Cell Biology Exam 4
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
what is cilia
-found in protozoa
- in respiratory system in the body it traps dust
ciliary escalator
decreased cilia activity as you age, makes you more prone to respiratory diseases
order of cytoskeleton components from thinnest to thickest
1. actin thinnest
2. intermediate filaments
3. microtubules thickest
what are actin filaments
- microfilaments made of long globular actin protein MONOMERS
- highly concentrated in cortex layer
what are intermediate filaments
- made of fibrous intermediate filament proteins
- form the nuclear lamina
- form ropes that have high tensile strength
what are microtubules
- hollow cylinders
- made of tubulin protein DIMERS
what are desmosomes
points of contact on the membrane that the cytoskeleton binds to which creates a network and then holds cells together to form tissue
general intermediate filament unit
2 alpha helices form a coiled coil
2 coiled coils form a dimer
two staggered antiparallel dimers form a tetramer
8 tetramers form an octamer = basic intermediate filament unit
what are the cytoplasmic intermediate filaments
1. keratin filaments - in epithelial cells, most diverse
2. vimentin and vimentin-related filaments - in connective tissue, muscle, glial cells
3. neurofilaments - in nerve cell axons
what are the nuclear intermediate filaments
nuclear lamins made of lamin protein present in all animal cells
what is laminin
different from the nuclear lamins proteins
laminin is a protein present in extracellular parts
what is epidermolysis
when the keratin filament gene is mutated -> intermediate filaments are affected -> skin blisters easily
what is plectin
protein that links the web of intermediate filaments to make them stable and stronger
what do plectin mutations cause
causes:
1. issues with muscle cells -> muscular dystrophy
2. issues with nerve cells -> neurodegeneration
3. epidermolysis
what is the nuclear lamins
- nuclear meshwork of intermediate filaments
- protects nuclear envelope from breaking down
- if nuclear lamins is phosphorylated then it becomes unstable and can be broken down
what is progeria
when there is a defect/mutation in the nuclear lamins
- causes impaired cell division and increased cell death
- person will age quicker since everything is sped up and DNA errors are not easily fixed
