AP Bio - Heredity
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
trait
genetically determined variant of a characteristic
how does inheritance determined by multiple genes differ from mendelian inheritance?
Why do organisms have two alleles for each gene?
Organisms are diploid, meaning that they inherit one allele from each parent for every gene. This allows for genetic variation through different combination of alleles
Genetic diversity arises in populations, not individuals - due to sexual reproduction, independent assortment, and crossing over during meiosis
What is independent assortment and how does it create genetic diversity?
Independent assortment is when chromosomes are randomly distributed into gametes during meiosis. This creates genetic diversity by mixing alleles, ensuring each offspring has a unique combination of genes
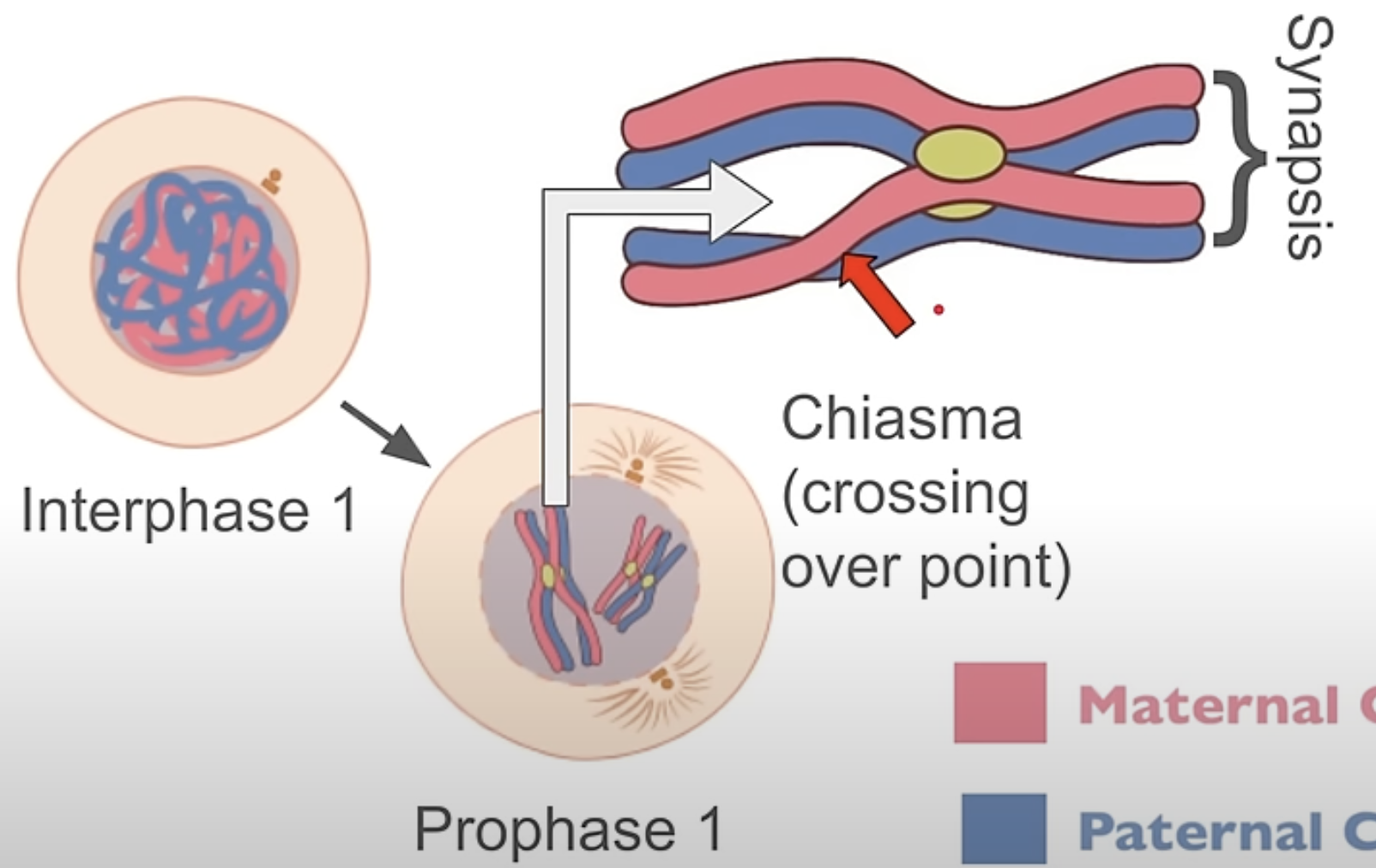
crossing over, and how does it create variation?
occurs during prophase 1 of meiosis, when homologous chromosomes pair up in a process called synapsis. At the chiasma, they exchange genetic material. This creates variation by producing new combinations of alleles, leading to genetically diverse offspring
