MAT E 273 Final
1/188
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
The binary compound with the highest measured melting point.
HfC
The binary compound with the second-highest measured melting point.
TaC
The pure metal with the highest measured melting point.
Tungsten
The pure metal with the second-highest measured melting.
Rhenium
reffered to as the plain carbon steel of ceramics. express crystallographic phase change with temp
Zirconia
What does adding yttria to Zr do?
allows higher temp phases
Coating for Gas-Turbine Engines
7YPSZ
YSZ TBC’s columnar layer:
insulating
Kitchenware
ZrO₂
Polymer structure that have more hydrogen have a lower or higher MP?
Higher
Porosity effect on optics if something is more porous…
less clear
PMMA common name
Plexiglass
Common for abrasives and heating elements
silicon carbide
Ceramic with metallic nature. Very hard, not completely brittle
Tungsten Carbide
Lightweight, very hard, used for ballistic armor
Boron Carbide
Dark shiny ceramic with low friction coefficient
Silicon Nitride
Wear resistant coating with gold color. Commonly used to coat steel cutting tools
Titanium Nitride
Produces local compression in the ceramic = hinders crack propagation. Best choice if max toughening.
TZP
room-temp toughening because secondary tetragonal-phase particles go within continuous phase, disrupting crack propagation, and increased stress near tip of propagating crack = martensitic phase-change Best choice for moderate toughening around 300oC for prolonged periods of time.
PSZ
The ceramic compound commonly added to zirconium oxide to promote stability of zirconia phases and microstructures.
Yttrium Oxide
A ceramic commonly used as a high-hardness and wear-resistant coating for cutting tools. A sufficiently thick coating of this compound tends to exhibit a golden appearance.
Titanium Nitride
A ceramic compound that has fairly high metallic tendencies. This ceramic is shiny and reflective (it looks like a typical metal), and also not completely brittle (unlike many ceramics). This ceramic is routinely sintered into spheres for high-hardness bearings, high-strength ball valves. It is also commonly used in composite form (embedded as particulate within other metals) to make cutting tools.
Tungsten Carbide
A ceramic compound that, in pure form, is mechanically unstable because of spontaneous fracture upon cooling. Specifically, fracture results because of microcracking that accompanies a martensitic phase change from a tetragonal to monoclinic form upon cooling, since this phase change invokes a relatively large volume expansion that is not easily accommodated by the strongly bonded ceramic.
Zirconium Oxide
A ceramic that is likely to appear in ceramic matrix composite form (CMCs) within fully-ceramic rotating jet engine components, after sufficient R&D and testing confirm their reliability as rotating parts in high-temperature, high-stress environments.
Silicon Carbide
The primary component of modern "glass" compositions (e.g. window glass, beverage containers, etc.).
Silica
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
The yttria content of the top coat layer (columnar grains) should be maximized and should comprise 40-50 wt% of the total turbine blade weight.
F
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
The use of a TBC is specifically to allow the underlying nickel to be comprised of less-expensive random polycrystalline grain structure (vs a textured polycrystal or single crystal).
F
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
The coefficients of thermal expansion for the TBC sublayers should be matched as close as possible - or very intentionally progress in value in decreasing sequence (from Ni towards coating) to prevent thermal stresses that could promote cracking and spalling of the TBC.
T
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
The thermal conductivities of the TBC sublayers should be relatively high and matched as close as possible to the underlying base metal (usually a Ni-based superalloy).
F
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
Air gaps between grains of top coat 7TZP should be minimized, since they act as stress concentrators for TBC coating.
F
T or F regarding the optimum design criteria of 7TZP TBC for nickel superalloy jet engine turbine blades:
Soda-lime glass is the preferred composition for the bonding layer of modern columnar TBCs.
F
Commonly used as a thermal barrier coating for jet engine blades, when modified with a small amount of yttrium oxide.
7PSZ
An oxide that is commonly used for radioactive thermal generators (RTG).
Plutonium Oxide
An oxide that is commonly used in fibrous form as a low thermal conductivity material within heat shield tiles.
