Module 6.2.3- Polyesters and polyamides
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Condensation polymerisation
a reaction in which monomers are linked together into a polymer with the release of a small molecule, such as water, as a by-product
Polyester
monomers are joined together by ester linkages in a long chain to form the polymer
How are polyesters made
made from a monomer containing a carboxylic acid group and an alcohol group
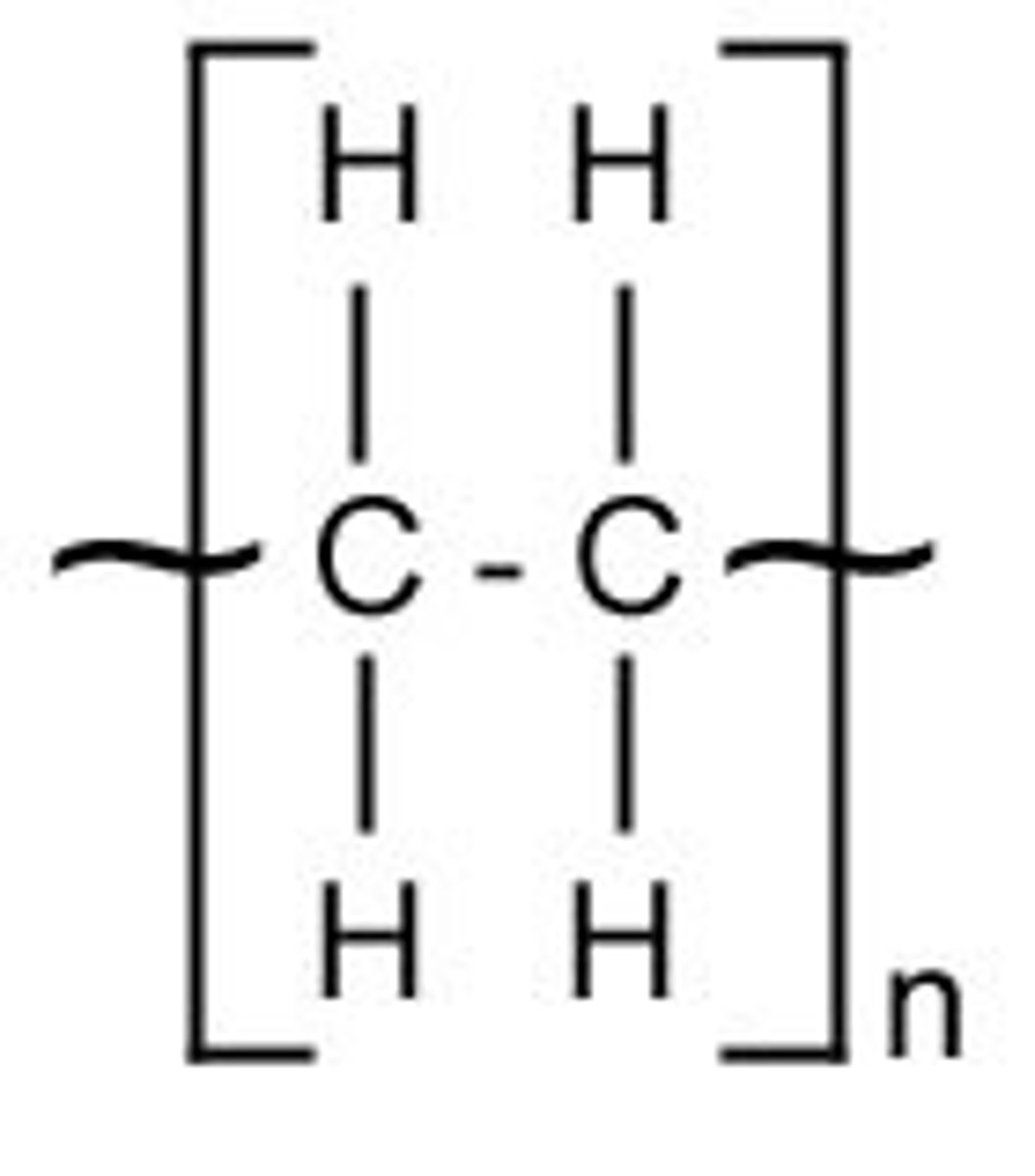
Repeat unit (revision)
A specific arrangement of atoms that occurs in the structure over and over again. Repeat units are included in brackets, outside of which is the symbol n.
