MCAT BIOCHEM CH 9: Carbohydrate Metabolism 1 (5%)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
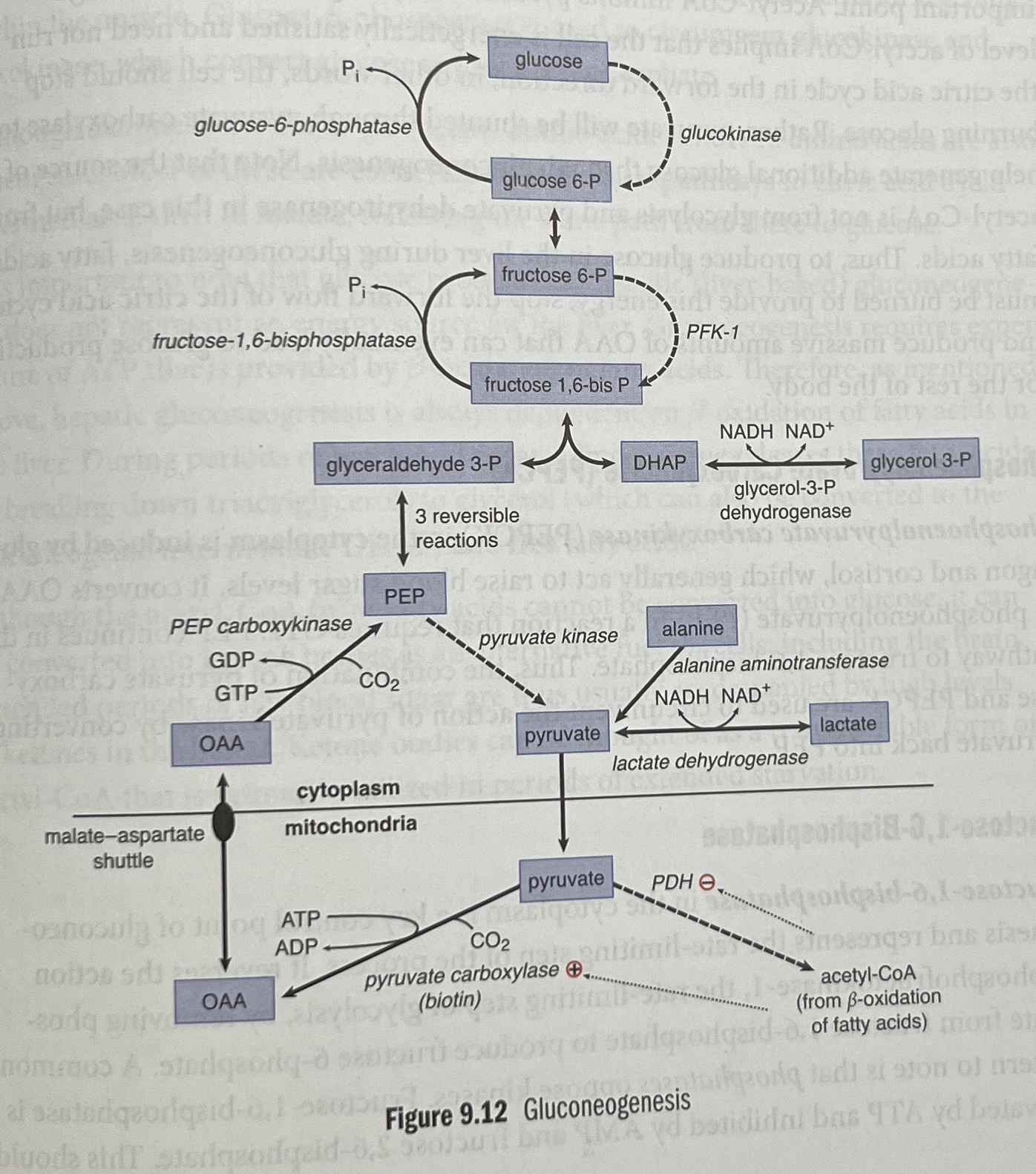
Where does gluconeogenesis primarily occur in the body?
