Darija Grammar Rules - ongoing (Peace Corps/Speak Moroccan)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Arabic script to English translation. This includes 1) Pronouns/Posessive Pronouns, Gendered Nouns
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
How do independent pronouns work?
I, He, She, We, Y’all, and They work exactly the same. Additionally, there are separate “You”s when you address a woman or a man (you-fem and you-masc).
How do possessive pronouns work?
Instead of saying “his book,” there is a suffix that attaches to the end of the word. Your, her, y’all’s, our, and their all work that way.
What are the exceptions for possessive pronouns?
“My” suffix and “his” suffix have two variations each. For words ending in consonants, you use -”i” for my and -”u” for his. For words ending in vowels, you use -”ya” or -”h”
What about words ending in ة, the letter pronounced like an a at the end of words?
Before adding a possessive pronoun to the end, you add a -t since this letter is actually a silent t. Example: magana “watch” becomes magan - t - i “my watch.”
When are nouns typically feminine? How can you specify that something/someone is feminine?
When ending in ة, the special form of taa’, a noun is feminine. You can add this to any masculine noun to make it feminine
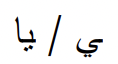
“my” possessive pronoun

“your” possessive pronoun
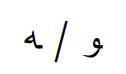
“his” possessive pronoun
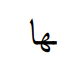
“her” possessive pronoun
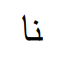
our
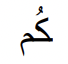
y’all’s (your plural)
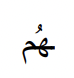
their

How does the possessive “dyal” work?
Instead of adding a possessive ending to words, you can use “the” (l-) in front of the word and add “dyal” to the end with its own ending. It will still mean “my book,” but closer to “the book that’s mine.”
What are the different forms of dyal? (mine, yours, his, hers, ours, y’all’s, theirs)
dyali, dyalk, dyalu, dyalha, dyalna, dyalkum, dyalhum