Silica
A ceramic that utilizes ferroelastic transformation as a toughening mechanism at elevated temperatures (e.g. 1200 C)
7PSZ
An oxide compound (among others with the same structure) that features natural electrical polarization, due to a slight distortion of the crystal lattice from its ideal structure.
Barium Titanate
A ceramic compound that has a very similar crystal structure compared to germanium.
Zinc Sulfide
A single-phase ceramic that features transformation toughening but is susceptible to low-temperature aging degradation.
TZP
A material commonly used as imitation diamond.
CSZ
A member of the oxide family that exhibits the highest practical strengths across all ceramic materials.
TZP
A ceramic compound that exhibits piezoelectricity.
Barium Titanate
A stabilized form of zirconia that offers inferior mechanical strength and toughness, but undergoes no phase crystalline changes with thermal cycling.
CSZ
An additive that is known to eliminate the low-temperature aging degradation of TZP ceramics.
Aluminum Oxide
A lightweight ceramic compound commonly used for projectile resistant plating / armor.
Boron Carbide
cleaves easy, decent electric conductor, thermal insulator
\Carbon Graphite:
Highest/Perfect pressure-free critical temps for superconductivity: insulator at room temp
infinite conductivity at low temps and/or high pressures.
Copper oxides
Carbon diamond, Si, Ge
Uses: Microelectronics, Solar Cells
Semiconductors
rocket salts, metal-like electric conductivity , use for heat resistant air and spacecraft. Often produced via powder sintering
HfC, TaC
Heating elements, ignitors, abrasives, crucibles, labware, gas turbine engine blades.
SiC
body armor, sintering of powder
B4C
often made sintering because it melts too high to cast. very hard = abrasion resistant. Shiny not completely brittle