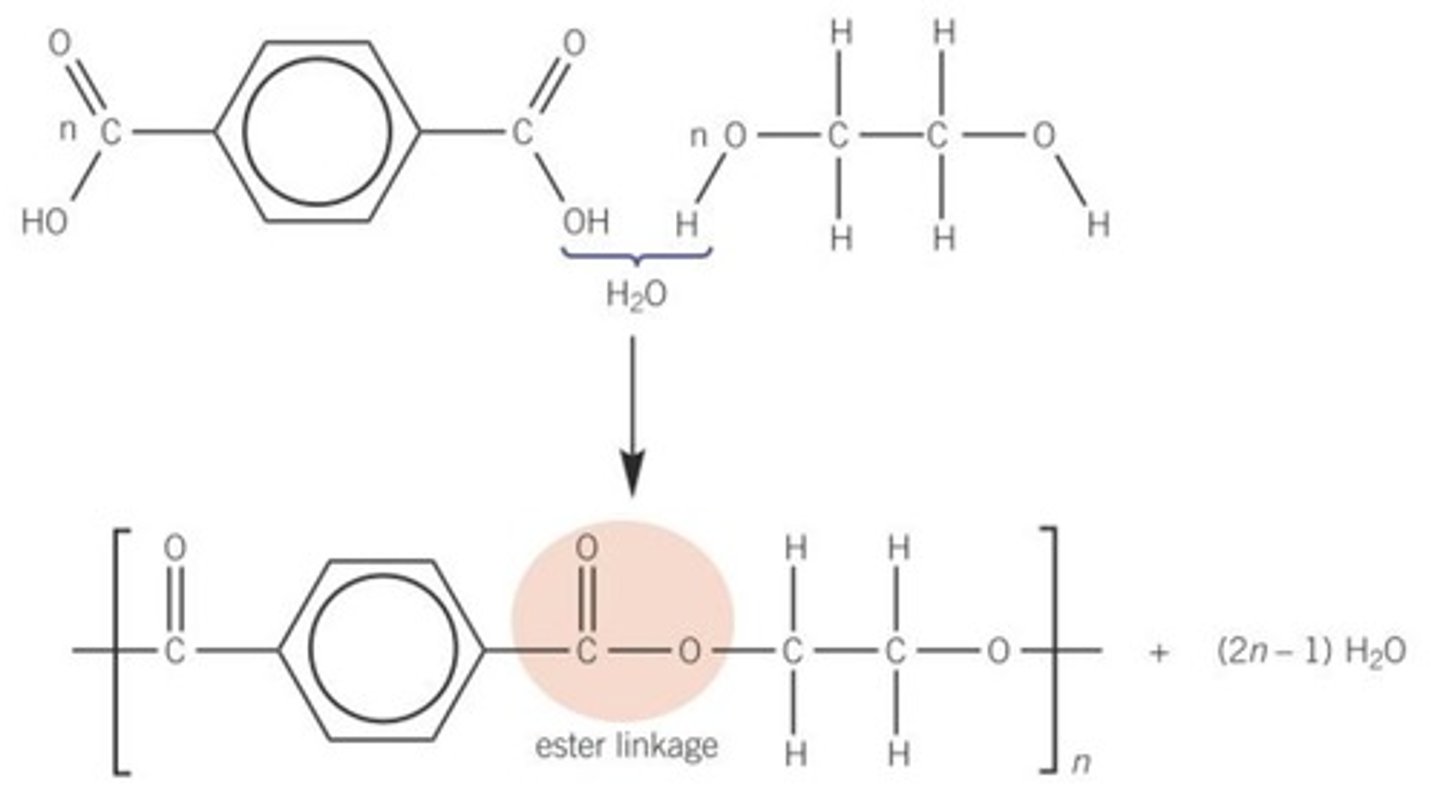
Polyesters made from two monomers each containing two functional groups
One monomer is a diol
One monomer is a dicarboxylic acid
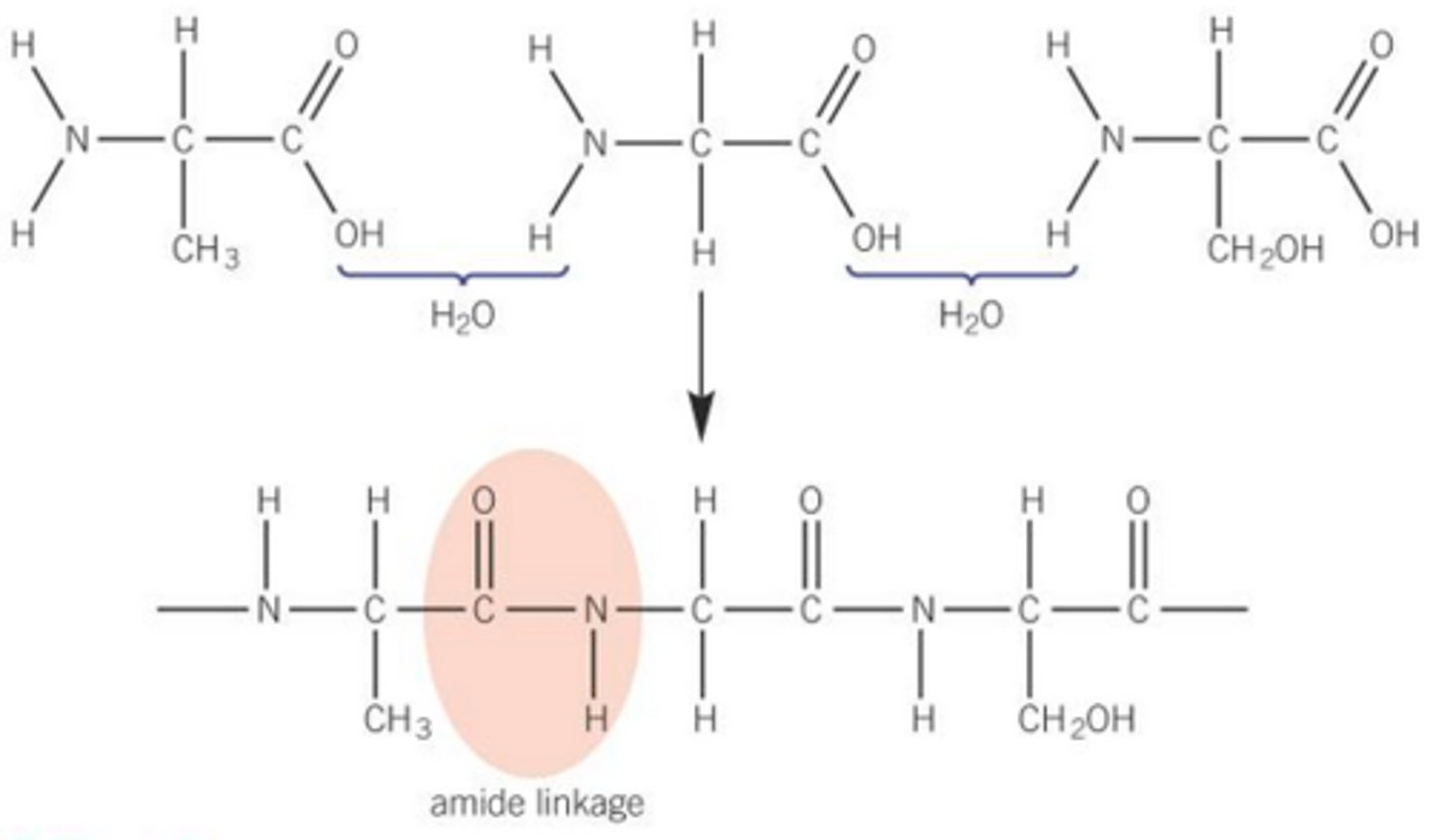
Polyamides
condensation polymers that contain the amide functional group
Polyamides from one monomer with two functional groups
