Ch. 2: The Anatomy and Evolution of the Nervous System
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
dorsal
top
rostral
front
caudal
back
ventral
bottom
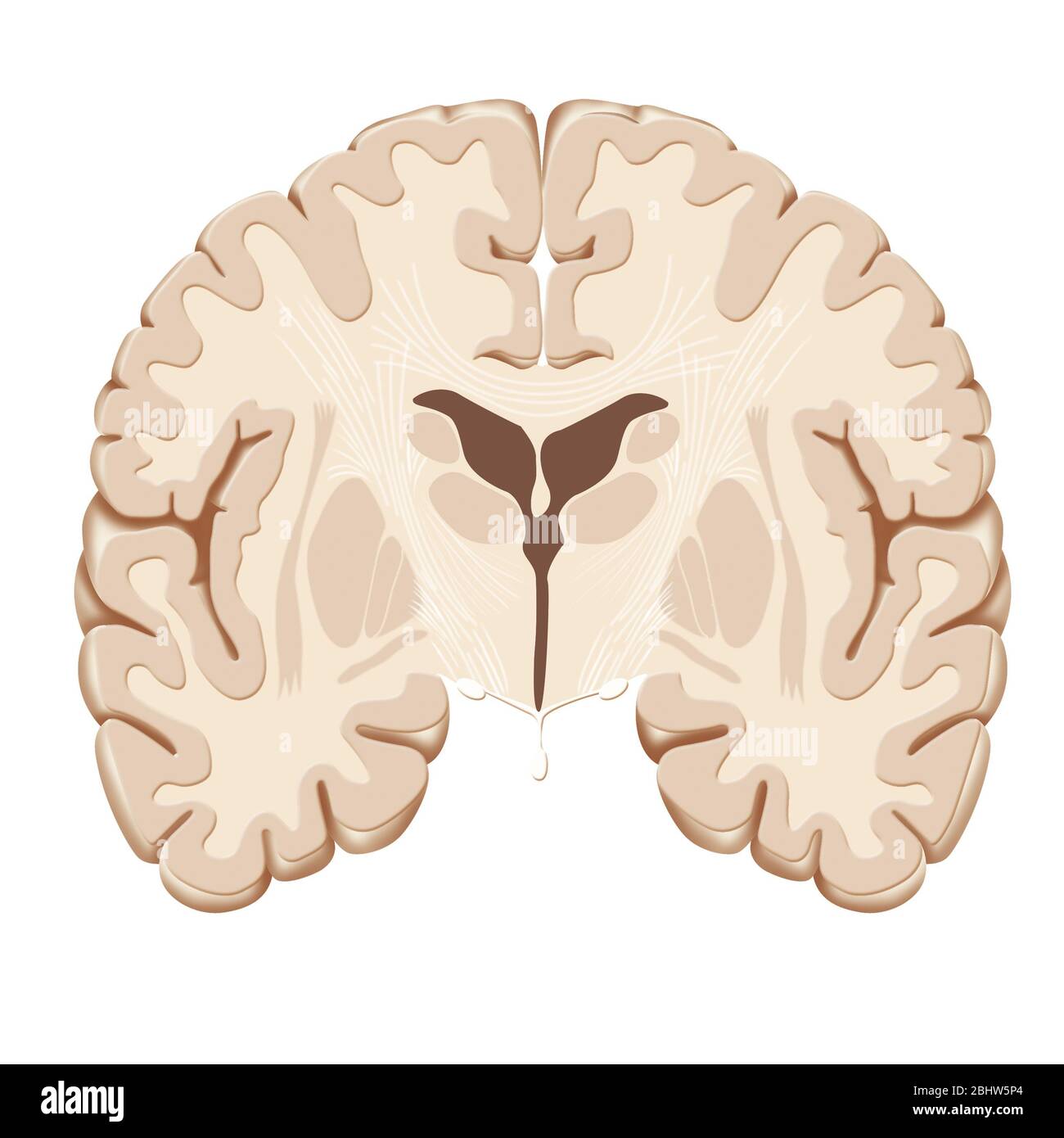
coronal (frontal) section
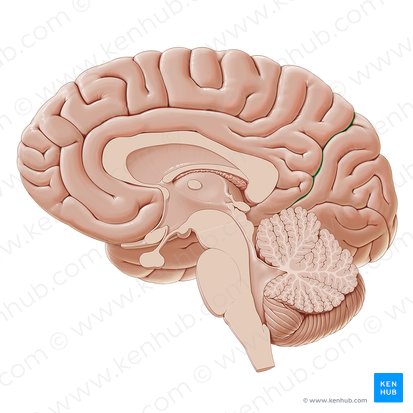
mid-sagittal (medial) section
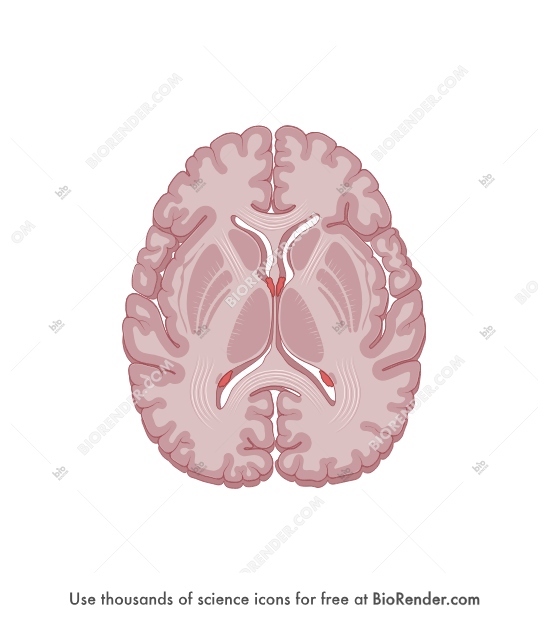
horizontal section
lateral
outer side in coronal and horizontal sections
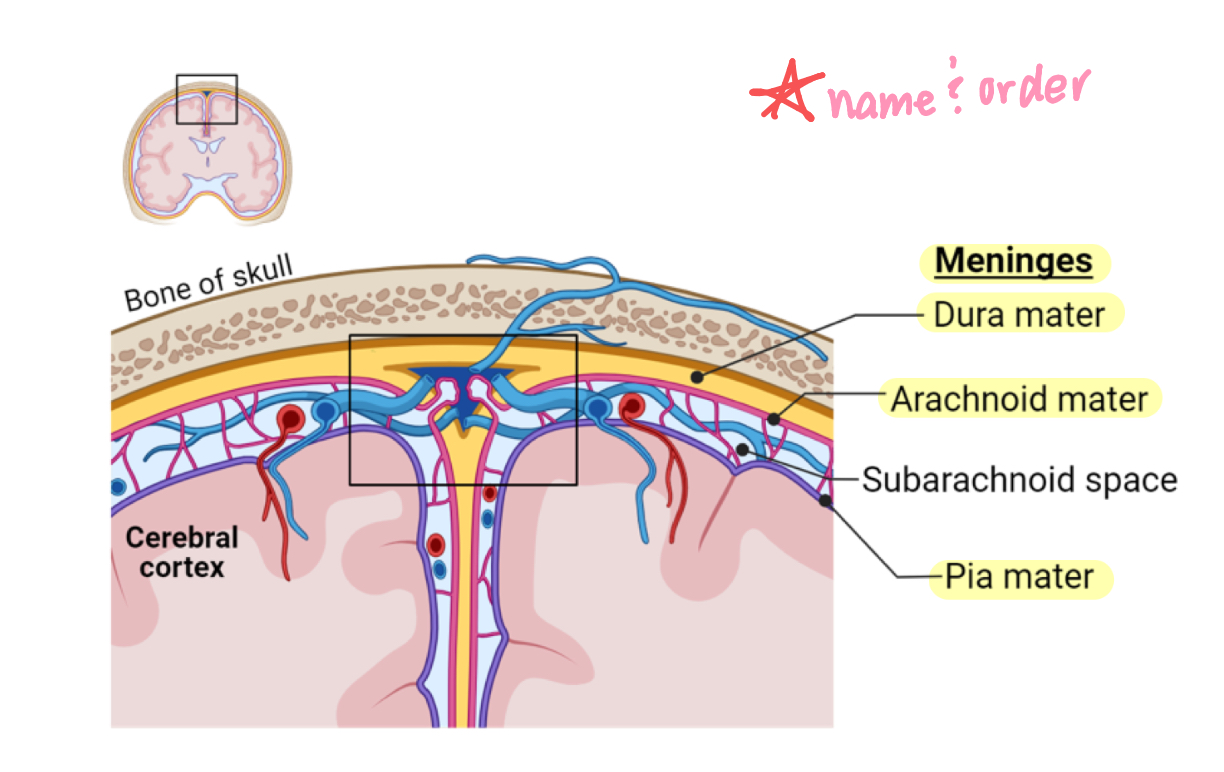
meninges
membranes that envelope the CNS
dura mater
arachnoid membrane
pia mater