In the liver, with a small contribution from the kidneys.
In cytoplasm and mitochondria
What is the primary relationship between gluconeogenesis and glycolysis?
Most of gluconeogenesis is simply the reverse of glycolysis, using the same enzymes except some irreversible steps/
What are the three irreversible steps of glycolysis that must be bypassed in gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate to oxaloacetate (by pyruvate carboxylase), Oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate
(by Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK))
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate
(by fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase).
Glucose-phosphate → glucose
(by Glucose-6-phosphatase)
What enzyme converts pyruvate into oxaloacetate in gluconeogenesis?
Pyruvate carboxylase.
What enzyme converts oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate?
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK).
What activates pyruvate carboxylase?
Acetyl-CoA from fatty acid oxidation.
What activates PEPCK?
Glucagon and cortisol.
What is the rate-limiting step of gluconeogenesis?
The conversion of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate by fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
What activates fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase?
ATP directly and glucagon indirectly (via decreased levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate).
What inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase?
AMP directly and insulin indirectly (via increased levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate).
What enzyme converts glucose 6-phosphate to free glucose?
Glucose-6-phosphatase.
Where is glucose-6-phosphatase found?
Only in the endoplasmic reticulum of the liver.
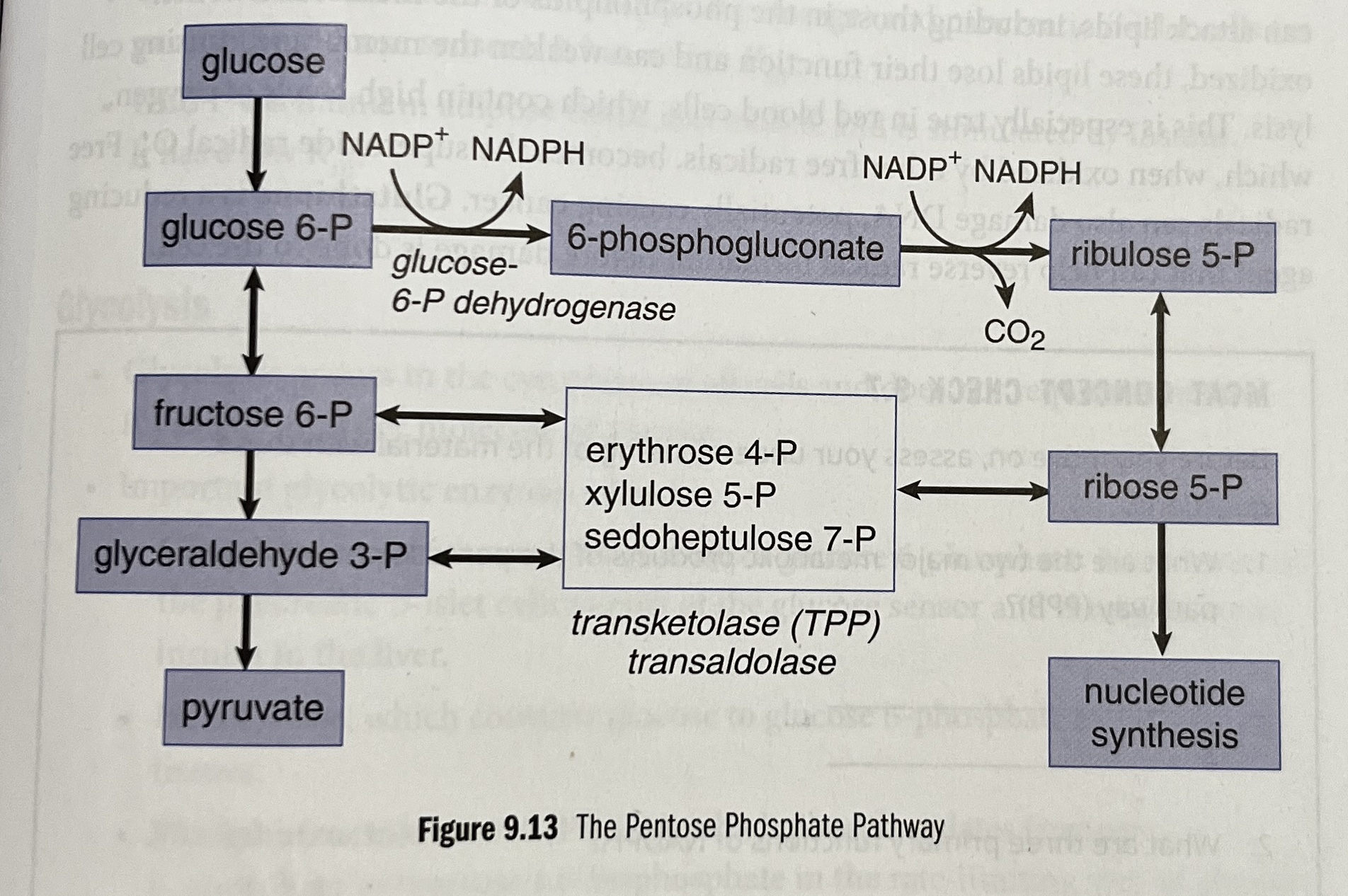
What is the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) also known as?
