Biology - Unit 1 test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Last updated 4:58 PM on 3/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Animal characteristics
* Multicellular
* Eukaryotic with no cell walls
* Heterotrophs (consumers)
* Aerobic
* Most are mobile
* Have a nervous system to respond to their environment
* Locomotion relates to ability to obtain food
* Common ancestor of animals was probably a flagellated protist, 700 million years ago.
* Eukaryotic with no cell walls
* Heterotrophs (consumers)
* Aerobic
* Most are mobile
* Have a nervous system to respond to their environment
* Locomotion relates to ability to obtain food
* Common ancestor of animals was probably a flagellated protist, 700 million years ago.
2
New cards
The three types of layers
* Ectoderm
* Endoderm
* Mesoderm
* Endoderm
* Mesoderm
3
New cards
Ectoderm
Outer layer, forms skin and nervous system
4
New cards
Endoderm
Inner layer, gut
5
New cards
Mesoderm
Middle layer, circulatory, reproductive, excretory, muscular systems
6
New cards
Types of symmetry
* Radial symmetry
* Bilateral symmetry
* Bilateral symmetry
7
New cards
Radial symmetry
* Numerous lines of symmetry, i.e. starfish
* Lacks one dominant region therefore slow movement
* Lacks one dominant region therefore slow movement
8
New cards
Bilateral symmetry
True head region, these animals move in one direction (forward)
9
New cards
Cephalization
Anterior concentration of nerves (sense organs)
10
New cards
Coelom
* Fluid-filled space between body gut and body wall
* Contains and protects internal organs
* Lined by the peritoneum (covers organs & holds them in place)
* Contains and protects internal organs
* Lined by the peritoneum (covers organs & holds them in place)
11
New cards
Acoelomates
Animals have three cell layers with a digestive tract but no body cavities.
12
New cards
Pseudocoelomates
Animals with a fluid-filled body cavity partly lined with mesoderm.
13
New cards
Coelomates
Animals with a body cavity completely surrounded by mesoderm.
14
New cards
Exoskeleton
A hard covering that supports and protects the bodies of some types of animals
15
New cards
Endoskeleton
An internal skeleton, such as the bony or cartilaginous skeleton of animals.
16
New cards
Advantages of an exoskeleton
* Provides protection against predators and strength against prey
* Used as a home
* Used as a home
17
New cards
Disadvantages of an exoskeleton
* Limited Movement
* Exoskeleton cannot grow
* Exoskeleton cannot grow
18
New cards
Advantages of an endoskeleton
* Provides support for the body
* Protects internal organs
* Allows for movement
* Protects internal organs
* Allows for movement
19
New cards
Disadvantages of an endoskeleton
* Vulnerable to the external environment
* Susceptible to disease
* Susceptible to disease
20
New cards
Swim bladder
A gas-filled organ in fish. Its primary function is to float.
21
New cards
Metamorphosis
Changes from egg to adult form
22
New cards
Amniotic egg
fluid filled sac to protect embryo
23
New cards
Phylum Porifera
Sponges
* Asymmetrical
* Most are marine but some freshwater
* Sessile as adults but larvae is motile
* Asymmetrical
* Most are marine but some freshwater
* Sessile as adults but larvae is motile
24
New cards
Phylum Cnidaria
Sponges
* Have nematocysts – stinging cells that inject toxins into prey
* Hydras, anemones, jellyfish and coral
* Radial symmetry
* Have nematocysts – stinging cells that inject toxins into prey
* Hydras, anemones, jellyfish and coral
* Radial symmetry
25
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Tapeworm
26
New cards
Phylum Nematoda
Hookworm
27
New cards
Phylum Annelida
Earthworm
28
New cards
Phylum Mollusca
Snails
* Three main unsegmented body parts: a foot, a visceral mass, a mantle
* Soft bodies, hard Shells (may be reduced or absent)
* Most have a radula - rasping tongue like organs with hard teeth to scrape or cut food
* Three main unsegmented body parts: a foot, a visceral mass, a mantle
* Soft bodies, hard Shells (may be reduced or absent)
* Most have a radula - rasping tongue like organs with hard teeth to scrape or cut food
29
New cards
Agnathans
Lamprey. hagfish:
* No jaws
* Parasite fish
* They have gill slits but no paired appendages
* No jaws
* Parasite fish
* They have gill slits but no paired appendages
30
New cards
Chondrichthyes
Sharks, rays
* Their skeletons are made of cartilage
* Their fins are often thick.
