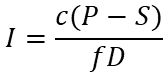Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
3 radiation events (rapid expansions of biodiversity)
Cambrian explosion (542 mya)
all major body forms: bilateral symmetry, skeletons, compound eyes, appendages, etc.
Silurian radiation (440 mya)
vascular plants
Triassic radiation (251 mya)
most modern fauna: corals, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals
5 mass extinctions prior to now
ordovician (86% of species)
devonian (75% of species)
permian (96% of species)
triassic (80% of species)
cretaceous (76% of species)
Buffon’s Law
Different species perform similar ecological roles in different places
ecoregion
Units of land containing distinct assemblages of species, with boundaries that approximate original extent of communities prior to major land-use change. 867 terrestrial ecoregions are recognized, and often used as units of management by conservation organizations
biodiversity hotspot
A defined geographic area with particularly high levels of biodiversity, which is also threatened by human activities
what are evolutionary drivers of biodiversity?
mutation, recombination, speciation, natural selection, genetic drift
what are ecological drivers of biodiversity
adaptive radiation, competition, predation and disturbance, dispersal and colonisation
allopatric speciation
form of evolutionary speciation, occurs when a physical barrier divides a population, and the divided populations diverge in genotype and phenotype.
genetic drift
Changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next, resulting from random chance.
genetic bottleneck
Extreme change in genetic and phenotypic makeup of a species that occurs when the size of a population is severely reduced.
Founder effects
Extreme change in genetic and phenotypic makeup of a species that occurs when a small group establishes a new colony
Competitive Exclusion principle
No two species can coexist when using the same resource, at the same time, in the same location.
adaptive radiation
The evolutionary diversification of a group of organisms into forms that fill different ecological niches in an environment.
rapid evolution
Evolution by natural selection (or drift) that produces new species over the course of just a few generations.
how does predation and disturbance affect biodiversity using the example of mortality events
Mortality events increase biodiversity only when they promote life-history trade offs that allow species to coexist through niche differences. Otherwise, they decrease biodiversity.
What do we use for Dispersal and Colonization modeling
Dependent variables
I = immigration rate (species per time)
E = extinction rate (species per time)
Independent variables
P = total number of species on mainland
S = species richness of island
D = distance of island from mainland
A = area of the island
Parameters
c = colonization probability
q = extinction probability
f = scaling factor for distance
m = scaling factor for area