Amide bond is formed and water is lost
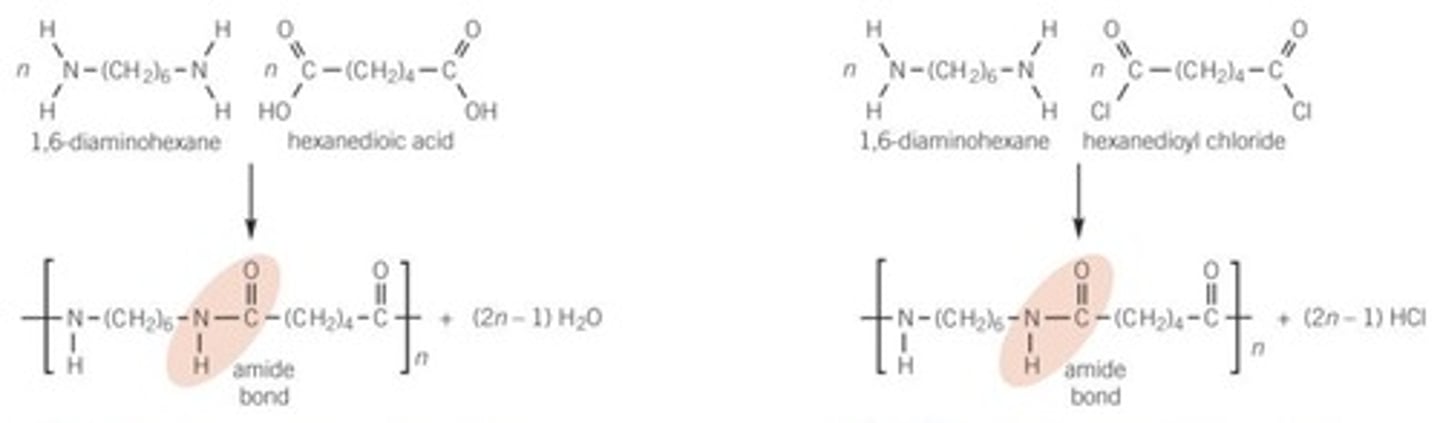
Polyamides from two monomers each with two functional groups
can be made with a diamine and a dicarboxylic acid (or acyl chloride)
What are the two reagents you can use to hydrolyse condensation polymers?
Hot aqueous alkali
