Tissues: Levels of Organization and Types
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
White fat (WAT) cells
store lipids
Brown fat (BAT) cells
burn lipids to produce heat and energy
SWAT
gives adipose tissue its structural integrity.
Atoms
Make up molecules.
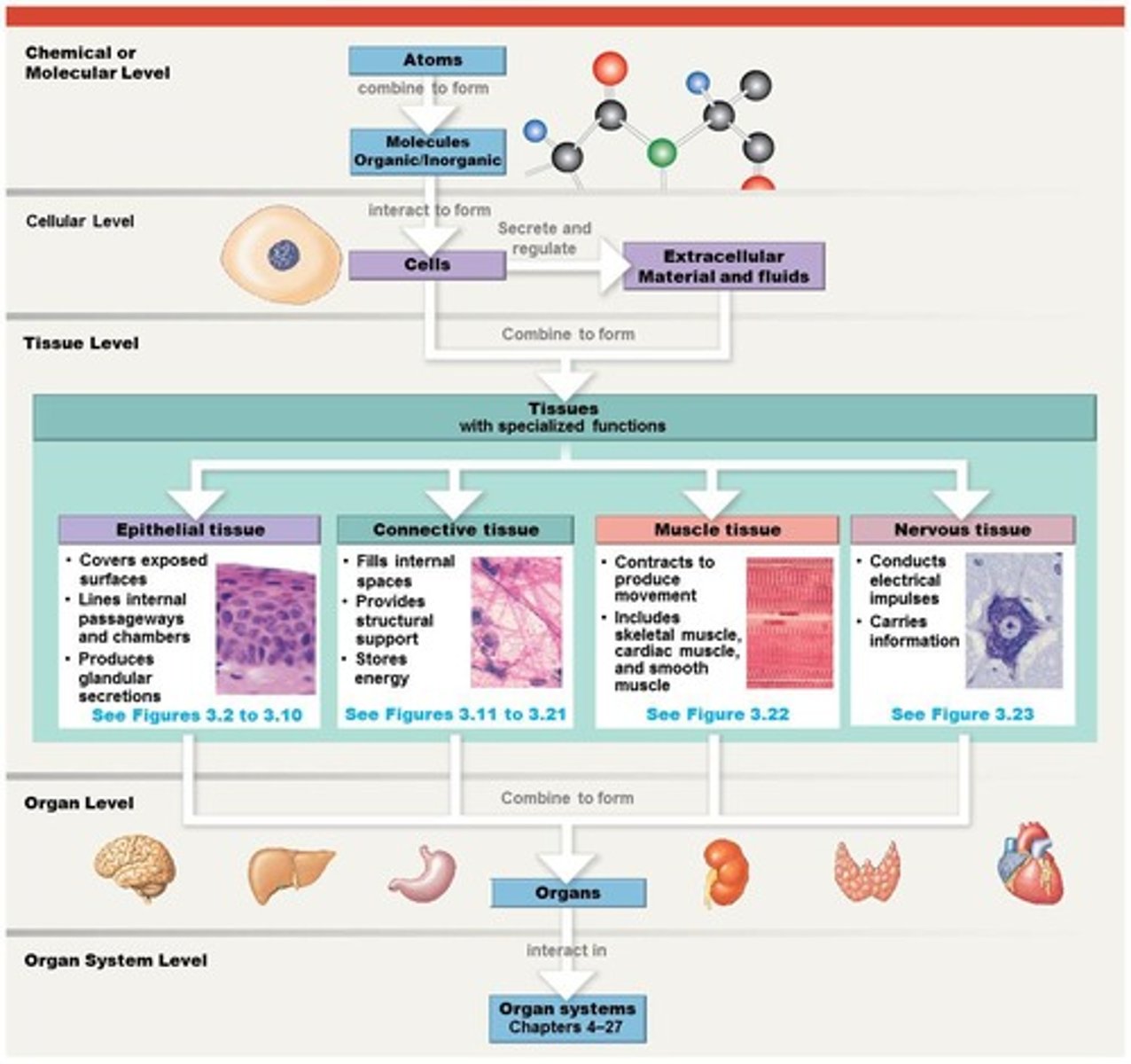
Molecules
Make up cells.
Cells
Make up tissues.
Tissues
Make up organs.
Organs
Make up organ systems.
Organ systems
Make up organisms.
Cells in the body
There are over 35 trillion cells.
Types of cells
There are approximately 200 types of cells.
Primary tissue types
All cells can be placed into one of the four primary tissue types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Neural.
Cellularity
Cells are bound close together with no intercellular space.
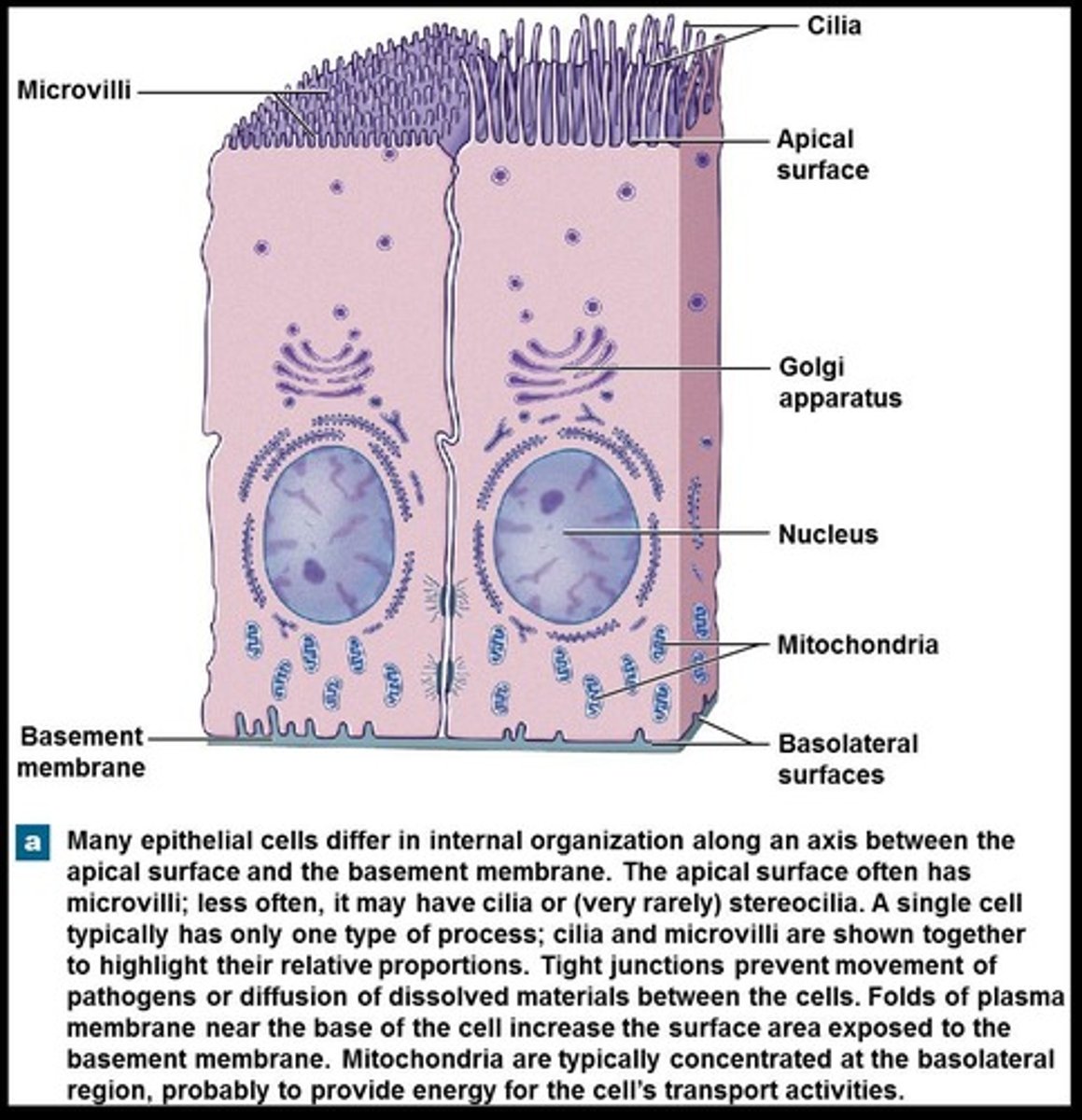
Polarity
Refers to the structural and functional difference between the exposed apical surface and the attached basal surface.
