FOS1 Final Exam :(
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Epidermis
Two layers that protect the leaf and are transparent to let light through
Guard Cells
Controls the pore that opens and closes on the bottom of the leaf
Palisade Mesophyll
Tall, closely packed cells where the majority of photosynthesis occurs
Waxy Cuticle
A waxy layer on the top of the leaf that helps prevent it from drying out
Xylem
The top part of the vein that carries water
Spongy Mesophyll
Round cells surrounded by air that also produce food for the plant
Stoma
Pores at the bottom of the leaf that allow gas exchange
Phloem
Bottom part of the vein that carries dissolved sugars
Write out the equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2+6H2O—>C6H12O6+6O2
What is the molecule that allows us to store energy in our bodies and carry out life’s activities?
ATP
Describe why ATP is carried in the body instead of glucose.
It is smaller and easier to break down.
Describe how energy is released from ATP.
Energy is released from this molecule by removing a phosphate group.
Describe why plants undergo the process of photosynthesis. In your description, include where in the plant cell these processes occur.
Plants undergo photosynthesis in the chloroplasts in order to turn solar energy into chemical energy that is usable for growth and metabolism.
What are two types of pigments found in plant leaves? What, related to pigments, causes leaves to change color from summer to fall?
Chlorophyll and carotenoids. During the fall chlorophyll production decreases, which leaves carotenoids as the dominant pigment. This pigment reflects fall colors.
What is the purpose of the digestive system?
The purpose of the digestive system is to break down large pieces of food into smaller molecules, such as glucose, that our cells can use.
How does digestion it relate to cellular respiration?
This relates to cellular respiration because digestion has to occur before cellular respiration can release energy from the molecules contained within the food we eat.
Name the two types of digestion and describe how each aids in the breakdown of food.
Mechanical - This type of digestion involves mashing, chewing and squeezing of food. This helps in that it makes food smaller and easier for the body to absorb.
Chemical – Enzymes in saliva and digestive juices break food down into smaller molecules that cells can use.
Where are carbohydrates broken down in the digestive system?
Starches in carbs are first broken down in the mouth by enzymes in saliva. Sugars are then broken down by bile and enzymes in the duodenum and absorbed in the Ileum.
Where are proteins broken down in the digestive system?
Proteins are initially broken down by enzymes in the stomach and then completely broken down by bile and enzymes in the duodenum and absorbed in the Ileum.
Where are lipids broken down in the digestive system?
Lipids are not broken down until they reach the duodenum. Here, they are digested and then passed to the ileum, which is where they are absorbed into the bloodstream.
Write the equation for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 +6 O2—>6 CO2+ 6 H2O
What is the overall purpose of the process of cellular respiration?
To covert the energy in the bonds of glucose from the food we eat in to ATP.
ATP transfers energy from the breakdown of _________.
Food molecules
ATP is a high-energy / low-energy molecule that is converted into higher-energy / lower-energy ADP when a phosphate group is removed and energy is released.
high energy, lower energy
ADP is converted back into ATP by _____________.
the addition of a phosphate group
Energy is
the ability to do work.
Work is
the act of moving something over a distance by applying a force
Non-renewable energy (provide example)
Energy that is not sustainable and cannot be replenished quickly. Examples: Coal, gas, petroleum
Renewable energy (provide example)
Their supplies can be replenished in a short time. Ex: wind, solar
Alternative energy (provide example)
Also renewable, but these do not produce harmful emissions. Ex: wind, solar
Why are Hydrogen Fuel Cells considered environmentally friendly sources of energy?
Hydrogen is the most abundant gas in the universe, and is considered to be renewable.
What are some downsides to using hydrogen as an energy source?
Hydrogen is hard to extract from the compounds it is found in. Doing so, through electrolysis or steam refining, requires energy and is costly.
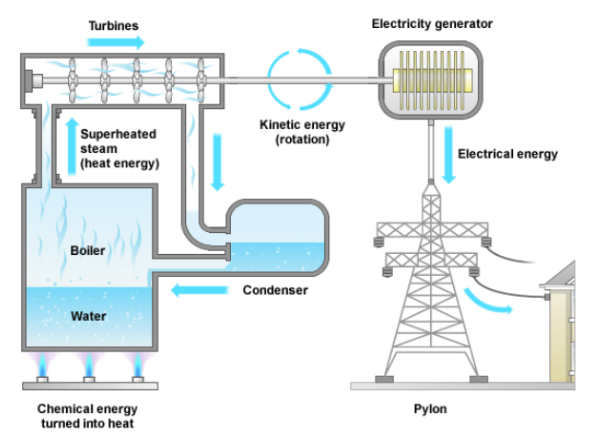
Diagram the process used to produce electricity in a thermal power plant.
