Extra Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:17 AM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
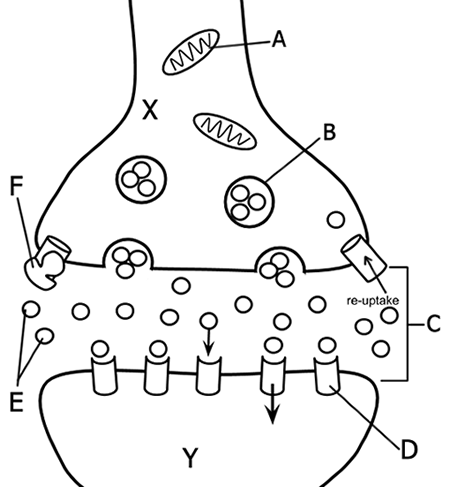
Label Each of the Letters
2
New cards
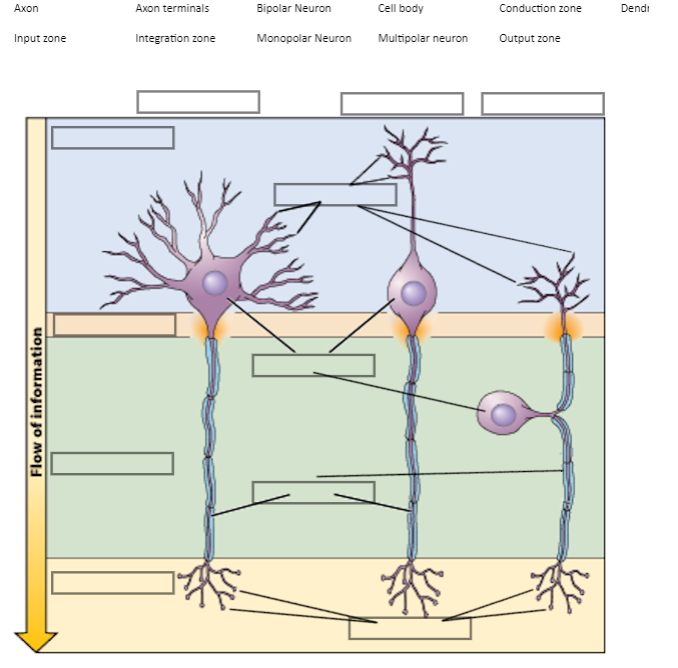
Label Each Component of the Neuron
1. Axon
2. Axon Terminal
3. Bipolar Neuron
4. Cell body
5. Conduction zone
6. Dendrites
7. Input Zone
8. Integration zone
9. Monopolar Neuron
10. Multipolar Neuron
11. Output Zone
1. Axon
2. Axon Terminal
3. Bipolar Neuron
4. Cell body
5. Conduction zone
6. Dendrites
7. Input Zone
8. Integration zone
9. Monopolar Neuron
10. Multipolar Neuron
11. Output Zone
3
New cards
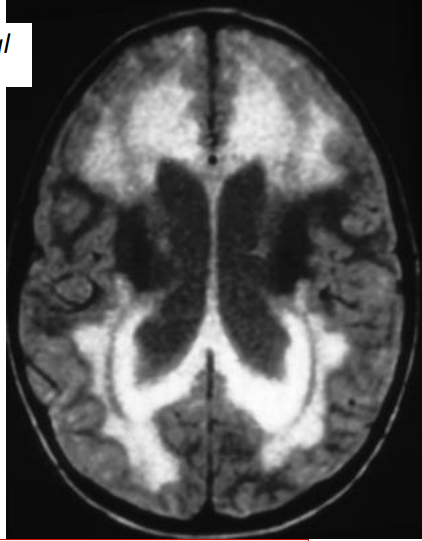
What disease is this
Alexander Disease
4
New cards
What is Alexander Disease?
the mutation of GFAP genes that causes the overproduction of GFAP protein causing cell to fail.
5
New cards
Astrocytoma
Type of Cancer that form in the brain or spinal cord
6
New cards
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
autoimmune disorder, where the body attacks and damages the myelin sheath of its own nerves
disrupts communication between the brain and body and causes symptoms such as vision loss, pain, fatigue, and impaired coordination.