The hexose monophosphate (HMP) shunt.
Where does the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) occur?
In the cytoplasm of most cells
What does the pentose phosphate pathway generate?
NADPH and sugars for biosynthesis.
What is the rate-limiting enzyme of the pentose phosphate pathway?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
What activates glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase?
NADP+ and insulin.
What inhibits glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase?
NADPH.
What is the function of GLUT 2 and where is it found?
In the liver for glucose storage
In pancreatic β-islet cells as part of the glucose sensor.
It has a high Km.
What is the role of GLUT 4 and how is it stimulated?
In adipose tissue and muscle
It is stimulated by insulin.
It has a low Km.
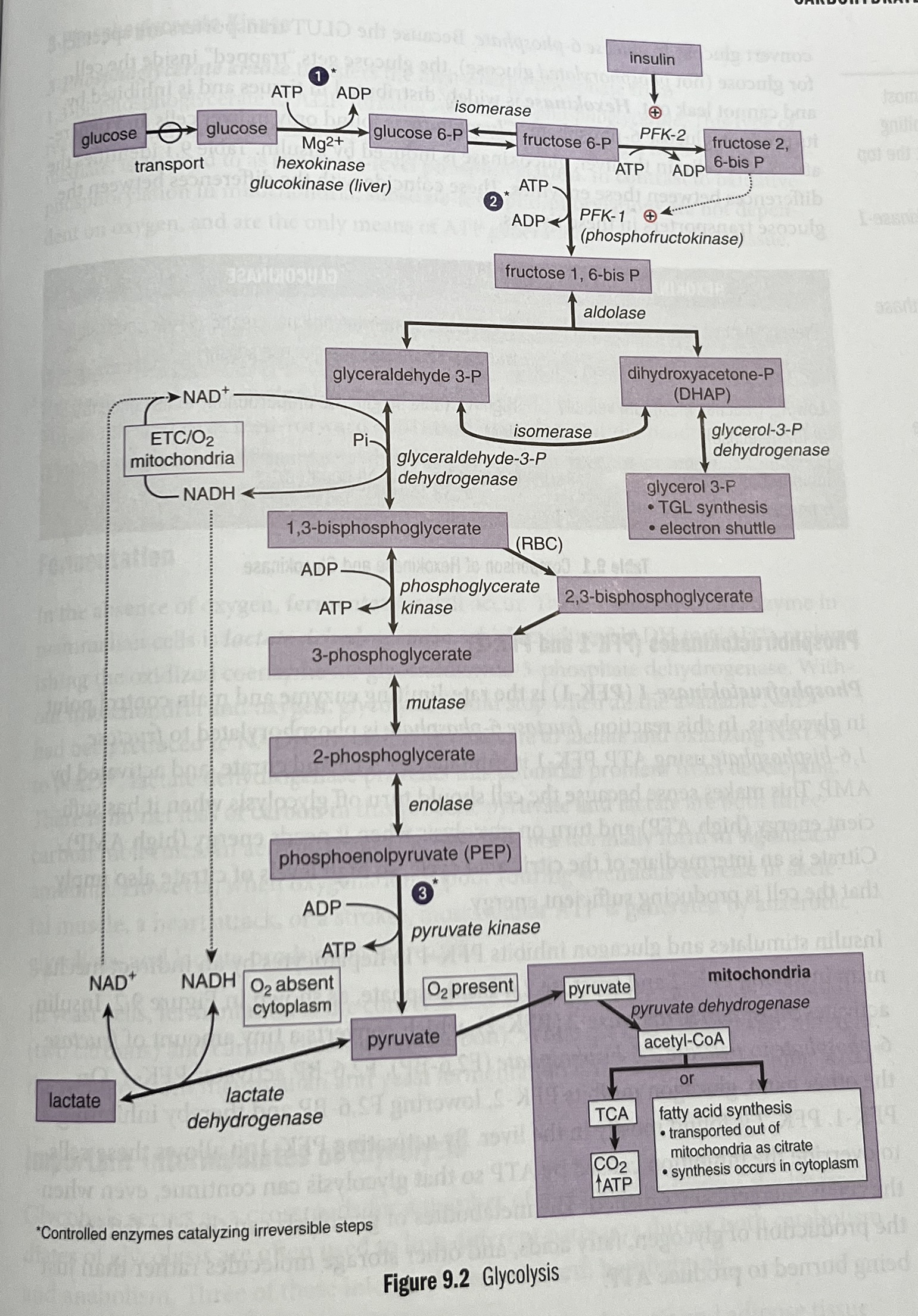
Where does glycolysis occur and does it require oxygen?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells and does not require oxygen.
How many ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis?
Glycolysis yields 2 ATP per molecule of glucose.
What is the function of glucokinase in glycolysis?
Converts glucose → glucose 6-phosphate
Is present in pancreatic β-islet cells and the liver
Responsive to insulin.
What is the role of hexokinase in glycolysis?
Converts glucose → glucose 6-phosphate
In peripheral tissues.
What is the significance of phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) in glycolysis?
PFK-1 phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate → fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
The rate-limiting step of glycolysis.
