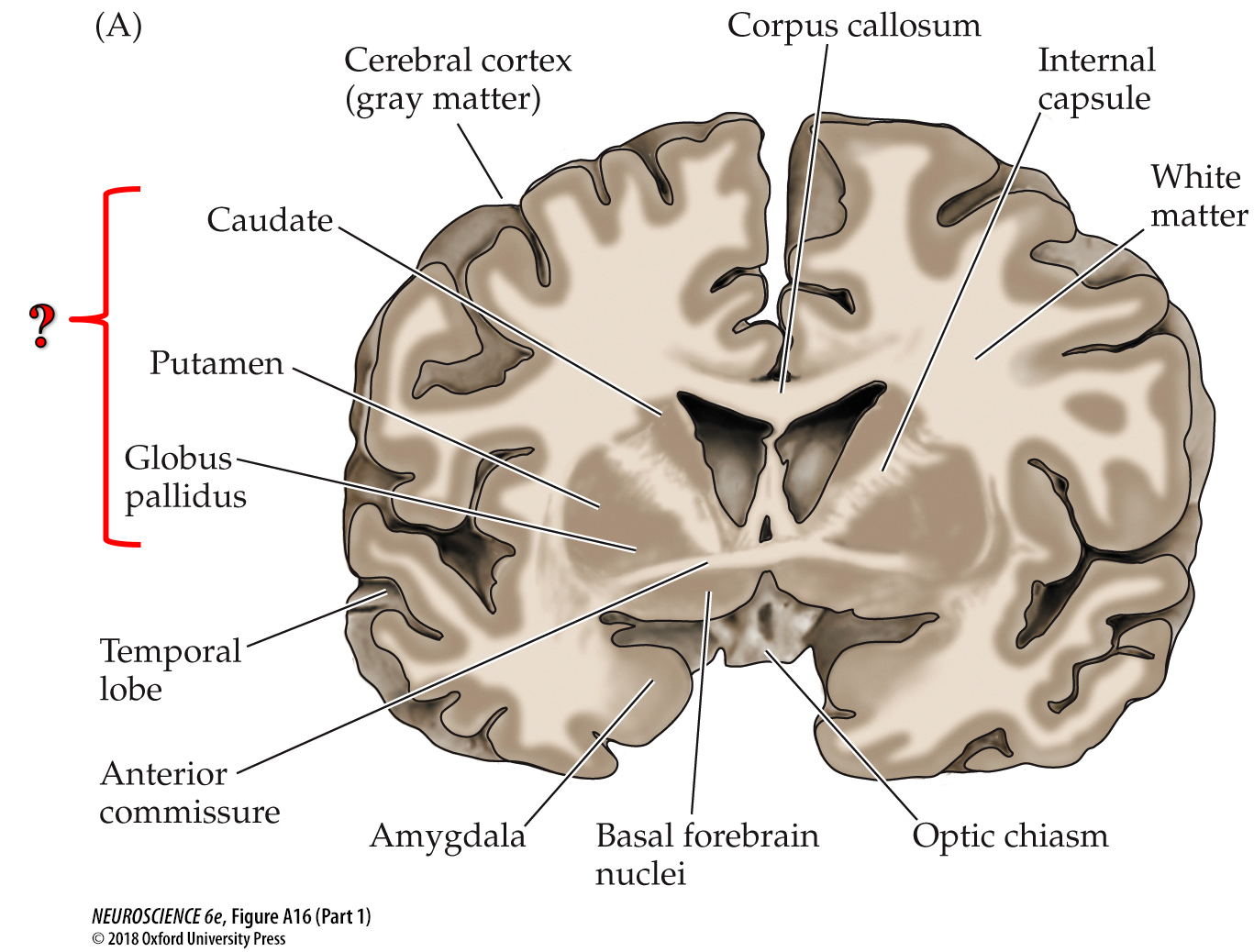
?
Thalamus
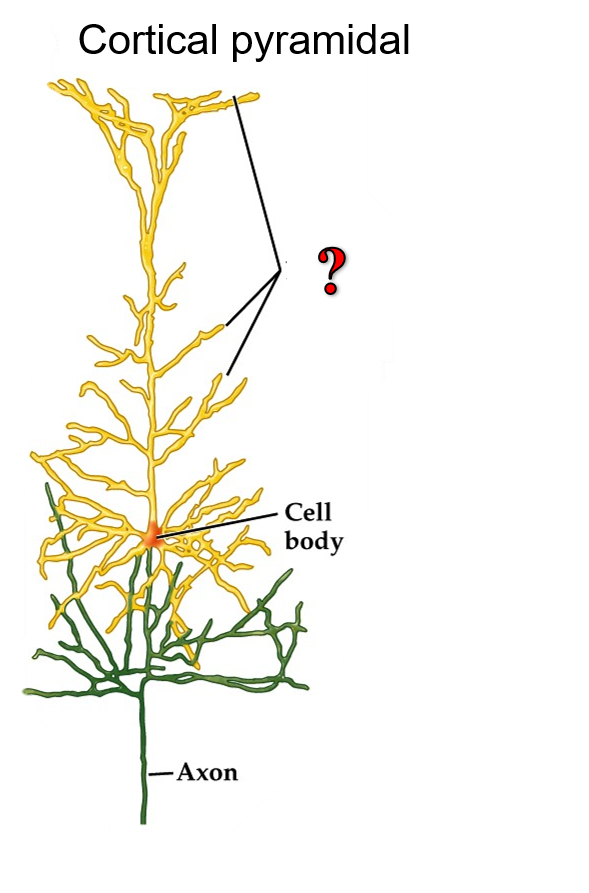
?
