Biochemistry 8.5; Coenzymes, Vitamins, and Essential Metals
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What are coenzymes or cofactors?
Ions or small molecules that are bound to enzymes but are not irreversibly changed during catalysis
What vitamins and metals are used in redox reactions? (7)
1) Riboflavin (B2)
2) Niacin (B3)
3) Lipoic Acid
4) Fe
5) Cu
6) Mo
7) V
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of Thiamine (B1)
Thiamine pyrophosphate; Activation and transfer of aldehydes
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of pantothenic acid (B5)
Coenzyme A; Acyl group transfer and activation
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of pyridoxine
Pyridoxal phosphate; Various amino acid activation reactions
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of biotin (B7)
Biotin; CO2 activation and transfer
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of lipoic acid
Lipoamide; Redox and acyl group activation
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of folic acid (B9)
Tetrahydrofolate; Activation and transfer of single-carbon functional groups
What is the coenzyme and coenzyme reaction of B12
Adenosyl and methyl cobalamin; Isomerizations and methyl group transfers
What is the related enzyme and role of Zn
Alcohol dehydrogenase; Helps bind NAD+
What is the related enzyme and role of Mn
Histidine ammonia lyase; Aids in catalysis by electron withdrawal
What is the related enzyme and role of Co
Glutamate mutase; part of cobalamin coenzyme
What is the related enzyme and role of Ni
Urease; catalytic site
What is the related enzyme and role of Se
Glutathione peroxidase; replaces S in one cysteine active site
What is the related enzyme and role of Mg
Many kinases; Helps bind ATP
What does the complexity of globular protein structure and variety of side-chain structures allow?
The formation of many kinds of catalytic sites
What does the variability of catalytic sites allow?
Allows enzymes to act as catalysts for many reactions.
What is important to note about coenzyme structure?
Complex organic structures that cannot be synthesized by some organisms (especially mammals).
What is another name for the water-soluble vitamins?
vitamin-B complexes
Why are the water soluble/vitamin-B complexes so important in metabolism?
They are precursors of several coenzymes.
What is an important concept regarding vitamin precursors?
Many essential vitamins are constituents of coenzymes
What is a major example of the nicotinamide nucleotides?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucelotide (NAD+)
What is NAD+ derived from?
Niacin
What are the oxidized forms of NAD?
O) NAD+
R) NADH
What is closely related cofactor of NAD?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)
How does NADP differ from NAD?
NADP has a phosphoryl group at the 2’ position of the ribose attached to the adenine base.
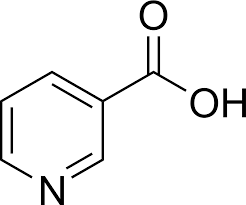
/What vitamin is this
Niacin (B3)
What are vitamin deficiencies often associated with?
Nutritional disease
How was the concept of a vitamin first described?
Observation that beriberi could be treated by thiamine
Where is thiamine present naturally?
Unpolished but not refined rice
What does a niacin deficiency cause?
Pellagra
Where is pellagra common?
Populations with high malnutrition or chronic alcoholism
What part of NAD+ is responsible for its metabolic functions, and why?
The nicotinamide portion because it can be reduced and serve as an oxidizing agent.
What does the oxidizing agent part of NAD do to a nicotinamide ring?
Adds 2 electrons and a proton.
Is the formation of NADH reversible?
Yes, and it is a reducing agent in some reactions.
What is the formal term for the reverse NADH reaction?
Hydride ion transfer
What is a typical reaction where NAD+ acts as an oxidizing agent?
The conversion of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones.
Which hydrogen is transferred to NAD+ in the NADH reaction?
The C-linked H, NOT the O-linked H
Is the hydride ion transfer stereospecific?
Yes.
How can a H be favored when the substrate molecule has a plane of symmetry?
It depends on the asymmetric nature of the enzyme surface that the NAD+ and the alcohol are bound.
What must happen for two atoms to be called prochiral?
The molecule itself must be bound by at least 3 points to an asymmetric object.
Why is the transfer of a hydrogen in a prochiral reaction always to a specific face of the ring?
The two faces are NOT equivalent in the asymmetric active site of an enzyme.
In what cases is a NAD+ acting more like a second substrate than a true cofactor?
After oxidizing the substrate, the reduced form (NADH) leaves the enzyme and reoxidized and ready to bind to another enzyme.
How is NAD+ different from most substrates?
They are continually recycled in the cell and- like a catalyst- continually ready to be reused by the cell.
“Metalloenzymes”
Metal ions that act like a coenzyme and giving the enzyme a property it would not possess in its absence.
What is an important concept regarding metal ions?
Some enzymes require metal ions for their catalytic function.
What is a reaction of a zinc metalloenzyme?
The reaction of carboxypeptidase A binding the water molecule that attacks the carbonyl of the scissile bond and acts as an electrostatic catalyst.
What does the zinc ion do in the carboxypeptidase reaction?
Stabilizes the tetrahedral oxyanion in the transition state and the intermediate state.
What is another use of the metal in a metalloenzyme?
Sometimes serve as a redox reagent.
Why is the iron in catalase an electron exchanger?
It involves reduction and oxidatoin of H2O2 and is reversibly oxidized and reduced.
Why is Mg2+ necessary in most ATP reactions?
The Mg-ATP complex is a better substrate than ATP itself.