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
clear, colorless bodily fluid found in brain and spine (CNS)
produced in the choroid plexus
flows from ventricles through the subarachnoid space, then reabsorbed into blood stream
Roles:
mechanical protection (cushion)
chemical stability/clears waste (pee)
maintains proper intracranial pressure
vascular system
blood vessels:
vertebral artery (back neck)
common carotid artery (front neck)
roles:
provides nutrients and oxygen
carries away waste
blood brain barrier (BBB)
prevents bad things from going to the brain
issue: oral medicine needs to be small enough to pass through barrier
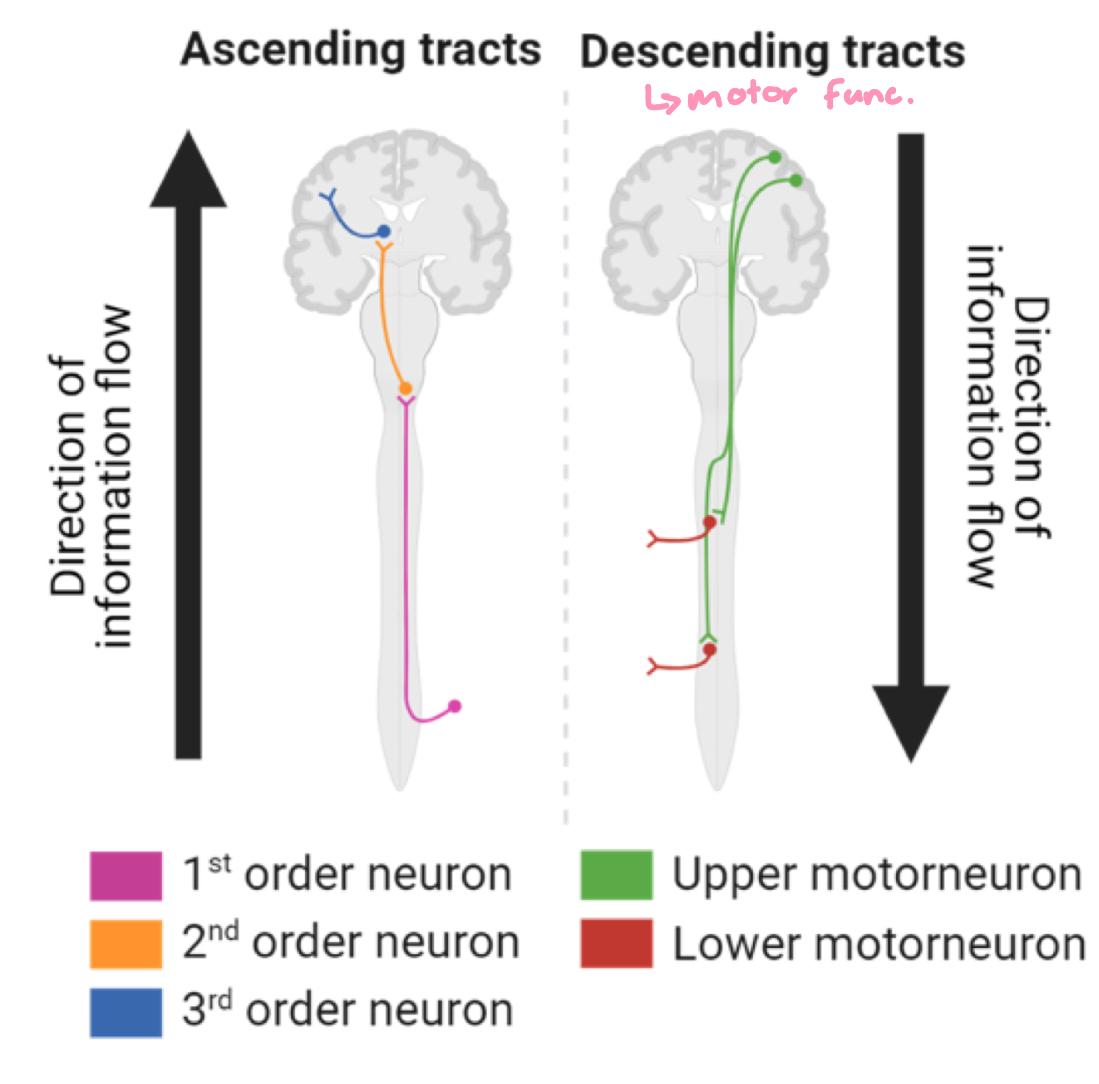
spinal cord tracts
tracts: carry sensory and motor info. to/from the brain
spinal cord anatomy
dorsal = sensory
ventral = motor
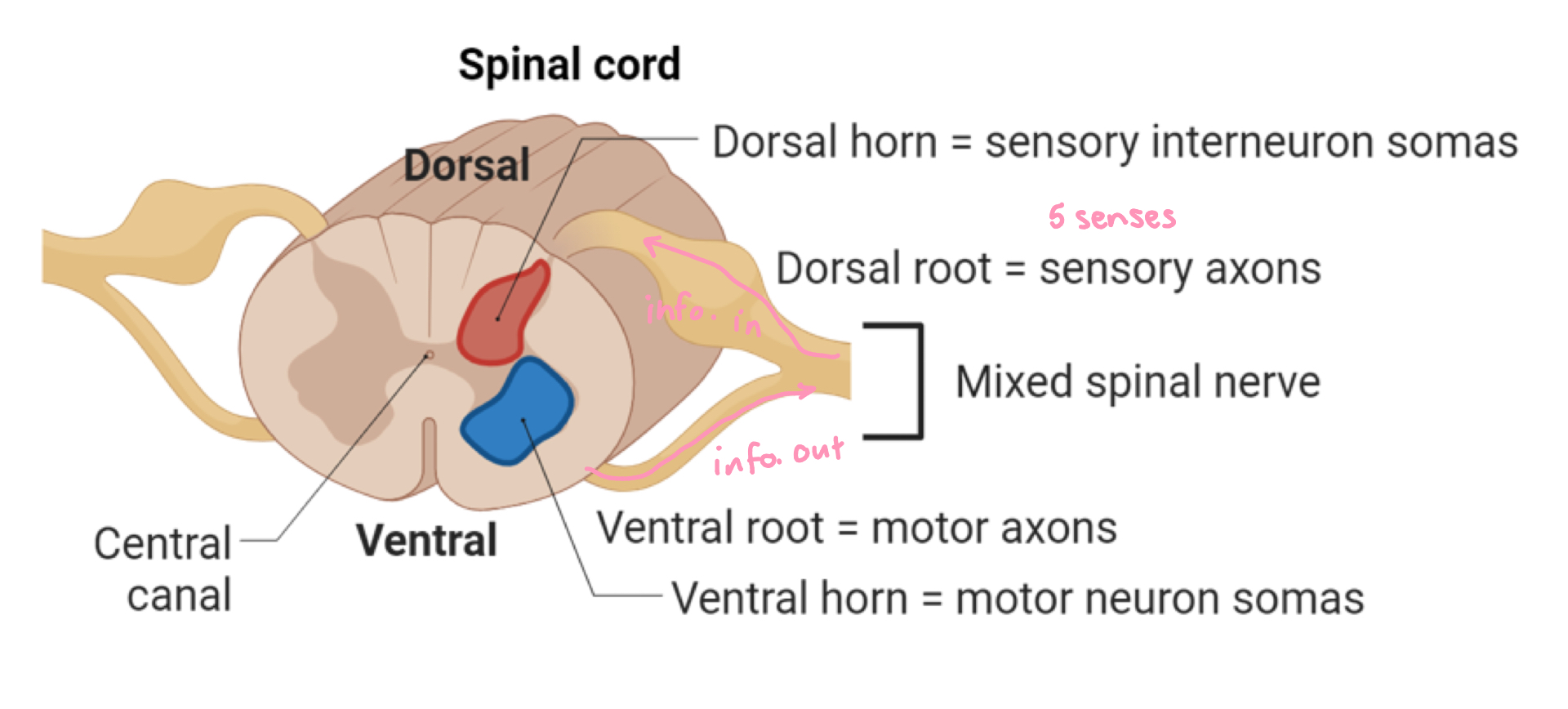
hindbrain
medulla
pons
cerebellum
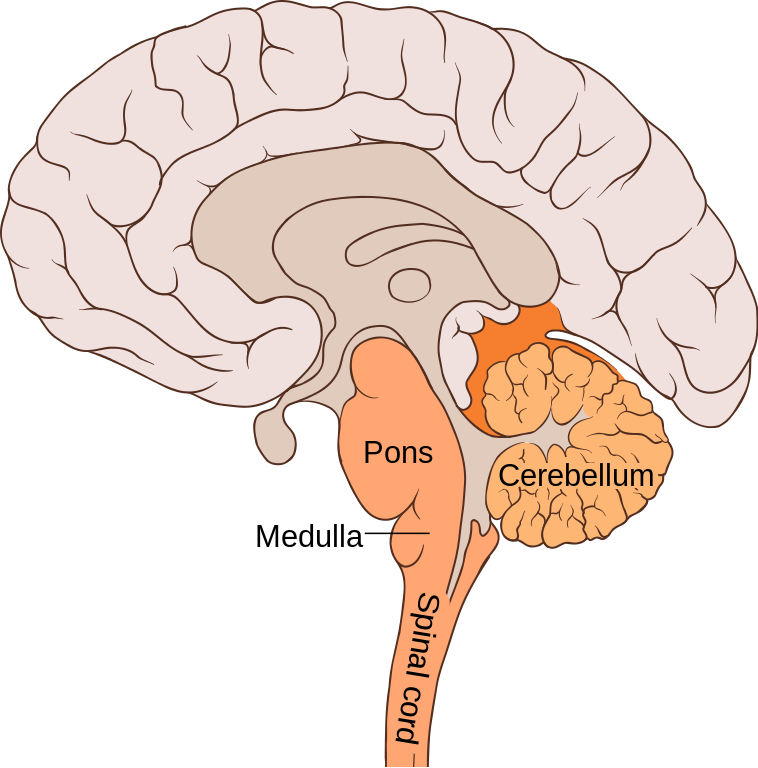
medulla
in hindbrain
connects the higher levels of the brain to the spinal cord
hosts the vagus nerve
contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor center (autonomic involuntary functions)
