all quiz q pt. 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
1. Intrasexual competition can result in which pattern(s) of phenotypic variation?
A. Larger body sizes in either sex (direct competition often favors larger body size)
B. Evolution of more competitive sperm (this is favored in sperm competition)
C. Ritualization of fighting behavior (when fights are common, they are more likely to be ritualized)
D. None of these
E. All of these
E
2. Which of the following statements are true about (i) intrasexual selection and (ii) intersexual selection:
A. (i) Intrasexual selection favors female-female competition and (ii) intersexual selection is when one sex chooses among potential mates of the opposite sex.
B. (i) Intrasexual selection really only occurs between males and (ii) intersexual selection really only occurs in response to females selecting among mates.
C. (i) Intrasexual selection can favor the most competitive offspring and (ii) intersexual selection can favor long female reproductive tracts
D. (i) Intrasexual selection can favor the males who are most attractive to females and (ii) intersexual selection can favor the females who are most attractive to males.
E. A&C
A
3. Intersexual selection favors which types of female competition?
A. Females protecting their offspring from potential death by other females
B. Competition for food resources that allow them to increase their fecundity
C. Access to resources that allow them to better ensure offspring survival
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
E
4. Is the following statement true or false: traits that evolve under intersexual selection are
sometimes similar to traits favored by intrasexual selection, but not always.
A. True
B. False
A
5. Which of the following is/are true about the outcome of sexual selection on males?
A. The traits favored by male competition often improve survival under natural selection whereas traits favored by female choice decrease survival
B. Traits favored by inter- and intra-sexual selection often have a cost in terms of survival under natural selection
C. The traits favored by male competition often decrease survival under natural selection whereas traits favored by female choice often increase survival
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
B
6. When should males compete strongly enough to risk injury?
A. When the costs of competing outweigh the costs of winning the competition
B. When the winner of the fight has a lot to gain from winning
C. When injuries are relatively uncostly compared to losing the fight
D. A&B
E. B&C
E
7. Which is/are true about “sneaker” male strategies?
A. The “sneaker” males are always less successful than the dominant or calling males. (genetic polymorphisms do not follow this!)
B. Females most often prefer the sneaker males (sometimes they do – they harass the females less and may be more attractive for other reasons)
C. The sneaker males do not always take the strategy of direct competition for females or territories (correct – they sneak or cooperate with females)
D. A & C
E. All of the above
C
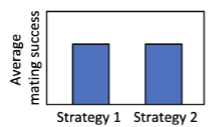
Males in a population of insects have two strategies for gaining mates – one fights to defend mates
and the other sneaks. Their average reproductive success over evolutionary time is illustrated in the
graph below. Are the alternative strategies more likely to be:
A. Genetically determined
B. Developmentally determined
C. Cannot tell from the grap
A
9. Which is/are true about alternative male mating tactics?
A. With both conditional and genetic polymorphisms, the different male strategies should have similar reproductive success on average.
B. With both genetic and conditional polymorphisms, different male phenotypes adopt different strategies for gaining access to mates
C. Changing the developmental environment can alter the proportion of each male morph in conditional polymorphisms
D. A&B
E. B&C
E
10. Which of the following are secondary sexual traits?
A. The presence of testes vs ovaries
B. The presence of bright coloration or large body size for competing
C. Hormonal surges when females are receptive
D. A&B
E. All of these
B
1 Which is/are true about indirect versus direct benefits models for the evolution of female preference?
A. For both models, male sexual traits must be heritable, and tied to offspring fitness (traits do not have to be heritable)
B. For both models, male fitness must be heritable, and the trait must reflect condition (this describes indirect benefits only)
C. For both models, the trait typically reflects the benefit(s) the female is likely to receive (yes, whether that is good genes or the direct benefit she receives).
D. A&B
E. All of the above
C
2. Some spiders provide flies as nuptial gifts to females to entice them to mate. What must be
true for female mate preference for males with larger flies to evolve?
A. Fitness of the male is heritable
B. The size of fly the male uses is heritable
C. Offspring of females mating with males with the largest gift have higher genetic quality
D. All of the above
E. None of the above (the gift must signal how much benefit the female will get, and
nothing else!)
E
What must be true for a female mate preference for larger red color patches on males to evolve under an indirect benefits model?