dendrites
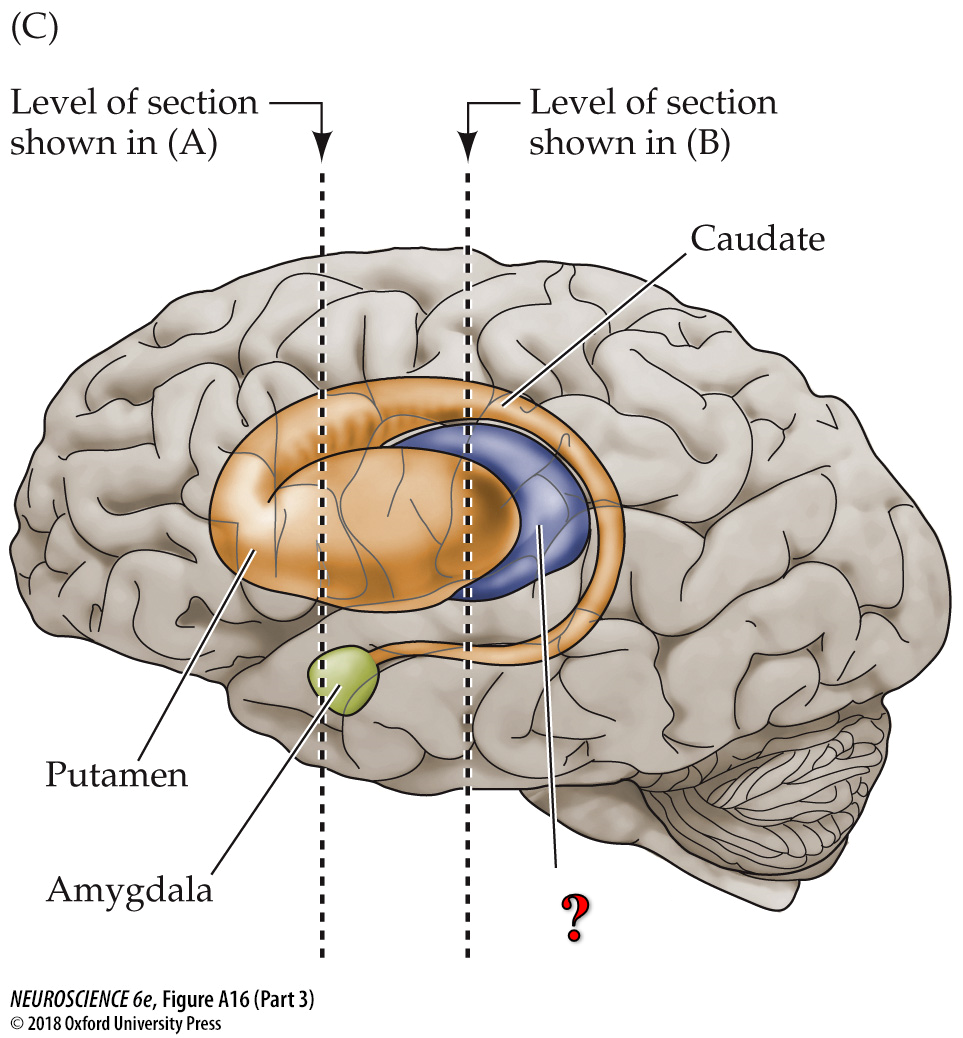
?
basal ganglia
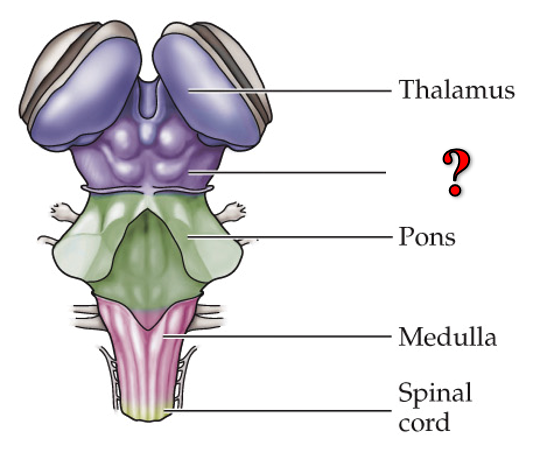
?
