hispanic and latino culture
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
do we generalize this information to everyone in a culture?
no, there will be variability so it shouldn’t be assumed when working with this population
a term used by the US government to describe Spanish speakers since the early 1990’s
hispanic
has “hispanic” been understood by many individuals?
no
an individual that comes from a Spanish speaking background regardless of race (US Census Bureau, 2008)
hispanic (“government term”
A term used among individuals that see themselves as coming from a Spanish speaking background
latino/a
A basic feature of the Hispanic/Latino American family is the __________, which plays a major role in each family member's life
extended family
There are strong bonds and frequent interaction among the extended family (cousins, aunts, uncles, etc.)
Grandparents, parents, and children may live in the same household or nearby. (within walking distance sometimes)
Families visit one another _________
frequently
what personality trait is strongly valued in hispanic and latino culture?
cooperativeness
The needs of the family are usually considered _____ of individual concerns
ahead (family comes first)
This family-first aspect of Hispanic/Latino family life has led to the erroneous conclusion that the family …
impedes individual achievement and advancement.
Observers of the Hispanic/Latino American culture must distinguish between being _________ and _________ and being _____ and ________ (what personality traits?)
cooperative and respectful; docile and dependent
Generally speaking, Hispanic/Latino American children and adolescents learn to show respect for _______, the _________ family structure, and ______ family members
authority, patriarchal, extended
Hispanic/Latino American children from traditional families tend to learn early the importance of: 4 things
(1) a deep sense of family responsibility,
(2) rigid definitions of sex roles,
(3) respectful and reverent treatment of the elderly,
(4) the male's position of respect and authority in the famil
Families with relatives in Mexico tend to …
who finds that more difficult?
stay close to those relatives
Cubans, Central Americans, and South Americans
Latinos tend to value:
Work hard, play hard
They respect hard work and do not balk at manual labor.
Entertainment is a priority; music, dance, food, festivals, ceremonies.
Religion and traditions are importan
Typically ________, though there are many small communities across south Texas and Mexico different with beliefs such as Jehovah Witness, Meninite etc.,
Roman Catholic
______choice can also varies within the different countries (Spain, Dominican Republic,. Etc)
Faith
_____ is not as essential, but ___________ is
faith; following tradition
Spanish speakers tend toward _______ in their treatment of one another.
formality
_____________ is a common practice between people as greeting and for leave-taking
A firm handshake
________________________ are also common greeting practices between women, and men and women who are close friends or family
A hug and a light kiss on a cheek
Hispanics usually give great importance to and place great value on _____ and __________ as a sense of _______, _______, and ______
looks and appearance as a sense of honor, dignity, and pride
what is their time orientation?
present time
Hispanics tend to be more relaxed and flexible about time and punctuality than most people of Northern European descent in the USA.
How can this impact your assessment/therapy?
For instance, people who are invited for an 8 a.m. event may not begin to arrive until 8:30 a.m. or later. Within the Hispanic community, not being on time is a socially acceptable behavior.
Expression of emotion in public tends toward …
restraint of feelings, particularly anger and frustration
Hispanics tend to limit verbal expressions toward authority figures. example?
it is not uncommon for one parent to speak during an evaluation session while the other parent may sit in silence
________ with authority figures may also be limited
eye contact
There may be a preference for closer _________
personal space
education is ________ in hispanic and latino culture
valued
Many Latinos immigrated for better _______and ________
education and opportunity
Teachers and authority figures are __________, but the educational system can be_________for immigrants
highly respected; intimidating
____________, ___________, and _____________ make focusing on education difficult for parents and children, especially in poverty
Language barriers, system differences, and financial pressure
Data shows that there is a difference between the US “general” population and Hispanic students in earning a high school degree:
Non Hispanic US high school males and females complete high school at a rate of ~______%
Vs
Hispanic males and females that have a high school completion rate of ~_____%
83.5%-84.6%
58.7% - 61.7%
___Hispanic students will graduate with a high school diploma
¼
___% of Hispanic students will graduate from college
12.9
Students from Colombia, Peru and Cuba tend to have higher rates of college graduation per data collected from the US census bureau (2006). While this information is now more than 10 years old, it is still telling about the …
educational attainment difficulties of many individuals from these cultural backgrounds
The Hispanic population continues to _____ in the US, especially ________(_______)
grow; children (younger population)
Many of this younger generation continue to be ________ than the “general” US population and _________
less educated; live in poverty
_____ appears to be the country has the highest rate of literacy (reading/writing abilities in those that are above the age of 15)
cuba
Survival rate of students to the last primary grade – fluctuation here: Honduras, Guatemala, El Salvador and Dominican Republic in the 60’s
Likely impacting the …
increasing number of immigrant children that come to the United States via very unsafe train routes from South America/Latin America
3 main variables that have the potential to affect the growth and development of Latino children in the US
1. the environment in which they live (ex, area with high amount of air pollution)
2. smoking habits of those they live with
3. amount of lead in the home and surrounding areas (grounds) (more common in lower income and urban areas)
Consider the developing brain of these children living in less than optimal conditions
How might this impact their speech and language development?
not as much language stimulation
nutrition= brain isn’t getting what it needs to grow
For the speech language pathologist, the individual’s cultural history, and particularly the individual’s language history are of importance.