WC
T or F: Ceramic materials are always inorganic compounds that feature bonding that is strictly ionic.
F
T or F: Ceramic materials are never crystalline. They always occur in glassy / amorphous form.
F
T or F: All ceramics are opaque (non-transparent to visible light).
F
T or F: Most ceramics are generally poor conductors of electricity at room temperature, compared to typical metal electrical conductors (e.g. copper).
T
T or F: Most ceramics are generally excellent conductors of heat at room temperature, compared to typical metal thermal conductors (e.g. copper).
F
T or F: The majority of annual worldwide ceramic production is associated with producing glass (e.g. silicate-based glasses such as soda-lime glass for window glass, etc.).
T
What characteristics is generally observed for ceramic materials at ambient conditions (e.g. near room temperature)?
increase modulus
Diamond, a metastable crystalline allotrope of carbon, is a famous example of extreme properties because it features _________ of all "practical" bulk materials.
highest thermal conductivity
higher density = increased VDW = harder = stronger = high MP = difficult diffusion. What is the crystallinity response?
Larger Crystallinity
Polymer mechanical behavior: Brittle behavior example
PS
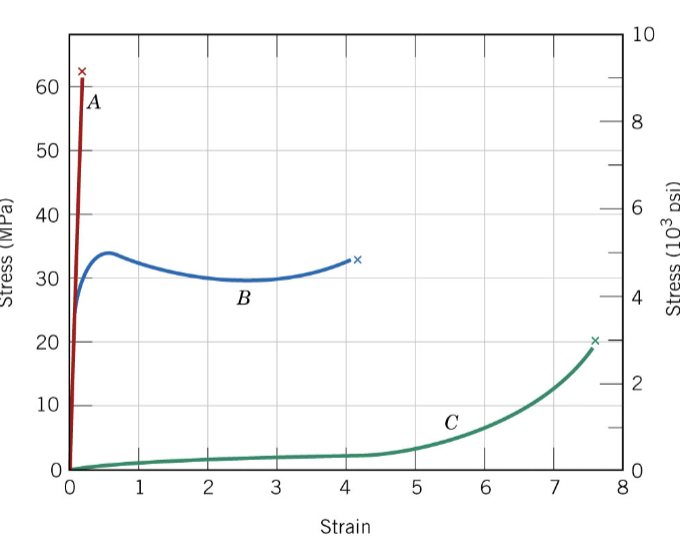
Polymer mechanical behavior: Ductile behavior examples
LDPE and HDPE
Comprised of alternating and random copolymers. All features are very flexible
What is it and give two examples
Synthetic Rubber
SBR: (rubber) tires
NBR: (rubber) Gasoline Hoses
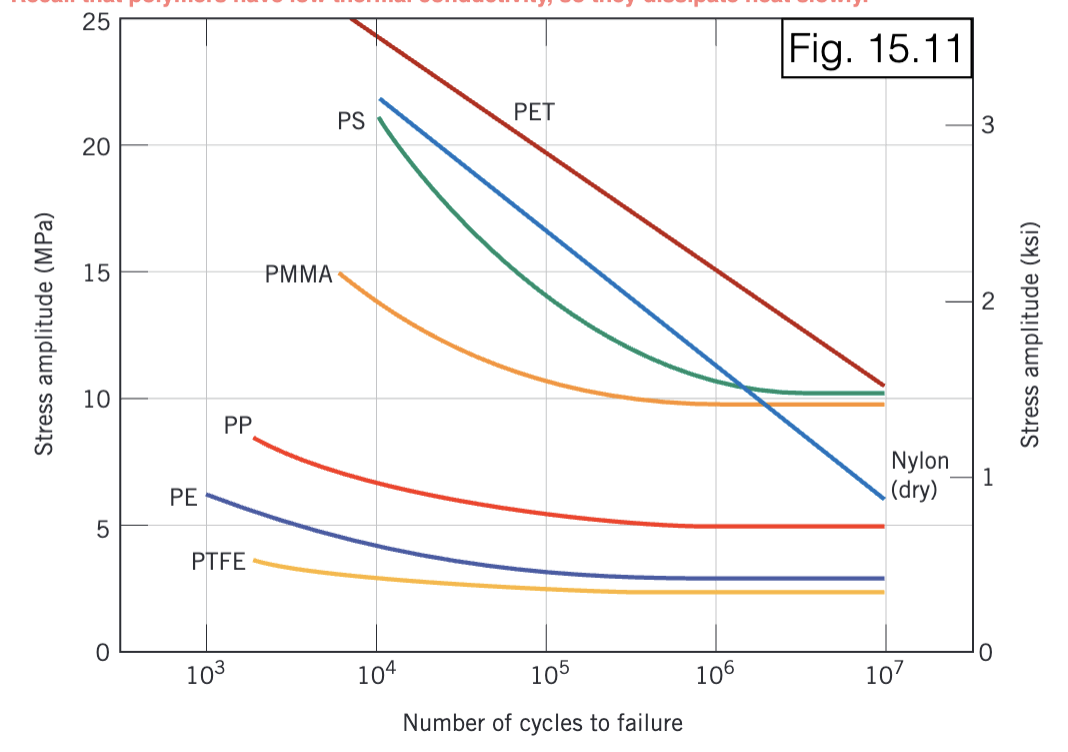
failure even for low-stress levels. Local heating can soften polymer = decreased strength.
cyclic loading
Most common plastic, packaging, bags, bottles, implants, etc.