P generation
parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
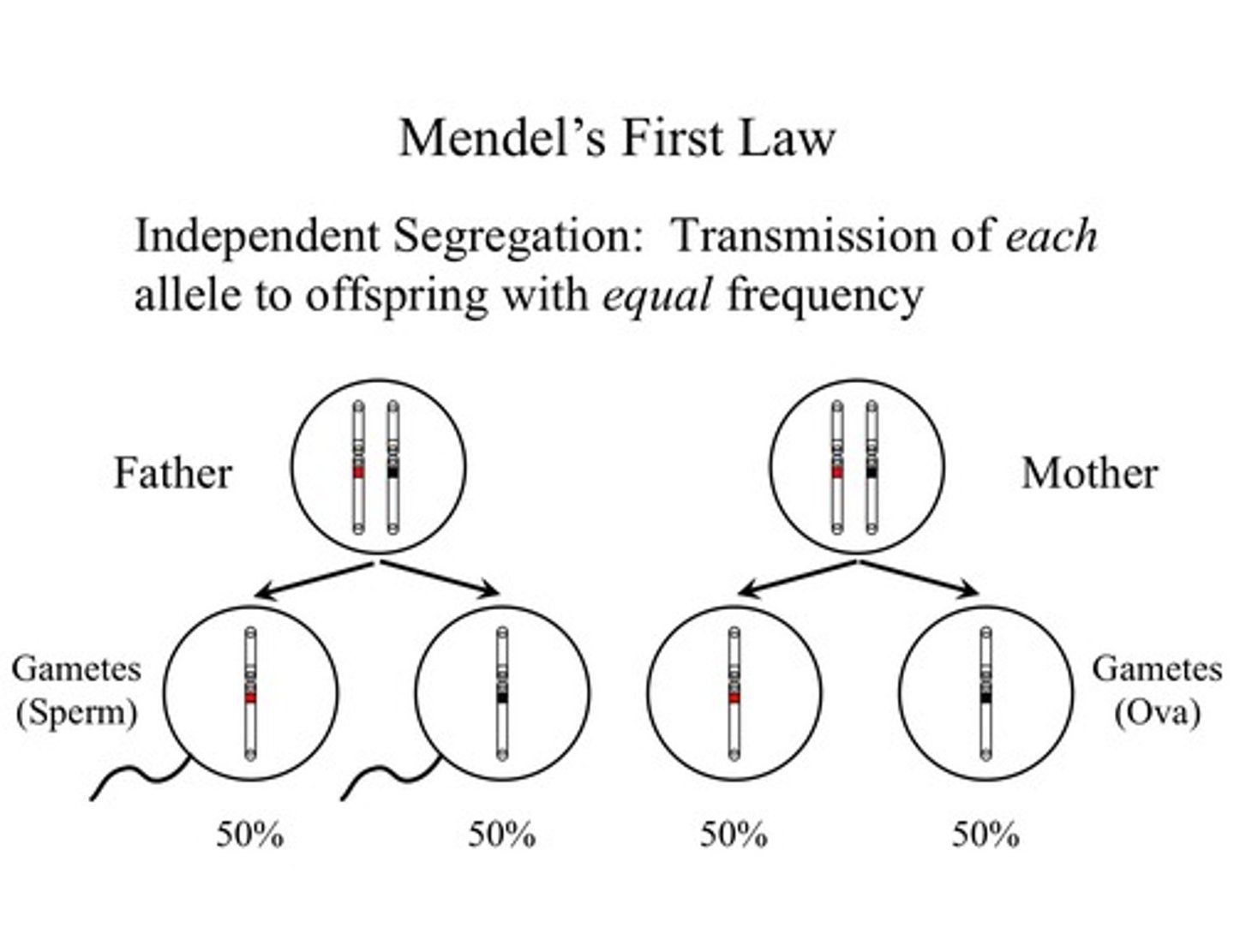
law of segregation
each individual has two alleles for a gene, and these alleles segregate during meiosis so that each gamete gets only one allele for that gene
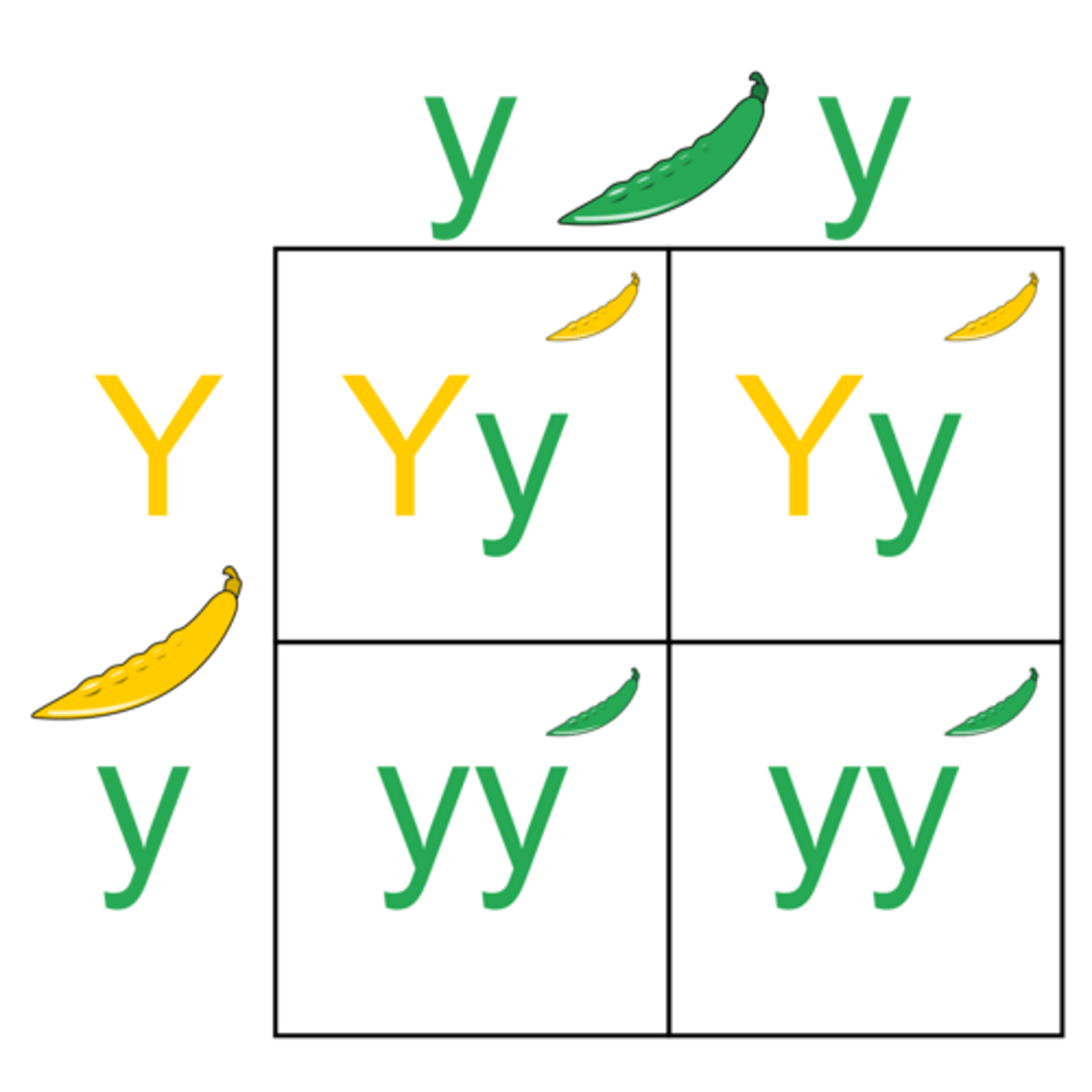
monohybrid cross
a cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
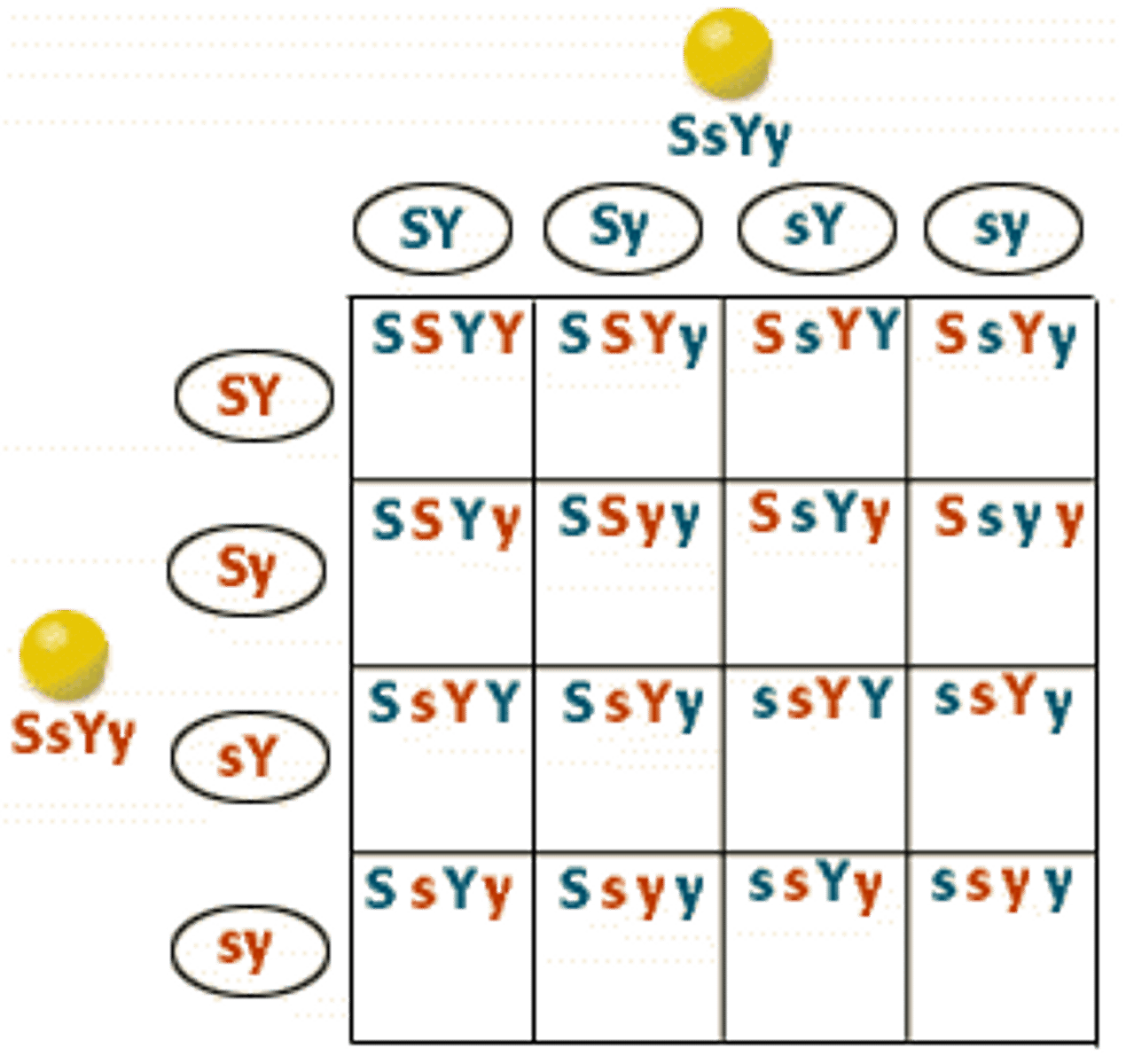
dihybrid cross
a cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
multiplication rule
The rule that states that to determine the probability, we multiply the probability of one event by the probability of another
addition rule
the probability that any one of two or more mutually exclusive events will occur is calculated by adding together their individual probabilities
codominance
a condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
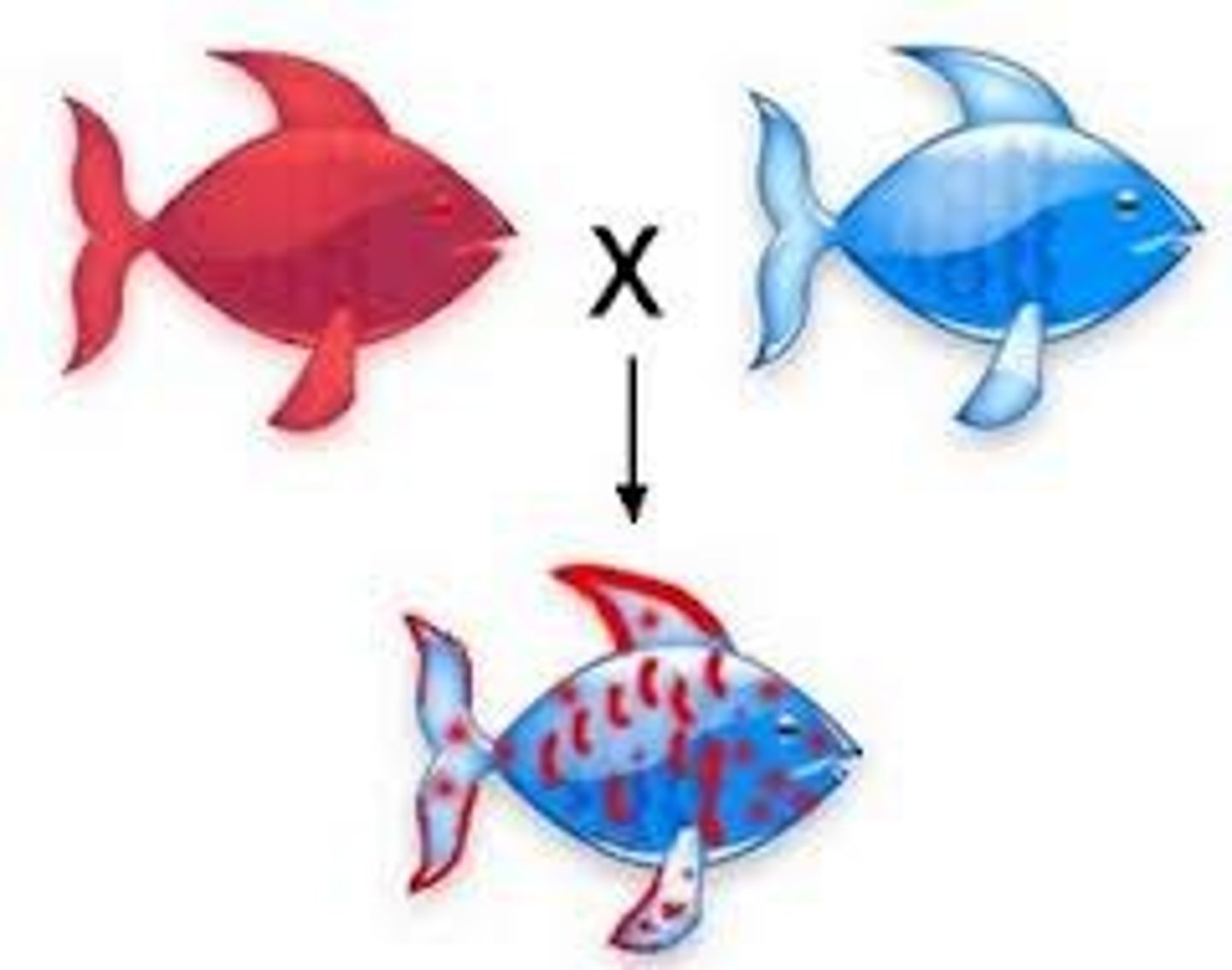
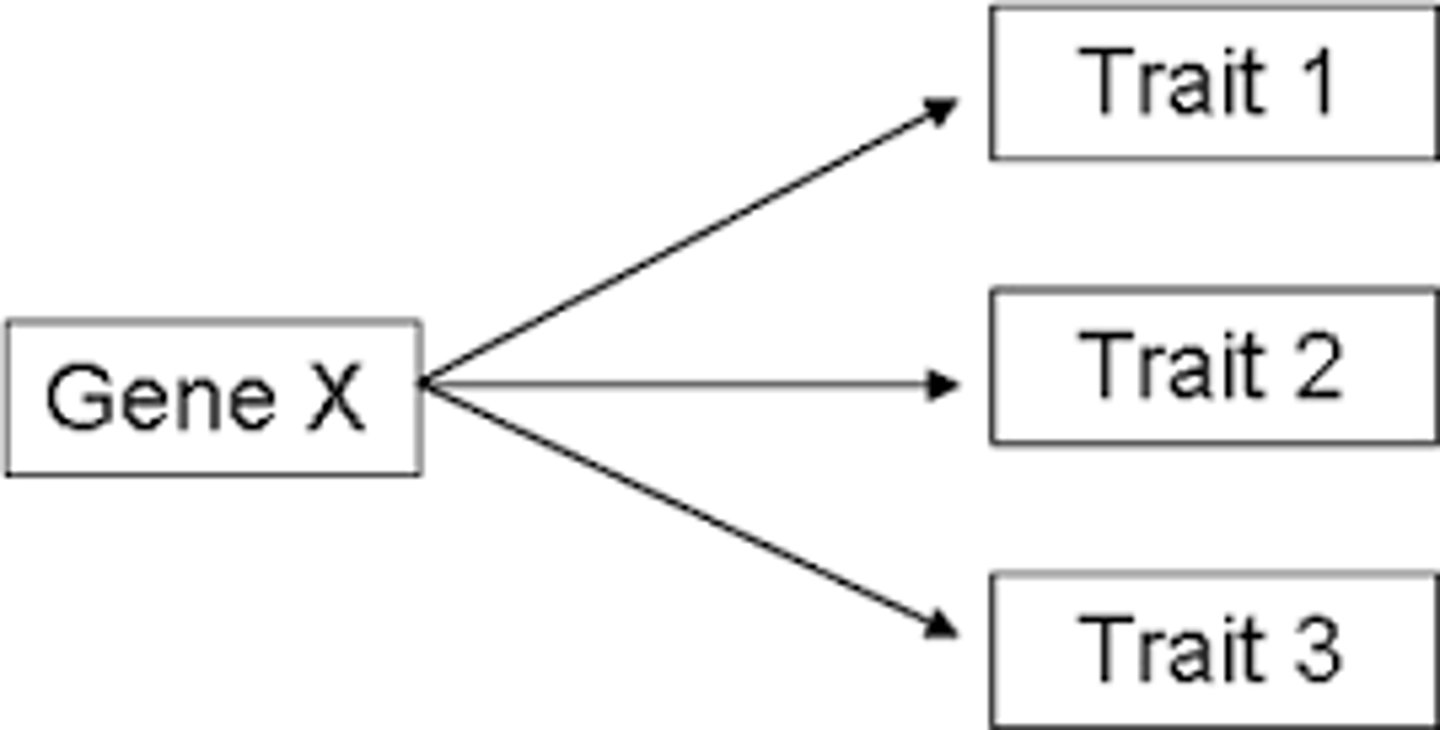
pleiotropy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
sex-linked dominant (pedigree)
more males than females affected. trait appears in every generation
barr bod
A dense body formed from a deactivated X chromosome.
