waves
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
which type of wave can be polarised, transverse or longitudinal?
transverse
principle of superposition
when two waves of the same type overlap, the displacement is the sum of the two separate displacements
phase
fraction/proportion of the wave cycle completed in comparison to the starting point, usually expressed as an angle
delete
delete
if phase difference is pi rad/180 degrees, the two points on the same wave are in
antiphase
exam q: explain why the core in an optical fibre is made as narrow as possible
to reduce multipath or multimode dispersion
(which would cause) light travelling at different angles to arrive at different times/pulse broadening/merging of adjacent pulses/‘smearing’/ poor resolution/lower transmission rate/lower bandwidth/less distance between regenerators
or to prevent light/data/signal loss (from core or fibre)
(which would cause) signal to get weaker/attenuation/crossover/data to be less secure

which characteristics of monochromatic light change when the light passes from air into glass?
speed and wavelength
define polarisation
The restriction of a wave so that it can only oscillate in a single plane. This can only occur for transverse waves.
The sound quality of a portable radio is improved by adjusting the orientation of the aerial, why?
The radio waves from the transmitter are polarised.
if phase difference is 0 or 2pi rad/360 degrees the two points on the same wave are in
phase
phase difference/2pi =
distance between points on the wave/wavelength
when waves are reflected off a surface they are out of phase with the original wave by
pi rad/180 degrees
what are standing/stationary waves caused by
the superposition of two progressive waves of equal frequency and amplitude moving in opposite directions
how many sources do there have to be to form a standing/stationary wave
can either be two different sources or a wave being reflected back on itself