* Reproduction uses internal fertilization.
* Their skeletons are made of cartilage
* Their fins are often thick.
* Reproduction uses internal fertilization.
31
New cards
Actinopterygii
Most common fish
* Their skeletons are bony.
* Most have a swim bladder
* Most species use external fertilization.
* Their skeletons are bony.
* Most have a swim bladder
* Most species use external fertilization.
32
New cards
Amphibia
Frogs, salamanders
* Most have an aquatic larval stage with gills
* Adults are tetrapods having four limbs adapted for moving on land
* Most species use external fertilization
* Most have an aquatic larval stage with gills
* Adults are tetrapods having four limbs adapted for moving on land
* Most species use external fertilization
33
New cards
Reptilia
Snakes, lizards
* Most are terrestrial tetrapods with dry scaly skin.
* They use internal fertilization.
* They have amniotic eggs with soft shells
* Most are terrestrial tetrapods with dry scaly skin.
* They use internal fertilization.
* They have amniotic eggs with soft shells
34
New cards
Aves
Birds
* They are tetrapods with forelimbs modified as wings.
* Most species are capable of flight.
* They have feathers.
* They are tetrapods with forelimbs modified as wings.
* Most species are capable of flight.
* They have feathers.
35
New cards
Mammalia
Mammals
* They are tetrapods and have hair.
* They nurse their young with milk produced in mammary glands
* They are warm blooded (endothermic)
* They are tetrapods and have hair.
* They nurse their young with milk produced in mammary glands
* They are warm blooded (endothermic)
36
New cards
Phylum Echinodermata
Sand dollar
37
New cards
Phylum Arthropoda
Ants
38
New cards
Species diversity
A measure of diversity that takes into account the quantity and variety of each species present. Ex: Different breeds of dogs
39
New cards
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains energy by consuming other dead or living organisms.
40
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that uses a source of energy (sun) to produce nutrients.
41
New cards
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified.
42
New cards
Taxon
Groups of organization into which organisms are classified.
43
New cards
Dichotomous Key
A method of identification when groups of organisms are divided into two categories.
44
New cards
Binomial nomenclature
The formal system of naming species where each species is assigned a genus name followed by a specific name.
45
New cards
8 major levels of classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species Dumb King Phillip Called Out For Good Soup
46
New cards
Phylogeny
The study of the evolutionary relatedness between, and among, species.
47
New cards
Phylogenetic tree
A branching diagram used to show evolutionary relationships between different species or groups.
48
New cards
Clades
A piece of a phylogeny that includes a single common ancestor and all its descendents.
49
New cards
Prokaryotes
* Unicellular
* Do NOT have membrane-bound organelles
* Ex: bacteria
* Do NOT have membrane-bound organelles
* Ex: bacteria
50
New cards
Eukaryotes
* Unicellular and multicellular
* Have organelles
* Have organelles
51
New cards
Conjugation
A temporary union of two organisms for the purpose of DNA transfer. (sexual)
* One bacterial cell passes a copy of a plasmid to a nearby bacterial cell through a hollow pilus
* One bacterial cell passes a copy of a plasmid to a nearby bacterial cell through a hollow pilus
52
New cards
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms when one cell divides into two cells
* Parent cell splits into two daughter cells.
* Each daughter cells receive an exact copy of the genetic material
* Replicate quickly therefore many mutations occur
* Parent cell splits into two daughter cells.
* Each daughter cells receive an exact copy of the genetic material
* Replicate quickly therefore many mutations occur
53
New cards
Budding
* In budding, the individual yeast cell acts like tiny hypha.
* The nucleus divides
* A septum forms between the two nuclei
* A small daughter cell is formed or the side of the original yeast
* The nucleus divides
* A septum forms between the two nuclei
* A small daughter cell is formed or the side of the original yeast
54
New cards
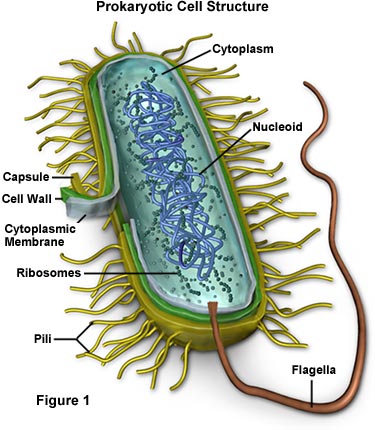
Bacteria structure
* DNA loose in cytoplasm - no nucleus.