Epithelioid cells
Epithelial cells without a free surface.
Attachment
The basal layer is attached to the basal lamina.
Avascularity
Epithelial tissues do not contain blood vessels.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Provides physical protection, controls permeability, provides sensation, and produces secretions.
Microvilli
Increases surface area for absorption of material, found on the apical surface of cells of the urinary and digestive tracts.
Stereocilia
Long microvilli, commonly found in the inner ear and male reproductive tract.
Ciliated epithelium
Moves substances over the apical surface, found lining the respiratory tract.
Intercellular connections
Extensive connection between the cells that holds them together and prevents the passage of chemicals and pathogens.
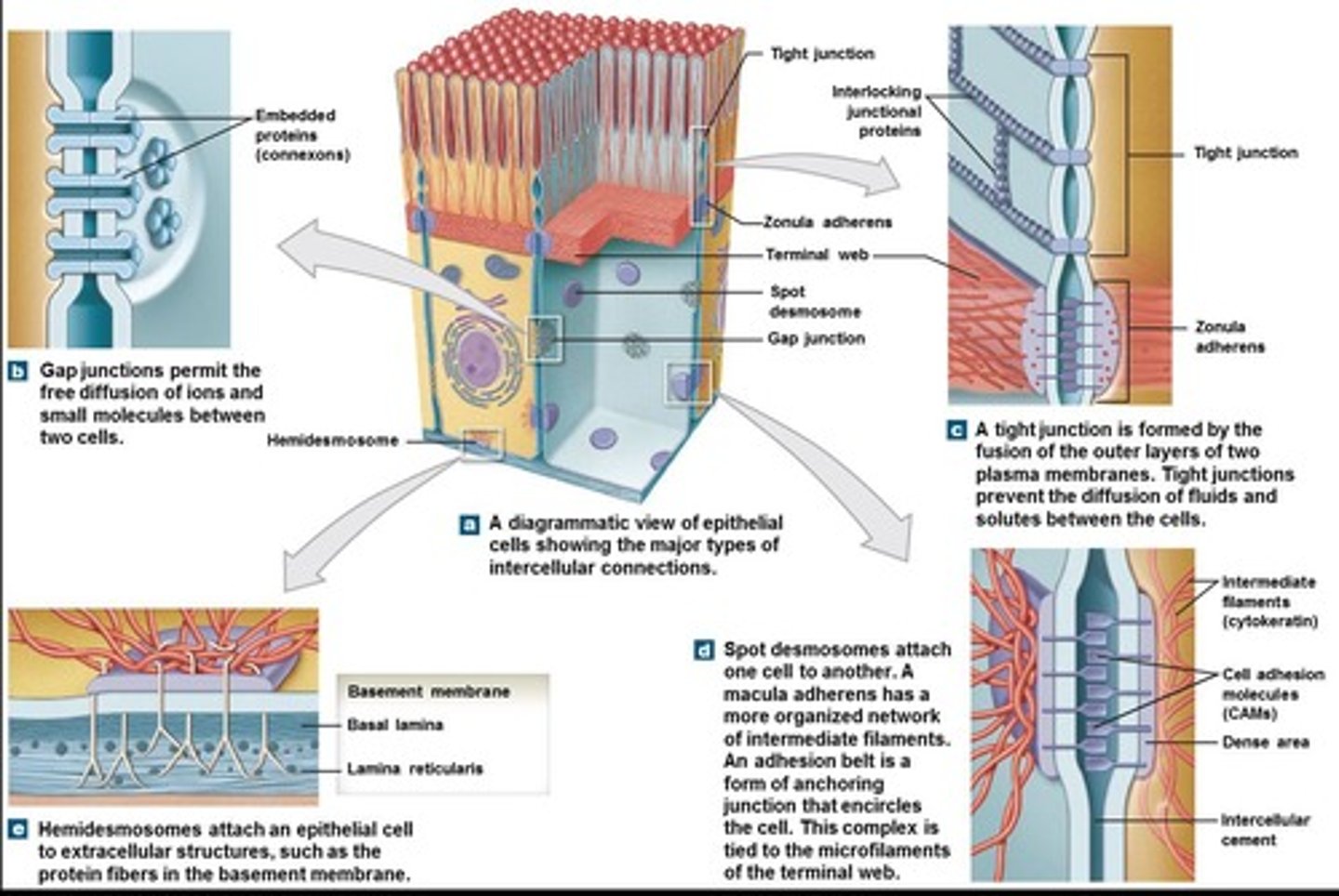
Basal lamina
The cell membrane attaches to the basement membrane, consisting of typically two layers.