what are the distinct ends of the microtubule
positive end and negative end
- microtubules have dynamic instability so they're constantly growing and shrinking
- it primarily grows on the positive end
what does microtubule growth/shrinkage depend on
1. a supply of tubulin dimers in the cytoplasm
2. energy from GTP in the beta subunit
3. how quick GTPase activity at the beta subunit is
how does a microtubule form, and what is the structure of it
tubulin heterodimer has a POS beta and NEG alpha end
- subunits stack pos neg pos neg
- heterodimers are added to the plus BETA end
- 13 protofilaments/heterodimer stacks form a microtubule
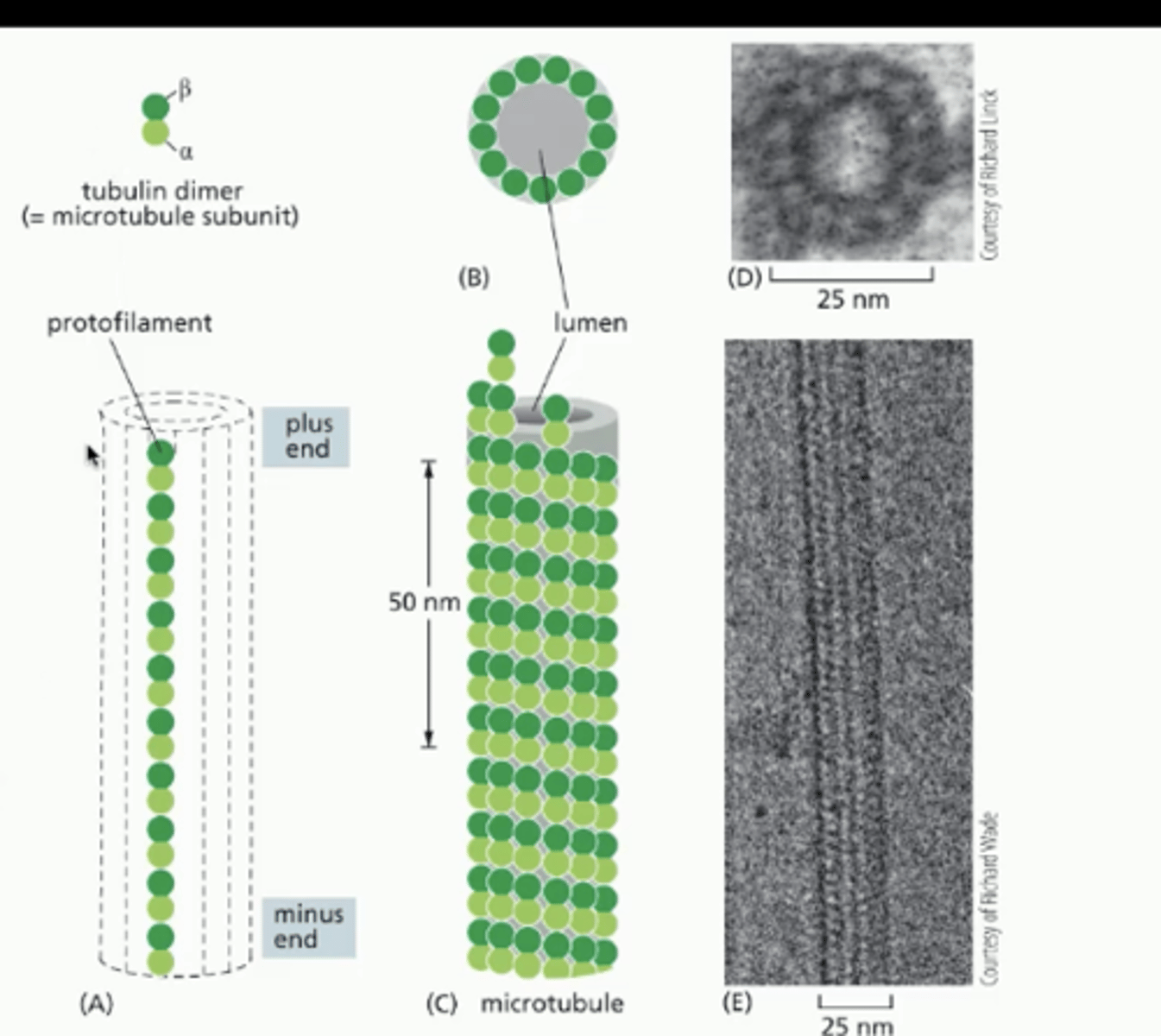
alpha, beta, and gamma tubulin
alpha-beta tubulin heterodimer forms the microtubule
gamma tubulin forms a ring on the centrosome surface that allows the microtubule to grow out of the centrosome
- microtubules extend out of the centrosome with positive end facing out
what are capping proteins
located underneath membrane, bind to growing end of microtubule to stabilize it so it doesn't shrink
what allows microtubule to GROW
when Beta unit of dimer has GTP it has affinity for accepting more dimers
what causes microtubule to shrink
1. GTPase activity at Beta subunit hydrolyzes GTP into GDP
2. when Beta subunit has GDP bound it has lower affinity with other dimers
3. growth is not favored so microtubule shrinks
what is taxol
binds to POS beta end and stabilizes microtubule which stops them at a certain length
*stops dynamic instability
what is colchicine/colcemid
binds to tubulin dimers and stops them from being added to the microtubule
*stops dynamic instability
what is vinblastine/vincristine
binds to tubulin dimers and stops them from being added to microtubule
*stops dynamic instability
what is dynein
motor protein that walks and moves cargo towards the NEGATIVE end of microtubule
what is kinesin
motor protein that walks and moves cargo towards the POSITIVE end of microtubule
how do motor proteins work
- made up of a tail and two globular heads
- the tail grabs an organelle
- it has ATPase activity -> hydrolyzes ATP so the globular heads can walk along the microtubule to move the cargo it's attached to
what is the function/purpose of motor proteins
organizes the cell interior by positioning organelles in the cytoplasm
what is the configuration of microtubules in cilia and flagella