Hot aqueous acid
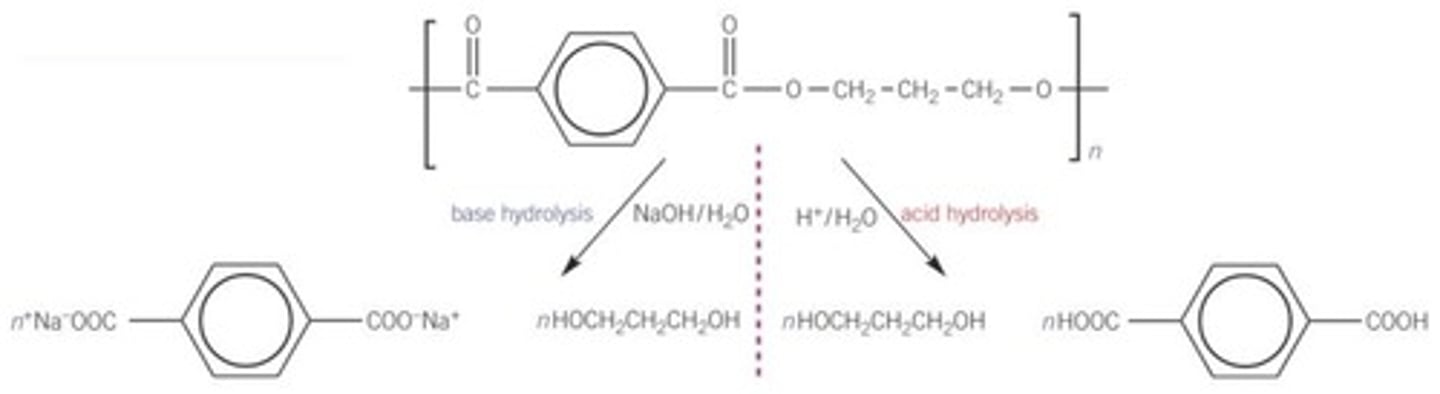
Hydrolysing polyesters
alkali hydrolysis forms a carboxylate ion salt
Hydrolysing polyamides
the H+ in acid hydrolysis can protonate COO- to COOH and NH₂ to NH₃+ in the monomers produced. there isn't a proton in base hydrolysis so this doesn't happen.