(get a piece of paper)
Draw a diagram or make a table that shows these layers of the atmosphere listed below. In your diagram above, show which layers of the atmosphere these objects can be found (Jet Stream, Ozone Layer, Northern Lights, Satellites, Weather, and High Winds).
(Get a piece of paper)
What is climate and how is it different from weather?
Climate is long term weather occurring over many decades. Weather is the state of the atmosphere at any particular time and place. Weather is short term.
Describe how modern day climate change differs from natural climatic cycles of warming and cooling.
Modern day climate change is caused by humans and has happened much more rapidly (since the early 1900s) than natural cycles of warming and cooling that occur over thousands of years.
Explain how the greenhouse effect leads to climatic warming.
Incoming solar short-wave radiation passes through Earth’s atmosphere. The light that bounces off of Earth’s surface goes from having a short wavelength to a long one, IR. Greenhouse gases trap in this heat.
Draw a diagram of the greenhouse effect
(Get a piece of paper)
.
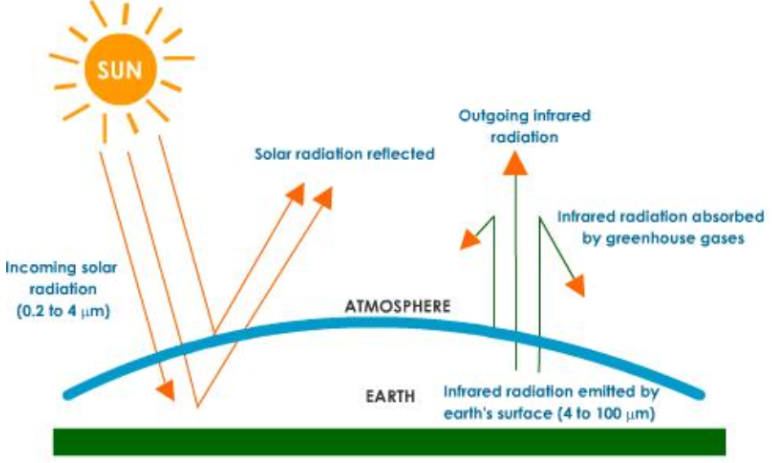
What are the main Greenhouse Gases and how are they different from other gases that are found in our atmosphere?
The main GHGs are methane, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and N20. These molecules trap in infrared radiation because they are unsymmetrical and unbalanced. Because of this, they are unable to vibrate and move, which allows them to absorb infrared photons and send them back into the atmosphere.
What are pieces of evidence that show climate is changing?
Sea level rise, permafrost melting, warming oceans, global temp increases, extreme weather, ocean acidification.
What are the possible effects of climate change?
Rising water levels, increase in disease, famine and starvation, changes in precipitation patterns.
Astronomical Hypothesis (Solar Energy and Milankovitch Theory)
Changes in Earth’s tilt, orbit, and wobble can affect the amount of radiation that the Earth receives, and can alter the timing of seasons and severity of seasons. Also, the sun changes the amount of radiation it puts out depending on the number of sunspots and solar flares.
Atmospheric Changes (CO2 levels and Volcanoes)
An increase in CO2 levels leads to the Greenhouse Effect, which can lead to global warming. We have seen, in ice cores, lower CO2 levels during glaciations. Volcanoes can lead to climactic cooling because the gases from an eruption block on the sun.
Continental Location and Ocean Currents
Continents move over time. Glaciers can only form on landmasses in cold, polar regions. Therefore, there has to be land in the North and South Pole for glaciations. Ocean currents also shape the Earth’s climate because they bring warm air and moisture across the globe.
How many ice ages have occurred in Earth’s history?
5
Briefly describe the formation of the Great Lakes. Include information on events occurring 350 million years ago, 18,000 years ago, and 14,000 years ago
350 million years ago, the Great Lakes were covered in warm shallow seas. This left behind a bedrock of sedimentary rock. When the glaciers advanced 18,000 years ago, they made deep depressions in this soft bedrock due to the force of their weight. When the glaciers last retreated 14,000 years ago, their melt water filled up these deep basins and left the Great Lakes and was held in by moraines that formed on the southern shores.
What is Acid Rain and what causes this problem?