9+2 configuration
9 microtubule doublets in a circle with a pair of microtubule singlets in the middle
- nexin links the doublets
- dynein holds the doublets in a circle position
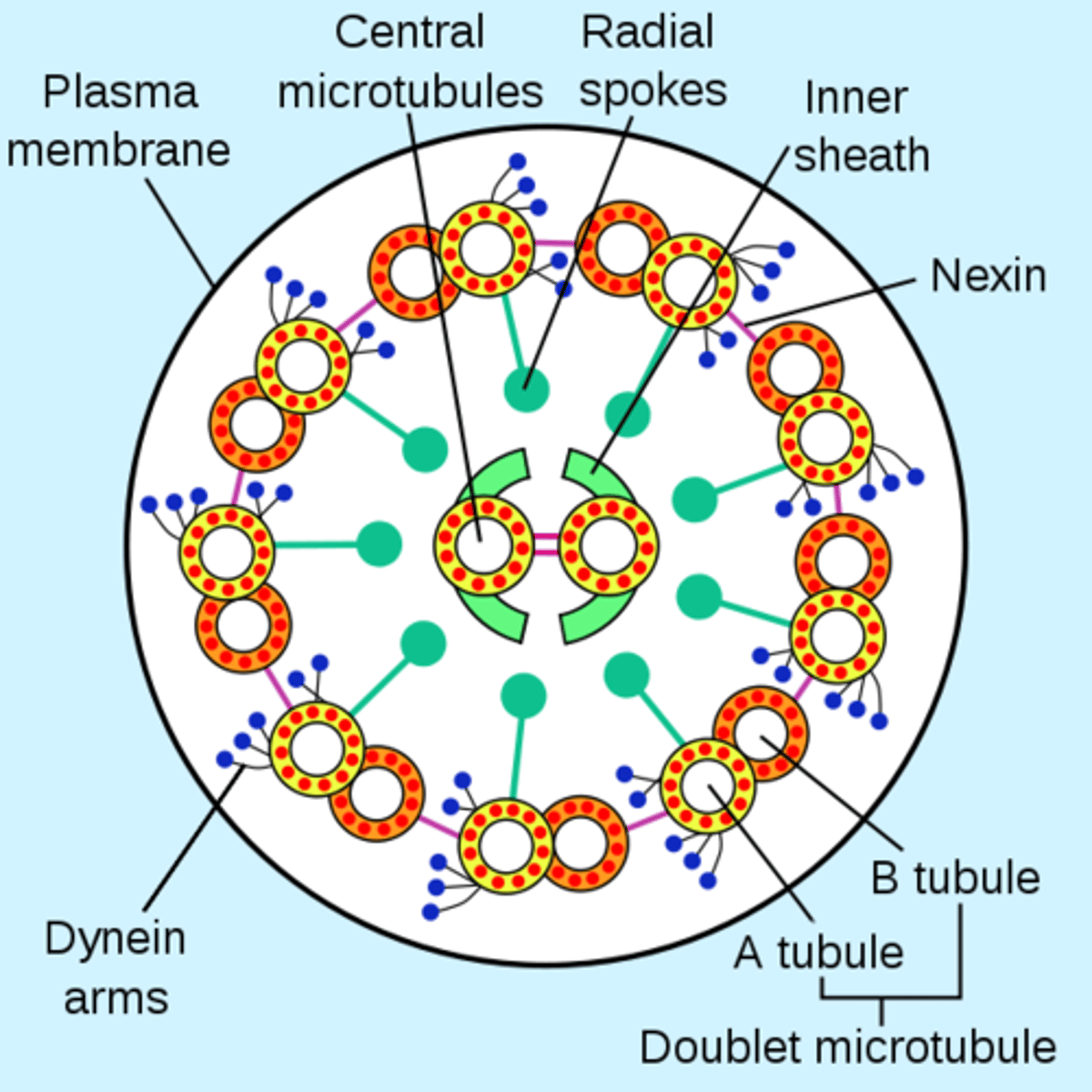
what is kartanger's syndrome
when the ciliary dynein is mutated it negatively affects cilia and flagella function
- can cause male infertility if sperm can't swim
- can cause respiratory infections in males and females
actin structure
has a positive and negative end
MONOMERS added to positive end for growth
what are cell components that are made up of actin
- microvilli
- contractile bundles
- pseudopodia
- contractile ring
what is myosin and what does it interact with
a protein involved in muscle contraction
actin-dependent movement depends on interaction with myosin and actin
how does actin form/polymerize
through treadmilling
1. ATP binds to actin monomer
2. monomer binds to positive end of growing actin
3. phosphate leaves the monomer
4. actin associated with ADP falls off at the negative end of the actin
what is phalloidin
binds and stabilizes actin filament to stop monomers from being added
what is cytochalasin
binds to actin filament and caps it at the positive end to prevent actin monomers from being added
what is latrunculin
binds to the free actin monomers to stop them from being added to growing actin polymer
what are thymosin and profiling and what do they do
naturally occurring proteins in the cytoplasm that bind to actin monomers and prevent polymerization
*regulates actin filament growth
what are formin and actin related proteins, and what do they do
naturally occurring proteins in the cytoplasm that promote actin polymerization
*regulates actin filament growth
what are filament-severing proteins
naturally occurring proteins in the cytoplasm that cuts the actin filament to make it shorter
*regulates actin filament growth
what are myosin motor proteins
naturally occurring proteins in the cytoplasm that interact with actin to drive contraction
what is the actin cortex
under the plasma membrane there is a cortex/meshwork of actin filaments
how do cells crawl
1. actin polymerizes at the plus end and a lamellipodium/pseudopod protrudes out
2. the pseudopod grabs the surface at focal contacts which have integrin protein
3. myosin and actin interact to contract at the back of the cell