non-nuclear inheritance
mitochondrial inheritance ( it is in the egg as well)
- chlorplasts contain DNA, in one circular double stranded molecule
- DNA apart from that found in the nucleus [e.g. mitochondria or chloroplasts] that is passed on to the next generation
phenotypic plasticity
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
oogenesis
Egg production
- 1 egg
- other three cells are polar bodies, getting a tiny amt of cytoplasm and eventually degenerate
- wants to conserve as much cytoplasm as possible for the surviving gamete, the ovum
translocation
- happens when recombination occurs incorrectly
Change to a chromosome in which a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome.
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
F2 generation
the second generation of offspring, obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms; the offspring of the F1 generation
alleles
different forms of a gene
dominant
observed trait of an organism that masks the recessive form of a trait
recessive
The inherited characteristic often masked by the dominant characteristic and not seen in an organism.
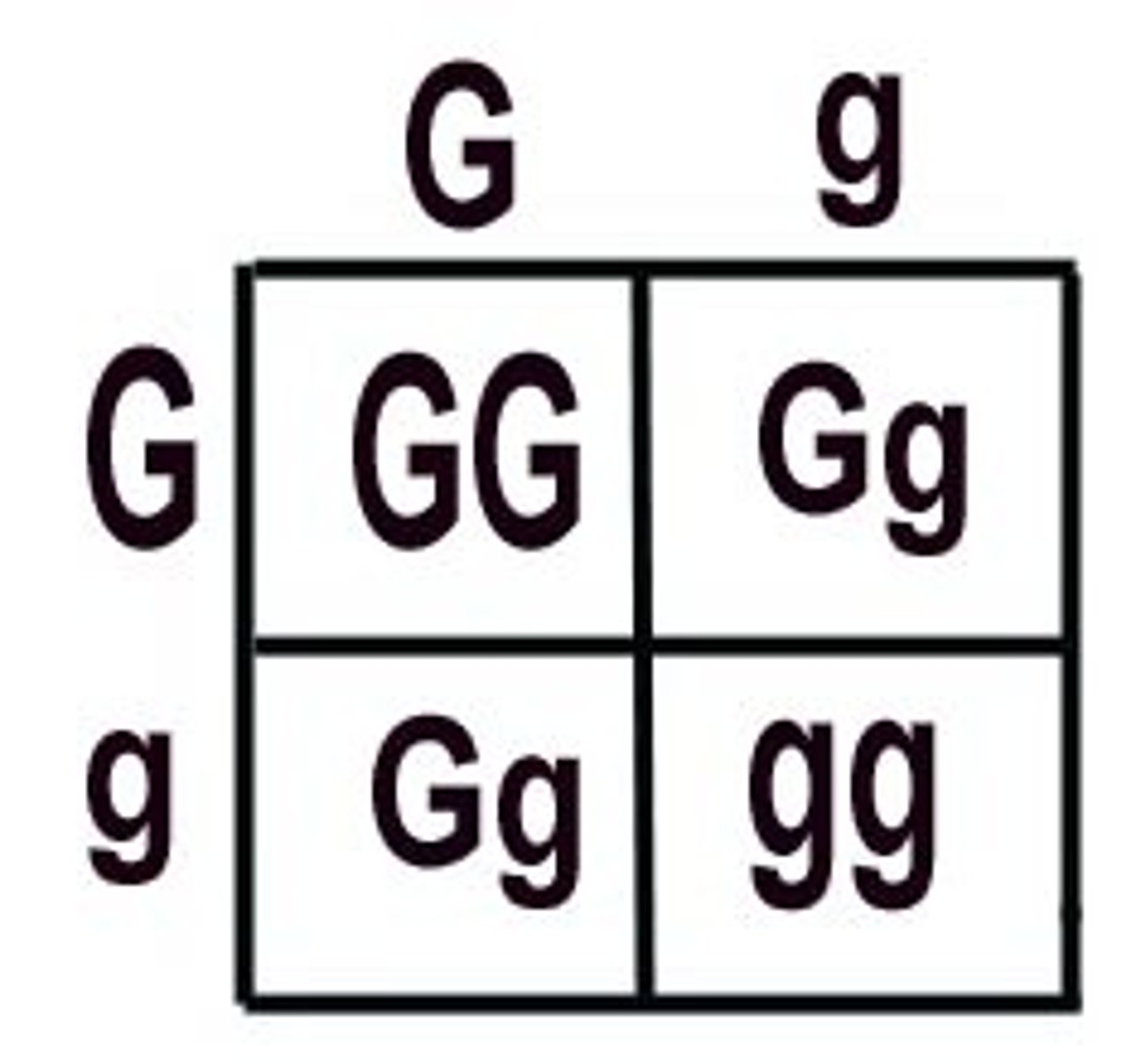
Punnett square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
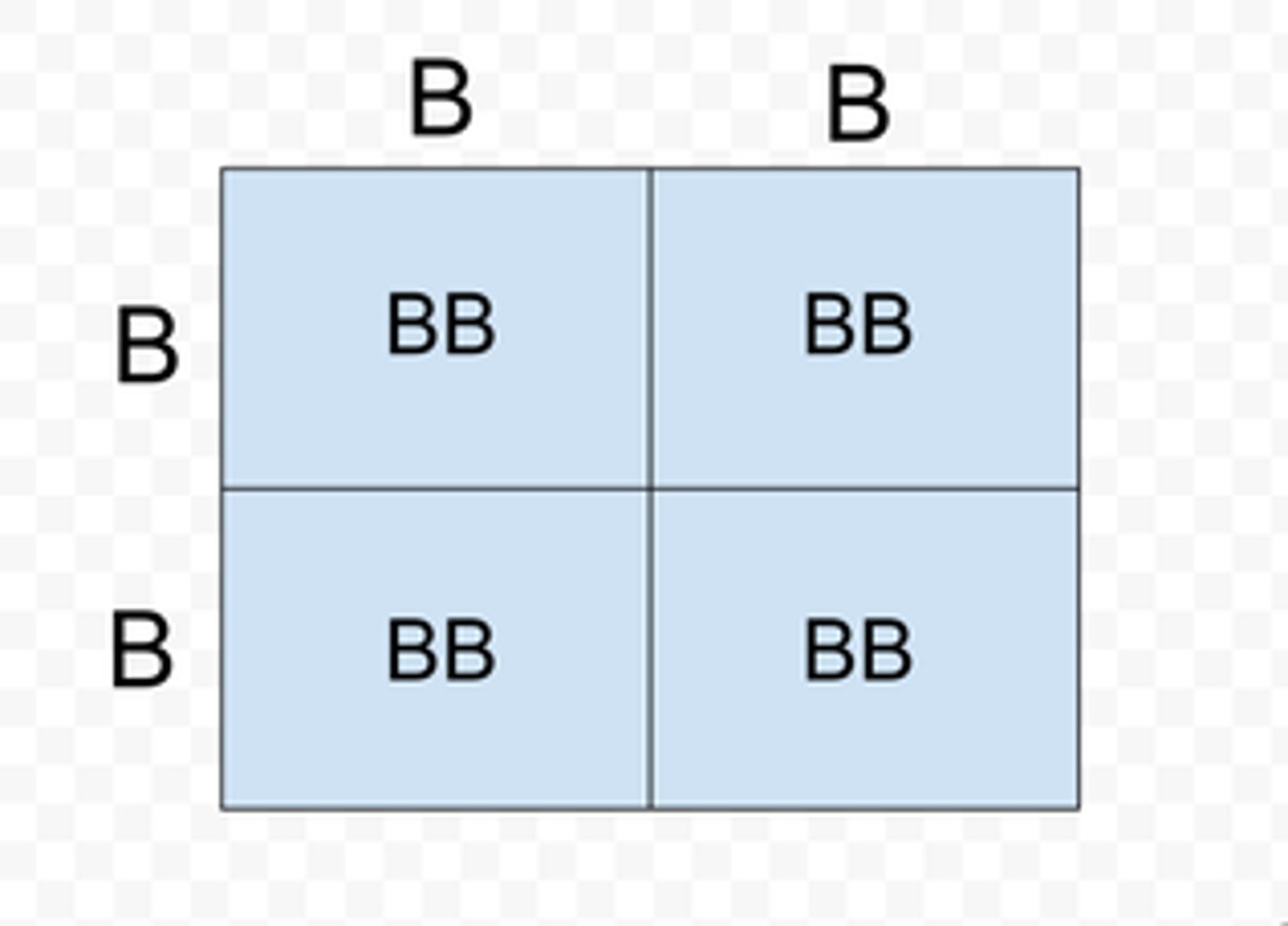
homozygous
having two identical alleles for a trait
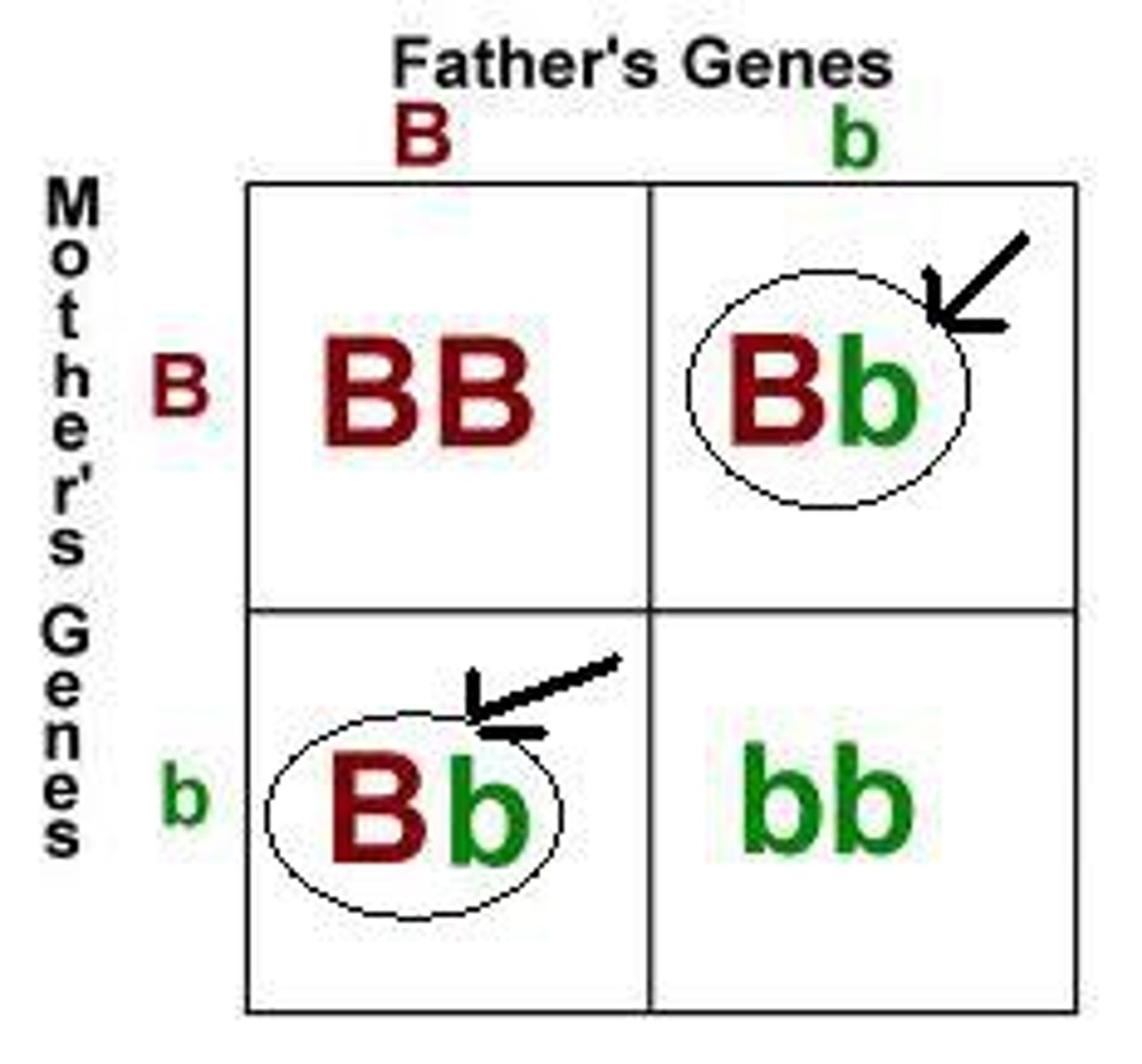
heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait
genotype
the particular alleles at specified loci present in an organism
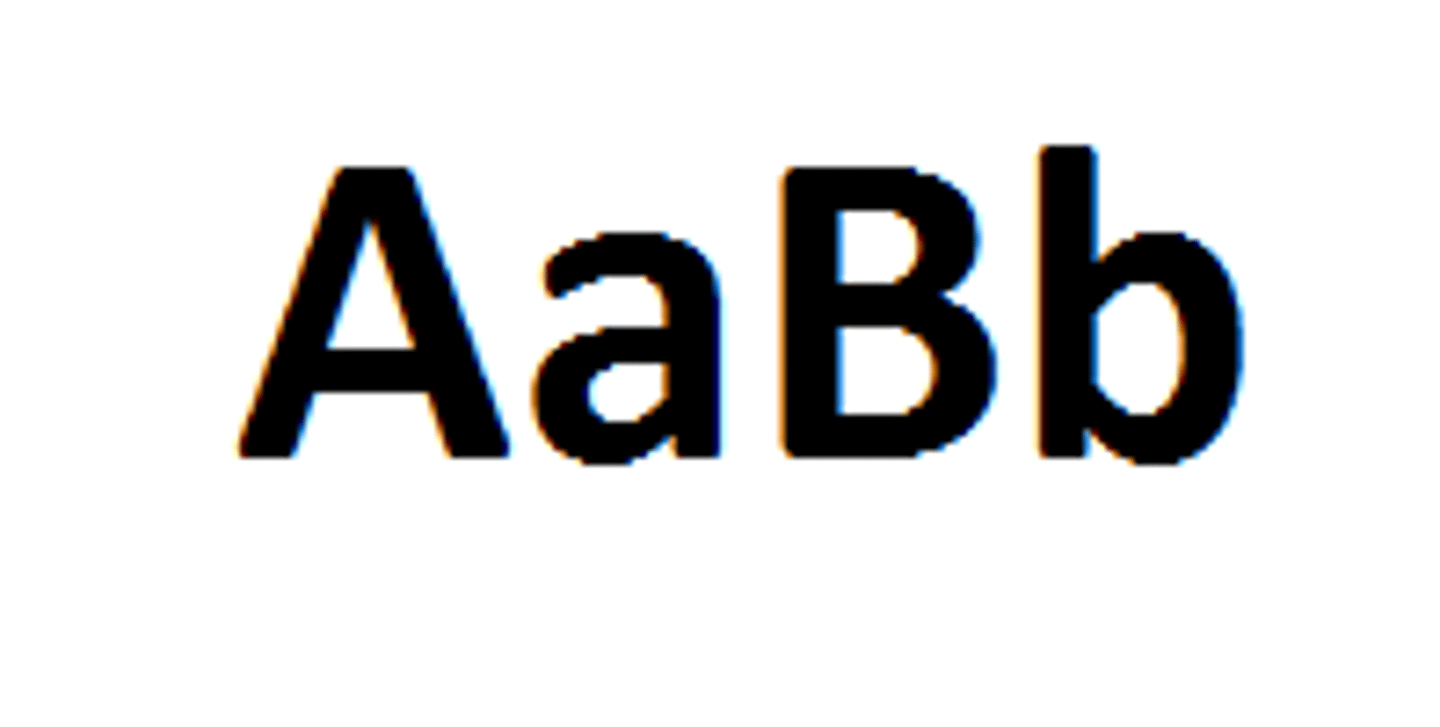