A. The size of the red patch is passed onto offspring
B. The patch size or brightness is correlated with fitness
C. Females that mate with males with larger patches receive more nutrition from male
D. A&B
E. All of the above
B
4. Which is/are true about female mate preferences for male traits that accurately reflect male genetic quality?
A. Offspring fitness will correlate with the male trait
B. The female preference for the male trait is heritable
C. The preferences guarantee females will mate with a preferred male (there is not a guarentee, just an increased likelihood of it happening)
D. A&B
E. all of the above
D
5. If you designed an experiment to test the hypothesis that female preferences are adaptive, which lines of evidence would support this hypothesis?
A. Females with stronger preferences have greater reproductive success
B. Females unable to mate with their preferred male have lower reproductive success
C. Females that mate with preferred males are more reproductively successful
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
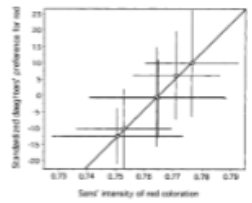
Which of the following requirements for the evolution of female preferences via Fisherian selection is illustrated in this graph?
A. The preference and signal are heritable and correlated
B. The male trait is heritable and accurately reflects male condition
C. Females mating with certain males receive more benefits of choice
D. A&B
E. All of the above
A
7. Females have evolved preferences for male guppies with orange spots on their bodies. What evidence would you need to determine the preference evolved via Sensory exploitation?
A. Closely related species of fish also have a preference for orange, but males of those species do not have orange spots.
B. Preference for the orange trait evolved before males evolved orange spots
C. Orange spots correspond with higher genetic quality of the male
D. A&B
E. All of the above
B
8. When would aggression in females not evolve due to selection favoring higher female aggression?
A. If females fight more in populations where more aggressive males are the most successful at mating (this is correlational selection)
B. If offspring survival increases as a result of female aggression
C. In lineages where males are highly competitive, females receive increased benefits from mating.
D. All of these
E. None of these
A
9. Intersexual selection favors which types of female competition?
A. Females protecting their offspring from potential death by other females
B. Competition for food resources that allow them to increase their fecundity
C. Access to resources that allow them to better ensure offspring survival
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
E
10. What types of benefits can females gain from competing for mates?
A. Mating with males that provide enough sperm to fertilize all of their eggs
B. Better care for their offspring when mating with males that invest in parental care
C. Less injury from other females
D. A&B
E. None, females don’t compete for mates
D
1. Genic capture can help reflect the genetic quality of males because:
A. Attractive ornaments are only possible to produce if a male has beneficial alleles at one or two key loci.
B. Elaboration of condition-dependent traits depends on how many resources a male has left over after he invests in somatic functioning
C. Reflects high quality in males across multiple functions like metabolism, physiology, and cellular functions
D. A&C
E. B&C
E
2. Which of the following is/are true about sexual selection and heightened condition-dependent male ornaments? Here, body size is a proxy for male condition.
A. Male ornaments under strong sexual selection should show a 1:1 increase in ornament size with body size.
B. When larger males show even larger ornaments relative to body size than small males, the ornament is a useful trait for females for selecting mates.
C. When male ornament size increases at less than a 1:1 rate with increasing body size, a tradeoff between ornament size and another trait that increases survival is likely.
D. A&B
E. B&C
E
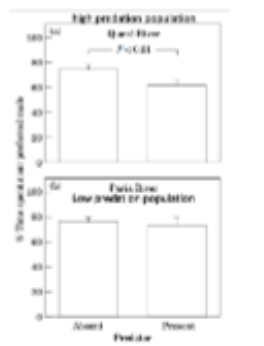
3. What does the graph to the right illustrate about female mate
preferences? The y-axis is a proxy for female preference. The
top panel is a population of fish that regularly experiences
predators in the wild.
A. Ecological factors can influence the expression of female
preferences
B. The benefits of expressing mate preference is likely to vary
with the environment
C. Male quality is not as important to females if predators are
nearby
D. A&C
E. All of the above
E
When genitalia evolve strictly under the lock and key hypothesis, which is/are true
A. The genitalia of closely related species are different
B. Evolution occurs mostly in the male genitalia and mostly in shape
C. The evolution of male genitalia is driven by female cryptic choice for particular morphological or behavioral genitalic traits
