Material Science Midterm 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Ionic Percentage
1-e^(E1-E2)/4
Point Defects
Vacancies, Interstitials, and Substitutions
Linear Defects
Edge Dislocations and Screw Dislocations
Caused by applied stresses
Volume Defects
Voids, Precipitates, and Inclusions
Interfacial/Planar Defects
Grain Boundaries
Twin Boundaries
Stacking Faults
Thermosets
Crosslinked and Networked
-Chains held with covalent bonds
-stiff/rigid
-formed by chemical reactions
-will not melt
Covalent Bonding
Highly Directional
Shares electrons
Thermoplastics
Linear and Branched
-Chains held with secondary bonding
-Melts when heated
-Flexible
FCC
4 atoms
CN 12
74% packed
BCC
2 atoms
CN 8
68% packed
SC
1 atom
CN 6
52%
FCC Interstitials
4 Octahedral (edges and center)
8 Tetrahedral (almost corners/diamond structure)
BCC Interstitials
6 Octahedral (faces and edges)
12 Tetrahedral (off-center faces)
Melting point/Bond length
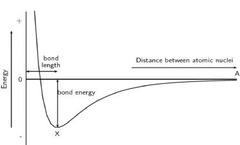
BCC Linear Atomic Density [100]
(√3)/4R
1/a
FCC Linear Atomic Density [100]
(√2)/4R
1/a
FCC Planar Atomic Density (100)
1/4R^2
BCC Planar Atomic Density (100)
3/16R^2
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
ΔL=αL0ΔT
Amorphous
Atoms are arranged irregularly (opposite of crystalline)
Twin Grain Boundary
ABCBA
HCP Stacking Sequence
ABABAB
FCC Stacking Sequence
ABCABCABC
SC Lattice Points
000
BCC Lattice Points
0 0 0
.5 .5 .5
Precipitates/Inclusions
Secondary phases in the material
strengthens the material
Voids
holes/pores in the crystal
weakens the material
can affect transparency
FCC Lattice Points
0 0 0
.5 0 .5
0 .5 .5
.5 .5 0
Molecular Weight
Based on length of chain
DP
Number of Mers per chain
Frenkel Defect
opposite charged pair of vacancy and interstitial
Shottky Defect
opposite charged pair of vacancies
Edge Dislocation
Burger's Vector Perpendicular to dislocation line
Screw Dislocation
Burger's Vector Parallel to dislocation line
Burger's Vector Steps
Define dislocation line
Use Right Hand Rule to determine Circuit direction
Calculate Burger's Vector from start to end
Grain Boundaries
High Energy States
High atomic mobility
High chemical reactivity
Will decide properties