midbrain
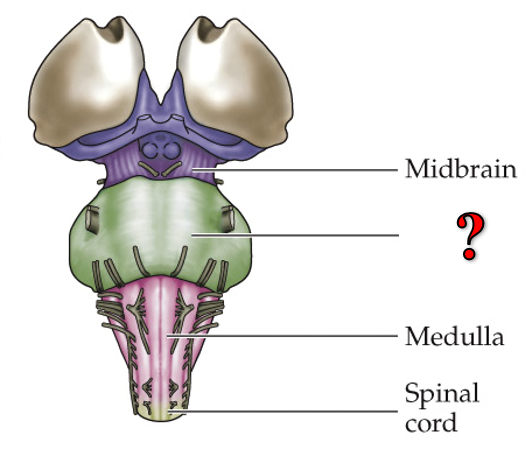
?
pons
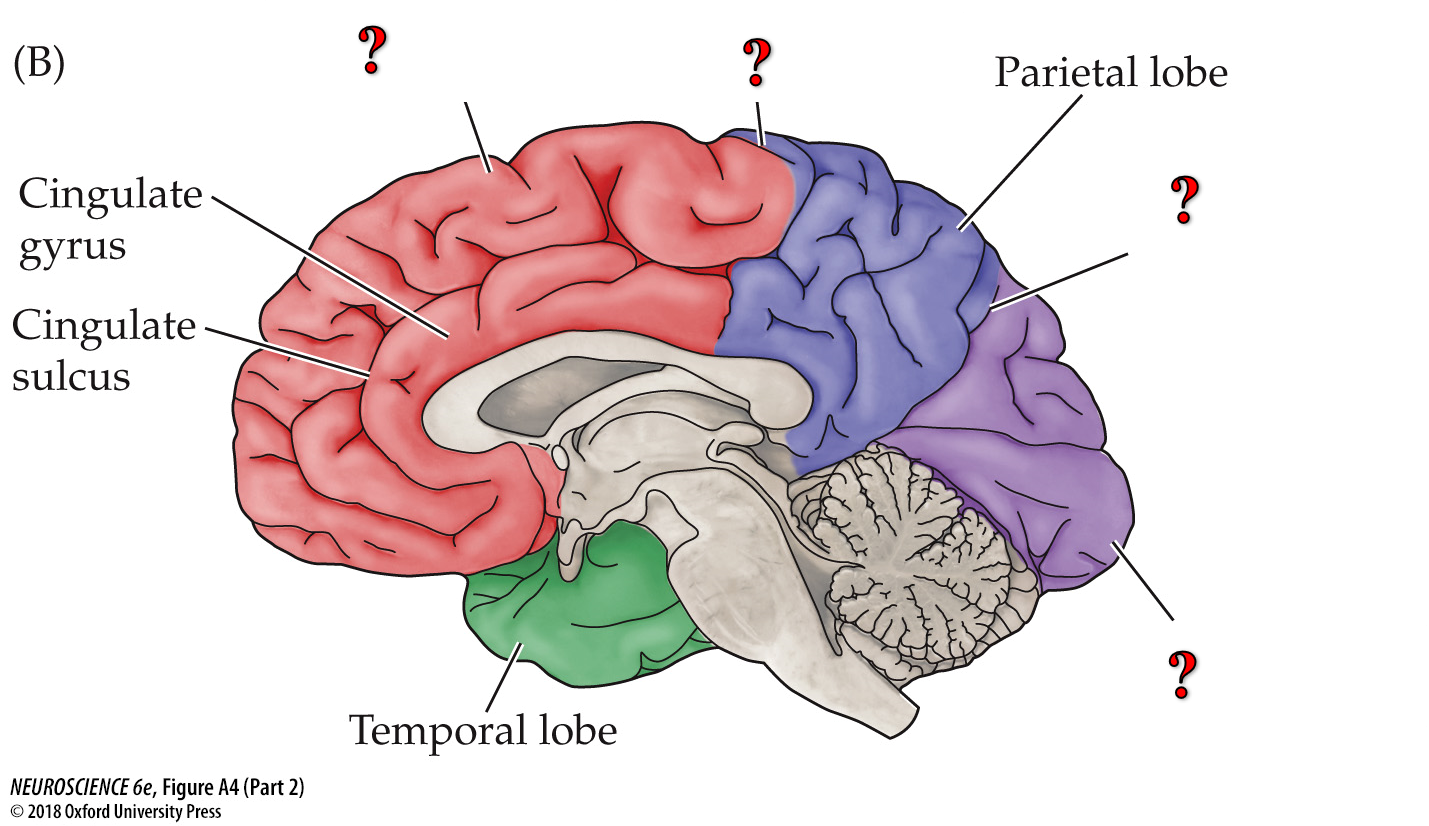
from top to bottom
frontal lobe
central sulcus
parieto-occipital sulcus
occipital lobe
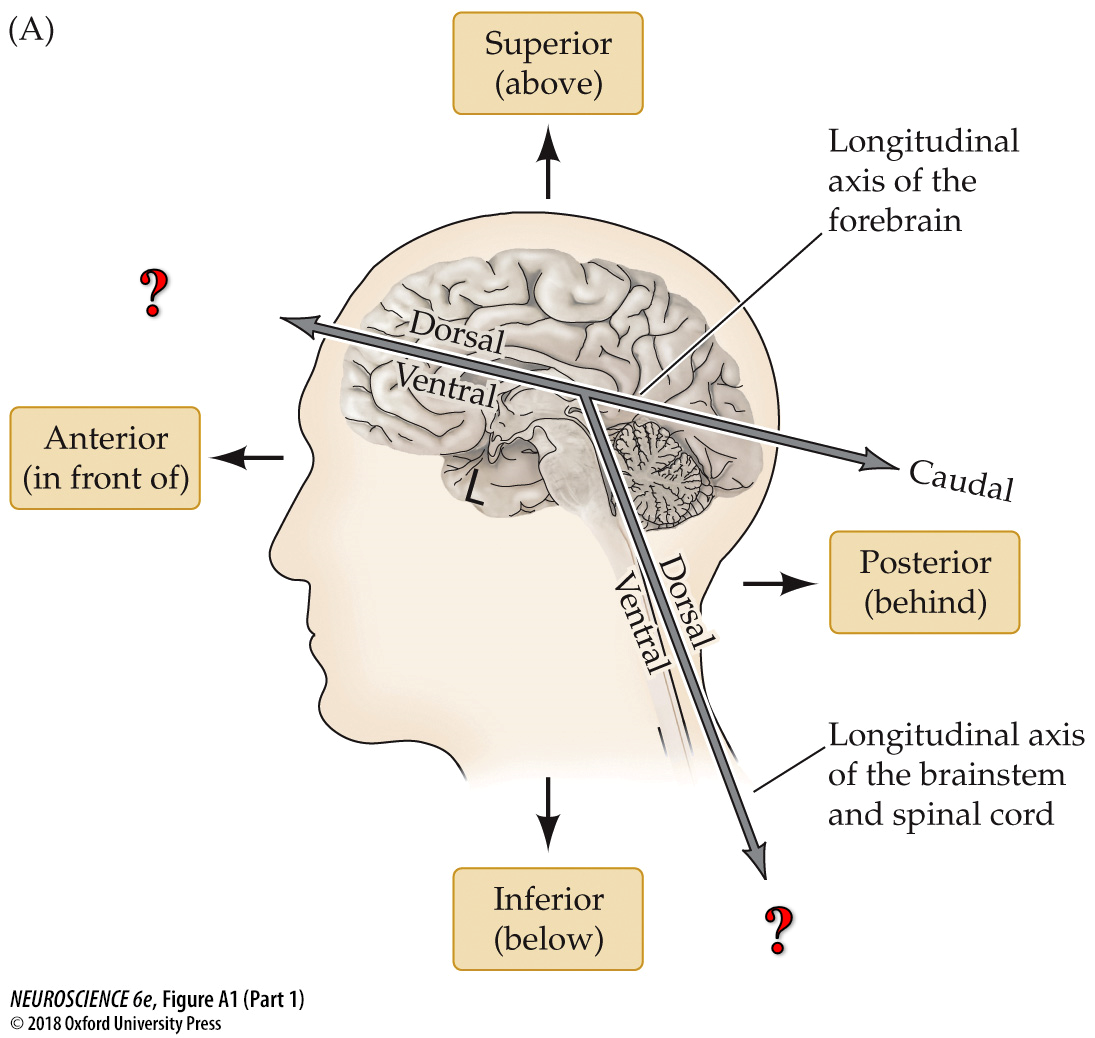
left to right
rostral
caudal
the brain imagining technique that makes use of a narrow x-ray beam is called
CT
the structural brain imagining technique that relies on the resonance frequencies of atoms in a small magnetic field…
MRI
which cell produces myelin in the nerves on the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann cell
which component is part of the peripheral nervous system?
spinal nerve
which statement best describes the function of a neuron with multiple, highly branched dendrites and one axon?
it integrates information from many neurons
which statement best describes most neurons?
they receive information via dendrites
which function is a characteristic primarily of neurons only, not glia?
transmits action potentials
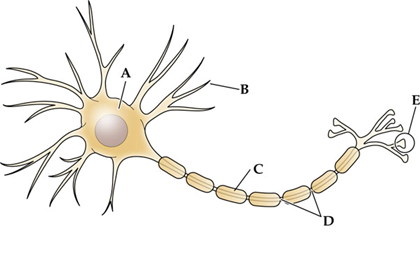
structure _____ insulates the axon following the action potential to travel more rapidly down its length.
C, Myelin
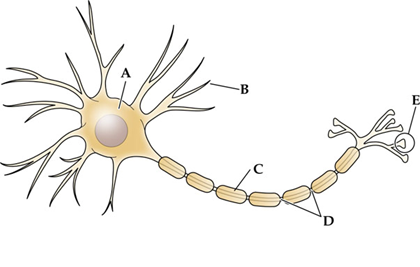
structure ___ is the main target for incoming signals received from the axons of other cells.