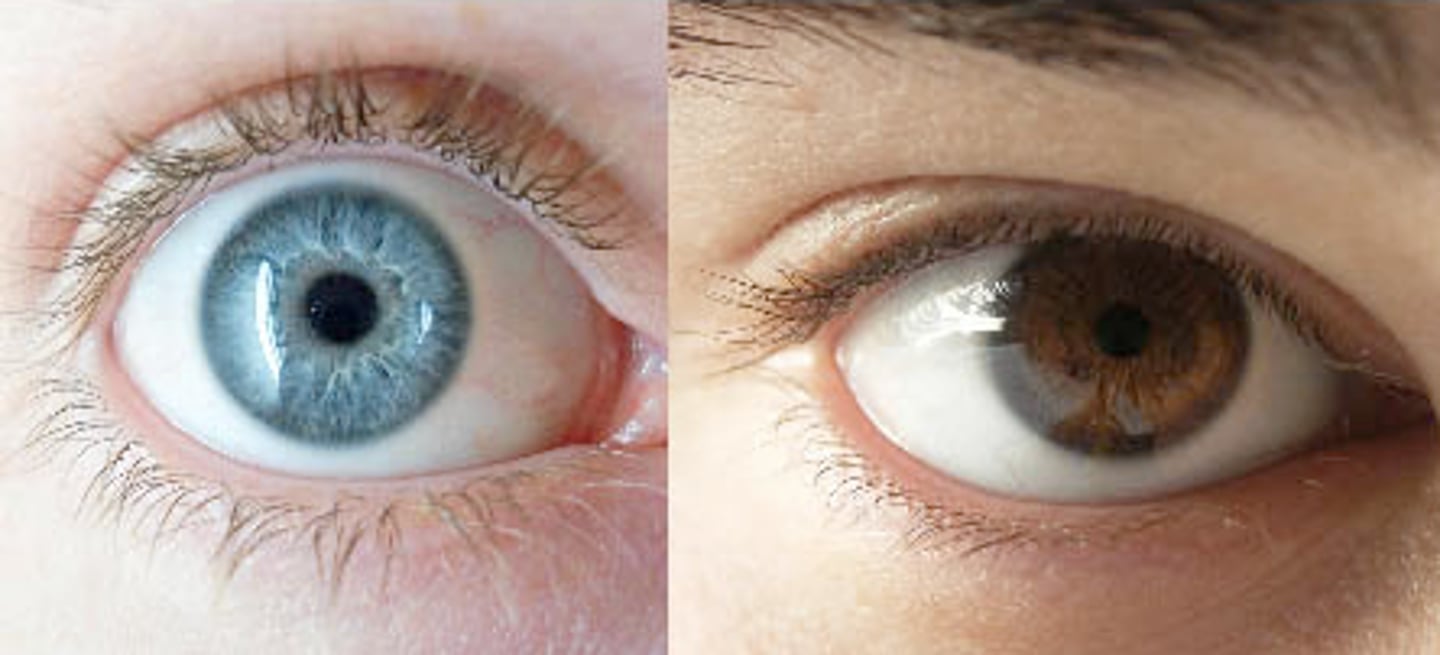
phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
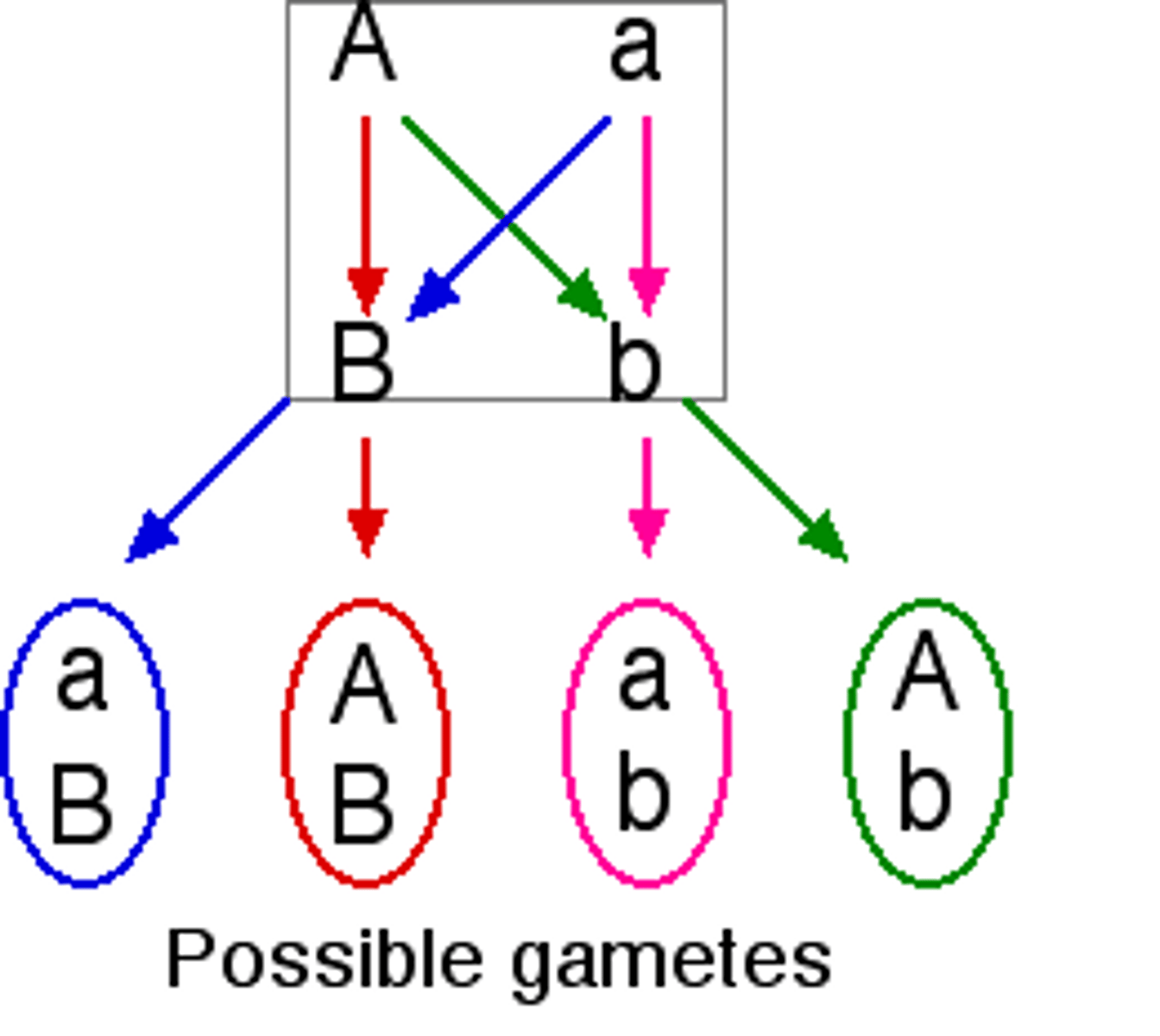
independent assortment
alleles for different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation
inheritance of one gene doesn’t affect the inheritance of another if the genes are on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosomes
happens during metaphase I of meiosis
complete dominance
a relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over another
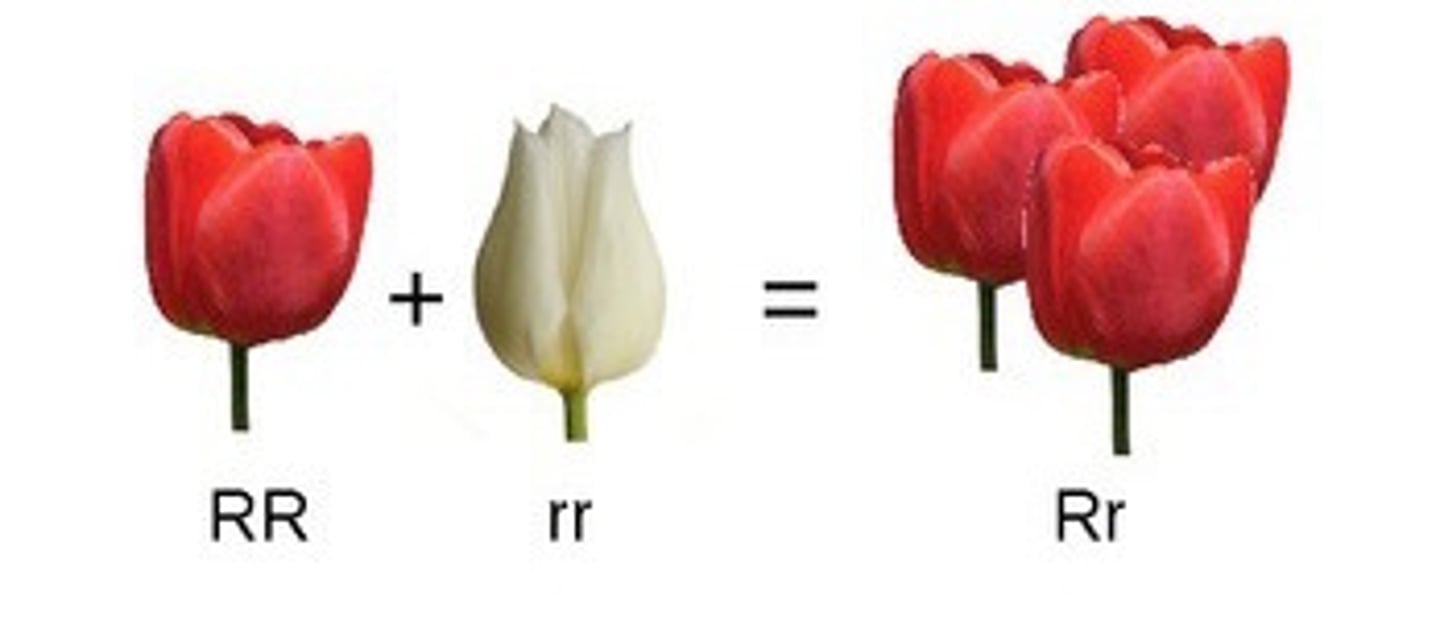
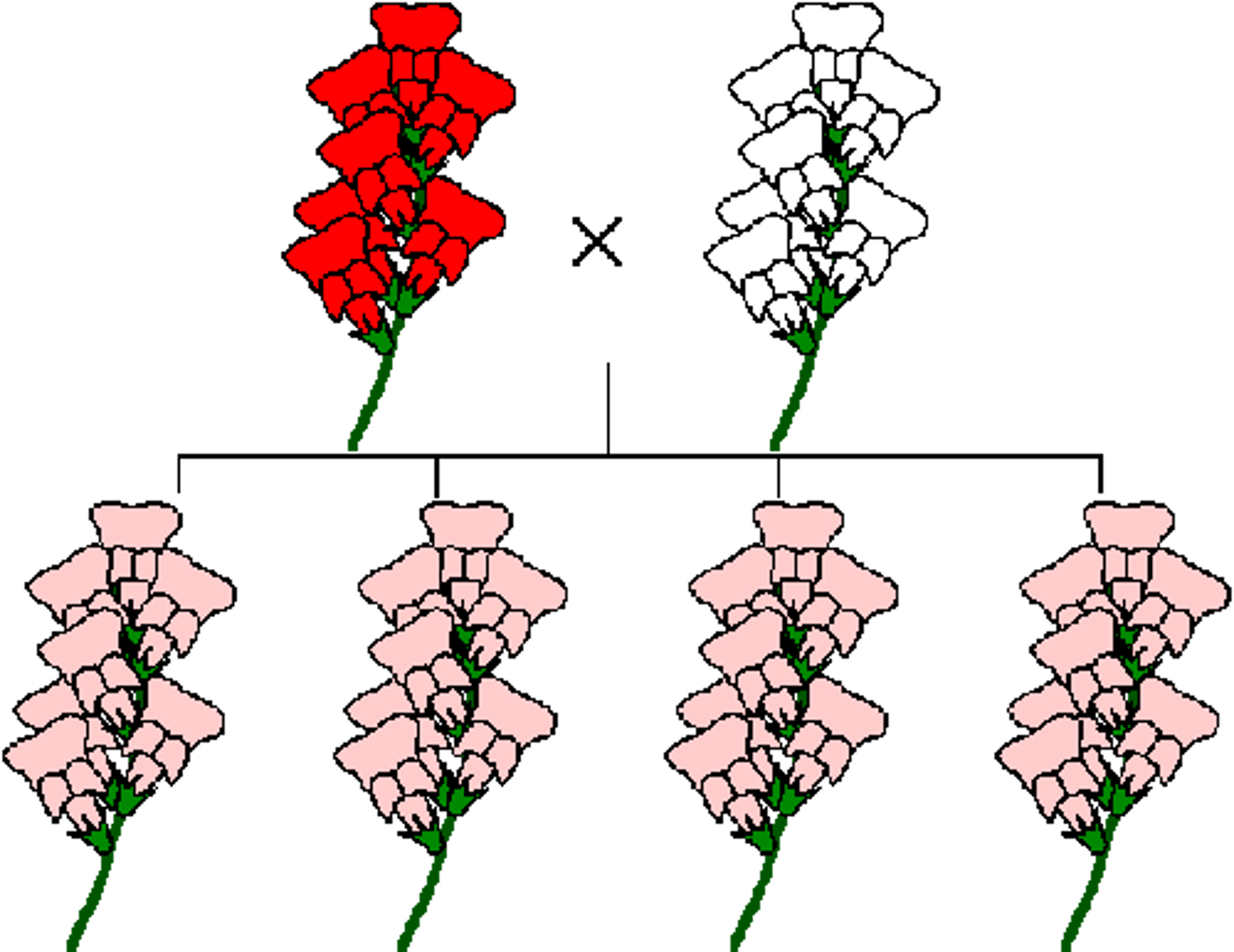
incomplete dominance
creates a blended phenotype; one allele is not completely dominant over the other
epistasis
the suppression of a gene by the effect of an unrelated gene