\n
disrupts communication between the brain and body and causes symptoms such as vision loss, pain, fatigue, and impaired coordination.
\n
7
New cards
What nerve is effected by Multiple Sclerosis?
Oligodendrocytes
8
New cards
What is HIV/AIDS Encephalitis?
Viral-Activated Microglia produce neurotoxins such as glutamate and NO, which damage the brain
9
New cards
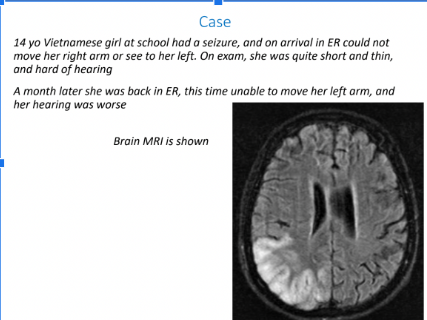
What is the Diagnosis?
Viral Activated Microglia
10
New cards
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The autonomic nervous system is the type of nervous system that activates when you panic
11
New cards
Medial
Toward the middle
12
New cards
Ipsilateral
Same Side
13
New cards
Anterior
Head End
14
New cards
Proximal
Near Center
15
New cards
Dorsal
Toward the Back
16
New cards
Lateral
Toward the Side
17
New cards
Contralateral
Opposite side
18
New cards
Posterior
Tail End
19
New cards
Distal
Toward Periphery
20
New cards
Ventral
Toward the belly
21
New cards
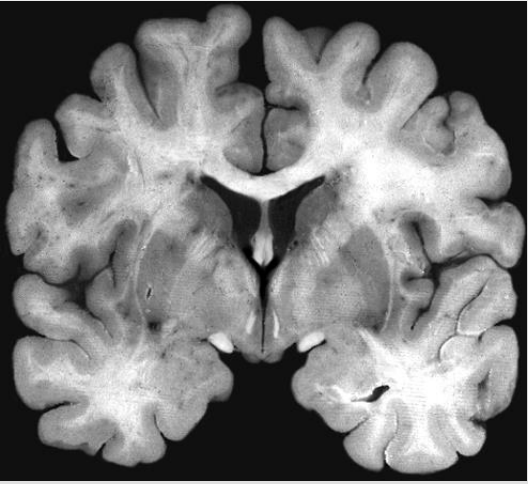
What is Coronal?
Separates the brain from front to back (Butterfly)
22
New cards
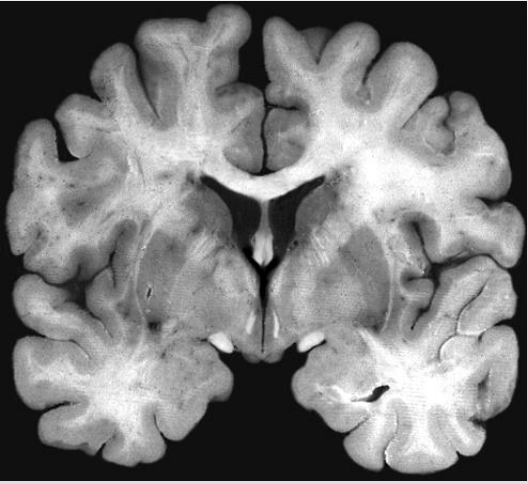
What Is this
Coronal
23
New cards
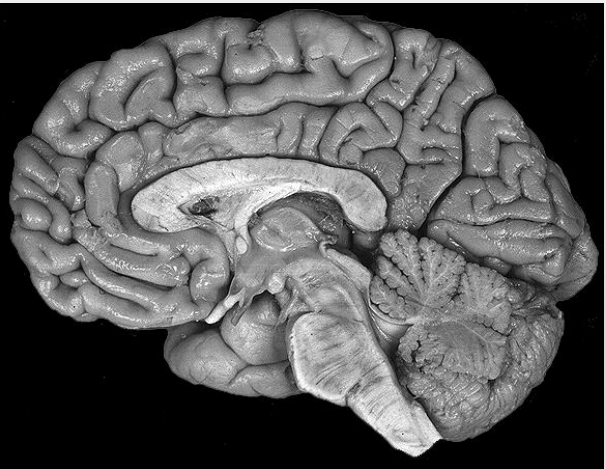
What is Sagittal?