D. Sexual selection is the primary driver of genitalia evolution
E. All of the above
A
5. Why is it important to study both male and female genitalia when testing hypotheses about the evolution of genitalia?
A. Considering the shape of both male and female genitalia can help reveal how the genitalia articulate together, and thus the likely mechanism shaping their evolution
B. It isn’t because male genitalia are often sufficient to understand processes like sperm competition and female cryptic choice without looking at the female genitalia
C. While changes in male genitalia are the most important primary drivers of genitalia evolution, looking at female genitalia provides clues as to the function of the male genitalia
D. A&B
E. All of the above
A
6. Females may exhibit weaker preferences when resources are limited because:
A. Females may need to compete with other females for high quality mates, but when resources are limited, only the best females can do so
B. Males that are found easily under low resource environments are usually better quality anyway
C. They may be nearing the end of their reproductive lifespans when it does not benefit them as much to be choosy about mates
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
7. Which is/are true about female mate preferences?
A. Female mate choice is an accurate reflection of female preference across all conditions and environmental contexts.
B. Females with more or less access to food may exhibit different preferences
C. Females in a population always have the same preferences as one another
D. A&B
E. B&C
B
8. When should male mate choice be the strongest?
A. When his potential reproductive rate is high
B. When females are all high quality
C. When females are receptive sequentially
D. A&C
E. None of the above
E
9. Which are reason(s) that mating is costly for males?
A. Ejaculate is costly to produce
B. Courtship can require a lot of energy
C. Ejecting sperm into the female tract takes energy
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
10. Which of the following are ways of demonstrating preferences that are considered “cryptic”
A. Remating quickly after mating with a non-preferred mate
B. Guarding a mate for a long time after mating
C. Choosing to mate with another individual
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
Females may exhibit weaker preferences when resources are limited because:
A. She may not find another male or may need to compete with other females and low resources means less energy to do so
B. Males that are found easily under low resource environments are usually better quality anyway
C. She may be nearing the end of her life and so it does not benefit to be choosy
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
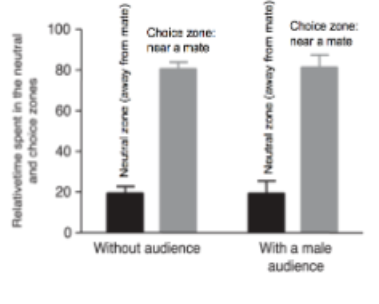
3. Inspect the graph of real data from zebra fish male behavior. This graph shows audience effects on male behavior because
A. Males spend more time near a mate than away from mate
B. Males behave differently in the presence vs absence of an audience
C. A&B
D. There isn’t an audience effect
E. The data are not informative as to whether there is an audience effect or not
B
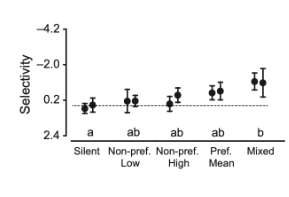
What can you deduce from this graph
Females changed how selection they were (how strong a preference they have), but not which mate they prefer when exposed to potential mates prior to becoming sexually mature
Mate choice copying is beneficial because:
A. Females can spend less time/energy looking for good mates
B. A male is high quality if another female is mating with him
C. A mated male is likely to be able to provide more sperm
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
The social environment can influence female mate preferences by leading to a change in:
A. How picky a female is
B. A female’s most preferred mate
C. The type of potential mate a female will eat
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
How might the social environment influence patterns of mating?
A. Some individuals could mistakenly mismate with another
species
B. Males may reduce the number of mates they copulate with
because they spend longer guarding a mate after copulation
C. If a lot of preferred males are around, females may only mate
with those males that closely match her preferred type
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
Under which scenarios is male or female mate choice likely to be stronger?
A. When the choosing individual has high reproductive potential
B. When the choosing individual has high potential reproductive rate
C. Both of these
D. Neither of these
A
Which of the following are ways the social environment is likely to influence patterns of mating?
A. Some individuals could mistakenly mismate with another species if lots of heterospecifics are present
B. Males may reduce the number of mates they copulate with because they spend longer guarding a mate after copulation due to high competition
C. If a lot of preferred males are around, females may only mate with those males that closely match her preferred type
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
Mating with the first individual of the opposite sex encountered may be beneficial to a choosing
individual even when they have abundant resources because
A. They may not find another mate
B. Potential mates that are found easily are usually better quality
C. They may not have much future reproductive potential and therefore it does not benefit to be choosy
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
What are the mechanisms by which the social environment can affect mating behavior?
A. How many competitors are around, and their quality and phenotypes, will affect how strongly an individual has to compete, and their likelihood to be successful, even if they are high quality.
B. High competition may make it less beneficial for males to be selective about which females they spend more time and energy courting
C. Social information exchanged among individuals can provide information about which mating decisions are likely to be most beneficial
D. A&B
E. All of the above
E
Which of the following are true about how the social environment can influence female mate preferences?
