Intro to Comp Sci Chapter 13
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Artificial intelligence
The study of computer systems that attempt to model and apply the intelligence of the human mind (ex: writing a program to pick out objects in a picture)
Alan Turing
An English mathematician who wrote a landmark paper in 1950 that asked the question: Can machines think?
He proposed a test to answer the question “How will we know when we’ve succeeded?”
Turing Test
A test to empirically (by means of observation or experience rather than theory or pure logic) determine whether a computer has achieved intelligence.
a human interrogator must determine which respondent is the computer and which is the human (A or B); procedure is repeated with numerous human interrogators and premise is that if it could fool enough interrogators, then it could be considered intelligent
Weak Equivalence
two systems (human and computer) are equivalent in results (output), but they do not arrive at those results in the same way
Strong equivalence
two systems (human and computer) use the same internal processes to produce same result
Hugh Loebner
New York philanthropist organized 1st formal instantiation of the Turing test; competition since 1991; grand prize of $100,000 and a solid gold medal will be awarded for the first computer whose responses are indistinguishable from a human’s (including text, visual, and audio input)
Loebner Prize
the first formal instantiation of the Turing test, held annually
Chatbots
a program designed to carry on a conversation with a human user
Knowledge representation
techniques used to represent knowledge so that a computer system can apply it to the intelligent problem solving
Expert System
computer systems that embody the knowledge of human experts
Neural networks
computer systems that mimic the processing of the human brain
Natural-language processing
the challenge of processing languages that human use to communicate
Robotics
the study of robots
Semantic networks and Search trees
promising techniques for representing knowledge
Semantic network
a knowledge representation technique that focuses on the relationships between objects
directed graph
used to represent a semantic network
nodes
represent objects
arrows
represent relationships; indicate the types of relationships
Inheritance relationship
indicates that one object is-a more specified version of another object
Instantiation
the relationship between an actual object and something that describes it (like a class)
search trees
Structure that represents all possible moves in a game, for both you and your opponent; represent a series of decisions made by the players.
pruning
eliminating path that no human player would consider reasonable
depth-first
A technique that involves analyzing selective paths all the way down the tree that we hope we will result in successful moves / searching down the paths of a tree prior to searching across levels
breadth-first
A technique that involves analyzing all possible paths but for only a short distance down the tree, which tends to yield the best results / searching across levels of a tree prior to searching down specific paths
network design
The objects in the network represent the objects in the real world; the relationships that we represent are based on the real-world questions that we would like to ask; the types of relationships represented determine which questions are easily answered, which are more difficult to answer, and which cannot be answered
Knowledge-based system
Software that uses a specific set of information (organized data), from which it extracts and processes particular pieces
expert system
A software system based on the knowledge of human expert
A rule-based system
a software system based on a set of if-then rules; set of rules in an expert system is referred to as its knowledge base
An inference engine
the software that processes rules to draw conclusions / determines how rules are followed
Executing Inference engine
System will ask user questions and based on users responses, it will determine which course of action will be recommended to user
Advantages of expert system
Goal oriented: it doesn’t focus on abstract or theoretical information but rather focuses on solving a specific problem.
Efficient: It records previous responses and doesn't ask irrelevant questions.
can usually provide useful guidance even if you don't know the answer to some questions.
Artificial Neural Network
A computer representation of the knowledge that attempts to mimic the neural networks of the human body
neuron
a single cell that conducts a chemically based electronic signal; at any point in time, a neuron is in either an excited state or an inhibited state
Excited State
Neuron conducts a strong signal
Inhibited State
neuron conducts weak signal
natural language processing
the challenge of processing languages that human use to communicate
3 basic types of processing occur during human/computer voice interaction
voice synthesis, dynamic voice generation, phonemes
Voice Synthesis
using a computer to recreate the sound of human speech
Dynamic Voice Generation
a computer examines the letters that make up a word and produces the sequence of sounds that correspond to those letters in an attempt to vocalize the word
Phonemes
the sound units into which human speech has been categorized; the way dynamic voice generation is completed
Voice Recognition
using a computer to recognize the words spoken by a human
Recorded speech
a large collection of words is recorded digitally, and individual words are selected to make up a message (ex: Siri, Alexa)
Problems with understanding speech
Each person’s sounds are unique
Each person’s sphere of mouth, tongue, throat, and nasal cavities that affect the pitch and resonance of our spoken voice are unique
Speech impediments, mumbling, volume, regional accents, and the health of the speaker are further complications
Humans speak in a continuous, flowing manner, stringing words together
Sound-alike phrases like “ice cream” and “I scream”
Homonyms such as “I” & “eye” or “see” & “sea”
Voiceprint
the plot of frequency changes over time representing the sound of the human speech
Natural-Language Comprehension
using a computer to apply a meaningful interpretation to human communication
Lexical ambiguity
the ambiguity created when words have multiple meanings

Syntactic ambiguity
the ambiguity created when sentences can be constructed in various ways

Referential Ambiguity
the ambiguity created when pronouns could be applied to multiple objects

mobile robotics
The study of robots that move relatively to their environment while exhibiting a degree of autonomy (the right or condition of self-government)
Sense-Plan Act (SPA) Paradigm
The world of the robot is represented in a complex semantic net in which the sensors on the robot are used to capture the data to build up the net

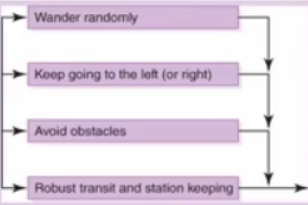
Subsumption Architecture
Rather than trying to model the entire world all the time, the robot is given a simple set of behaviors, each associated with the part of the world necessary for that behavior
3 Laws of Robotics by Isaac Asimov
A robot may not injure a human being, or through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
A robot must obey orders given to it by a human being.
A robot must protect its own existence.