B, dendrites
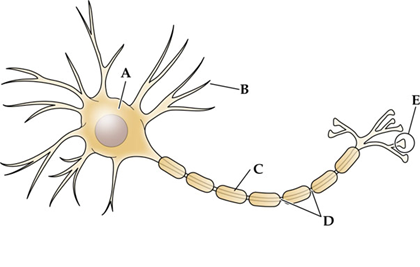
structure ___ contains the most concentrated number of synaptic vesicles and is the structure from which neurotransmitters are released.
E, terminal bouton
the visual area is located most caudally in the human brain is area
V1
what percentage of ganglion cell axons do not cross the optic chaism?
40%
a person with cerebral achromatopsia generally has trouble ____, because of damage to the ___.
recognizing colors of objects; extrastriate cortex
neurons in straite cortex are not tuned to which property of a stimulus?
speed
retinal ganglion cell axons cross at the ___.
optic chiasm
the ocular dominance columns occur in what layer of the V1?
4
retinal axons project to the
superior colliculus, pretectum, hypothalamus, thalamus
the visual area that is located most anteriorly in the human brain is area
MT
the koniocellular pathway terminates in what layer of the V1
2/3
the strictly monocular portion of the visual field is represented exclusively by which region of the retina?
nasal
which muscle is primarily responsible for abduction of the eye?
lateral rectus
how are the upper motor neurons in the superior colliculus organized?
as a topographical map of the eye movement vectors
where are the lower motor neuron cell bodies that innervate the lateral rectus muscle located?
abducens nucleus
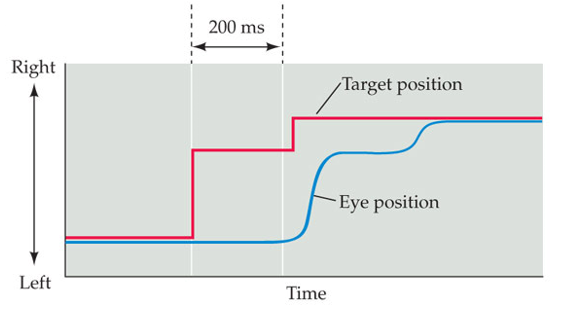
A subject in an eye movement experiment is instructed to focus on a specific target. After the start of the scene, the target is moved. The target is moved again (solid red line in figure) 200 ms later. which graph depicts the change in the subjects eye position that the researchers would expect to see?
how do vergence movements differ from other eye movements?
in vergence movements, the eyes move in different direction
the frontal eye field influence horizontal eye movement by innervating the
superior colliculus and the paramedian pontine reticular formation
what is the function of tiny saccades and drift during visual perception
to change retinal stimulus during fixation, preventing retinal adaptation
Huntington’s disease is associated with which of the following eye-movement dysfunctions?
inability to initiate voluntary saccades
Schizophrenia is associated with which of the following eye-movement dysfunctions?
impairment in smooth pursuit movements
damage to the dorsal visual stream in the parietal lobe would affect which type of eye movement?
smooth pursuit
how many layers make up the neocortex?
6
A husband reports that his wife has begun acting strangely. For example, she refuses to eat the food on the left side of her plate at meals, claims she has finished all her food. She also neglected to put her left arm in her shirt the last few days and begun putting make up on only the right side of her face. Hearing these symptoms, where would you expect to find damage in the women’s nervous system?
right posterior parietal cortex
a patient is asked to draw a house by copying the model shown in the picture. His version is shown on the right. which of the following disorders would you suspect the patient has?
contralateral neglect syndrome
which behavioral task would lead to increasing firing rate in the neurons in the location outlined in the figure?
attending to a visual target
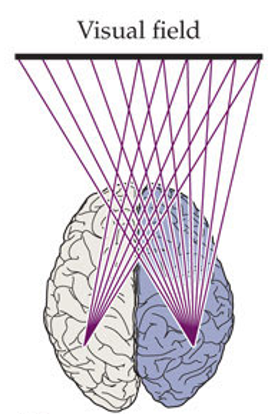
which figure best illustrates the control of attention by the two hemispheres?
if thalamic output to the cortex was disrupted, which layer of the neocortex would be affected?
layer 4
early in the twentieth century, scientists divided the brain into approximately 50 regions based on which characteristics?
histological features
the part of cerebral cortex that is especially important for selecting and planning appropriate behavior responses is the ___ lobe.
frontal
if neocortical output from layer 5 was disrupted, communication with which structure would be affected?
striatum
if output from neocortical layer 6 is blocked, which structure would lose significant input?
thalamus
a major function of the temporal lobe is
recognition and identification of stimuli
individuals with prosopagnosia
cannot recognize the face of a familiar person
damage to which region would lead to language-related agnosia?
lateral surface of left temporal lobe
during an mri, a subject is shown an image of the face. In which of the following regions would you expect to see an increase in neural activity?