4. cell moves forward
lamellipodia vs filopodia
both are actin projections
lamellipodia - branched projections for cell movement
filopodia - finger like projections that act as sensors
how do signals affect actin
a signal from a neurotransmitter can tell actin and myosin to contract
myosin molecule vs filament structure?
******??????
how does contraction occur
- myosin heads face left and right and tails are antiparallel
myosin pulls on actin filaments so they overlap
*NO change in actin or myosin filament length
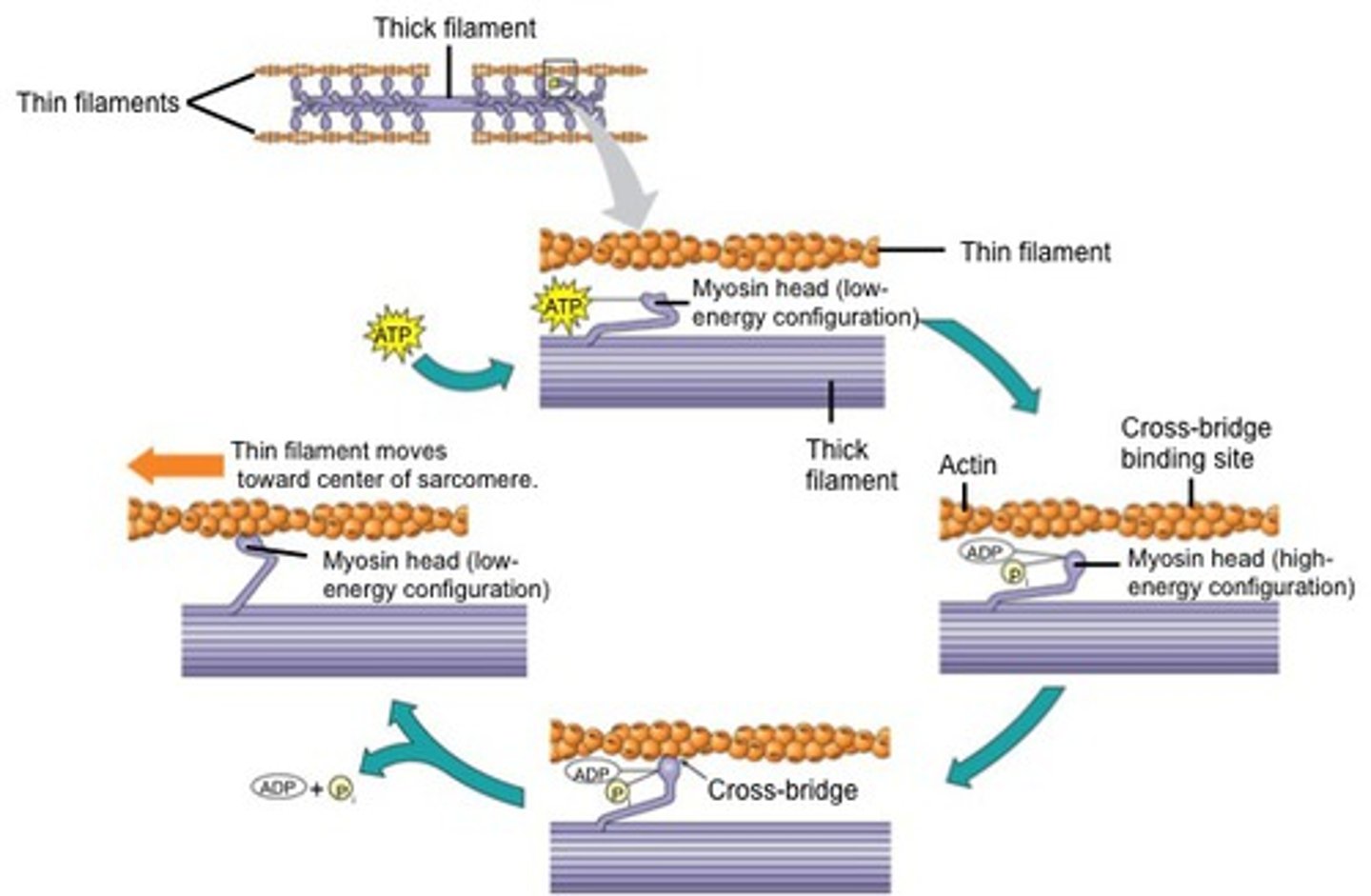
structure of muscle cells
muscle cell is a hollow tube
the tube is stuffed with many long myofibril stacks
myofibril made up of actin and myosin filaments/myofilaments
sarcomere is the unit where contraction takes place between two z discs
what is a sarcomere
the section between 2 Z discs made up of the overlapping actin and myosin filaments
during contraction the Z disc moves like an accordion and the sarcomere length shortens

what molecule triggers muscle contraction
sudden rise in cytosolic Ca2+
specialized ER in myofibrils called the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases Ca2+
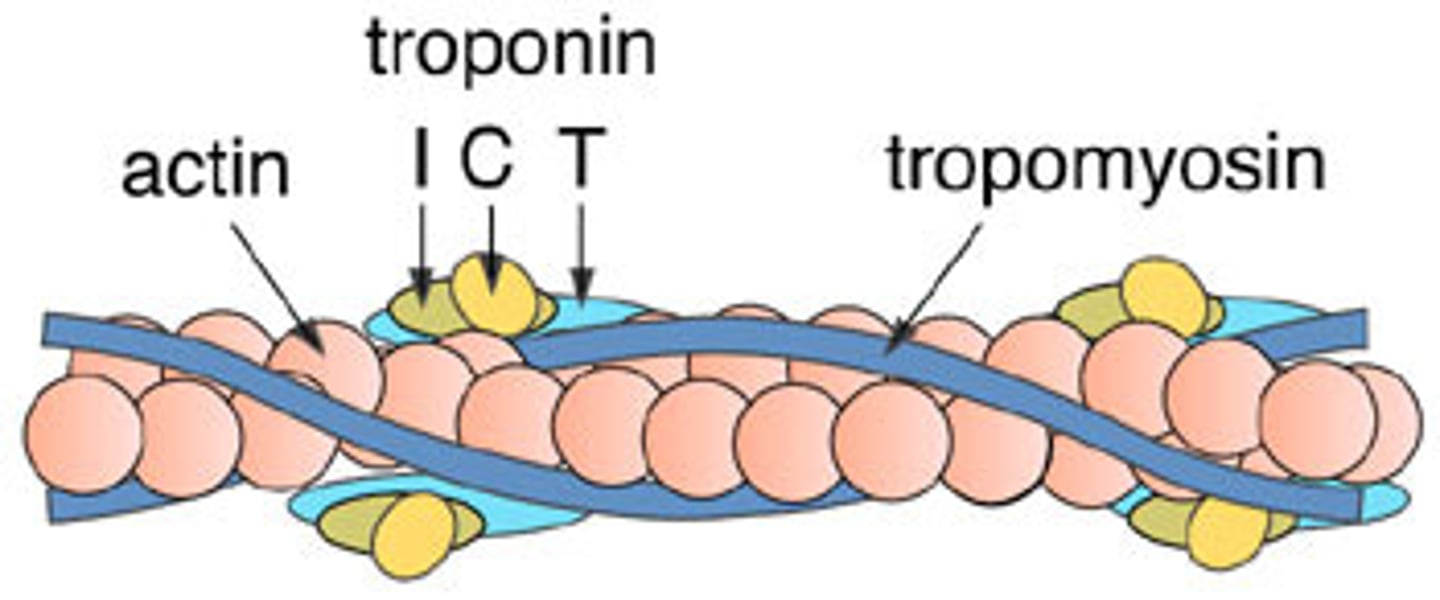
what is the mechanism that triggers muscle contraction to start
1. Ca2+ binds to C subunit of troponin complex
2. shape change pulls tropomyosin away from actin; tropomyosin doesn't let myosin interact with actin when it's bound to actin
3. allows myosin to bind to actin
4. contraction starts
what is different about early embryonic cells vs normal cells
early embryonic cells divide very quickly which doesn't allow enough time for them to grow before dividing -> daughter cells get tinier
normal cells grow before division to make cloned daughter cells
what is anaphase promoting complex
involved in controlling cycle during anaphase
where are each of the cell cycle check points
End of G1
End of G2
During Anaphase of M Phase
what is cdk and when is it activated
cdk triggers steps within the cell cycle
it is activated by cyclin at each of the three checkpoints
different cdks and cyclins for different stages of cell cycle
cyclic activation
cdks are cyclically activated so their concentration goes up and down in cycles based on which stage of the cell cycle is occuring
what are the types of cdks that exist and what stage are they for