Sagittal slices the brain down the midline and horizontal separates the brain from top to bottom.
24
New cards
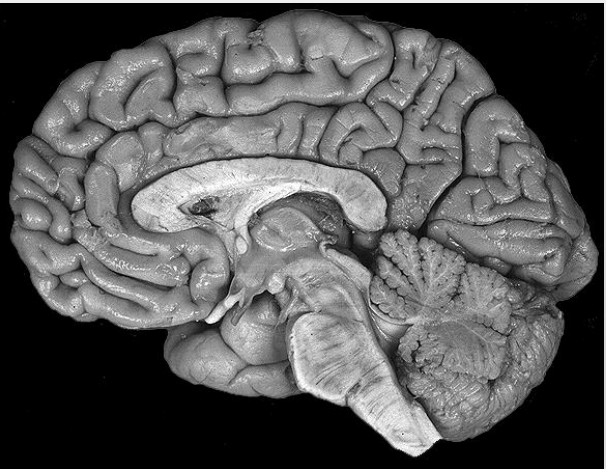
What is this?
Sagittal
25
New cards
What is Horizontal?
separates brain from top to bottom
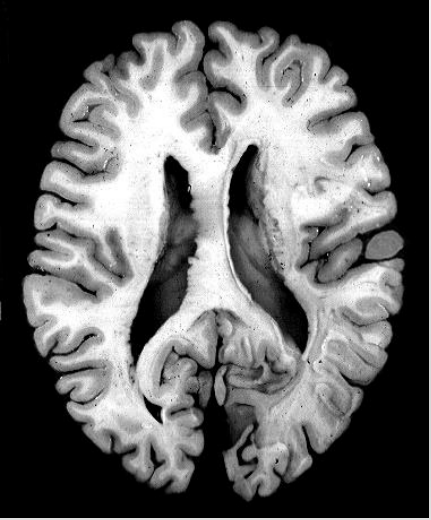
26
New cards
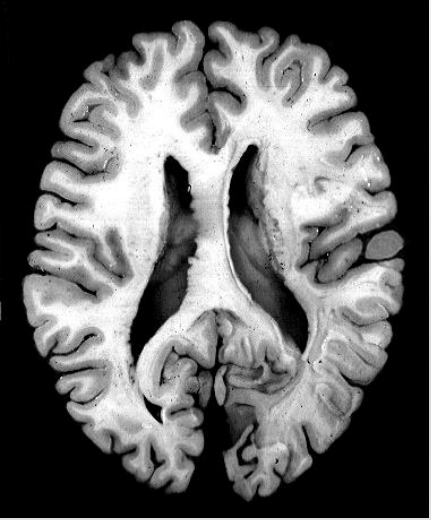
What is this?
Horizontal
27
New cards
Explain White Matter Vs Grey Matter
White Matter
* Composed Of an Axon bundle
* White because myelin sheaths cover the axon
Grey Matter
* Composed of clusters of neuron cell bodies
* have a dark grey appearance
* Composed Of an Axon bundle
* White because myelin sheaths cover the axon
Grey Matter
* Composed of clusters of neuron cell bodies
* have a dark grey appearance
28
New cards
What’s the Four Cortical lobes
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
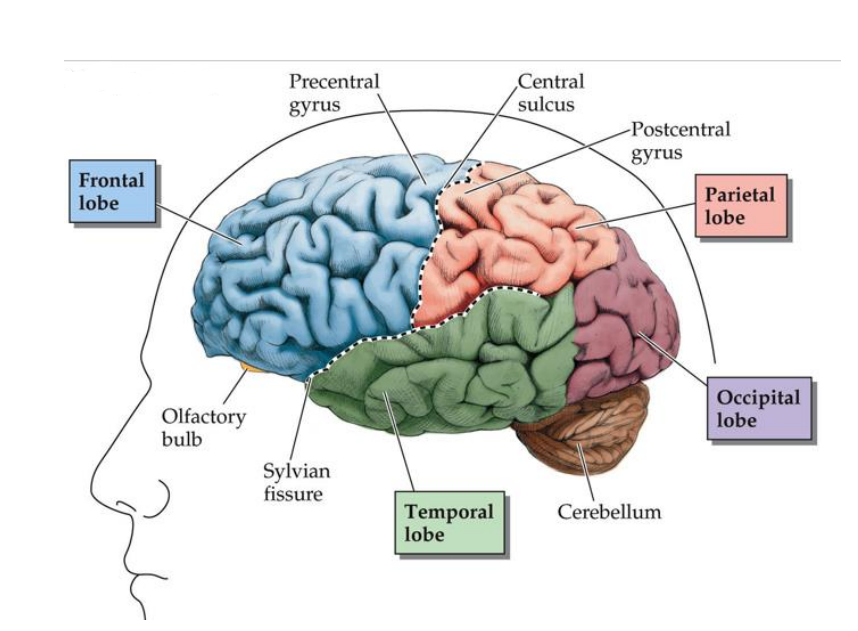
29