A. Females may become choosier if they experience lots of different types of males
B. The types of males that a female interacts with prior to mating do not affect their preference
C. Females may alter the type of male(s) they are willing to mate with depending on their experience with potential mates
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
If a female copies the choice of another female, she is ensuring that:
A. She is mating with a high quality male
B. She is more likely than random to mate with a higher quality male
C. She will reduce costs associated with comparing males to each other
D. A&B
E. B&C
E
Same sex sexual behavior can benefit an individual by
A. Allowing for males to learn to recognize females in the population
B. Allowing for males to have offspring with better health
C. Facilitating females mating with many males
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
A
Which are/is example(s) of proximate explanations for same-sex sexual behavior
A. It generates social bonds that provide fitness benefits
B. High aggression over e.g. resources can trigger same sex sexual behavior
C. In species where mates are hard to find, mating indiscriminately increases fitness
D. A&C
E. None of the above
B
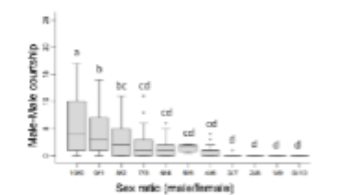
This graph illustrates the rate of same sex sexual behavior in relation to the ratio of males to females in a population. What does the data suggest about why same sex sexual behavior occurs in fruit flies?
A. It is adaptive to mate with any individual encountered because the costs of forgoing mating with the opposite sex are high.
B. Attempting to mate with the same sex allows male fruit flies to practice courtship and mating so that when they encounter the opposite sex, they will be more successful.
C. Males do not show strong discrimination among individuals that are male and female, so accidentally court males more when more males are around.
D. Males court whichever sex is most common because they sexually imprint on the common phenotype.
E. None of the above
C
10. Same sex sexual behavior may evolve because:
A. It is costly to produce the sensory systems necessary to accurately identify males versus females and/or costly to produce signals that accurately represent the sex of an individual.
B. It is less costly to mate with the same sex than it is to mistakenly discriminate against the opposite sex
C. Hormonal cascades elicit sexual behavior in the presence of another individual
D. A&B
E. All of the above
D
22. One experiment showed that when females mate with the same
male multiple times, they do not gain additional reproductive success,
but when they mate with multiple males, they do. Why is this?
A. Females mate multiply to ensure they get enough sperm to fertilize
all their eggs
B. Females mate multiply to increase the likelihood they mate with a
genetically compatible male
C. Females mate multiply to increase the number of nuptial gifts they
receive.
D. B&C
E. All of the above
A
38. What factors determine the sex that is choosier in selecting
mates?
A. Gamete size
B. Relative body sizes of the sexes
C. Nutritional investment of each sex in the offspring
D. A&C
E. All of the above
E
If the graph to the right illustrates female mating success,
which conclusions can you make?
A. Males must be the more competitive sex
B. It is difficult for a single male to dominate matings
C. Resources are likely to be clumped
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
D
Which of the following would likely favor a mating system that favors large
male weaponry?
A. Females gain social information from associating with each other
B. Resources are evenly distributed and male territories are equal
C. Males defend territories with unevenly distributed resources
D. A & B
E. A & C
C
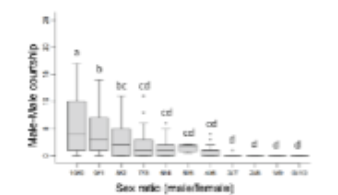
This graph illustrates the rate of same sex sexual behavior in relation to the ratio of males to females in a population. What does the data suggest about why same sex sexual behavior occurs in fruit flies?
A. It is adaptive to mate with any individual encountered because the costs of forgoing mating with the opposite sex are high.
B. Attempting to mate with the same sex allows male fruit flies to practice courtship and mating so that when they encounter the opposite sex, they will be more successful.
C. Males do not show strong discrimination among individuals that are male and female, so accidentally court males more when more males are around.
D. Males court whichever sex is most common because they sexually imprint on the common phenotype.
E. None of the above.
C
Under which scenarios is male or female mate choice likely to be stronger?
A. When the choosing individual has high reproductive potential
B. When the choosing individual has high potential reproductive rate
C. Both of these
D. Neither of these
B
Which of the following is/are true about the outcome of sexual selection on males?