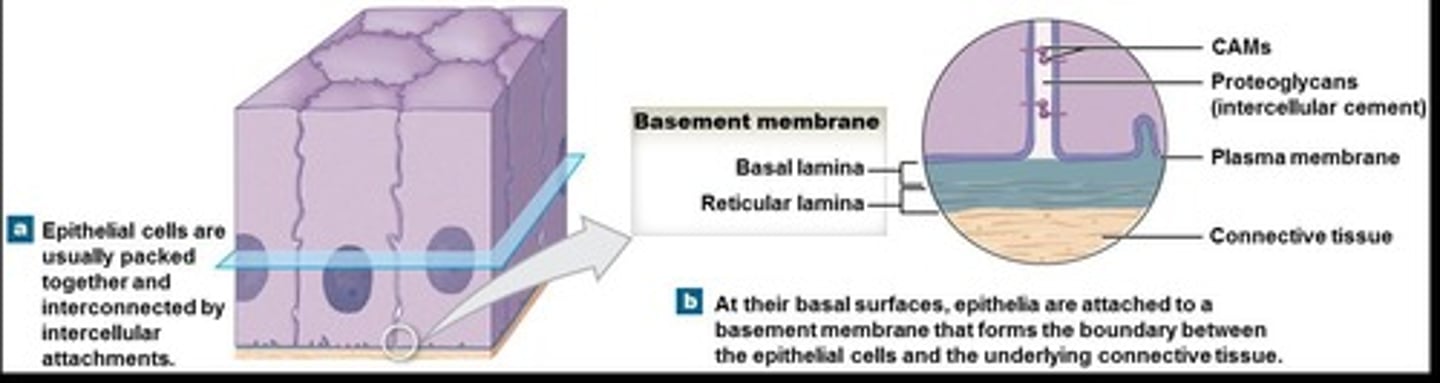
Reticular lamina
Attaches to underlying connective tissue.
Epithelial Maintenance and Renewal
Must be replaced frequently due to exposure to disruptive enzymes, toxic chemicals, pathogens, and mechanical abrasion.
Simple epithelium
Epithelium has only one layer of cells, found in protected areas such as internal compartments of the body.
Stratified epithelium
Epithelium has two or more layers of cells, found in areas with mechanical or chemical stresses.
Squamous epithelium
Cells are relatively flat in appearance.
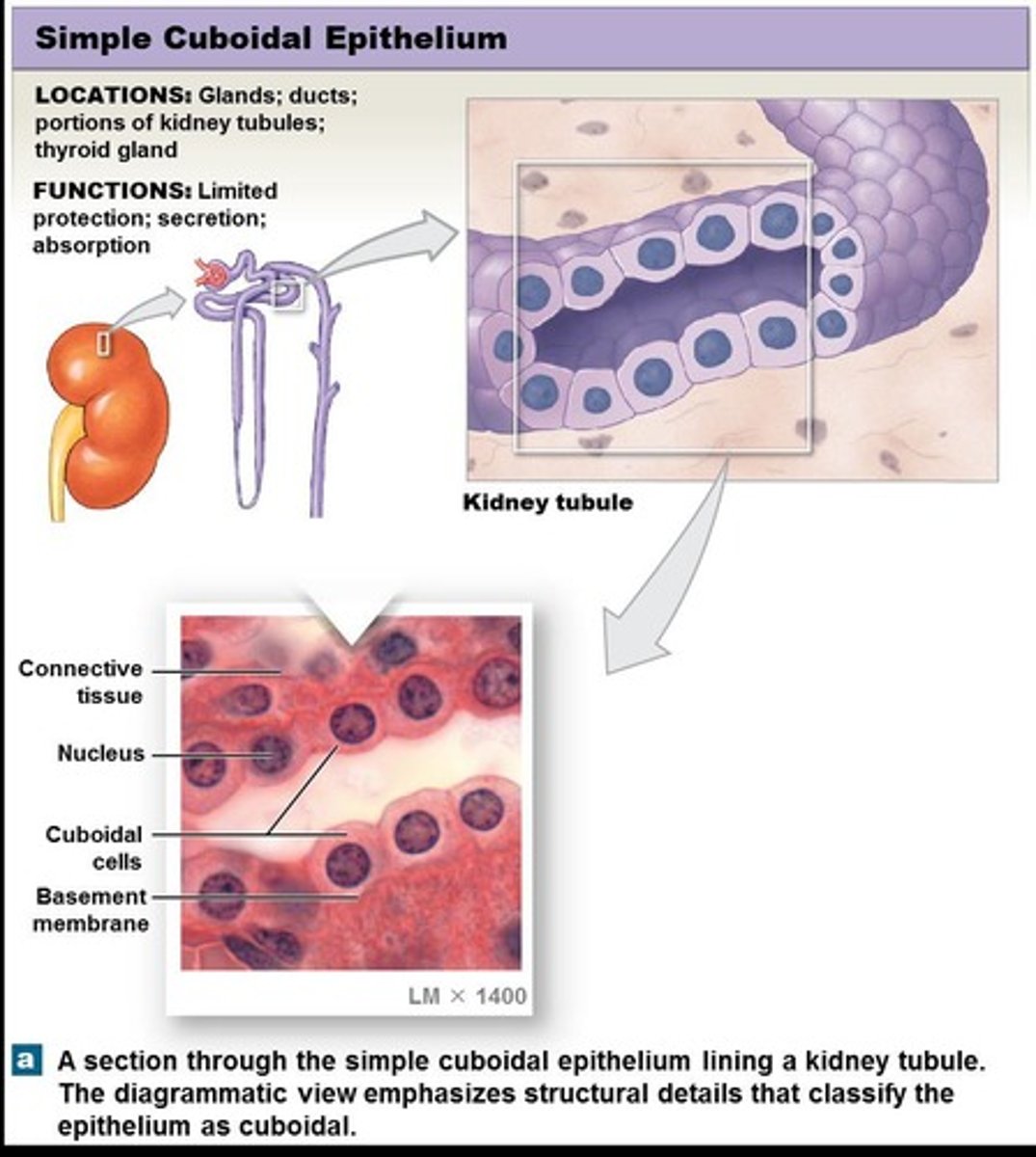
Cuboidal epithelium
Cells are shaped like cubes.