It is activated by AMP and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
Inhibited by ATP and citrate.
What does phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2) do?
PFK-2 produces fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6-BP) that activates PFK-1.
Activated by insulin
Inhibited by glucagon.
What is the role of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase produces NADH, which can feed into the electron transport chain.
What type of phosphorylation do 3-phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase perform?
Both perform substrate-level phosphorylation, placing an inorganic phosphate onto ADP to form ATP.
Which enzymes catalyze irreversible reactions in glycolysis?
Glucokinase/hexokinase
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
Pyruvate kinase.
What happens to NADH produced in glycolysis when oxygen is present?
It is oxidized by the mitochondrial electron transport chain when oxygen is present
What occurs to NADH in the absence of oxygen or mitochondria?
It is oxidized by cytoplasmic lactate dehydrogenase
Seen in red blood cells, skeletal muscle during intense exercise, and any cell deprived of oxygen.
Glycolysis steps
What is galactose and how is it metabolized?
Galactose comes from lactose in milk.
Is trapped in the cell by galactokinase
Converted to glucose 1-phosphate via galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase and an epimerase.
How is fructose metabolized in the body?
Fructose comes from honey, fruit, and sucrose
Is trapped in the cell by fructokinase
Cleaved by aldolase B to form glyceraldehyde and DHAP.