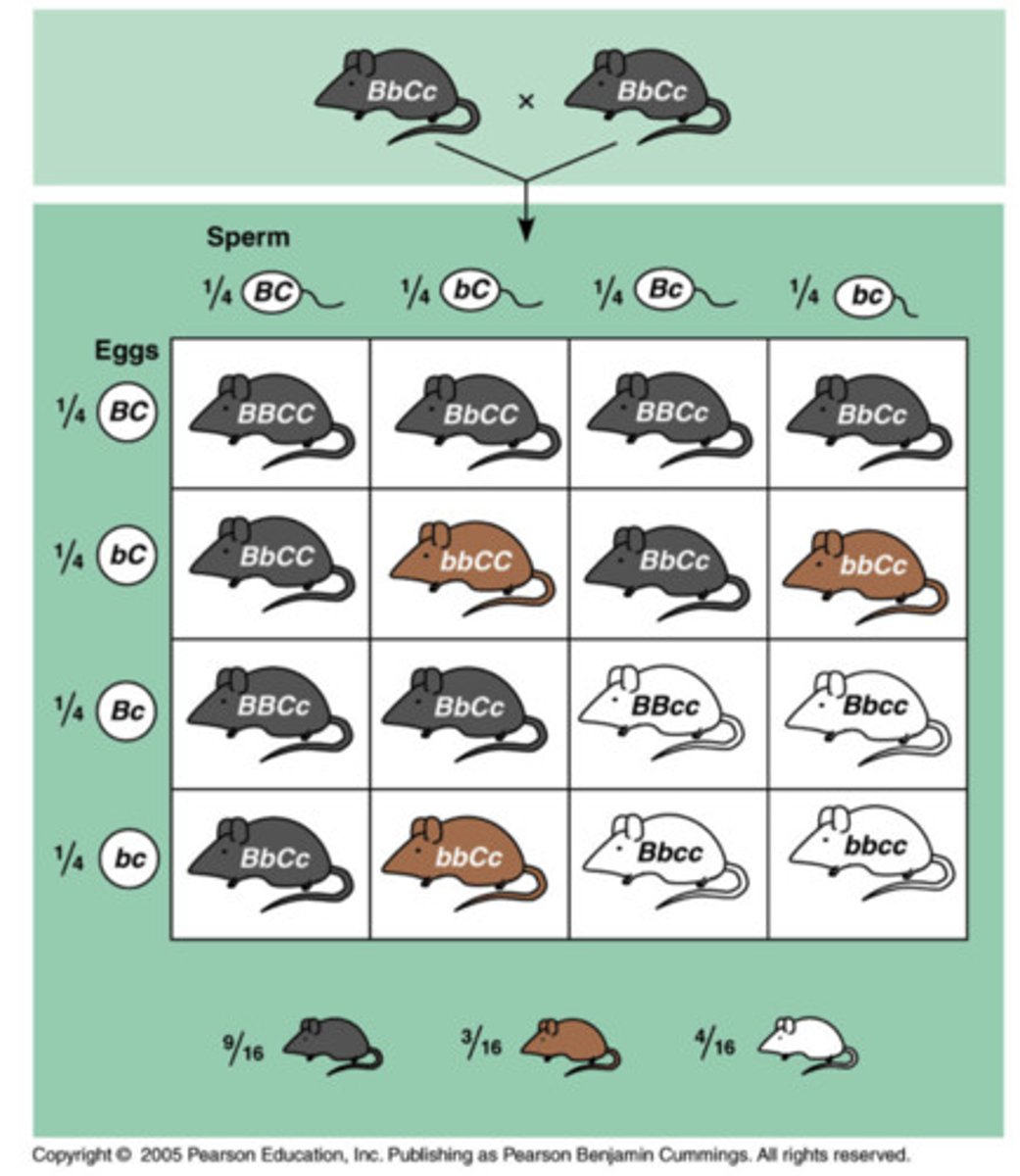
polygenic inheritance
An additive effect of two or more gene loci on a single phenotypic character.
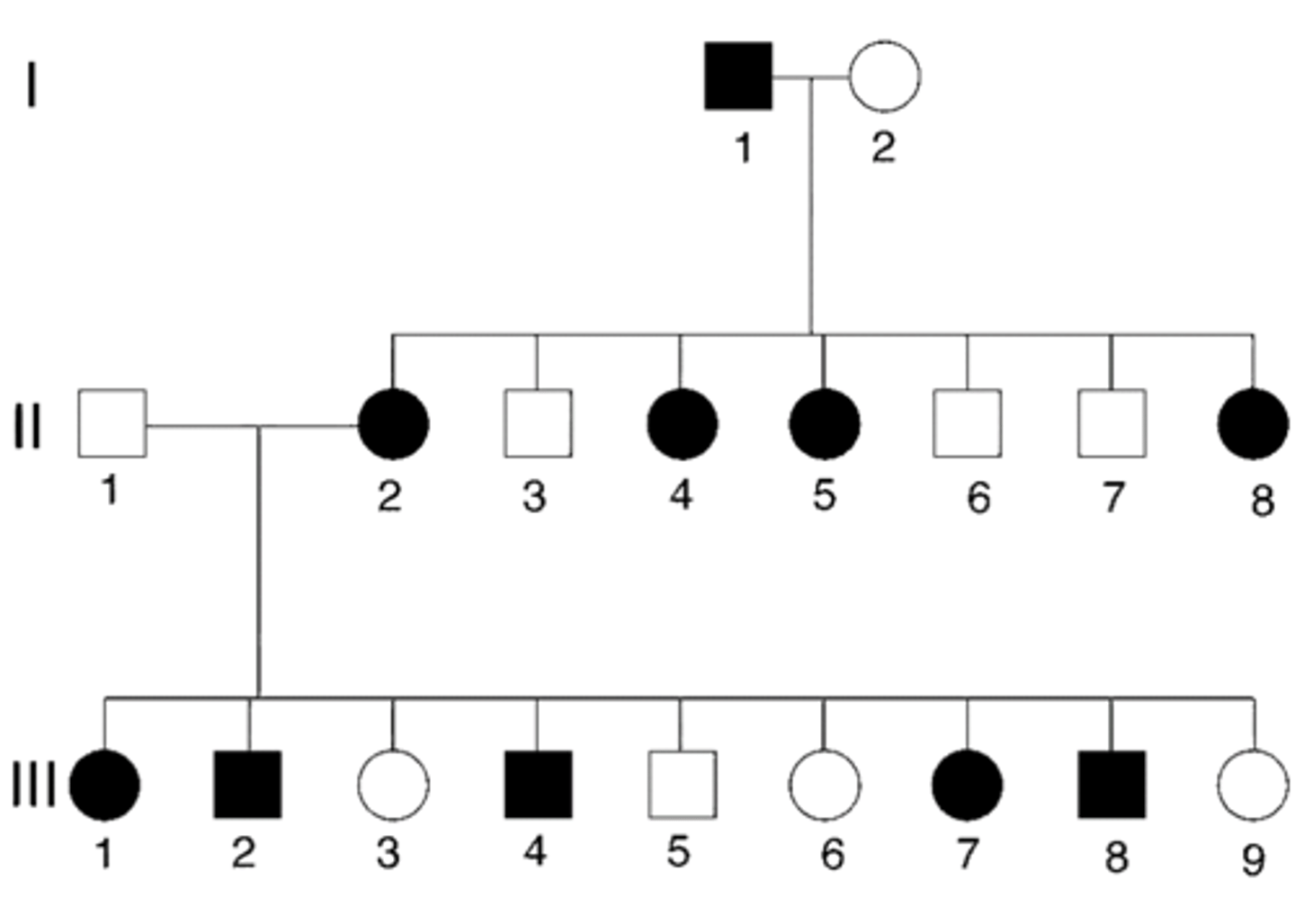
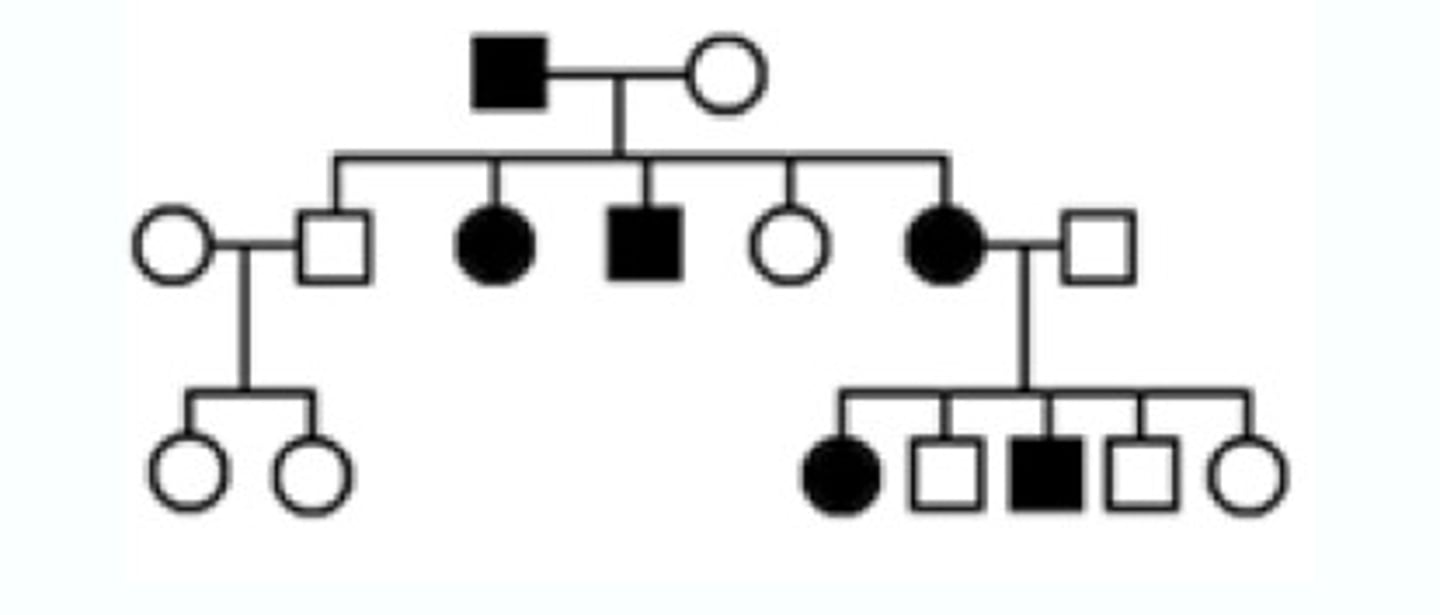
pedigree
a diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family
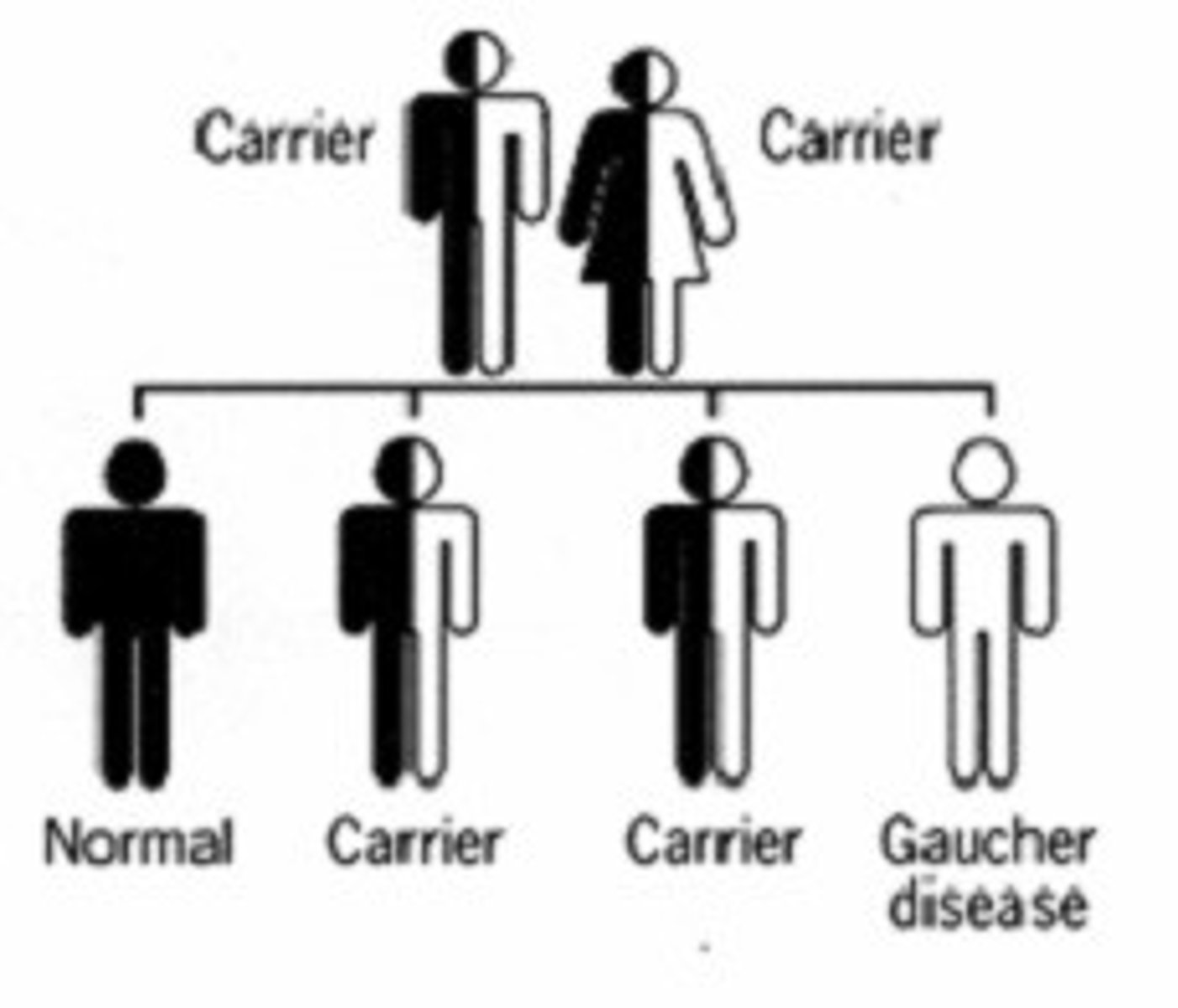
carriers
individuals who have one copy of a recessive autosomal allele
Chi-square test
a statistical test used to determine the probability of obtaining observed proportions by chance, under a specific hypothesis
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Allele
An alternative form of a gene.
Mitochondrial inheritance
Disease occurs in both males and females, inherited through females only
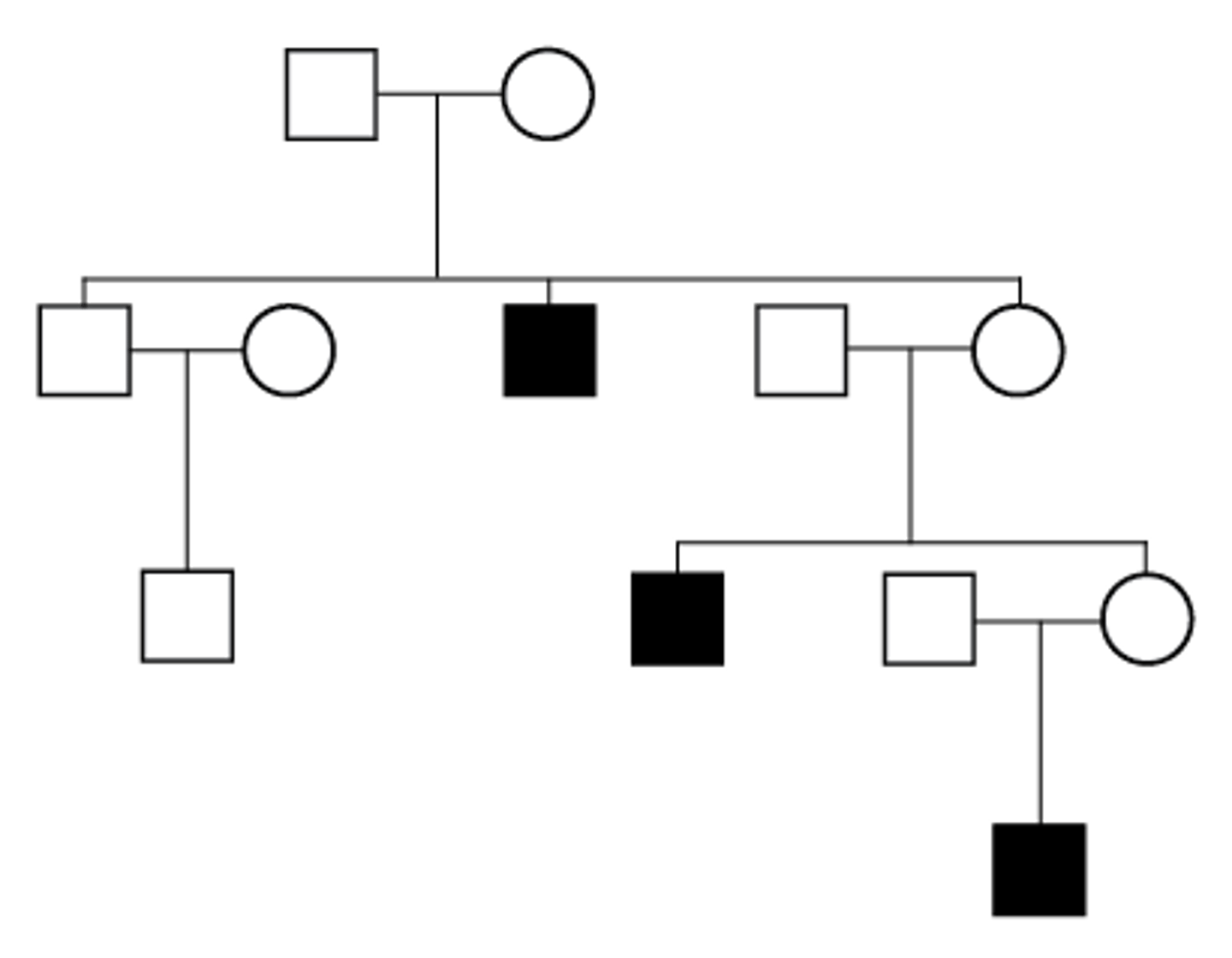