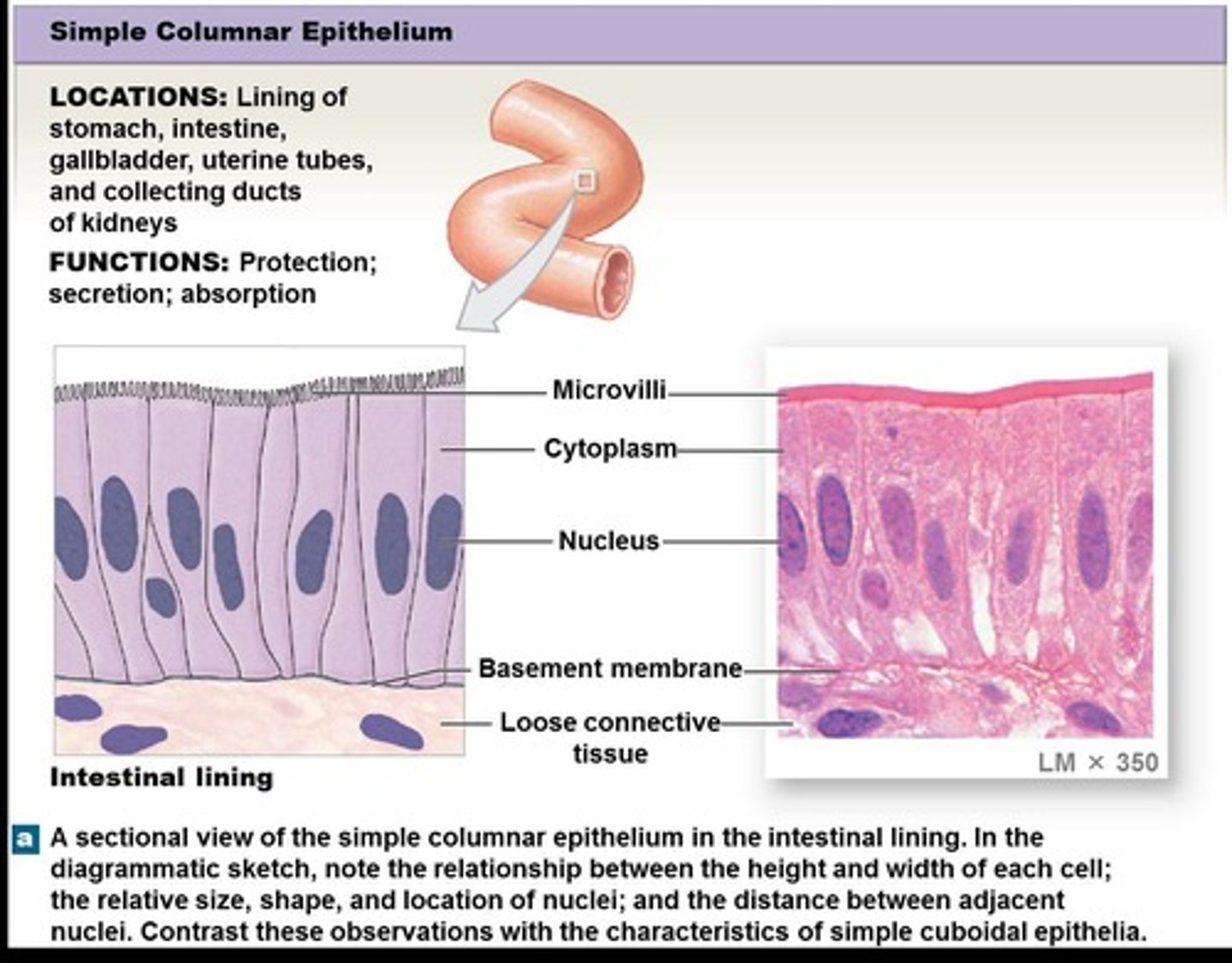
Columnar epithelium
Cells are longer than they are wide, shaped like columns.
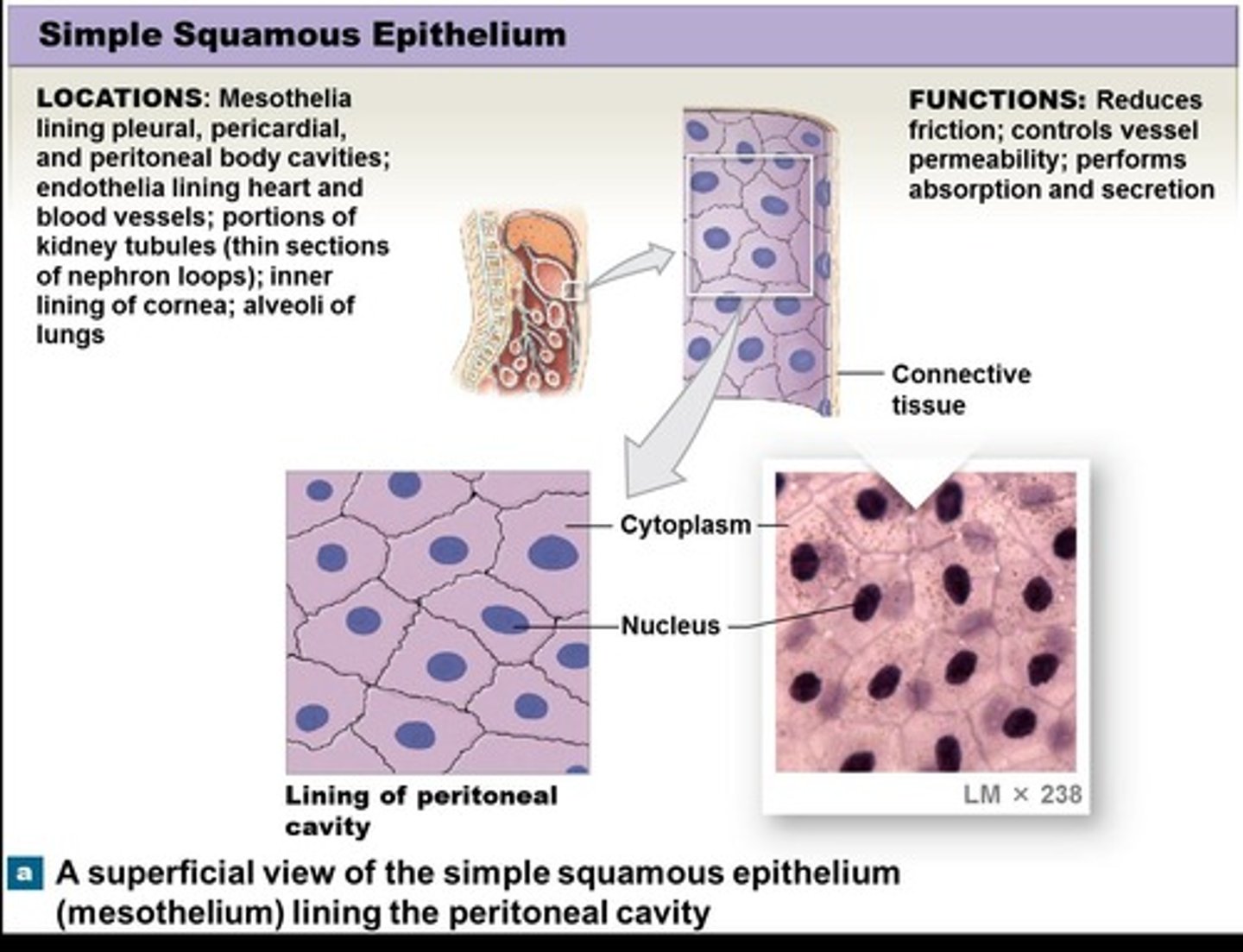
Simple squamous epithelium
Consists of very delicate cells, reduces friction, absorbs and secretes material.
Stratified squamous epithelium
Located on the surface of skin and lines the mouth, anus, esophagus, vagina, providing protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemicals.