right fusiform gyrus
The data in the graphs representing the firing of a neuron in a monkey brain recorded while presenting the monkey with the corresponding images. In which region was the neuron being recording located?
inferior temporal cortex
Which symptom would you expect a patient with a right temporal lesion to exhibit?
deficit in recognizing faces
The ___ association cortex is involved in recognizing objects, while the ___ association cortex is involved in deciding what to do with the object.
temporal; frontal
A teacher at a local school feels frustrated whenever the seasons change because her students begin wearing different shoes to school. This troubles her because she usually identifies her students by their footwear, and with that clue, she must wait for each student to talk before she knows who they are. Considering her symptoms, where would you expect to find damage in her nervous system?
right fusiform gyrus
Which evidence suggests that unattended information is processed in the brain and that filtering occurs late in the sensory processing pathway?
a person attend to his name when it is mentioned in an unattended conversation
When subjects are presented with a picture of a person, they tend to focus their attention on the face and eyes of the individuals. However, when they are asked to draw conclusions about the individual in the image, like wealth, they shift their gaze to look at the clothes or surrounding environment. What does this test measure?
overt attention
While subjects are focusing on a blank screen, a flash of light unexpectedly appears in one of two locations. Following the flash, a target image appears on the screen. Half the time the target image is in the same location as the flash, and half the time it is presented on the other side of the screen. The data collected are presented in the graph. What phenomenon occurs when the target is presented more than 300 ms after the cue?
inhibition of return
A subject is instructed to focus on an image of a person. While the subject examines the image, an auditory stimulus is presented from the same location. What does this test measure?
supramodal attention
A patient is presented with the images in the figure one at a time and asked to report how many colors she can see. When the two colors are presented as separate objects, as in the random or single display, she reports that she can see only one color. When the two colors are presented as part of the same object, however, she reports seeing both colors. What would the most likely diagnosis of this patient be?
Balint’s syndrome
A patient experienced a severe head trauma and now is unable to point to an object in space under visual guidance and has difficulty moving his eyes toward a visual target. What would the most likely diagnosis for this patient be?
balint syndrome
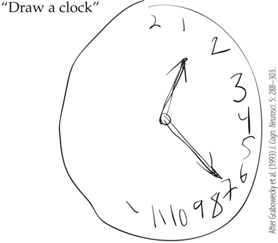
A subject is instructed to draw a clock from memory. Her version is shown in the figure. What would the patient diagnosis most likely be?
hemispatial neglect syndrome
Subjects are asked to focus on a center point until a space appears, and then name the shape. Before the shape appears, an arrow either pointing in the direction the shape will appear (valid), pointing in both directions (neutral), or pointing in the opposite direction from which shape will appear (invalid). How would the subjects reaction time for naming the shape differ among these conditions?
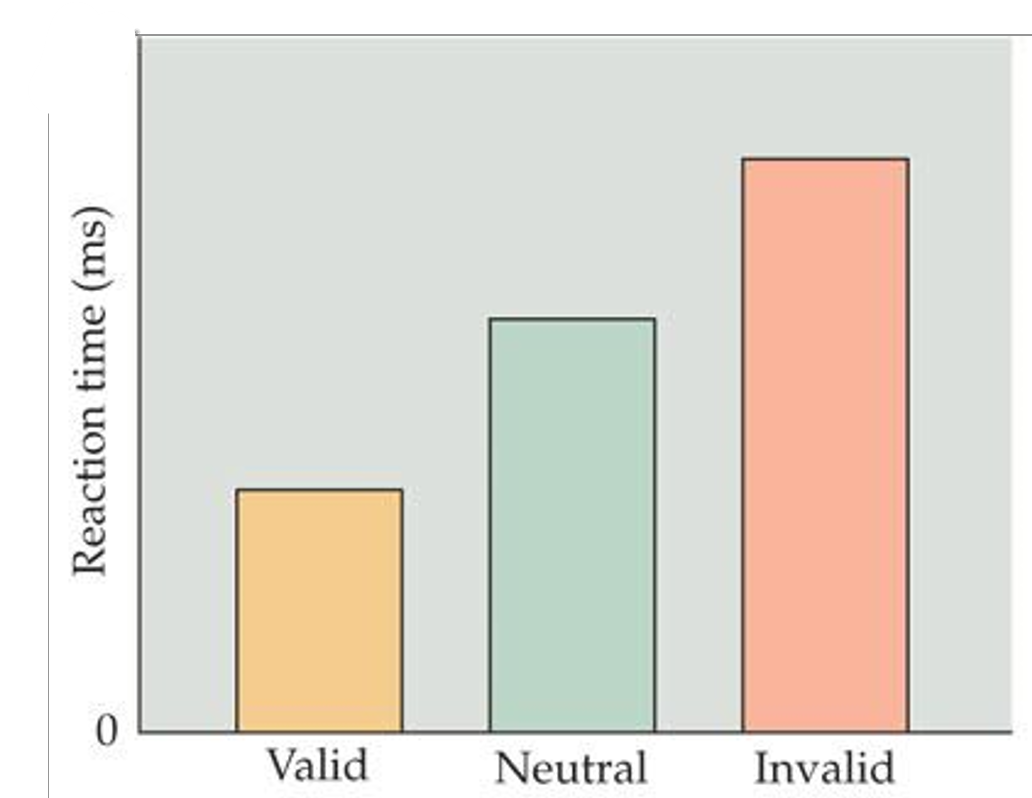
While subjects are focusing on a blank screen, a flash of light unexpectedly appears in one of two locations. Following the flash, a target image appears on the screen. Half of the time the target image is in the same location as the flash, and half the time it is presented on the other side of the screen. What does this test measure?