PE
hydrophobic, non-reactove. One of the lowest coefficients of friction of all solids (Non-stick, tubing, implants)
PTFE (Teflon)
Family of polymers with the backbone of alternating silicon and oxygen. Oil, grease, rubber, resin, solid
Silicones
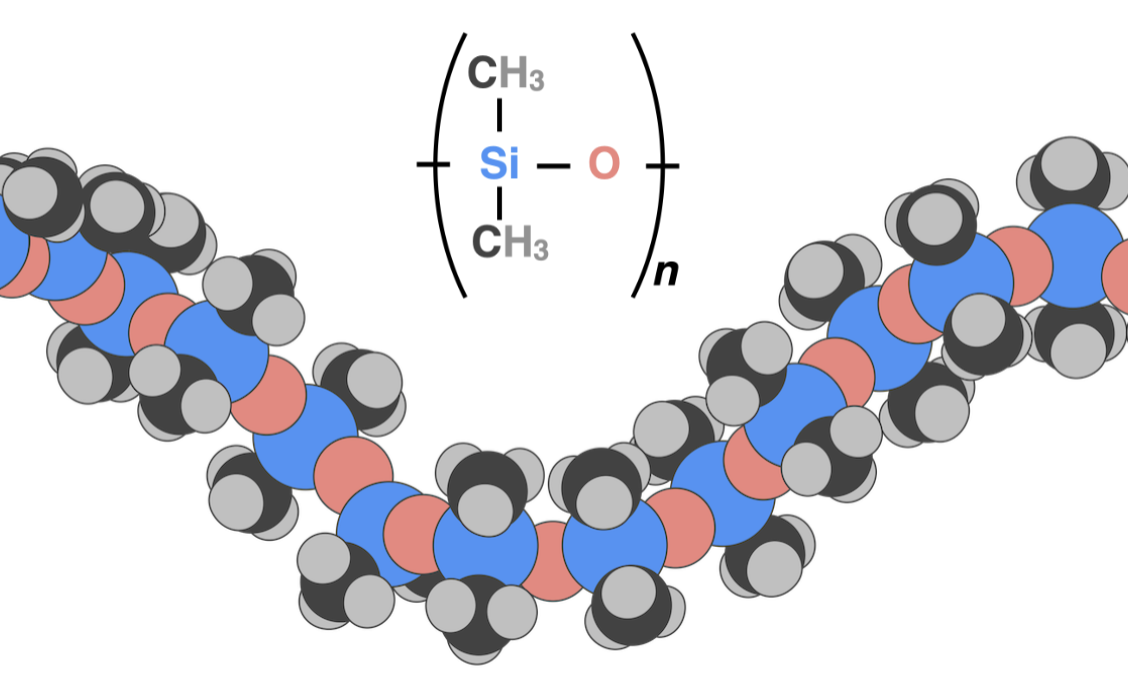
The simplest silicon. All side groups are CH3
PDMS
Silicone Rubber Film: synthetic medical membrane
PDMS
Silicone rubber resistant to heat. Low thermal conductivity.
RTV 615
Synthetic fiber used as steel replacement in racing tires.
Kevlar
High specific strength (5 times stronger than steel)
Strength is from aromatic rings in the backbone = limit flex. Strong H-bonding between close-packed parallel molecules
Kevlar
Cryogenics
PPE
Sport Equipment:
Tires
Armor/bulletproof Vests
Kevlar
T or F: All other factors being equal, the strength of a polymer tends to increase as the degree of polymerization increases.
T
T or F: All other factors being equal, a polymer's strength tends to increase as the average chain length of the polymer increases because of the increased opportunities for secondary bond formation.
T
What will decrease the yield strength of a given polymer ?
branching
The process of introducing sulfur crosslinks within ________ (otherwise known as natural rubber) is called __________ .
poly(cis-isoprene), vulcanization
T or F:
Above its glass transition temperature, a polymer is brittle.
F
T or F:
Below the glass transition temperature, polymer chains lose their mobility (they are less capable of bending, flexing, raveling, and rotating about covalent bonds along the backbone.
T
T or F:
The glass transition temperature of a material is normally above its melting temperature.
F
T or F:
The elastic modulus of a polymer decreases when it is heated above its glass transition temperature
T
Mechanical response characterized by extremely high, but completely recoverable, elastic strain, that is often non-linear with respect to the applied stress.
Elastomeric
Mechanical response characterized by partially recoverable strain. Upon sufficient deformation, some deformation of the polymer is permanent.
Ductile
Mechanical response is characterized by little to no strain at failure.
Brittle
The room-temperature mechanical response of a typical thermoplastic polymer.
Ductile
The room-temperature mechanical response of a typical thermosetting polymer.
Brittle
Mechanical response exhibited by liquids that offer resistance to flow. A behavior that is common for thermoplastic polymers above their melting point.
Viscous
A mechanical response characterized as elastic for short durations, but viscous for long durations.