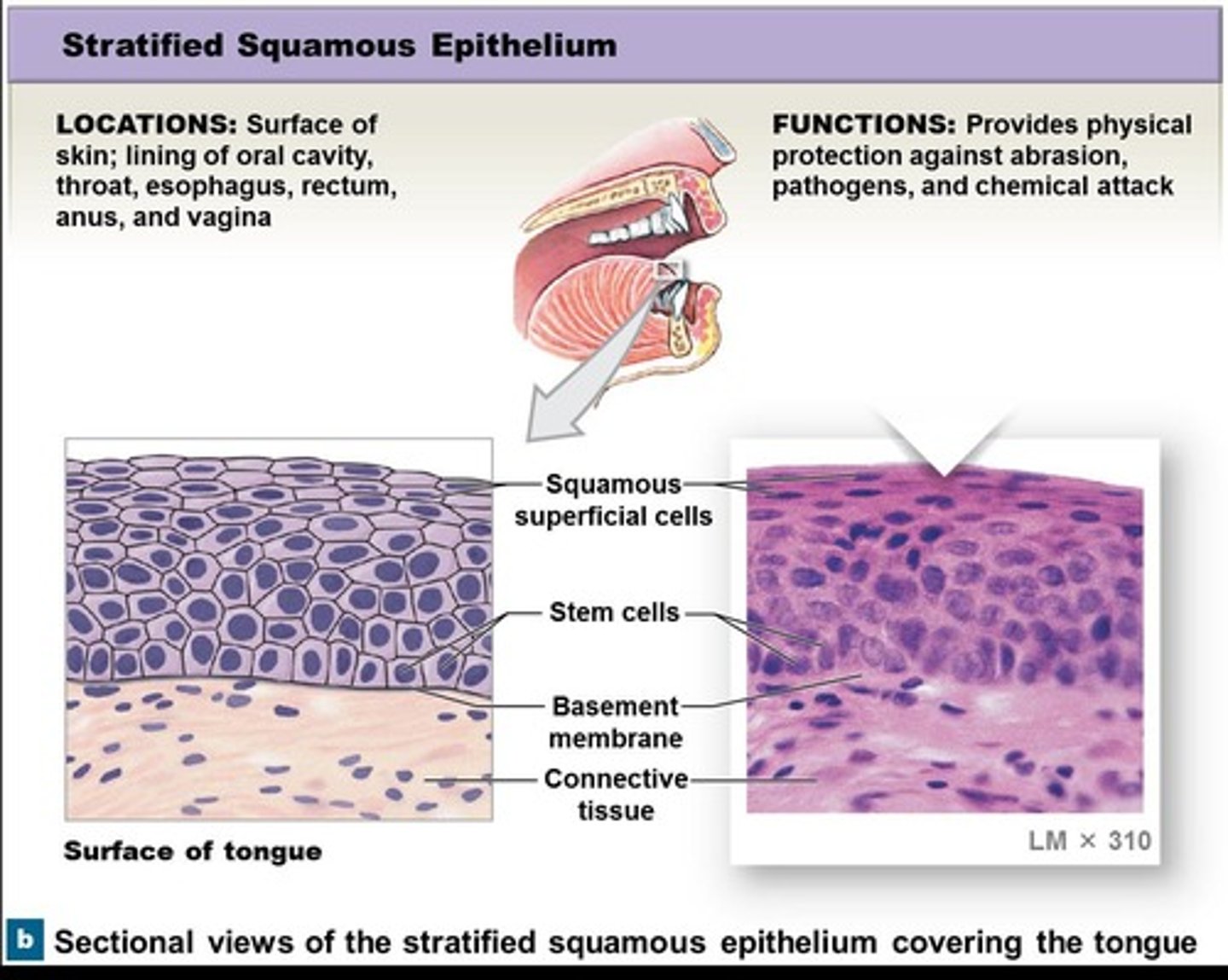
Keratin
A protein produced by cells.
Nonkeratinized
Refers to mucosal lining that does not contain keratin.
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Epithelium located in the thyroid gland, ducts, and kidney tubules, functioning in secretion and absorption with very limited protection.
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
A rare type of epithelium found in the ducts of sweat glands, primarily functioning in secretion and absorption.
Simple columnar epithelium
Epithelium lining the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of the kidneys, functioning in secretion, absorption, and protection.
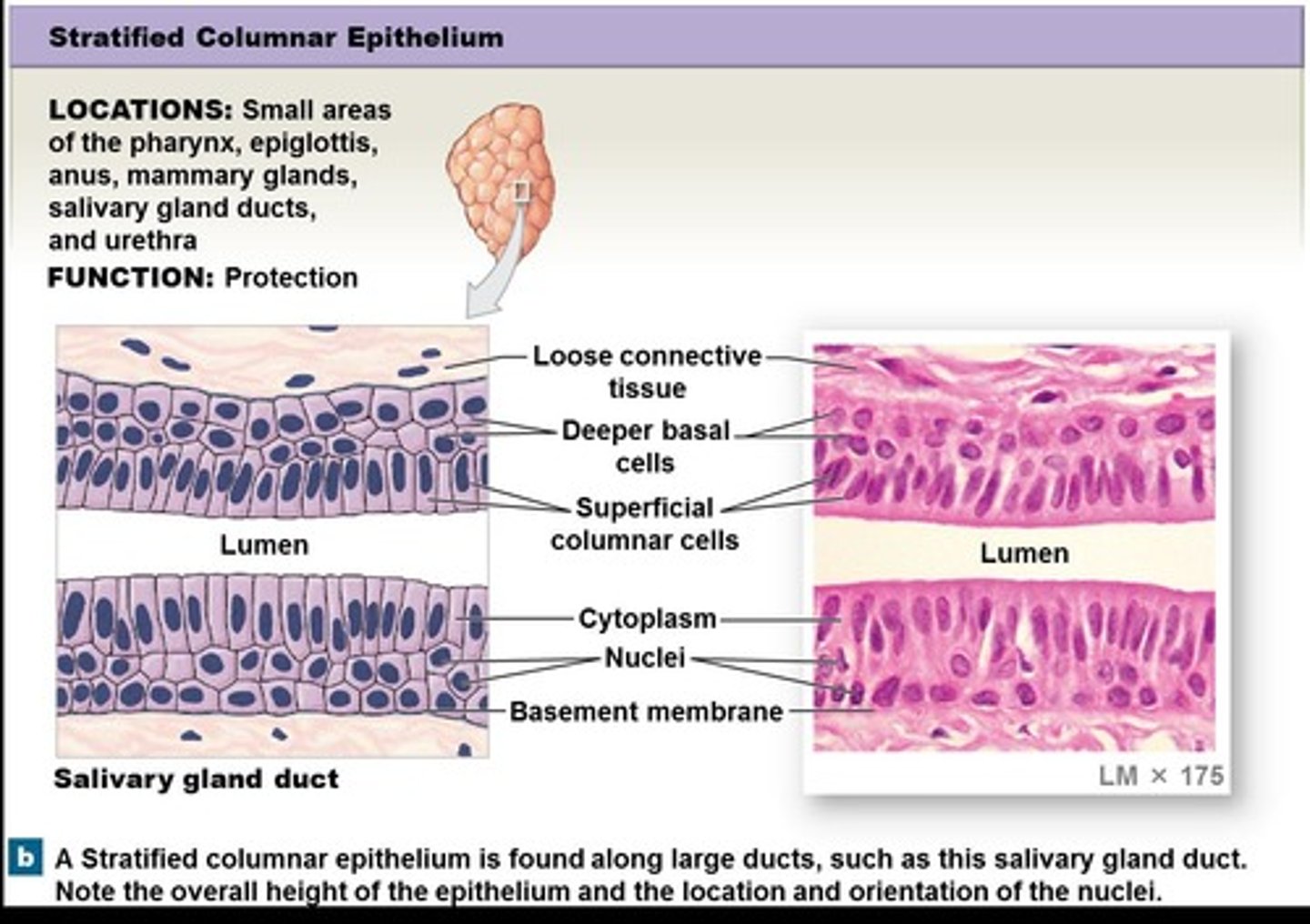
Stratified columnar epithelium
Epithelium located in the pharynx, epiglottis, anus, mammary glands, salivary glands, and urethra, primarily functioning in protection.