G1 cdk - G1 phase
G1/S cdk - S phase
S cdk - S phase
G2 cdk - G2 phase
M cdk - M phase
what are the three ways cyclin concentrations are regulated
transcription: expressing the genes that produce cyclin
proteolysis: breaks down cyclin
APC: specifically breaks down M-cyclin by adding ubiquitin to it which sends it to proteosome
How does APC regulate cell cycle
APC causes Ubiquitylation on M-cyclin
this adds a protein tag which sends M-cyclin to the proteosome to be broken down -> M-cdk activity is stopped so cell can focus on anaphase and not rush into mitosis
What are the ways to regulate kinase activity which thus regulate cell cycle stages
1. regulating expression and destruction of cyclin
- use APC
- transcription
- through proteolysis
2. phosphorylating to block cyclin from binding and dephosphorylating cdk to activate it
3. inhibitory proteins clamp cdk and cyclin so they can't interact with things
what is cdc 25
an activating phosphatase that removes inhibitory phosphate from M-cdk to activate it
what is Wee1
kinase that adds the inhibitory phosphate to M-cdk to inactivate it
what happens when cdk is phosphorylated
phosphorylated cdk changes its conformation and then is blocked from binding with cyclin -> inactivated
what is p27
inhibitory protein that grabs onto an active cyclin-cdk complex and inactivates it
how does the cell fix a small problem that needs a quick pause
inactivate the cyclin-cdk complex for a quick pause
-> can do it through inhibitory protein p27
how does the cell fix a bigger problem that needs more time
cell will sit at G0 phase until problem is fixed
or the cell is never fixed and dies
what are terminally differentiated cells
highly differentiated cells will stop replication
ex. cornea cells
what is a mitogen
anything that promotes production of cyclins to start cell cycle
why do people with retinoblastoma have uncontrolled cell div
mutated Rb protein is always inactive, so transcription of cyclins and cell cycle proteins is never blocked
what does Rb do when its active vs inactive
active Rb protein - attaches to a transcription regulator and inactivates it -> blocks cell cycle
G1 cdk and G1/S cdk when active phosphorylate Rb which pulls it away from transcription regulator
inactive Rb protein - it's pulled away from transcription regulator which activates it and allows transcription of cell cycle proteins