We must distinguish among Hispanic individuals who are:
1) monolingual English speakers
2) those who speak a Spanish influenced dialect of English
3) Bilingual speakers of Spanish and English (at differing levels of a bilingual continuum)
In general, there are two ways in which children may learn a second language:
simultaneously or sequentially
include young children ~under the age of ______ who are exposed to two languages at the same time
3 or 4; simultaneous learners
These children may include those who are exposed to one language by parents at home and another language by providers in their early childhood program or who hear two languages at home especially from different family members (e.g., English from mother, Spanish from grandmother, etc.)
simultaneous learners
These children may include those who are exposed to one language by parents at home and another language by providers in their early childhood program or who hear two languages at home especially from different family members (e.g., English from mother, Spanish from grandmother, etc.)
simultaneous learners
Before ______ of age, __________ learners tend to learn both languages at similar rates and do not prefer one language over the other. why? what is up for debate?
6 months; simultaneous; they build separate but equally strong language systems in their brains for each of the languages they hear.
How these systems are visualized in the developing brain is up for debate.
These separate but related systems allow children to learn…
more than one language without being confused
In fact, the pathways infants develop in their brains for each of the languages they hear are ______ to the single pathway developed by children who are only exposed to English.
similar
cognitive benefits:
greater neural activity and denser tissue in the areas of the brain related to memory, attention, and language than monolingual learners
These indicators are associated with long-term positive cognitive outcomes for children and even potential delayed onset of Alzheimer’s disease in adults
children who have become familiar with one language, but are then introduced or required to learn a second language
sequential learners
when a non-English speaking child enters an English-dominant classroom (ex, Kindergarten) is an example of…
sequential learning
Unlike simultaneous language learning, sequential learning of languages can occur __________ and can be influenced by factors like ________________ or _________
at any age ; the child’s temperament or motivation
Some children go through stages of second language learning when they are immersed in a new language environment:
what are stages I-IV?
stage 1: home language use
stage 2: silent period
stage 3: telegraphic and formulaic speech
stage 4: productive language
For the first few days, children may persist in using their first or native language even if others do not understand them
stage 1: home language use
After children realize their first language is not working, they enter a silent period in which they barely speak and rely heavily on nonverbal means to communicate with others. The younger the child, the longer the silent period may last.
stage 2: silent period
Children will start to speak in the new or second language. In this stage, they will only speak in small utterances (e.g., Me Down) or by repeating the words of others
stage 3: telegraphic and formulaic speech
Children are more ready to express their own thoughts and construct their own sentences. In the beginning, these sentences may be very basic or grammatically incorrect; however, this improves over time with language output experience.
stage 4: productive language
Parents of dual language learners (and SLPs) ________ be alarmed if their children exhibit any of the above behaviors . example? why?
should not; silent period
These behaviors are common for children who are learning a second language
Also, research has found that children who begin to learn a second language before the age of ____ are more able to speak the new language like a native speaker than children who didn’t start until after ages ____
6 or 7
So how does learning Spanish as L1 (language 1 or first language) and English as L2 (language 2 or second language) affect dual language learning and dialect?
Example: influence of the L1 is highly apparent in L2 _________.
According to Flege’s Speech Learning Model, the starting point for L2 speech development is the L1 _____________ (Flege, 1999).
For example, Spanish L1–English L2 children aged 4 to 7 years were found to be more accurate in their production of ________ that are ______ between the two languages than of _______ that are present ____ in the English L2
phonology
phonetic categories
phonemes; shared; phonemes; only
This initial L1 influence can be _____, even for child L2 learners. Both languages have the ability to ___________ in that you may see evidence of even the new language impacting the dominant language.
life-long; influence each other
___________ is an important task for L1 minority children not only for achieving adequate oral proficiency in their L2, but also for ______________ since vocabulary knowledge is an important component in literacy development
Building a lexicon
performance in a majority L2 school
Umbel, Pearson, Fernández, and Oller (1992) studied the vocabulary knowledge of 151 dual language children in first grade in Miami, some of whom had been introduced to English at school (L2), and some of whom had been exposed to both English and Spanish at home before school entry (bilingual).
Umbel et al. (1992) found that the English L2 learners scored lower than the bilinguals on the English standardized tests, both groups scored the same on the Spanish standardized tests, and both groups scored higher in Spanish than in English.
Neither the L2 learners nor the bilinguals scored at the mean; both groups; whereas both groups scored close to the mean for the monolingual Spanish normative sample
this study indicates that _______________ in the _______ language for both L2 and bilingual learners is a ________, but at the same time, ______________did not adversely affect the children’s ability to maintain age appropriate ___________ knowledge in their minority L1 into first grade.