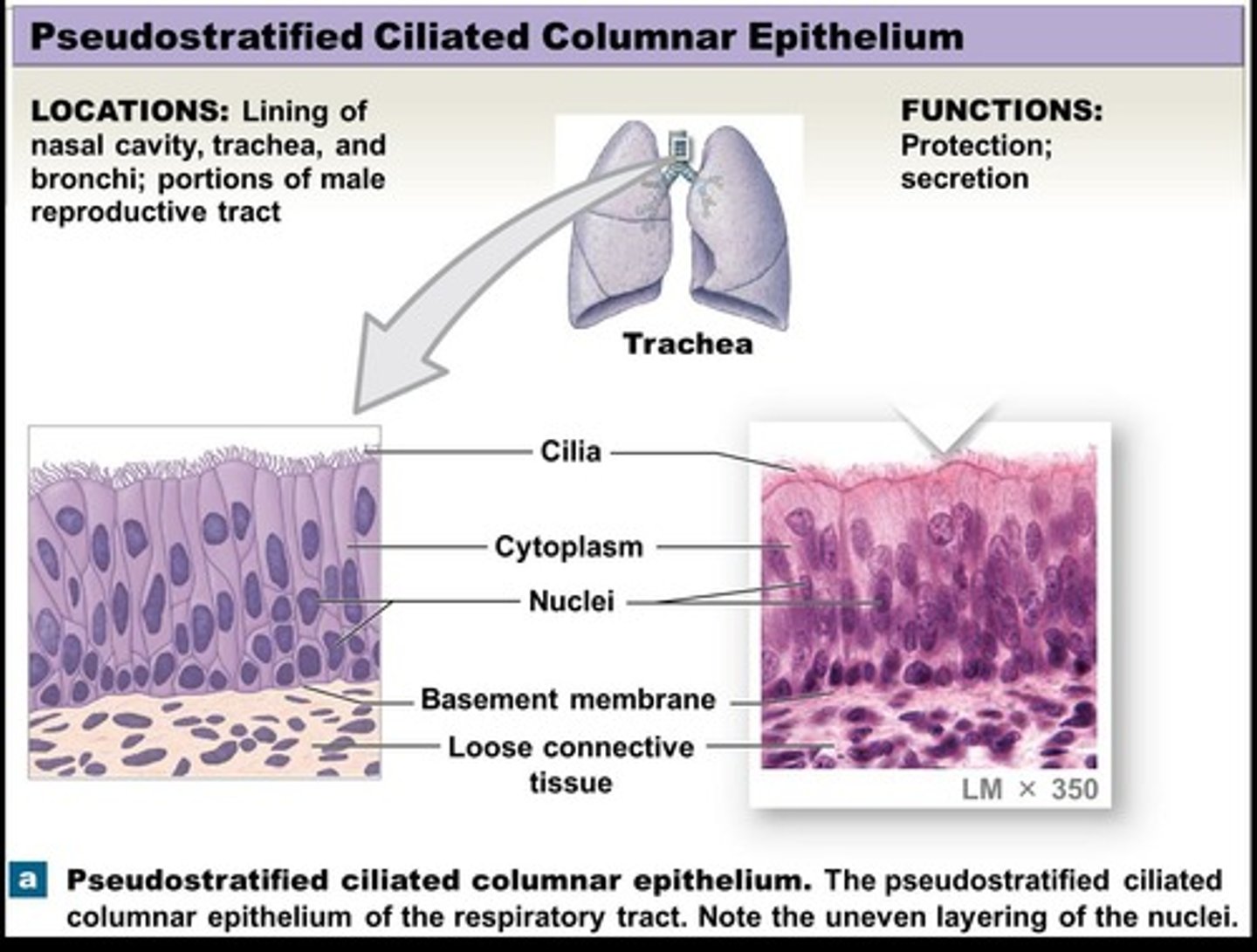
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Epithelium with nuclei situated at different levels, found in the nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi, functioning in protection and secretion.
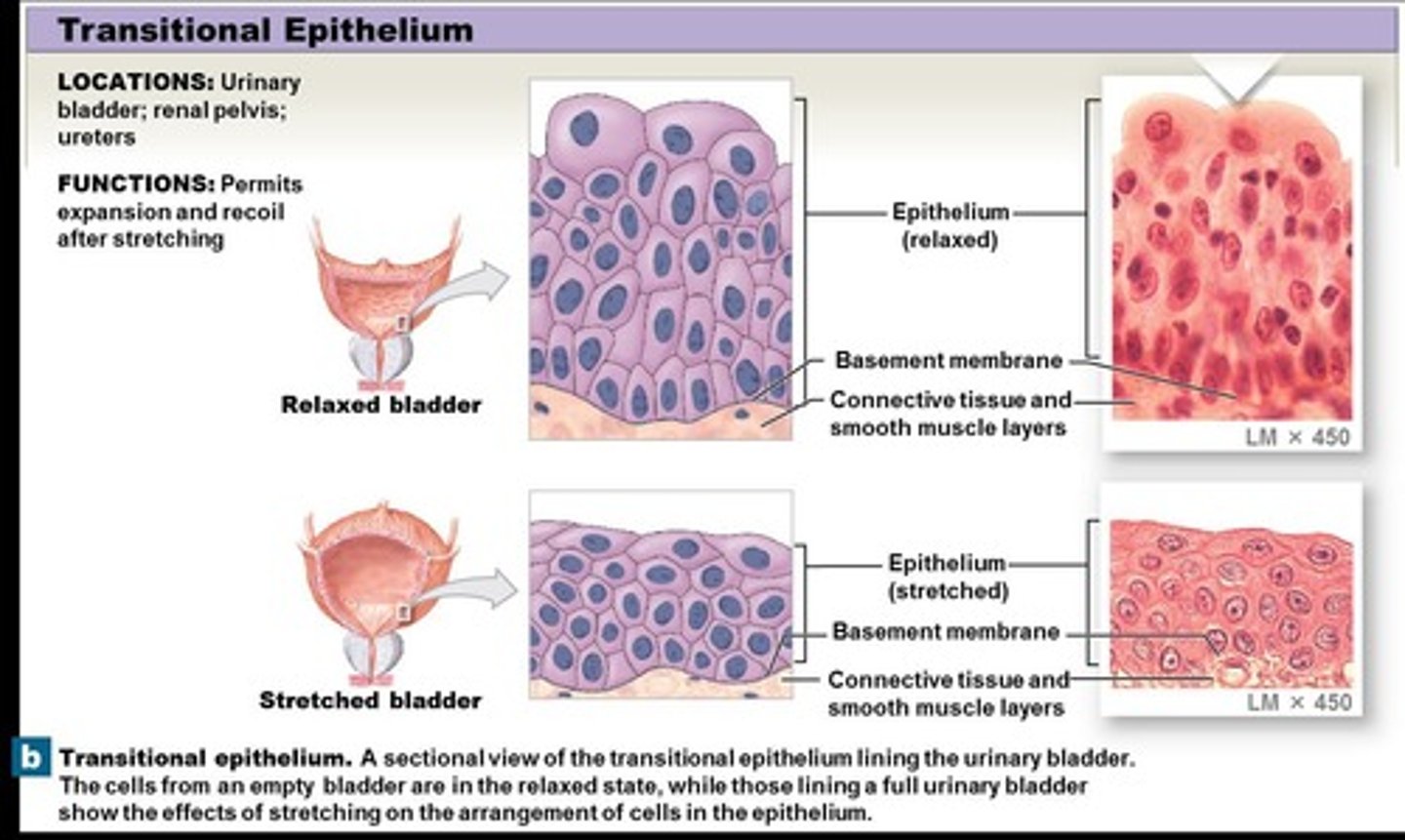
Transitional epithelium
Epithelium consisting of many layers and a combination of cuboidal and oddly shaped cells, located in the urinary bladder, renal pelvis, and ureters, with the ability to stretch extensively.