what is the mechanism/events that occur after DNA damage
1. DNA damaged by X-rays or something
2. causes protein kinases to be activated and phosphorylate p53
3. p53 activated and binds to p21 regulatory gene
4. p21 gene is transcribed
5. p21 inhibitory protein clamps G1/S cdk and S cdk and inactivates
6. cell division is halted at the G1 PHASE
what happens if p21 gene is mutated
if p21 gene is not transcribed, then p21 inhibitory protein can't be active
cell cycle will continue but with damaged DNA, which can cause cancer
what is cdc 6
prevents progression from G1 to S phase
binds to ORC (origin recognition complex) and attracts helicase to the strands
eventually cdc6 dissociates and is replaced by helicase
how does the cell progress from G1 to S phase
1. cdc 6 dissociates from ORC after being phosphorylated by S cdk and helicase binds
2. S-cdk adds phosphate to helicase to activate it
3. helicase separates the strands and DNA replication starts
4. **cdc 6 gets degraded so that replication only happens once during S phase
what does the cell do if replication is incomplete
if there's errors in DNA replication the cell will stop at G2
- make sure M-cdk is not activated by making sure cdc 25 is inactivated
cdc 25 phosphatase activates M-cdk by dephosphorylating it
what does cohesin do
cohesin forms rings along the length of the chromosome to keep sister chromatids together
what happens if cell lacks cohesins
chromosomes can't stick together so an unequal amount of chromosomes are sent to either cell
what are condensins
form rings around chromosomes to help condense them
what is the contractile ring
made out of actin and myosin and pinches cell into two daughter cells
interpolar microtubules direct the formation of the ring
what happens during interphase
1. cell size increases
2. DNA replicated
3. centrosome duplicated during S phase because of G1/S cyclin-cdk
what happens during prophase
1. condensins make chromosomes visible
2. mitotic spindle starts to form bc of dynamic instability
3. centrosomes start moving to opposite poles
what happens during prometaphase
1. M-cdk phosphorylates lamin proteins so nuclear envelope breaks down
2. kinetochore microtubules attach to kinetochores of each sis chromatid
what happens during metaphase
1. chromosomes align at equator of spindle due to dynamic instability