However, as L2 children are ___________, the communicative demands on them in school and from native-speaker peers are often in advance of what they can produce
vocabulary accumulation; majority; gradual process; exposure to English;vocabulary
accumulating vocabulary
So what are some important differences in Spanish and English that may challenge young bilingual learners?
consonants
vowels
syllables
pitch
dialectal variations
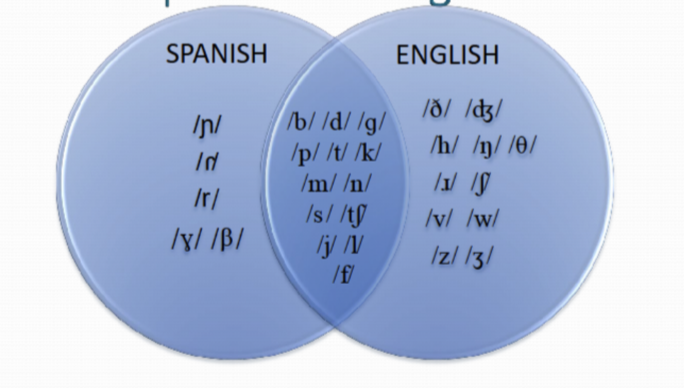
There are many differences between the consonants in English and Spanish. There are ___ phonemes that occur in both languages, __ that occur in Spanish only, and _ that occur in English only.
15; 5; 9
what two phonemes in spanish are produced interchangebly?
“ch” and “sh”
“v” and “b”
“s” and “z”
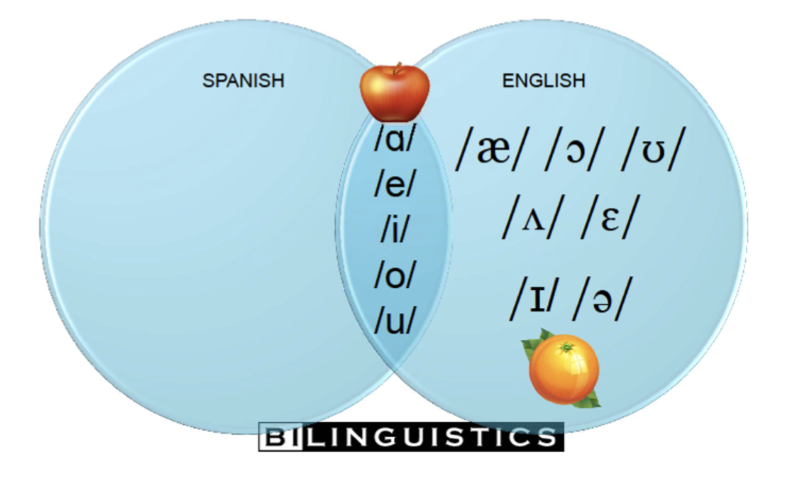
there are only ___ vowels found in the Spanish language. There is no __________________. This is very different from the ___ vowels found in English
5; unstressed schwa / ə /;30+
vowel inventory ven diagram
phonemes inventory ven diagram
Spanish is a ________ language. This language has ______ that fall …
syllabic; syllables that fall within and between words
This is often why many English speakers may perceive Spanish speakers as “rapid” talkers.
Each syllable has the same duration, no matter where the stress in the word may fall.
In contrast, English has an accentual rhythm of speech in which the accented syllables have a longer duration than the unaccented syllables. For example, “I stayed a while” has two accented areas of stress that have a slightly longer duration than the other sounds in the sentence.
In Spanish, _____ does not vary as it does in English. Therefore, a student whose primary language is Spanish may sound ________ when speaking English
pitch; monotone
It is important to note where the Spanish student is from because, depending upon the student’s region/country, there will be different types of ________ and _______ common to his/her ______. Articulation and language differences occur in different countries
variations and substitutions
dialect
For example, some Caribbean (i.e., Puerto Rico and Cuba) communities will simply delete the final / s / in words. An example would be los amigos produced as “lo amigo.”
This will have an effect on ________, as well as _______.
Students may carryover this final / s / deletion into ______.
Spanish speakers with a Castilian dialect may produce the “th” sound in place of the / s /. For example, cena would sound like “thena” in certain dialects.
articulation, as well as language.
english
Obviously we must be cautious in evaluations when judging whether a language difference exhibited in English is caused by ______________ or ______________.
transfer from Spanish or by a language impairment
The answer to the question of who provides audiology and/or speech-language pathology services to bilingual clients varies depending on…
each client's linguistic abilities in his/her first and second language.
_________________ who have the necessary clinical expertise to treat the client may not always be available. what is a viable option?
bilingual clinicians
When a bilingual speech-language pathologist (SLP) and/or audiologist is not available, using an interpreter is a viable option
There are circumstances in which a clinician who does not have _____ or __________ in the target language ______ use the skills he or she does have to provide services to a client.
In determining the appropriateness of this solution, the clinician considers both ______________________________ and _____________ of the client and family.
native or near-native proficiency; is able to
his or her own language proficiency in the target language and the language demands