pons
in hindbrain
“bridge”
relays message from the cortex and the cerebellum
regulates sleep and basic functions (breathing)
cerebellum
in hindbrain
coordinates movements (find adjustments based on sensory information)
may be involved in complex behaviors (social behaviors)
midbrain
tectum
tegmentum
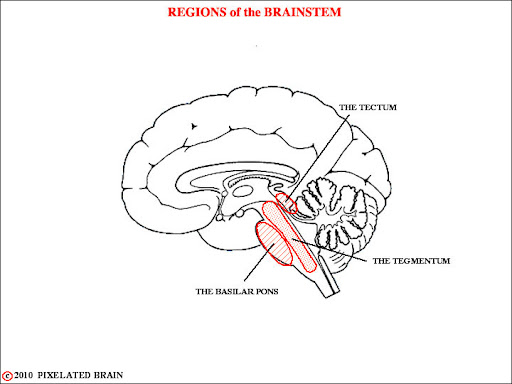
tectum
in midbrain
dorsal position: auditory and visual processing
tegmentum
in midbrain
ventral position: many unconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways
ventral tegmental area (reward)
red nucleus (motor coordination)
substantia nigra (movement)
main region involved with Parkinson’s
as neurons die, you lose control of movement
forebrain
diencephalon:
thalamus
hypothalamus
telencephalon:
cortex
basal ganglia
hippocampus
amygdala
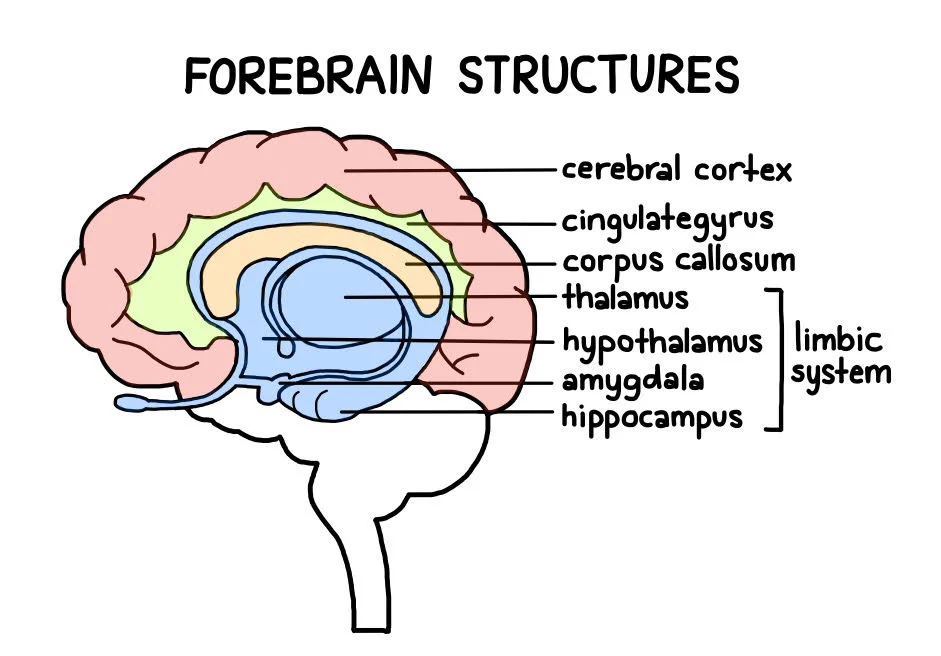
thalamus
forebrain - diencephalon
sensory center
hypothalamus
forebrain - diencephalon
regulatory center
regulation of hormones and homeostasis
e.g.) eating
diencephalon
thalamus
hypothalamus
telencephalon
cortex
basal ganglia
hippocampus
amygdala
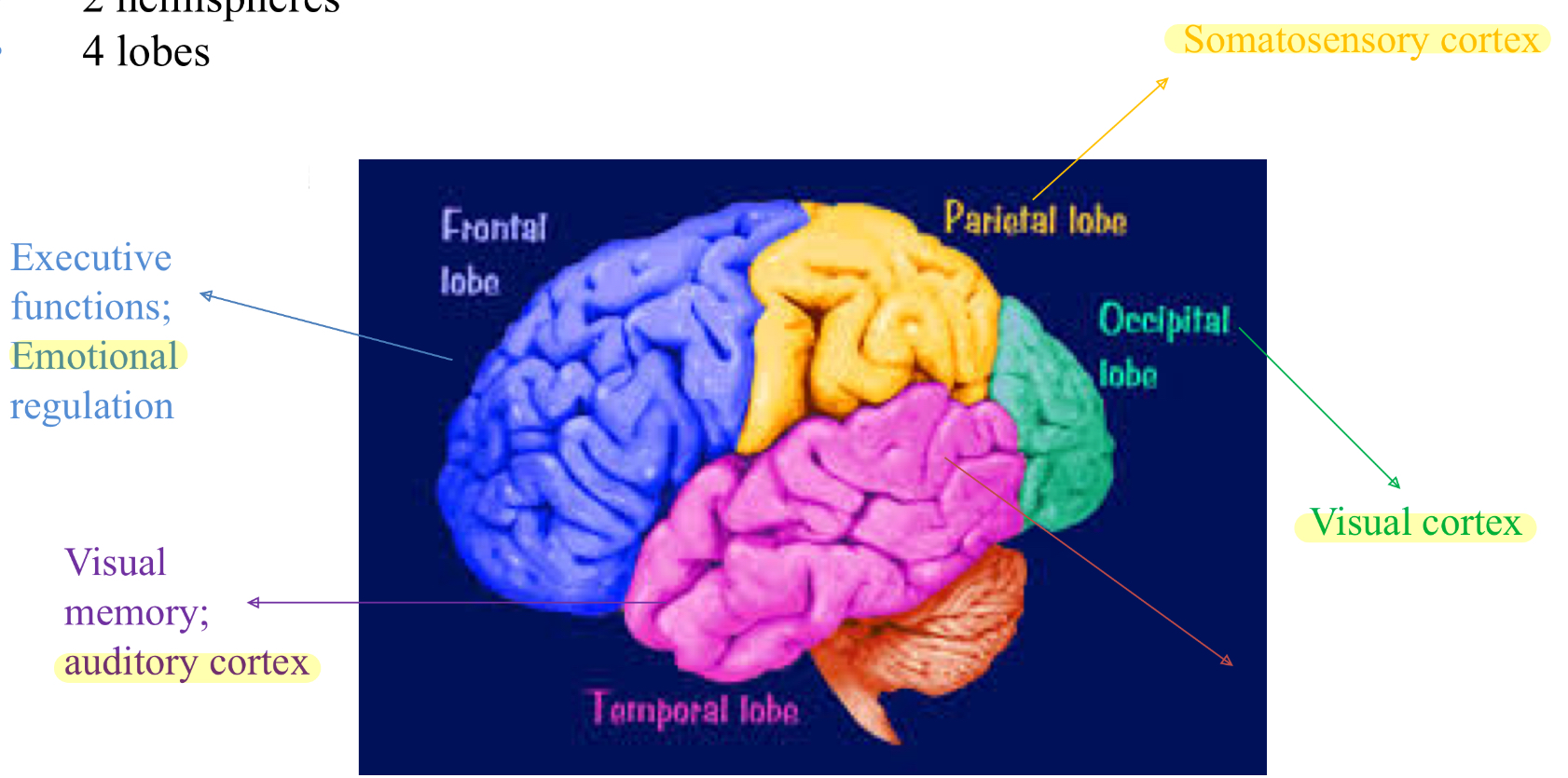
cerebral cortex
forebrain - telencephalon
outermost layered structure of neural tissue of the brain
6 layers; 2 hemispheres; 4 lobes
frontal lobe: executive functions; emotional regulation
parietal lobe: somatosensory cortex
occipital lobe: visual cortex
temporal lobe: visual memory; auditory cortex
basal ganglia
forebrain - telencephalon
motor control: planning, movement, reward
receives info. from cortex, sends info. to thalamus
limbic system
emotions and memory
forebrain - telencephalon
hippocampus
amygdala
hippocampus
forebrain - telencephalon
part of limbic system
memory
amygdala
forebrain - telencephalon
part of limbic system
emotions
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
ganglia and nerves connecting CNS to muscles, organs and skin
somatic nervous system
PNS
brings sensory input to the brain and spinal cord and returns commands to muscles
cranial nerves =12 pairs
spinal nerves = 31 pairs
autonomic nervous system
directs the activity of the glands, organs and smooth muscles
PNS
sympathetic system
fight or flight
parasympathetic system
rest and digest