New cards
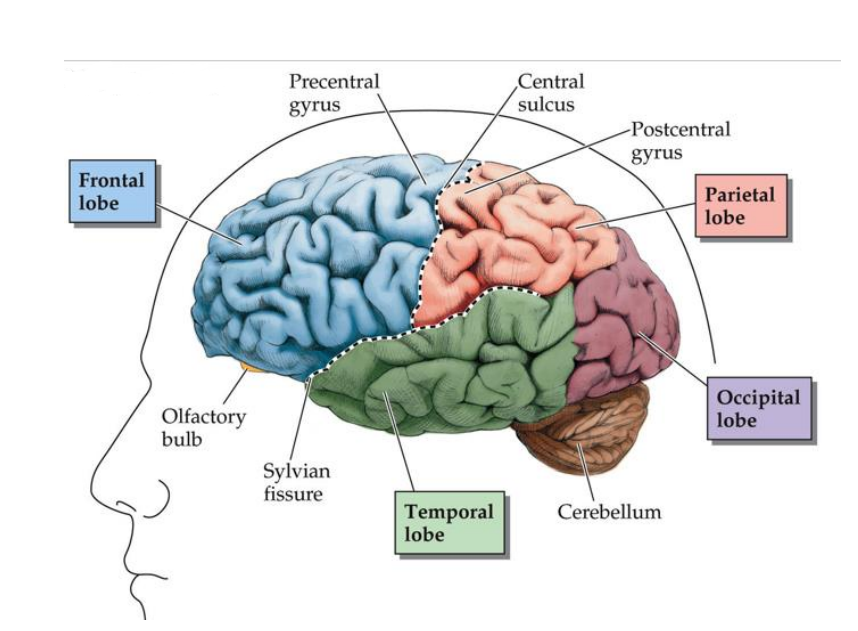
What view is this?
Lateral
30
New cards
What view is this?
Horizontal
31
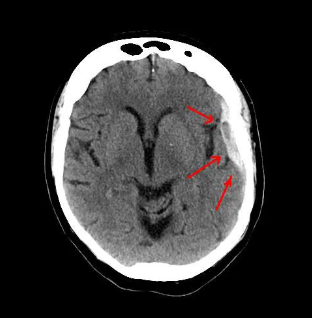
New cards
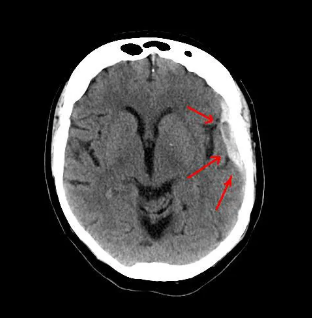
What is this diagnosis?
Subdural Hematoma
(Blood is in the subdural space but under the skull (underneath the dura)
(Blood is in the subdural space but under the skull (underneath the dura)
32
New cards
What affects the speed that information is transmitted?
* Neuron diameter (thicker = faster)
* Myelin sheath (more myelin = faster)
* Number of neurons involved (fewer = faster)
* Myelin sheath (more myelin = faster)
* Number of neurons involved (fewer = faster)
33
New cards
What benefits is there with larger neurons?
* Can make more connections
* Can cover greater distances
* Transmit information faster
* Can cover greater distances
* Transmit information faster
34
New cards