Glandular epithelia
Epithelia that contain gland cells, classified based on type of secretion released, structure of the gland, and mode of secretion.
Exocrine glands
Glands whose secretions travel through ducts to the epithelial surface.
Serous glands
Exocrine glands that secrete watery fluid with enzymes.
Mucous glands
Exocrine glands that secrete glycoproteins called mucins (mucus).
Mixed exocrine glands
Glands that contain both serous and mucus secretions.
Endocrine glands
Glands whose secretions enter into the blood or lymph, primarily hormones.
Unicellular glands
Glands that secrete mucins, including goblet cells and mucus cells.
Goblet cells
Unicellular glands found within the trachea.
Mucous cells
Unicellular glands found within the salivary glands.
Multicellular glands
Glands that secrete mucins and produce secretory sheets.
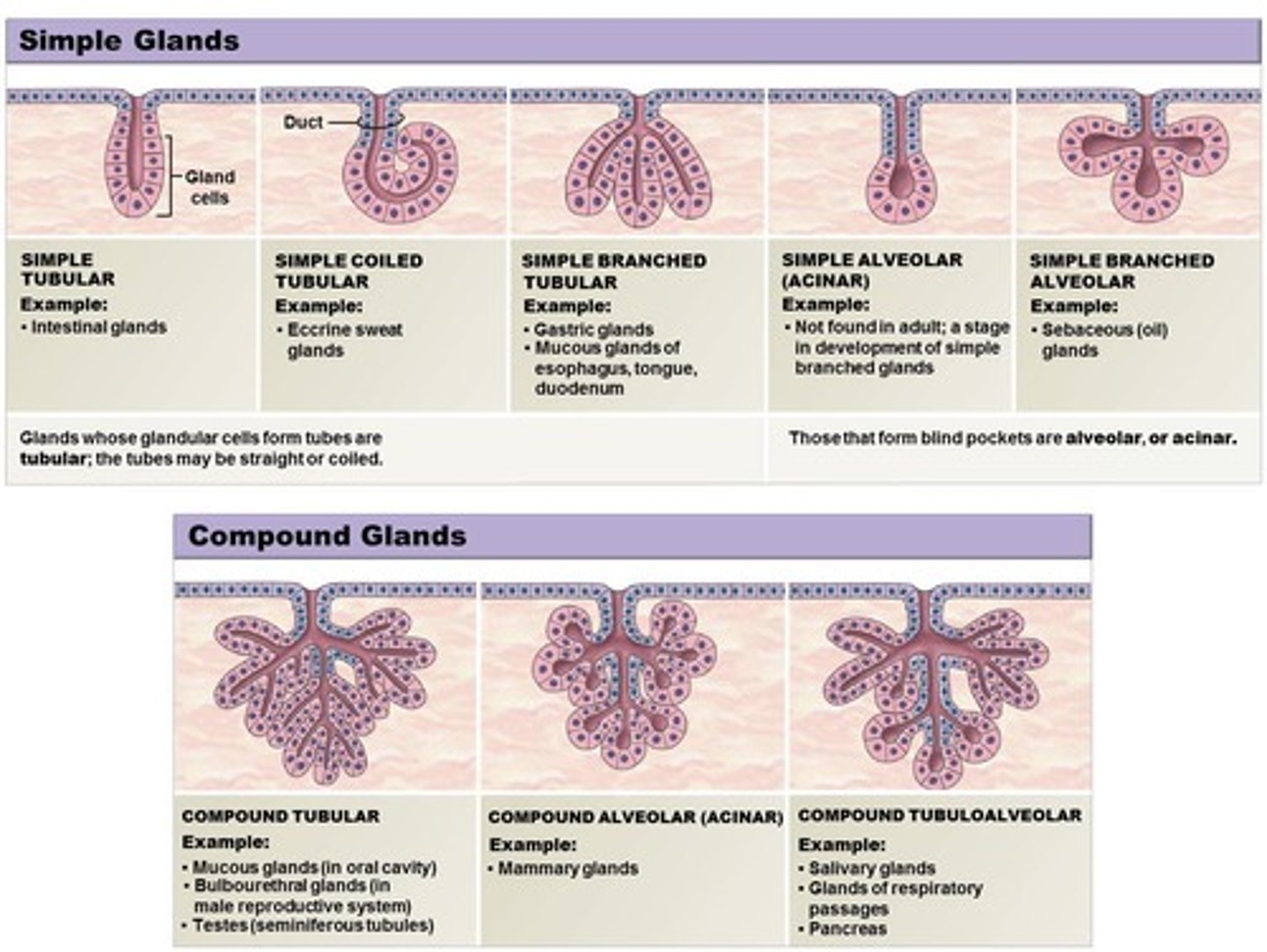
Tubular gland
Gland where cells are arranged in a tube.
Alveolar (acinar) gland
Gland where cells form a blind pocket.
Tubuloalveolar (tubuloacinar) gland
A gland that combines tubular and alveolar structures.
Simple duct structure
Duct structure with no branching.
Compound duct structure
Duct structure with repeated branches.
Eccrine secretion
A method of secretion involving exocytosis, found in salivary glands.