what are points of 0 amplitude on a stationary wave called
nodes
do progressive waves transfer or store energy
transfer
do standing waves transfer or store energy
store
the displacement of a point on progressive waves varies between peaks and troughs, so amplitude is
the same for each point
the amplitude for a point on a standing wave
varies between 0 (nodes) and a maximum (antinodes)
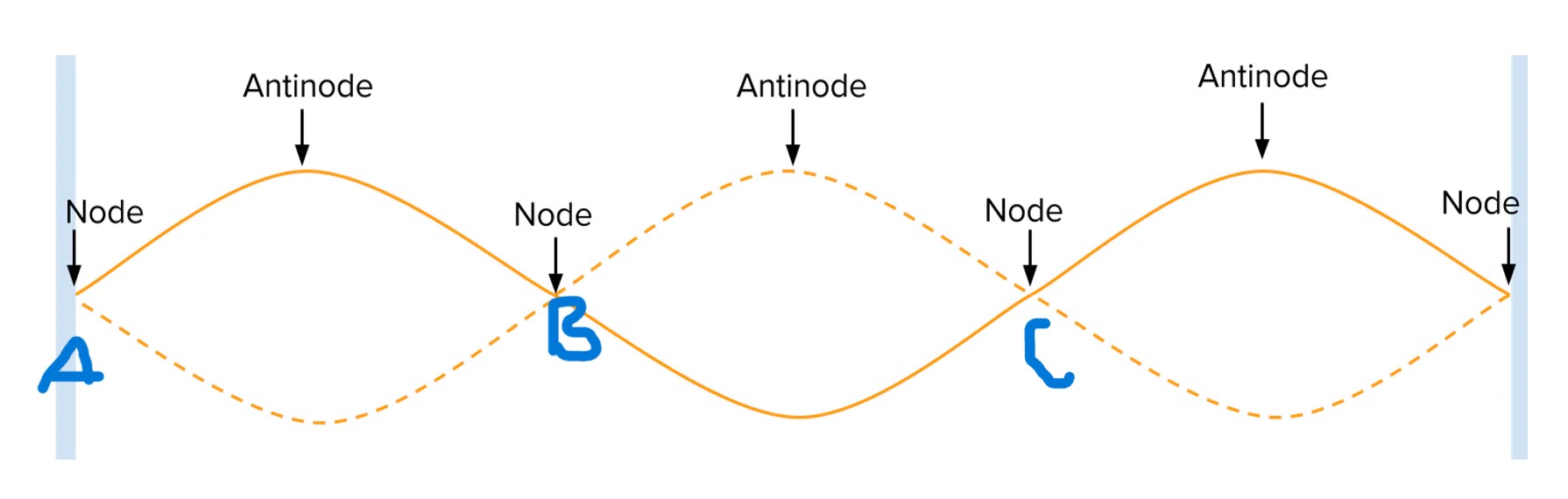
any point between a and b have phase difference of
0
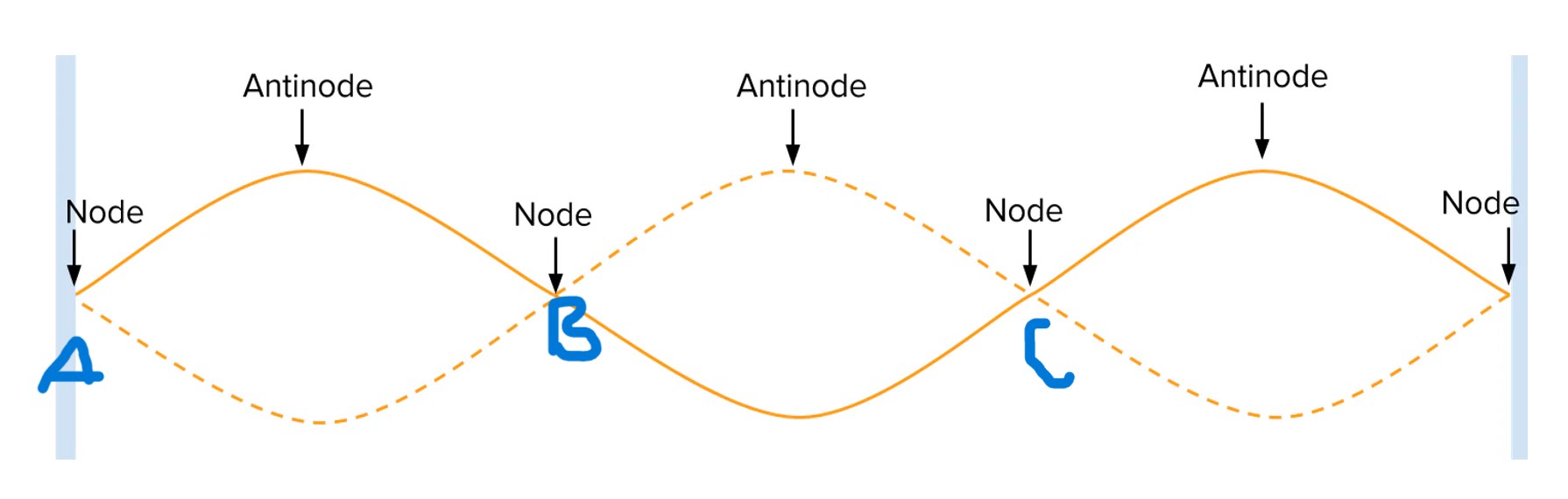
any point between a and b has a phase difference with a point between b and c of
pi
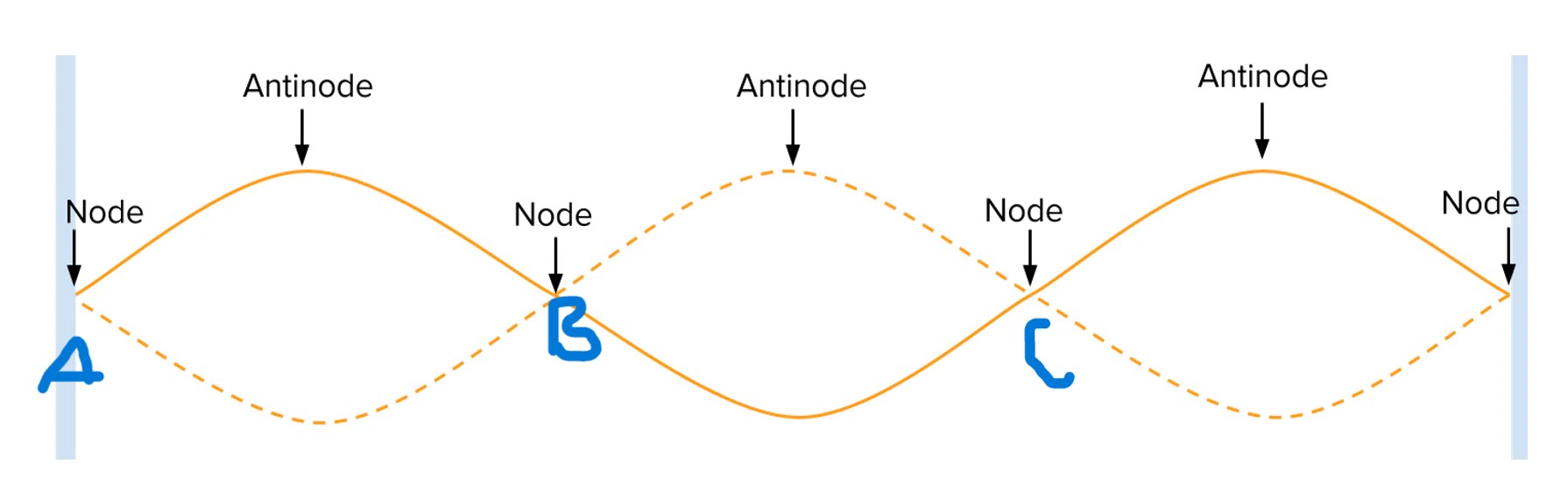
for fundamental harmonic, length of string =
½ wavelength
define harmonic
overtones that have frequencies that are a whole number of the fundamental frequency are called harmonics
at the point of overlap of two waves if they have the same sign displacement (both + or - ), what type of interference occurs
constructive
at the point of overlap of two waves if one has + displacement and the other -, what type of interference occurs
destructive
constructive interference occurs when the path difference between coherent sources is
a whole number of wavelengths
define coherent
sources have a constant phase relationship and same frequency
describe a diffraction grating
a plate with many, closely spaced, parallel slits
interference pattern from diffraction grating compared with from a double slit arrangement
diffraction grating - brighter and sharper fringes, more rays of light reinforcing the pattern
can calculate wavelength more accurately
describe a progressive wave
transfers energy without transferring material, is made up of particles of a medium that are oscillating
describe superposition
the displacements of two waves are combined as they pass each other, the resultant displacement is the vector sum of each wave’s displacement
do stationary waves transfer energy?
no
how does using white light for a double slit experiment compare with using monochromatic light