A. The traits favored by male competition often improve survival under natural selection whereas traits favored by female choice decrease survival
B. Traits favored by inter- and intra-sexual selection often have a cost in terms of survival under natural selection
C. The traits favored by male competition often decrease survival under natural selection whereas traits favored by female choice often increase survival
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
C
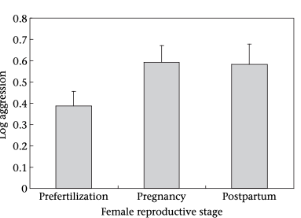
The graph below show the level of aggression that female lizards show at different stages (note:prefertilization occurs prior to mating). What does this graph suggest in terms of the most likely reason that females have evolved aggression in this species?
A. Sexual selection favors aggression so that females can attain better quality mates
B. Natural selection favors aggression so that females can protect their hatched young
C. Natural selection favors aggression so that females can acquire more resources to increase offspring survival and/or fitness
C
Which of the following statements are true about (i) intrasexual selection and (ii) intersexual selection:
A. (i) Intrasexual selection favors male-female competition and (ii) intersexual selection is when one sex chooses among potential mates of the opposite sex.
B. (i) Intrasexual selection can favor the most competitive females or males and (ii) intersexual selection occurs only between males.
C. (i) Intrasexual selection favors the most competitive males but not females and (ii) intersexual selection can favor the most attractive males or females
D. (i) Intrasexual selection can favor males that are most attractive to females and (ii) intersexual selection can favor the females who are most attractive to males.
E. None of the above
A
Which of the following describe(s) a likely outcome of selection from sperm
competition?
A. Males evolve larger testes in monandrous systems
B. Males that produce more sperm are more likely to fertilize more of a female’s eggs.
C. Female reproductive tracts evolve to promote fertilization by specific sperm types
D. A&B
E. None of these
E
Some spiders provide flies as nuptial gifts to females to entice
them to mate. What must be true for female mate preference for
males with larger flies to evolve?
A. Fitness of the male is heritable
B. The size of fly accurately indicates the nutritional (or other)
benefits the females receives when mating with a given male
C. Offspring of females mating with males with the largest gift
have higher genetic quality
D. All of the above
E. B&C
B
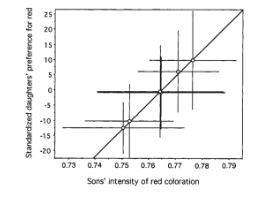
Which of the following are likely true based on this graph and your
knowledge of models of female preference evolution?
A. Red intensity indicates the genetic quality of the males.
B. The red trait is heritable
C. Mothers are likely to have a similar preference for red as her
female offspring
D. A&C
E. B&C
E
Genic capture can help reflect the genetic quality of males
because:
A. Attractive ornaments are only possible to produce if a male
has beneficial alleles at one or two key loci.
B. Elaboration of condition-dependent traits depends on how
many resources a male has left over after he invests in
somatic functioning
C. Ornaments reflect high quality in males across multiple
functions like metabolism, physiology, and cellular functions
D. A&C
E. B&C
E
When should male mate choice be the strongest?
A. When his potential reproductive rate is high
B. When females are all high quality
C. When females are receptive sequentially
D. A&C
E. None of the above
E
Cryptic female choice is likely very widespread
because
A.We often observe complex behaviors occuring when
male and female genitalia are coupled
B.Males often transfer products to females that seem
to have no effect on fertilization
C.Female genitalia are invariant within species but
highly variable across species
D.A&B
E.All of the above
D
Female cryptic choice allows for females to:
A. Select among males after she has mated with them
B. Be able to sneak extra copulations without her
partner knowing
C. Use the sperm of the best male she mated with
D. A&C
E. All of the above
D
Which of the following are true about the evolution of genitalia?
A. The lock and key hypothesis predicts parallel evolution in primarily size
of male and female genitalia
B. They take a very long time to evolve differences among populations
C. Genitalia are very similar among closely related species
D. A&C
E. None of the above
A
When pleiotropy is the main factor driving the evolution of genitalia, which is/are typically true?
A. Male and female genitalia are affected in similar ways by selection on other genes
B. The genitalia of one sex will evolve “ahead” of the other
C. Male and female genitalia co-evolve
D. A&C
E. None of the above
E
Why is it important to study both male and female genitalia when testing hypotheses about the evolution of genitalia?
A. Variation in female genitalia within a species can help indicate what mechanisms of selection shape the evolution of male and females genitalia
B. Male genitalia are often sufficient to understand processes like sperm competition and female cryptic choice
C. While changes in male genitalia are primary drivers of genitalic
evolution, looking at female genitalia provides clues as to the function of the male genitalia
D. A&C
E. None of the above
A