Acid rain is any form of precipitation that has a pH of 5.0 or below. It is caused by precipitation mixing with sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
What is the ozone layer? What is it made of and how does it protect the Earth?
The ozone layer is a portion of the stratosphere made up of O3 molecules. These molecules block ultraviolet light and limit this type of radiation from reaching from reaching the earth.
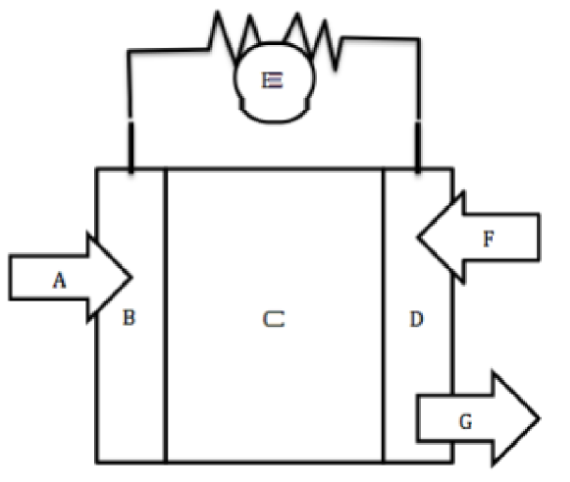
A
Hydrogen fuel goes in
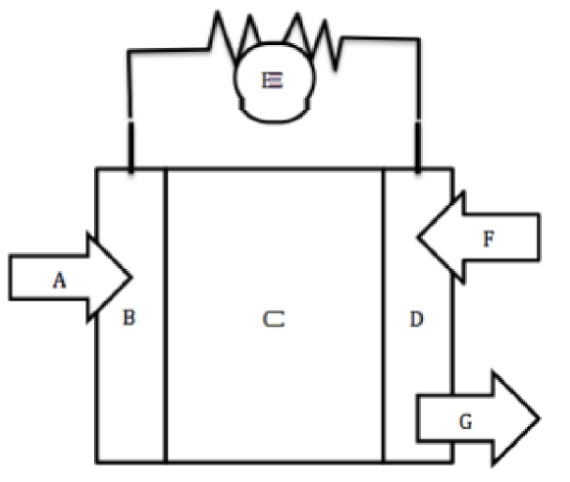
B
Negative Anode
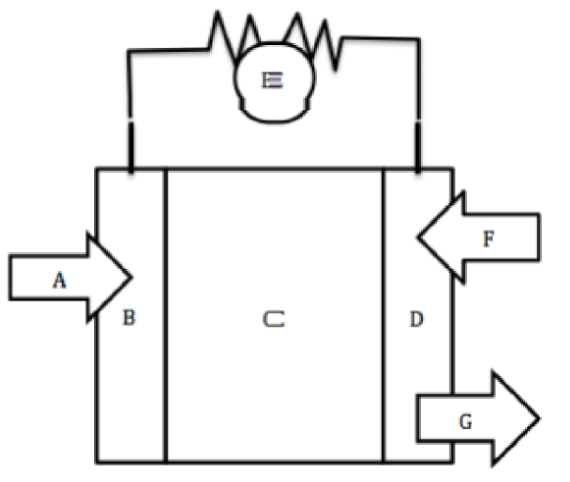
C
Electrolyte
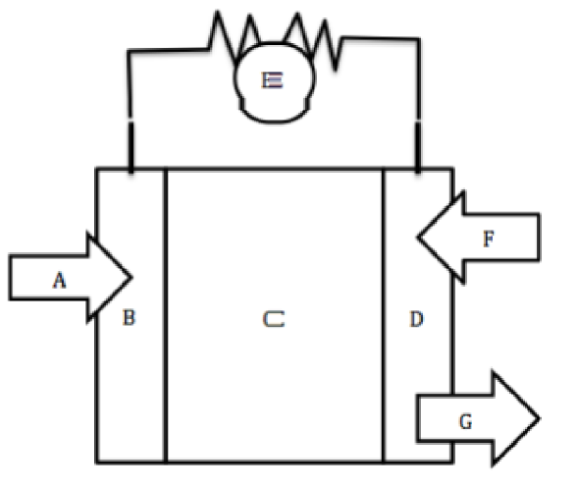
D
Positive Cathode
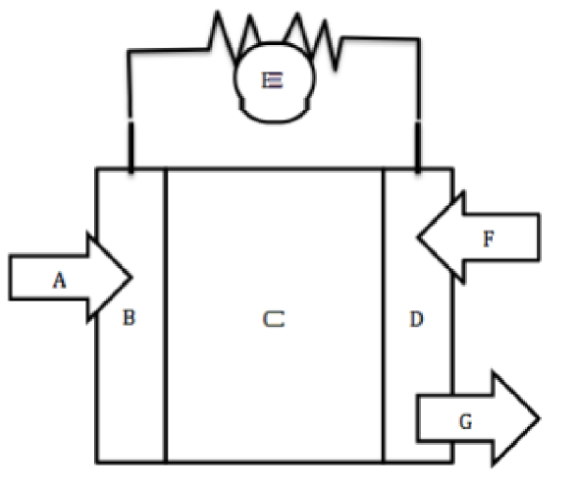
E
Wire for electron flow with bulb