central white fringe
alternating bright fringes contain a spectrum
violet is closest to the central fringe and red is furthest
less intense diffraction pattern
wider maxima
what does the double slit experiment tell us about light, and how?
light is a wave
diffraction and interference are wave properties
what is diffraction?
spreading out of waves when they pass through or around a gap of similar size to the wavelength
when is there the most diffraction
when gap size = wavelength
what happens when the gap is larger than the wavelength
less diffraction
what happens when the gap is smaller than the wavelength
most waves are reflected
what happens when a wave meets an obstacle
it diffracts round the edges
what does a wider obstacle (in comparison to the wavelength of the light) mean?
there is less diffraction
what effect does increasing the slit width have in a single slit arrangement?
less diffraction
central maximum becomes narrower and more intense
what effect does increasing the wavelength have in a single slit arrangement?
more diffraction as the slit is closer in size to the wavelength
central maximum becomes wider and less intense
use of diffraction gratings
light from stars is split up to show which elements are present
what is modal dispersion?
light rays enter the fibre at many different angles
many different paths = different lengths of time to travel down the fibre
pulse broadening
what is material dispersion?
light with different wavelengths travel at different speeds
different lengths of time to travel down the fibre
how to prevent modal dispersion
use a narrower core
larger critical angle
how to prevent material dispersion
use monochromatic light
when does refraction occur?
when a wave travels across a boundary between different media and changes speed
purpose of cladding in optical fibres
protection
restricts the amount of total internal reflection, reduces pulse broadening
prevents cross-talk (light going into another core next to it)