* Ribosomes are also scattered in the cytoplasm.
* Many have one or more plasmids.
* Peptidoglycan - protective coating ONLY on bacteria
* Makes up its cell wall.
* Bacteria may have an outer capsule for protection
* Ribosomes are also scattered in the cytoplasm.
* Many have one or more plasmids.
* Peptidoglycan - protective coating ONLY on bacteria
* Makes up its cell wall.
* Bacteria may have an outer capsule for protection
55
New cards
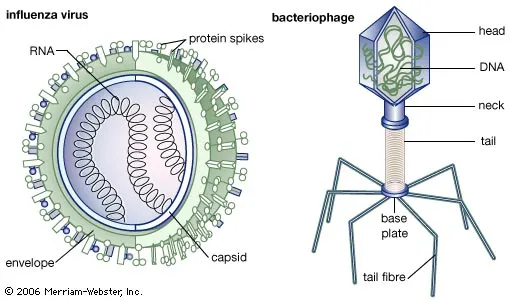
Virus structure
* Capsid
* DNA/RNA
* DNA/RNA
56
New cards
Organisms that reproduce asexually
Some plants, some fungi, and many microorganisms.
57
New cards
Organisms that reproduce sexually
Animals and humans.
58
New cards
The three domains are
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
59
New cards
Nonpathogens
A microorganism that is not capable of causing a disease
60
New cards
Pathogens
A microorganism that cause disease
61
New cards
Capsid
Protein coat surrounding a virus
62
New cards
Lysis
The bursting of a cell
63
New cards
Lytic cycle
* Virus is active
* Symptoms occur
* Viral reproduction occurs
* Cells burst
* Symptoms occur
* Viral reproduction occurs
* Cells burst
64
New cards
Lysogenic
* Virus is dormant
* No symptoms
* Reproduction does not immediately occur
* These latent viruses may remain inactive for years
* No symptoms
* Reproduction does not immediately occur
* These latent viruses may remain inactive for years
65
New cards
Bacteriophage
Species that infect bacteria
66
New cards
Vaccine
* A weakened form of a virus is injected
* This triggers an immune response but not illness
* The 'antibodies' are stored in memory in case of contact with the true form of the virus
* This triggers an immune response but not illness
* The 'antibodies' are stored in memory in case of contact with the true form of the virus
67
New cards
Capsule
* Covers the cell wall in prokaryotes
* Reduces water loss
* Resists high temp
* Resists antibiotics and high viruses
* Reduces water loss
* Resists high temp
* Resists antibiotics and high viruses
68
New cards
Endospore
* A small, rounded, thick-walled, resting cell that forms inside a bacterial cell
* Metabolically inactive
* Highly resistant to harsh conditions for long periods
* Metabolically inactive
* Highly resistant to harsh conditions for long periods
69
New cards
Obligate aerobes
Microorganisms that need oxygen to survive
70
New cards
Facultative aerobe
Uses oxygen when it is present but lives anaerobically when oxygen is absent
71
New cards
Obligate anaerobe
Microorganisms killed by oxygen
72
New cards
Archaebacteria
A group of microorganisms whose cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan and that live in extremely harsh environments.
73
New cards
Antibiotic
A chemical that kills bacteria or slows their growth without harming body cells by stopping the cell wall from building
74
New cards
Plasmid
A small loop of DNA that carries genes that often provide an advantage to the cell
75
New cards
Cocci
Spherical
76
New cards
Bacilli
Rods
77
New cards
Spirilla
Spiral
78
New cards
Diplo
Double
79
New cards
Strepto
Chains
80
New cards
Staphylo
Clusters
81
New cards
When do we use antibiotics?
Antibiotics are only needed for treating certain infections caused by bacteria
82
New cards
When do we use vaccines?
When people are at risk of contracting a diseas
83
New cards
What are protists?
