GENCHEM2 concepts
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
proton donor
Bronsted-Lorwry Base
proton acceptor
Arrhenius acid
Ionise in water to produce H+ ions
Arrhenius Base
Ionise in water to produce OH_
Lewis Acid
Electron pair acceptor
Lewis Base
Electron pair Donor
Can an acid/base do one or more of being brownsted-lowry, arrhenius. lewis?
Yes. Pwedeng combination, pwedeng isa lang, pwedeng tatlo
this means there is a large amount of dissolved solute per unit volume
Concentrated
this means there is a small amount of dissolved solute per unit volume
Dilute
FULLY ionises in aqueous solution
Strong
Only PARTIALLY ionises in aqueous solution
Weak
Weal acids/base = reaction is —-
Reversible
Strong acid/base = reaction goes to —-
completion
Acid + Base yields
Salt + Water
Acid + Metal oxide yields
Salt + Water
Acid + Metal carbonate yields
Carbon dioxide + salt + water
Acid + Metal yields
Salt + Hydrogen
What is the substance that forms once an acid has donated a proton?
Conjugate base
What is the substance that forms that forms once a base has accepted a proton?
Conjugate acid
How to determine which element will donate a proton if 2 ACIDS are reacting?
The stronger acid will force the weaker acid to accept a proton
pH depends on —
Hydrogen ion concentration
the lower the pH, the stronger the —-
acid
Define pH
-log[H+]
In monoprotic solutions, since strong acids fully ionise in aqueous solution, we can conclude that [acid] = —?
[acid] = [H+]
moles of acid = moles of Hydrogen ions
concentration of acid = concentration of hydrogen ions
Note that this does NOT apply to diprotic or multiprotic solutions.
At 298K, Kw is equal to
1×10-14
Dissociation is breaking of bonds = equilibria shifts to
right side (ENDOTHERMIC)
If Hydrogen ion concentration increases, pH —- & Kw —-
pH decreases, Kw increases
Above 298K, pure water pH is — 7, while Kw is — 1×10-14
pH is less than 7
Kw is greater than 1×10-14
Below 298K, pure water pH is — 7, while Kw is — 1×10-14
pH is greater than 7
Kw is less than 1×10-14
Pure water is ALWAYS considered to be neutral because [H+] = [OH-]
TRUE
If we know Kw and [OH-], what can we solve?
[H+], pH, pOH
because…
Kw=[H+][OH-]
Adding water to a solution REDUCES the ion concentration
True, therefore pH will change
If you add water to an acid, [H+] —-, and pH —-
[H+] decreases, pH increases (less acidic)
If you add water to a base, [OH-] —-, and pH ——.
[OH-] decreases, pH decreases (less basic)
The stronger the acid, the —- the Ka value
larger
Stronger acid = — Ka = — pKa
larger, smaller
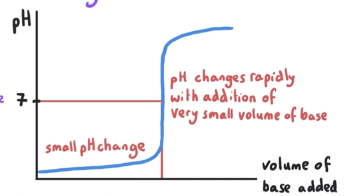
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence point is 7. This is a strong acid-strong base reaction
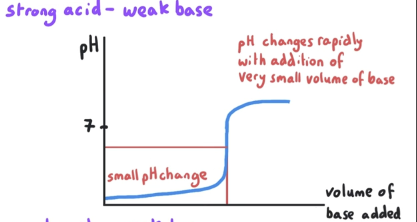
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence point is <7. This is a strong acid-weak base reaction.
Because the salt that is produced is not exactly pH 7. Salt is a proton donor.
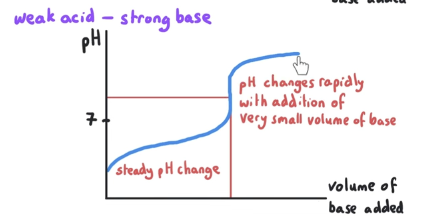
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at the equivalence point is >7. This is a weak acid-strong base reaction.
Salt is a proton acceptor.
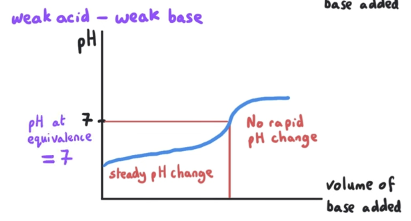
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence is = 7. This is a weak acid-weak base reaction.

What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence is = 7. This is a strong base-strong acid reaction.
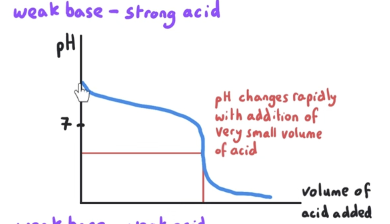
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence is < 7. This is a weak base-strong acid reaction.
Salt is the proton donor

What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence is > 7. This is a strong base-weak acid reaction.
Salt is a proton acceptor.
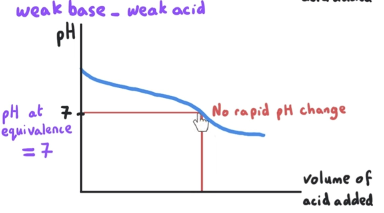
What is the pH at equivalence point? What is mixed?
pH at equivalence is = 7. This is a weak base-weak acid reaction.
The pH range over which the indicator changes color is pKa —
positive or negative 1
What needs to be mixed to create a buffer?
Weak acid + conjugate base
or
Weak base + conjugate acid
Ca(OH)2 is a strong base if
concentration is less than or equal to 0.02M
Sr(OH)2 is a strong base if
concentration is less than or equal to 0.01M
Ba(OH)2 is a strong base if
concentration is less than or equal to 0.02M