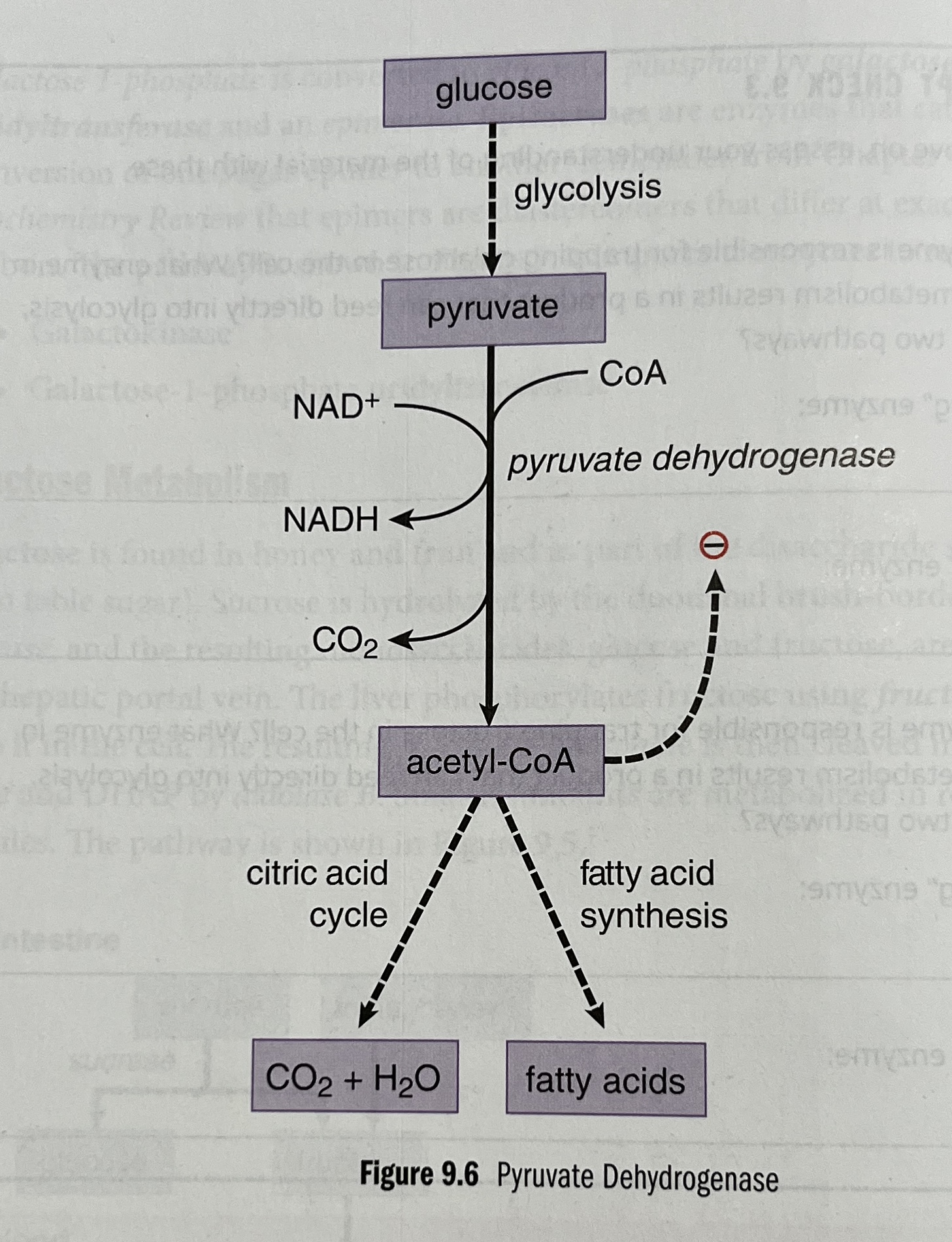
What is the function of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
A complex of enzymes that converts pyruvate → acetyl-CoA
Stimulated by insulin
Inhibited by acetyl-CoA.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
What is glycogenesis and which enzymes are involved?
The production of glycogen using:
Glycogen synthase - creates α-1,4 glycosidic links,
Branching enzyme - adds branches using α-1,6 glycosidic links.