* Most diverse kingdom (odds and ends)
* Includes very small, single-celled, mobile organisms such as amoeba and very large, multicellular, stationary organisms such as large green kelp.
* Includes very small, single-celled, mobile organisms such as amoeba and very large, multicellular, stationary organisms such as large green kelp.
84
New cards
Protist Characteristics
* Eukaryotes
* Most unicellular, few multicellular
* Some are motile
* Some have cell walls
* NOT bacteria, fungi, plants or animals
* Most unicellular, few multicellular
* Some are motile
* Some have cell walls
* NOT bacteria, fungi, plants or animals
85
New cards
Plant-like protists
* Spirogyra – long green strands
* Volvox – green spheres
* ==Algae== – green rods
* Diatoms – brown & shiny
* Volvox – green spheres
* ==Algae== – green rods
* Diatoms – brown & shiny
86
New cards
Animal-like protists
* Stentor – small, greenish
* Euglena – tiny, green rods
* ==Amoeba== – larger blobs
* Paramecium – oval shaped, cilia
* Mixed protozoa – lots of neat ones!
* Euglena – tiny, green rods
* ==Amoeba== – larger blobs
* Paramecium – oval shaped, cilia
* Mixed protozoa – lots of neat ones!
87
New cards
Fungus-like protists
* Cellular slime molds
* Acellular slime molds
* Water molds
* Acellular slime molds
* Water molds
88
New cards
Cuticle
To reduce water loss
89
New cards
Stomata
To regulate gas exchange and reduce water loss
90
New cards
Xylem and phloem
* Specialized for the transportation of water and nutrients
* Allows plants to grow to great heights
* Lignin (in vascular tissue) provides the strength of wood
* Allows plants to grow to great heights
* Lignin (in vascular tissue) provides the strength of wood
91
New cards
Bryophytes
* Includes mosses, liverworts and hornworts.
* Do NOT have specialized conductive tissues or true leaves, roots or seeds
* Only a few centimeters in height
* Have ‘rhizoids’ (primitive roots)
* Do NOT have specialized conductive tissues or true leaves, roots or seeds
* Only a few centimeters in height
* Have ‘rhizoids’ (primitive roots)
92
New cards
Lycophytes and Pterophytes
* Development of vascular tissue = xylem and phloem
* Seedless plants
* Simple roots
* Simple stems = rhizomes
* Fronds (a fern leaf)
* Seedless plants
* Simple roots
* Simple stems = rhizomes
* Fronds (a fern leaf)
93
New cards
Gymnosperms
* Conifers (ex. Pines, spruces, cedars, etc.)
* Produce unprotected seeds in cone-like structures
* Leaves are thin and needlelike and are covered by a hard waxy cuticle
* Roots extend over wide surface area → this anchors the tree and prevents erosion
* Produce unprotected seeds in cone-like structures
* Leaves are thin and needlelike and are covered by a hard waxy cuticle
* Roots extend over wide surface area → this anchors the tree and prevents erosion
94
New cards
Angiosperms
* More than 90% of all modern plant species
* Flowers produce both pollen and eggs
* In the female part of the flower, the eggs are enclosed in an ovary
* After fertilization, seeds in the ovary, and the outer tissues of the ovary become a fruit.
* Flowers produce both pollen and eggs
* In the female part of the flower, the eggs are enclosed in an ovary
* After fertilization, seeds in the ovary, and the outer tissues of the ovary become a fruit.
95
New cards
Rhizome
Underground plant stem capable of producing the shoot and root systems of a new plant
96
New cards
Frond
The leaves of ferns
97
New cards
Fungus structure
* Its reproductive structure grows out of the ground.
* Most of its body often remains hidden below the ground.
* Most of its body often remains hidden below the ground.
98
New cards
Hyphae
* Hyphae are often microscopically thin
* They consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei which may be separated into compartments by cell walls called septa.
* The cytoplasm is contained by a cell wall made of chitin – a complex chemical
* Hyphae also form the “fuzz” often associated with mold.
* They consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei which may be separated into compartments by cell walls called septa.
* The cytoplasm is contained by a cell wall made of chitin – a complex chemical
* Hyphae also form the “fuzz” often associated with mold.
99
New cards
Mycelium
A network of fungal threads or hyphae
100
New cards
Chitin
A complex chemical that is used to make cell walls in fungus