what happens during anaphase
anaphase a:
- kinetochore microtubules shrink
anaphase b:
- centrosomes move apart
1. cohesins broken down
2. sister chromatids pulled apart
what happens during telophase
1. sis chromatids now considered chromosomes
2. chromosomes arrive at each spindle pole
3. nuclear envelope reassembles when nuclear lamins proteins are dephosphorylated
4. contractile ring assembly begins
what happens during cytokinesis
1. contractile ring pinches
2. cell splits non specifically into 2 daughter cells
what are aster microtubules
extend from centrosome to connect spindle pole to plasma membrane
what are interpolar microtubule
microtubules that bind each other from opposite ends of the cell
kinetochore microtubules
attach to kinetochores of each sister chromatid
why are cohesins broken down
so that sister chromatids can separate during anaphase
how are cohesins broken down
1. active APC adds ubiquitin to securin
2. securin unbinds from separase
3. securin is proteolysed, while separase is released and thus activated
4. active separase cleaves cohesins during/allowing anaphase
what is anaphase a
kinetochore microtubules shorten which causes forces to move the chromosomes toward their spindle pole
what is anaphse b
interpolar microtubules generate sliding force which pushes the centrosomes at either pole apart
what happens if a microtubule isn't attached to a chromatid
in prometaphase if not all chromatids are attached to microtubule, then separation is stopped
1. unattached chromosome sends stop signal
2. signal blocks activation of APC
3. securin not degraded
4. separase not released
5. cohesins not degraded
6. sis chromatids stay glued together
what does spindle assembly checkpoint do
stops cycle from proceeding to anaphase if all chromosomes didn't attach to microtubule during prometaphase
what is the mechanism of nuclear envelope reforming
during telophase nuclear envelope reforms when proteins are dephosphorylated
nuclear envelope vesicles and pore proteins fuse when dephosphorylated
how do mitochondria and chloroplasts assort into daughters
they divide during cell growth and are separated unevenly but there's so many that it's enough for each daughter
how is ER assorted into daughter cells
ER fragments when nuclear envelope fragments, and is then rearranged and taken into daughter cells by microtubules