Viscoelastic
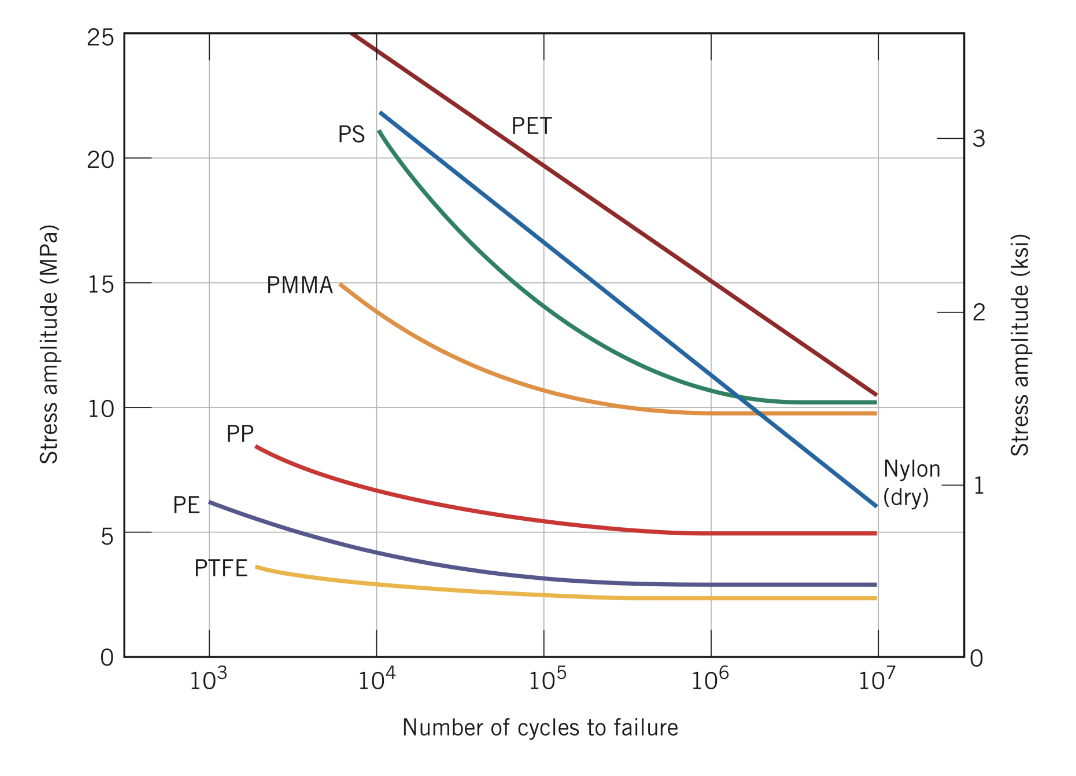
PET is a commonly used polymer for food and beverage containers.
For a PET specimen that experiences cyclic loading with a mean stress of +22 MPa, what is the maximum cyclic tensile stress that the part can experience such that it survives at least 1 million cycles?
37
This polymer is commonly used for high-strength fabrics and it acquires its strength from numerous hydrogen bonds between polymer molecules.
Kevlar
The most produced polymer annually.
PE
A class of polymer that is commonly used for medical coatings, membranes, and tubing, because it is relatively inert and also anticoagulant in nature.
silicone
A natural polymer that is extremely elastomeric, exhibiting very high elastic strains for relatively low stresses.
Poly(cis-isoprene)
A polymer that offers an impressively low friction coefficient.
Teflon
A very strong and very tough polymer that is transparent, and therefore useful as a substitute for ceramic glass.
PC
A polymer that is transparent in pure form and is hard and brittle.
PS
A copolymer that is used for Legos and is a common filament material for 3D printing.
ABS
polymer that is commonly used as a coating on medical needles to produce a smoother surface compared to the underlying metal needle (which reduces discomfort for the patient)?
Silicone
Can offer stiffness (E) and fracture toughness on par with metals but doesn’t have great temperature resistance and are cost prohibitive. fiber reinforced, continuous (aligned) or discontinuous (short), and randomly oriented
composites
embedded in polymer matrix. often polyester or epoxy.
GFRP (fiberglass)