What can pass the lipid bilayer? (WEEK 1)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
The lipid bilayer is permeable to…
small hydrophobic molecules
small uncharged polar molecules
The lipid bilayer is impermeable to…
large polar molecules
ions
O2
permeable
CO2
permeable
N2
permeable
benzene
permeable
H2O
permeable
glycerol
permeable
ethanol
permeable
amino acids
impermeable
glucose
impermeable
nucleotides
impermeable
H+
impermeable
Na+
impermeable
HCO3-
impermeable
K+
impermeable
Ca2+
impermeable
Cl-
impermeable
Mg2+
impermeable
What makes the lipid bilayer selectively permeable?
transport proteins
What is the purpose of the cytoskeleton? 3 components of Cytoskeleton are . . .
To provide cell shape and movement; F actin, intermediate filaments, microtubules(tubulin)
F actin (build of, rate limiting step, purpose, size, ATP dependent?)
Made up of: ATP bound G-actin subunits
Rate limiting step: Nucleation
Purpose: supports cell’s plasma membrane → microvilli formation
Size: 7-9 mm
ATP dependent; ATP G actin hydrolyzed to add G actin to polar double helical filament
treadmilling
F-ACTIN!!! Cytosolic concentration of ATP-bound G-actin is higher than the critical concentration at the (+) end, and lower than the critical concentration at the (-) end (Cc- > C cyto > Cc+)
no overall filament change
Profilin
G actin (+) regulator
Adds ATP to G actin
Thymosin
G actin (-) regulator
Deactivates G actin ATP —> No filament growth
Cofilin
G actin (-) regulator
Destabilizes (-) end of F actin—> (-) end depolymerization
Capping Proteins
Protects F actin (+) end from depolymerization
look at picture (yellow ball)
Nucleators/Nucleation Promoting Factors/Formins
Formins
Nucleator necessary for the nucleation of actin filaments at (+ end/cell periphery)
look at picture (blue ring)
Arp2/3 complex w/ WASP
Protein complex necessary for formation of branches actin filaments
-associated with (-) end
look at picture (purple ball with orange disk)
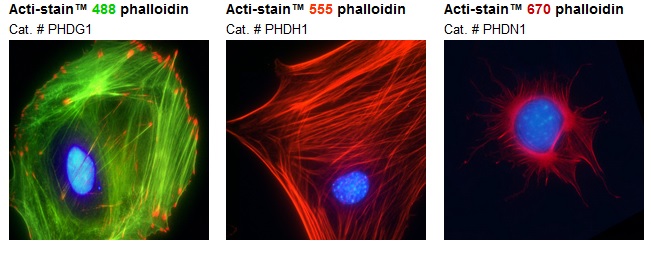
What color is F actin out of the 3 cytoskeletal elements?
Red (7-10nm)
Supports plasma membrane (also microvilli)
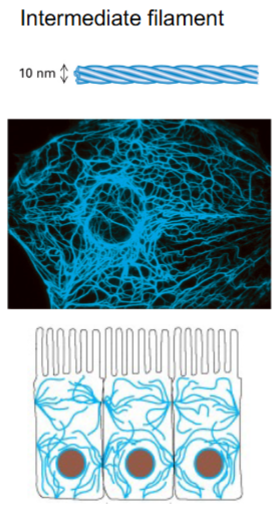
What color is Intermediate Filaments out of the 3 cytoskeletal elements?
Blue (10nm)
Structural role; found everywhere in the cell
connects between cells
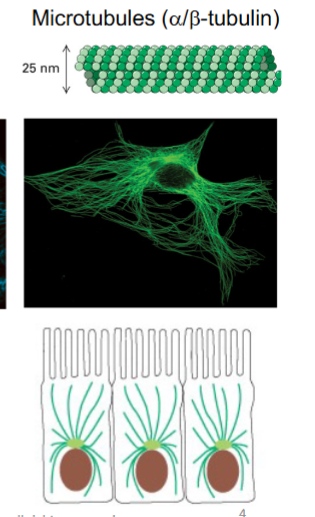
What color are Microtubules out of the 3 cytoskeletal elements?
Green (25nm)
nucleated @ Microtubule Organizating Center (MTOC)
radiates towards cell periphery
AMINO ACIDS!!! nonpolar, negative, positive, uncharged polar
write out and compare