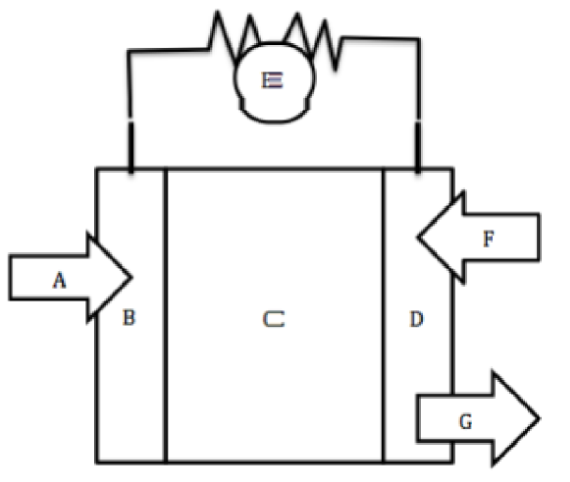
F
Oxygen goes in
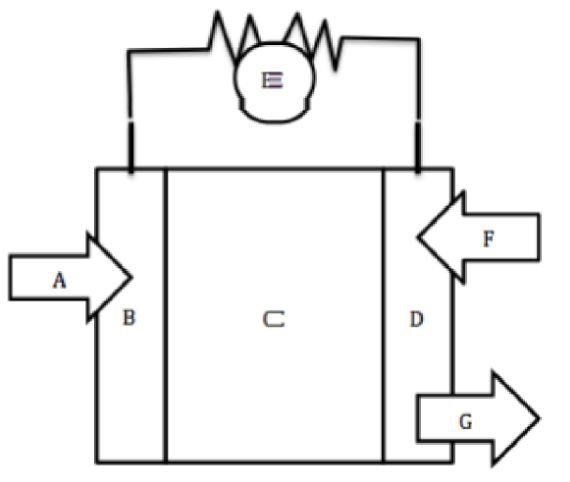
G
Water byproduct
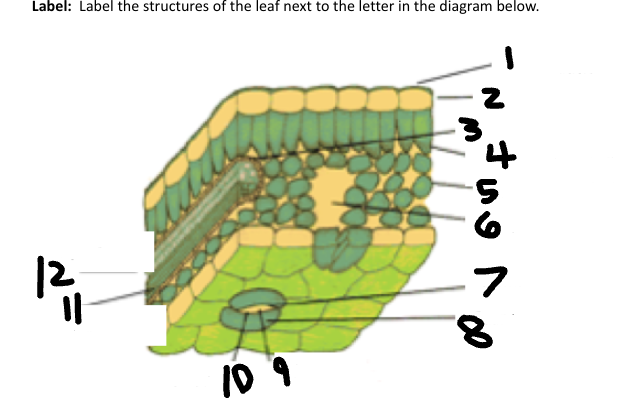
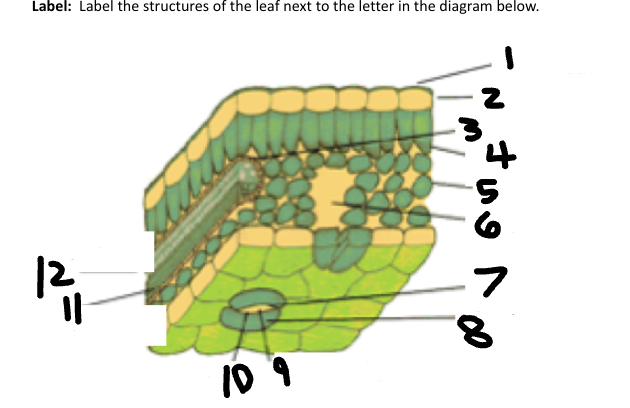
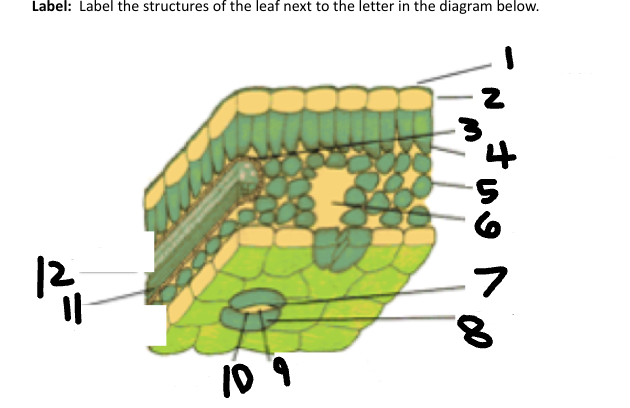
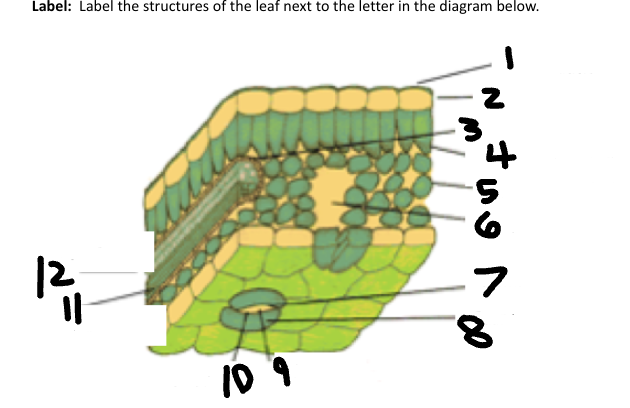
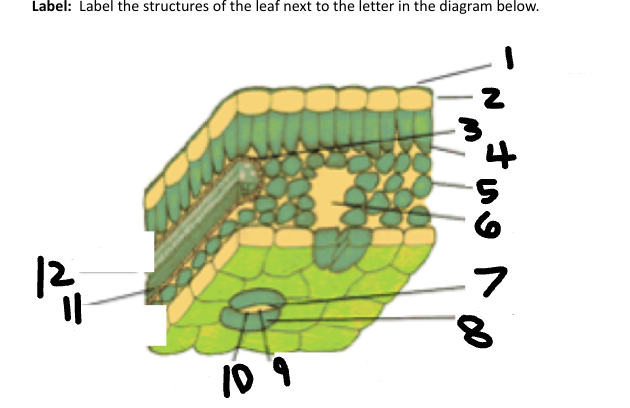
1
Waxy cuticle
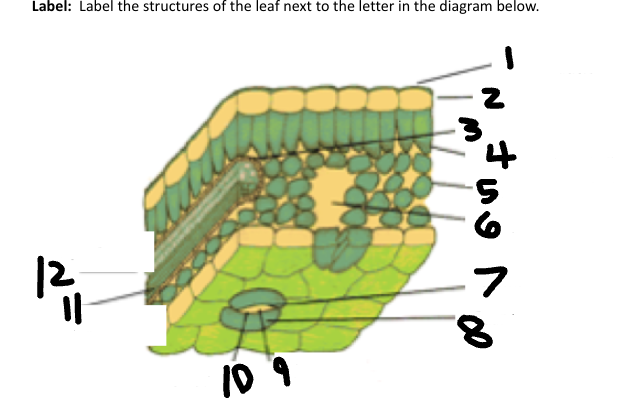