autosomal dominant (pedigree)
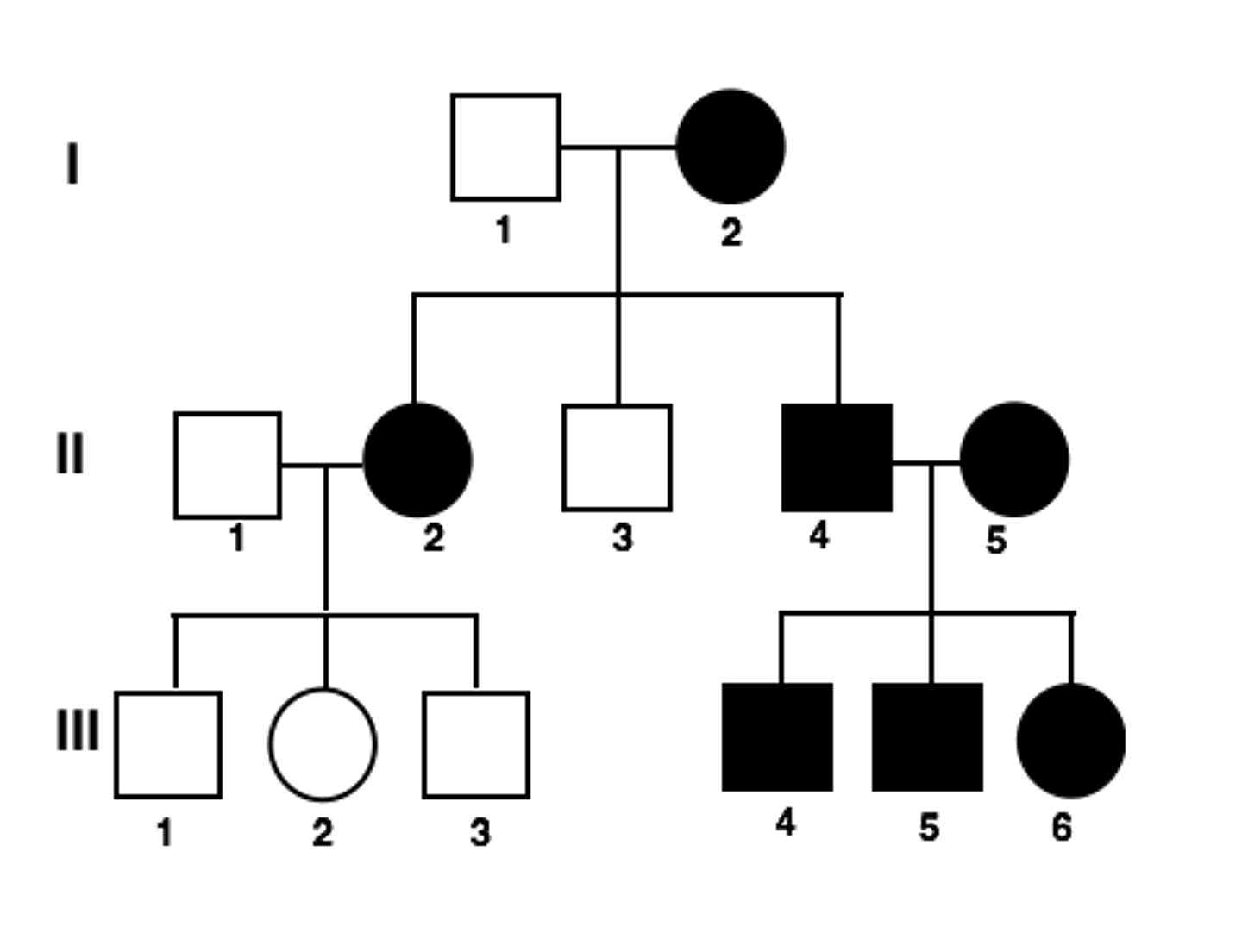
autosomal recessive (pedigree)
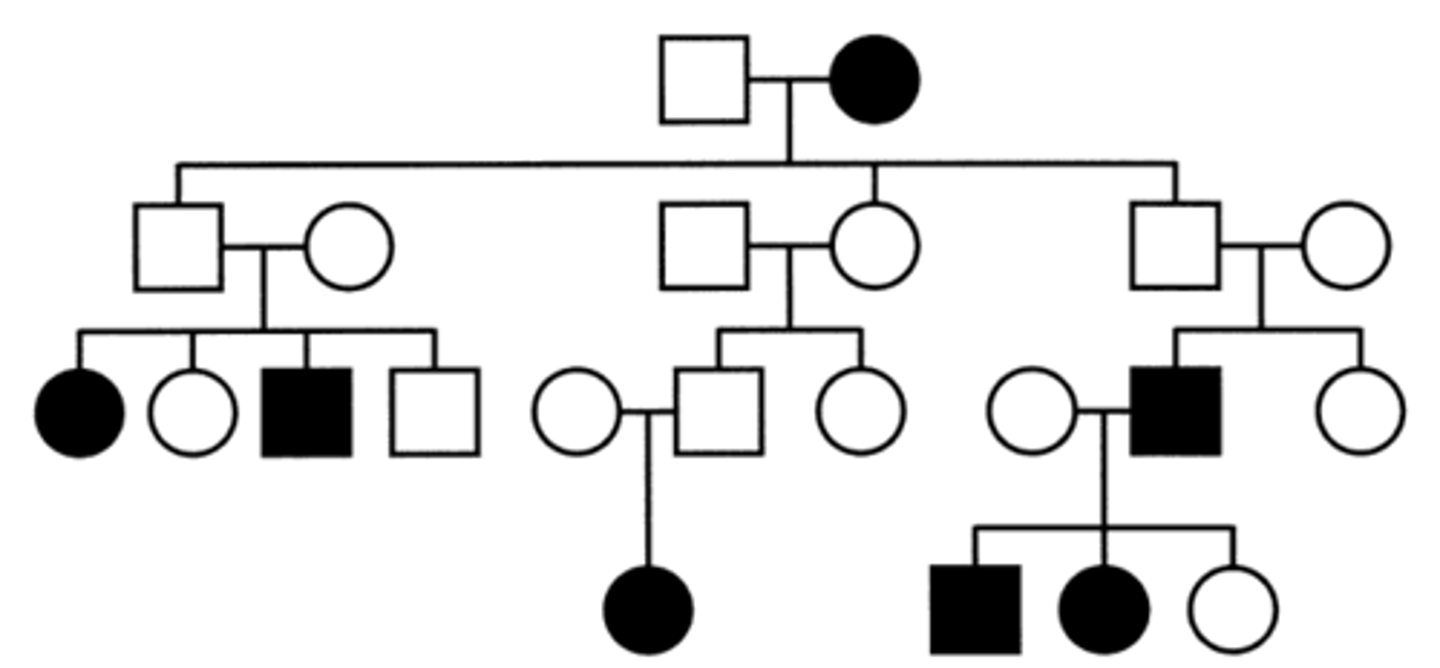
Mitochondrial inheritance (pedigree)
Transmitted only be females
ALL of females offsprings show sings of disease
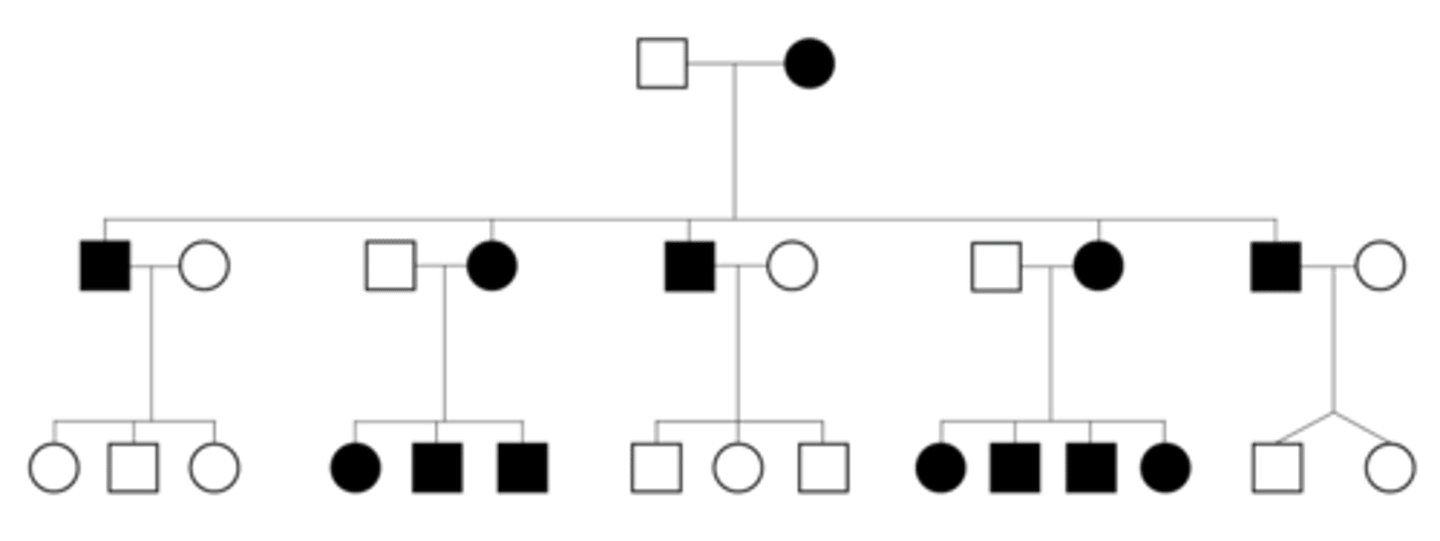
sex-linked recessive (pedigree)
Can skip generation, males more affected
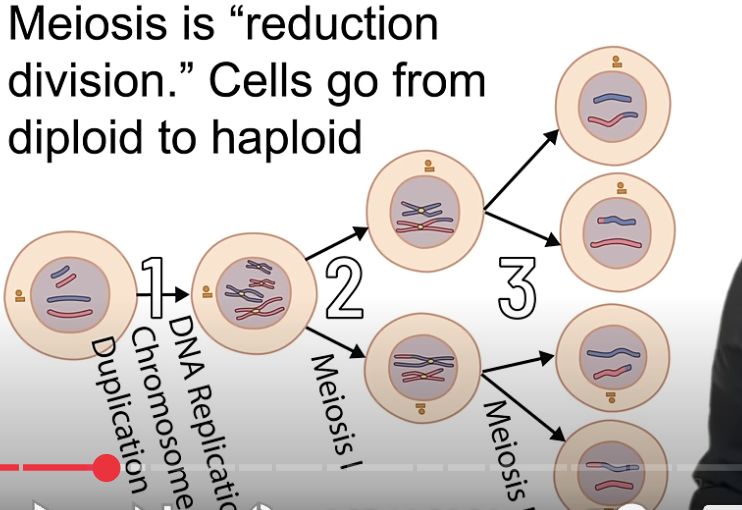
gametogenesis
production of gametes
spermatogenesis
Formation of sperm - four sperm cells produced for each diploid cell
reduction division
meiosis —> cells go from diploid to haploid
how does the law of segregation account for genetic variation?
the law of segregation states that each gamete only carries one allele for each gene, therefore each gamete receives only one allele - this provides opportunity for more varied combination when fertilization occurs
define nondisjunction and how it contributes to genetic variation
failure to fully separate during the formation of gametes
results in too many or too little chromosomes in the sex cells
how does fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms lead to genetic variation
genetically unique combinations of chromosomes are due to geneticaly uniquer sperm and eggs joining together
effect of chromosomal inheritance on genetic variation and human disorders
mutated alleles can be inherited
the law of segregation and independent assortment explain that mutated alleles can be randomly distributed into gametes
mutations can contribute to genetic diverstiy