exogenous attention
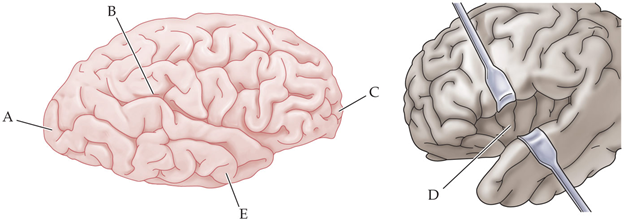
which region is likely to cause hemispatial neglect syndrome when damaged?
B
After a stroke, an individual has difficulty understanding speech, but can form and speak words, albeit nonsensically. Which disorder do those symptoms implicate?
Wernicke’s Aphasia
where is the visual word form area located?
left occipito-temporal sulcus
the structure that is important to the production of virtually all vocalization is the…
larynx
which statement about language in people who are deaf is false?
Studies of congenitally deaf individuals indicate that Broca's area is specific to spoken language, whereas a region in the anterior temporal lobe is specific for visual and signed communication
which element of language is controlled mainly by the right hemisphere?
prosody
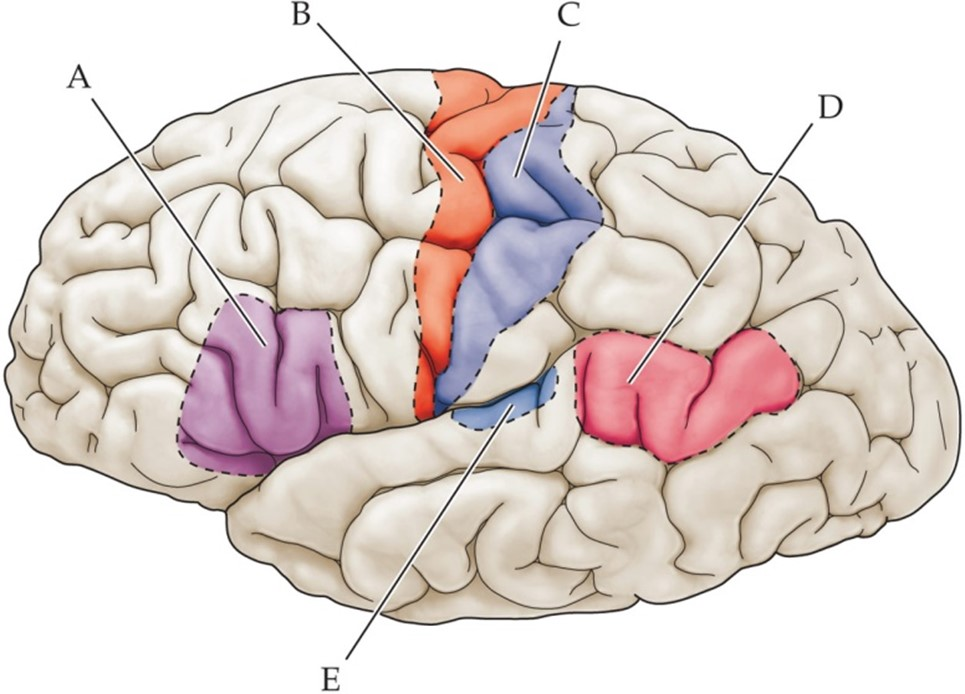
identify the following
Primary auditory cortex: E
Wernicke's area: D
Broca's Area: A
Studies of deaf patients with either left or right hemisphere lesions demonstrated that...