2
Epidermis
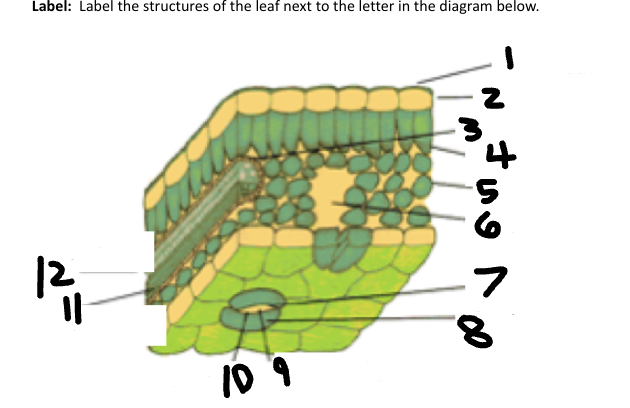
3
Vein
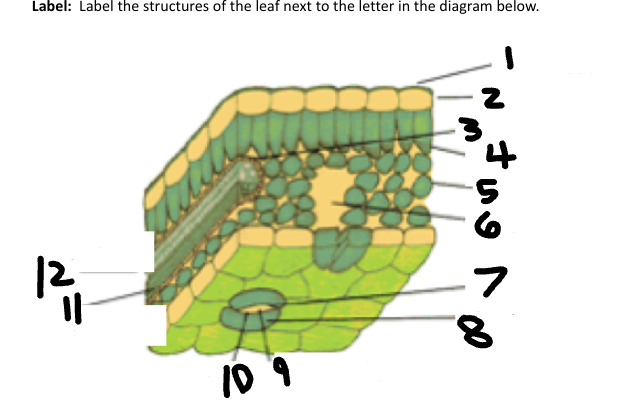
4
Palisade Mesophyll
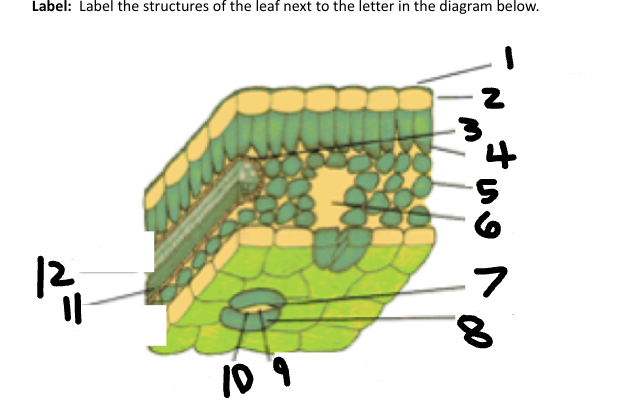
5
Spongy Mesophyll
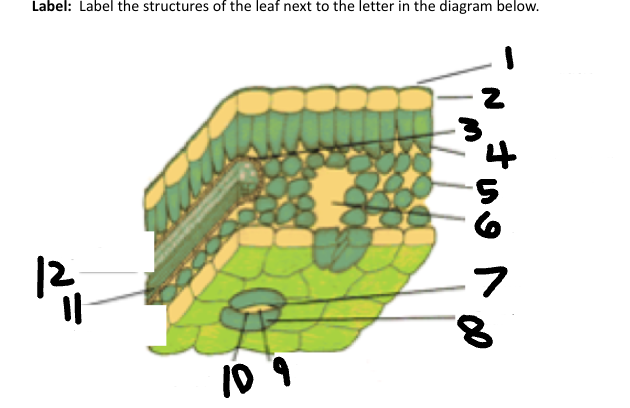
6
Air space
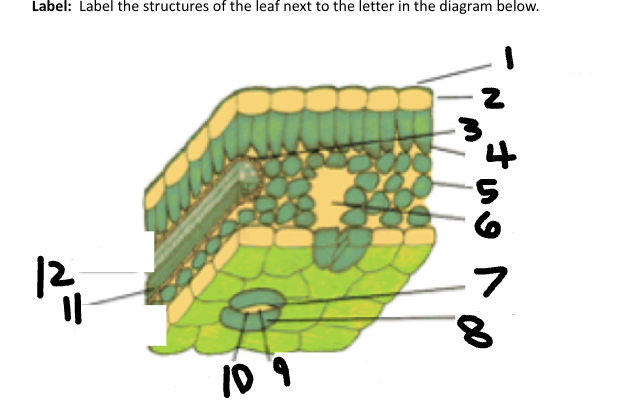
7
Stoma
8
Guard Cell
9
CO2 in
10
O2 out
11
Phloem
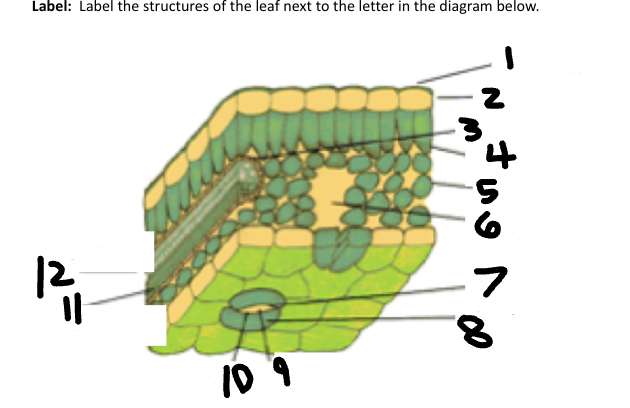
12
Xylem