Glycogenesis steps
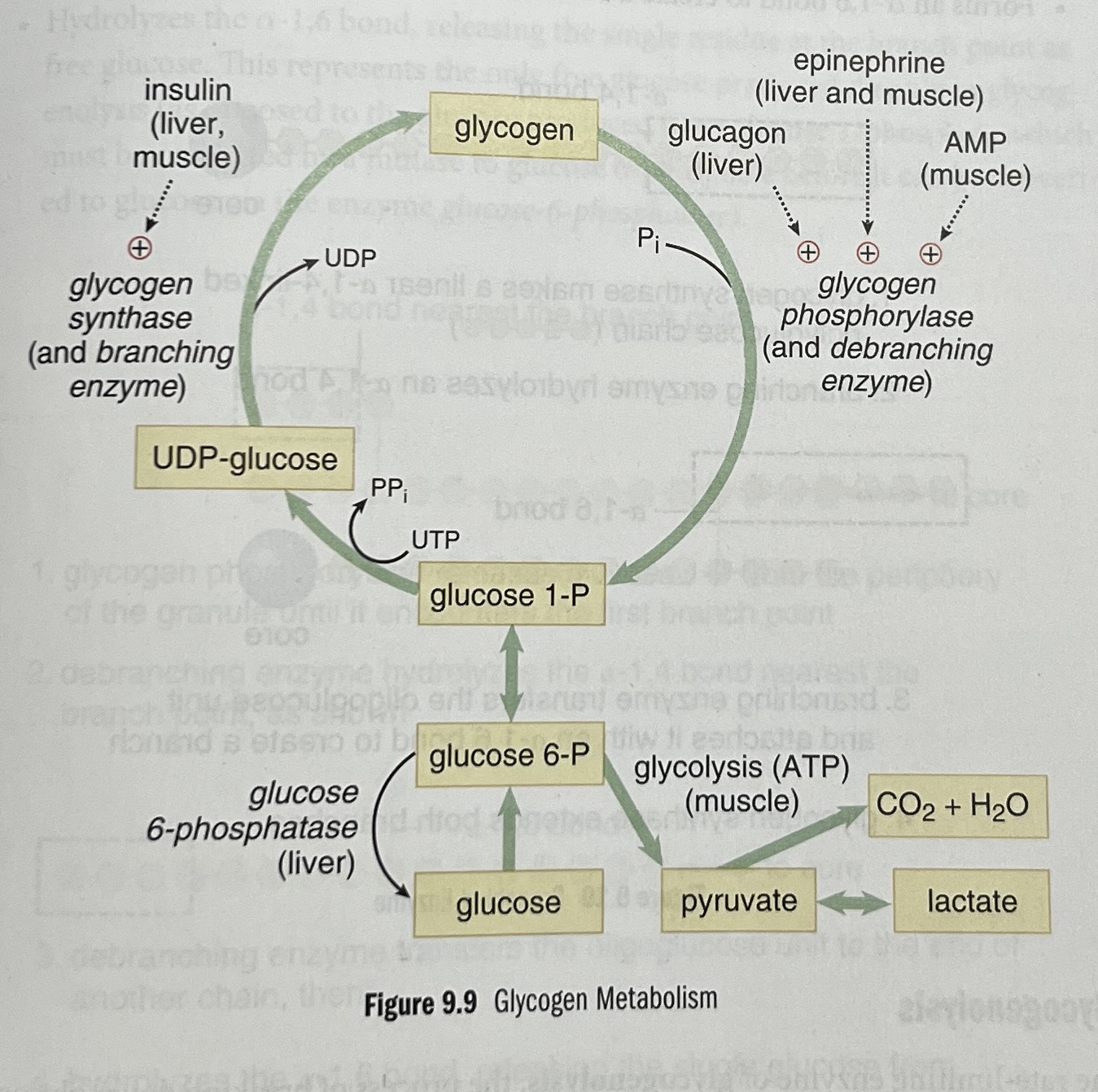
What is glycogenolysis and which enzymes are involved?
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen using:
Glycogen phosphorylase - removes glucose 1-phosphate
Debranching enzyme - connects branches and releases free glucose.
How is glycogen phosphorylase regulated in the liver and muscle?
In the liver, it is activated by glucagon to prevent low blood sugar.
In exercising skeletal muscle, it is activated by epinephrine and AMP.
Gluconeogenesis steps
Pentose Phosphate Pathway Steps