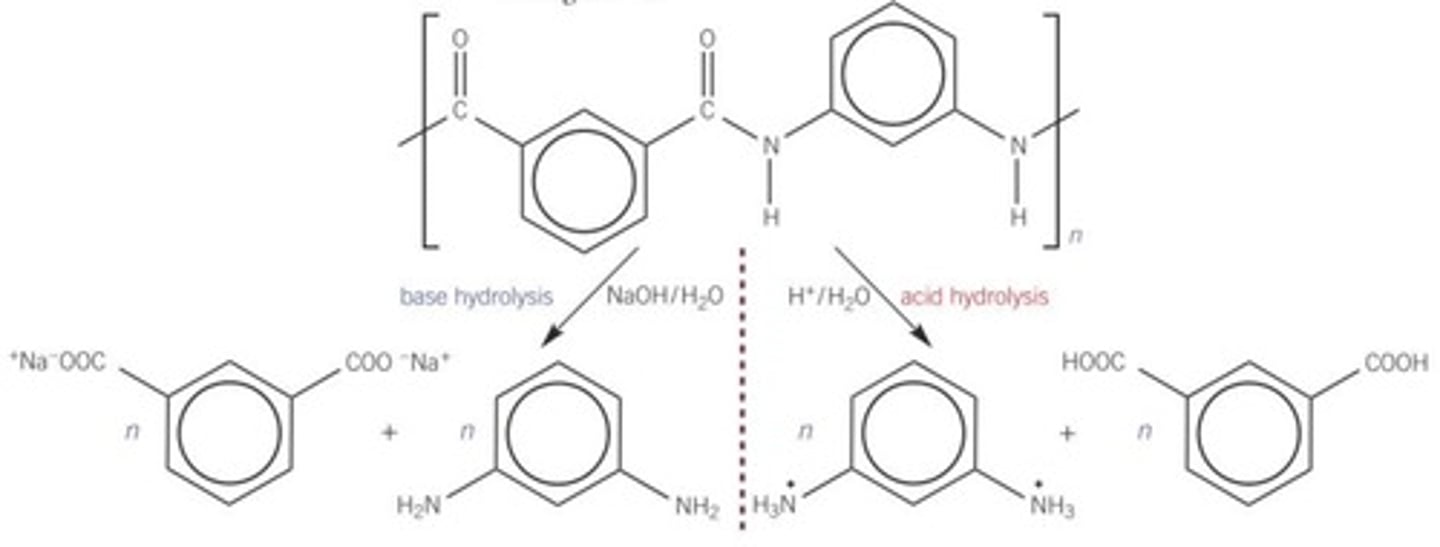
Summary of acid and alkali hydrolysis on condensation polymers (regarding NH2 and COOH)
Hot aqueous acid = NH3+ and COOH
Hot aqueous alkali= NH2 and COO-