The language centers of the brain are specialized for pairing symbols with meaning, rather than specialized for heard and spoken language
phonemes are…
The percepts elicited by different speech sounds
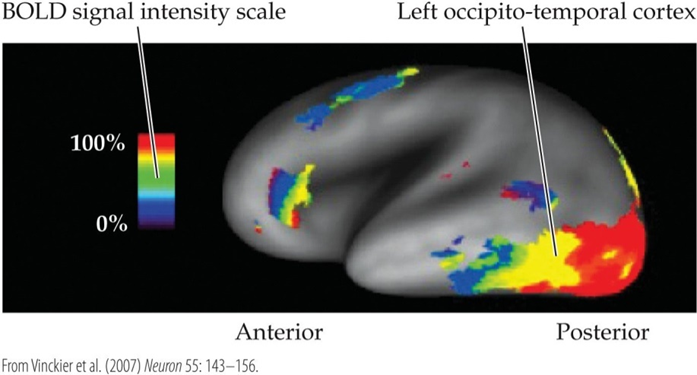
The figure shows an fMRI scan of a subject completing a laboratory task. What was the subject most likely doing during the task
reading a story
the method of clinically assessing language lateralization in humans by anesthetizing one hemisphere was devised by…
John Wada
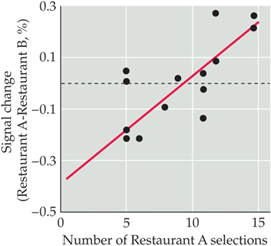
Subjects indicate whether they prefer French fries from restaurant A or B. they are then given French fries from the restaurant they prefer while being evaluated using fMRI. The figure shows the activation of a particular brain region in response to tasting fries from restaurant A compared to restaurant B (y axis) plotted against the number of times a subject chose A over B. which brain region showed differences in activation?
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
Which change or deficiency was not reported in early case studies of individuals with frontal lobe damage?
difficulty with intellectual functioning
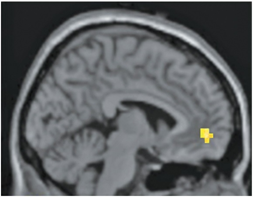
The activated region in the fMRI scan above is responsible for which function?
The planning and execution of appropriate behavior
Why did the medical community stop performing leukotomies around 1950?
Effective psychotropic drugs were developed
In terms of brain anatomy, the largest lobes in humans are the ___ lobes.
frontal
What symptom would you expect bilateral lesion to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex to produce in a monkey?
Delayed or abolished success during the delayed response task
While a monkey participates in a delayed response task, data form a prefrontal cortical neuron is collected. Each bar in the graph represents an action potential in the neuron, and the red box is the time the screen is closed. The activity of the neuron during the delay period is thought to represent the neural correlate of:
Short-term memory and planning
During behavioral testing, a monkey is unable to complete the delayed response task. Neurological damage to which area would produce this symptom?
Bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
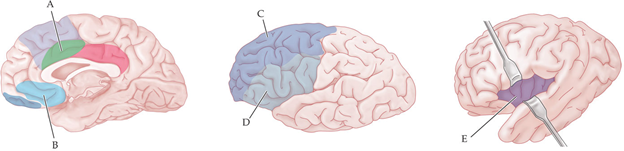
Which region is responsible for monitoring unconscious body states to regulate behavior?
E
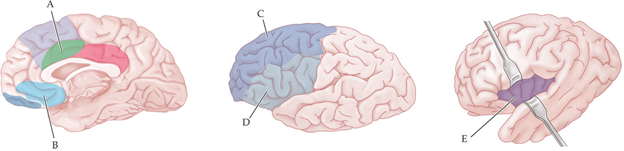
which brain region is believe to be responsible for evaluating options?
C
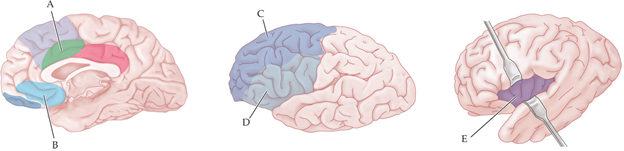
Which region is believed to be responsible for being flexible in different situations?
C
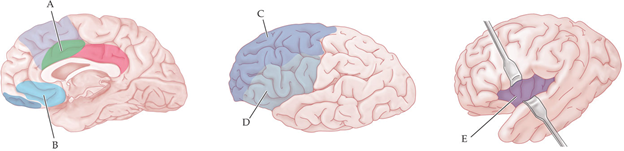
which brain region is believed to be responsible for self-control?
D
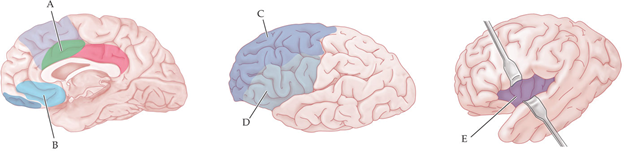
A subject completes a stroop task while being scanned in an fMRI machine. Where would you expect you to see in an increase in brain activity?
A
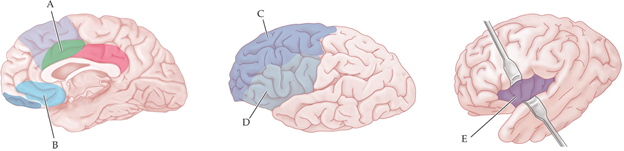
Which region is believed to be responsible for self-awareness?
B
which statement correctly describes a characteristics of the prefrontal cortex?
Brodmann cytoarchietechtonic areas are well established
which region does not directly communicate with the orbitofrontal cortex?
premotor cortex
which region is not considered to be a part of the default- mode network?
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
changes in blood flow to which brain region can be used to predict purchasing behavior based on personal preferences?
orbitofrontal cortex