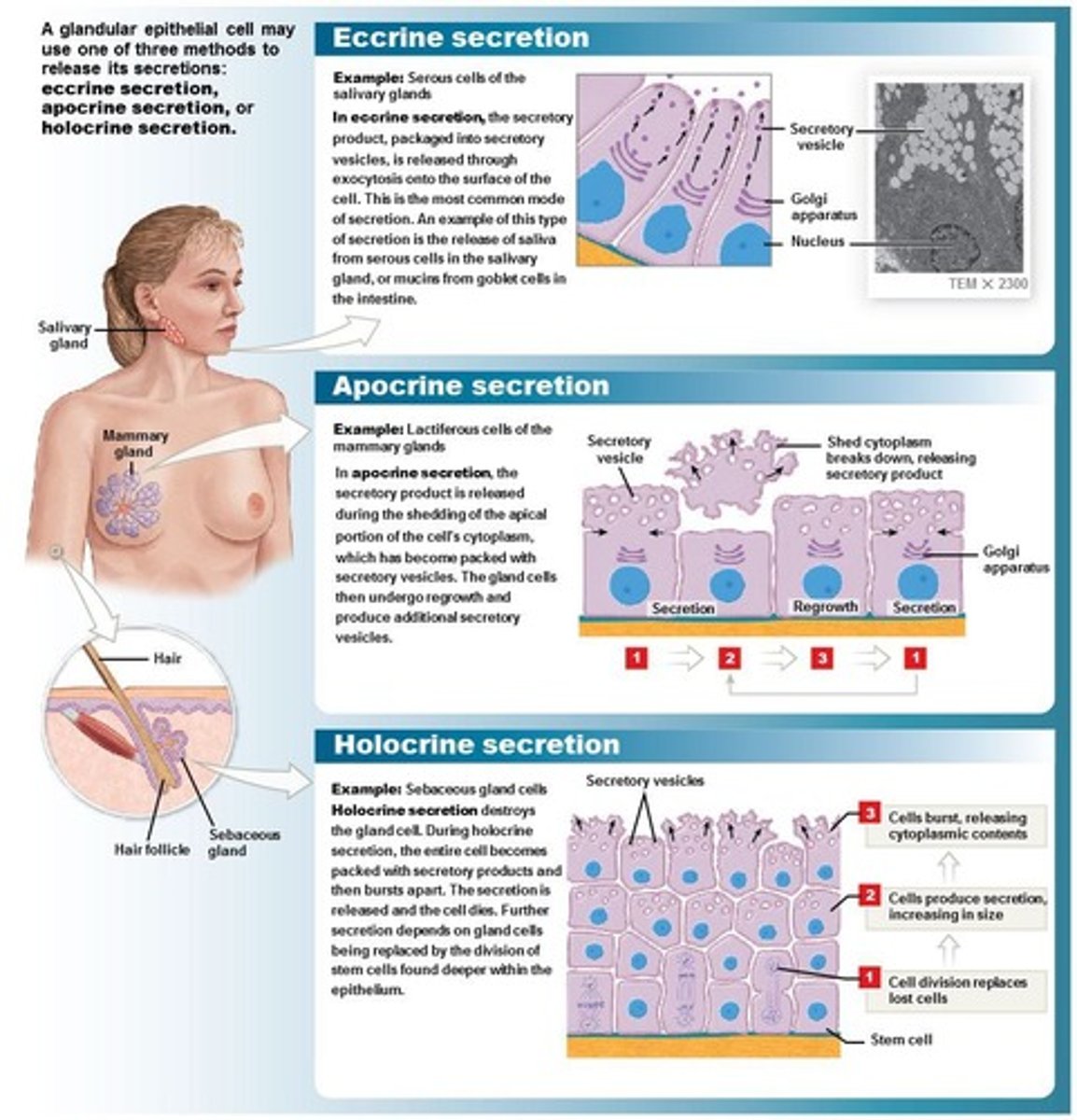
Apocrine secretion
A method of secretion involving shedding of the apical portion of the cell, found in mammary glands.
Holocrine secretion
A method of secretion where the cell bursts apart, found in sebaceous glands.
Connective tissues
Tissues that have three main components: specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers, and matrix.
Matrix
The collective term for the extracellular component of any connective tissue made of protein fibers and the ground substance.
Functions of connective tissue
Includes establishing structural framework, transporting fluids, protecting organs, supporting other tissues, storing energy, and defending against microorganisms.
Connective Tissue Proper
Has a matrix of fibers (loose fibers and dense fibers)
Fluid Connective Tissue
Has a matrix of liquid (blood and lymph)
Supporting Connective Tissue
Has a matrix of fibers and, in some cases, insoluble calcium salts
Connective Tissue Proper
Two classes of connective tissue proper cells: Fixed cells and wandering cells
Fixed Cells
Cells that remain in the connective tissue and perform specific functions
Wandering Cells
Mobile cells that move through the connective tissue and respond to injury or infection
Fibroblasts
Produce connective tissue fibers
Fibrocytes
Maintain connective tissue fibers and matrix
Fixed Macrophages
Phagocytize pathogens and damaged cells
Adipocytes
Store lipid reserves
Mesenchymal Cells
Connective tissue stem cells that can differentiate into other cell types
Melanocytes
Synthesize melanin
Free Macrophages
Mobile/traveling phagocytic cells (derived from monocytes of the blood)
Mast Cells
Stimulate local inflammation
Lymphocytes
Participate in immune response; mobilize during infection or tissue injury
Neutrophils and Eosinophils
Types of white blood cells involved in immune response
Collagen Fibers
Designed to develop tensile strength, which is the ability to resist tension
Reticular Fibers
Support the structure of organs
Elastic Fibers
Contain protein called elastin
Areolar Tissue
Connects skin to muscle and provides minimal support but independent movement
Adipose Tissue
Cushions and insulates; consists of white fat (white adipose cells) and brown fat (brown adipose cells)
Reticular Tissue
Provides a supporting framework in organs like liver, spleen, and lymph nodes
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Connects muscle to bone (tendons), muscle to muscle (aponeuroses), or bone to bone (ligaments)
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Provides strength and forms a fibrous capsule around organs
Fluid Connective Tissues
Includes blood and lymph
Blood
Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide; consists of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Lymph
Involved with the immune system; consists of lymphocytes
Cartilage
Made of chondrocytes; has a gel matrix made of chondroitin sulfate
Bone
Solid matrix made of calcium phosphate; provides support and strength
Hyaline Cartilage
Provides flexible support and reduces friction in joints
Elastic Cartilage
Provides flexible support in structures like the auricle of the ear
Fibrous Cartilage
Resists compression and absorbs shock in pads within the knee joints
Epithelial Membranes
Consist of a sheet of epithelial cells and an underlying connective tissue
Mucous Membranes
Line digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts; provide a barrier against pathogens
Serous Membranes
Line body cavities and consist of a parietal and visceral layer
Cutaneous Membrane
Makes up the skin and consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Synovial Membrane
Lines joint cavities and produces synovial fluid to reduce friction
Embryonic Connective Tissue
Includes mesenchyme and mucoid connective tissue
Fascia
Layers of connective tissue that connect organs with the rest of the body