Topography and functional levels
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What do the meninges do?
Support and protect the CNS (brain + spinal cord).
What is the order of the meninges from external to internal?
Dura mater → Arachnoid → Pia mater (PAD the brain).
Are the meninges around the brain and spinal cord continuous?
Yes
What is the dura mater made of?
Strong, fibrous connective tissue with 2 layers.
Around the brain, how are the dura mater layers arranged?
Fused and adhere to the inner surface of the skull, except where they split to form venous sinuses.
What do venous sinuses do?
Carry blood from the brain to the veins of the neck.
How many internal compartments does the inner layer of the dura create?
Four
What does the falx cerebri separate?
Lies in the longitudinal groove between the cerebral hemispheres.
What does the falx cerebelli separate?
The upper parts of the cerebellar hemispheres.
What does the tentorium cerebelli separate?
Posterior cerebral hemispheres (above) from cerebellum (below).
What does the diaphragma sellae cover and house?
Covers the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland.
Where is the arachnoid located?
Between the dura and pia mater.
What does the outer part of the arachnoid adhere to?
The dura mater.
What are trabeculae in the arachnoid?
Spiderweb-like projections extending internally from the arachnoid to the pia mater.
Where is the epidural space located?
Between the bone and the dura mater.
Where is the subdural space located?
Between the dura and arachnoid.
What is the pia mater?
A thin membrane that closely envelops the brain and spinal cord.
What is unique about the pia mater’s blood supply?
It is highly vascular with small blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord
Which human cells cannot reproduce?
Neurons
Is damage to a neuronal cell body reparable?
No, it is irreparable.
Can axons regenerate?
Yes, but regeneration is generally limited to the PNS.
What is the term for the brain’s ability to adapt after injury?
Neuroplasticity
What is Myasthenia Gravis (MG)?
An autoimmune disease of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the post-synaptic membrane.
What is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Acute Schwann(PNS) cell inflammation → demyelinating neuropathy affecting spinal roots and proximal nerve trunks, causing symmetric progressive weakness and possible respiratory paralysis.
What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease?
The most common hereditary polyneuropathy, involving demyelination of sensory and motor axons.
What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
An immunologic, acquired demyelinating disease of the CNS with cycles of relapse and remission (affects cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, spinal cord).
What does neuropathy mean?
Nerve pathology.
What is the main role of the spinal cord?
Provides the conductive link between the body and the brain.
What does the spinal cord transmit from body → brain?
General sensations (touch, pressure, vibration, motion, pain) from limbs, neck, trunk.
Afferent Neuron
Arrives info toward the brain
Efferent Neuron
Exits the brain
What does the spinal cord carry from brain → body?
Commands for voluntary movements in limbs, neck, and trunk.
Where is the spinal cord located?
In the vertebral canal, housed by the vertebrae.
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7 (CV).
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12 (TV).
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5 (LV).
How many sacral vertebrae are there?
5 (SV).
From where to where does the spinal cord extend?
From the foramen magnum to the first lumbar vertebra.
About how many new spinal cord injury cases occur annually in the USA?
~10,000.
What percentage of spinal cord injuries result in permanent disability?
Nearly 50%.
About how many people in the USA use wheelchairs due to spinal cord injury?
~200,000
What are the common causes of spinal cord injuries?
Automobile and sports accidents.
What age group makes up nearly 2/3 of spinal cord injuries?
30 and younger.
What gender makes up the majority of spinal cord injuries?
Males
What are common vertebral dislocation sites in spinal cord injuries?
CV5–CV6, TV12–LV1, CV1–CV2.
How many spinal cord segments are there?
31
How many cervical spinal cord segments are there?
8 (C).
How many thoracic spinal cord segments are there?
12 (T).
How many lumbar spinal cord segments are there?
5 (L).
How many sacral spinal cord segments are there?
5 (S).
How many coccygeal spinal cord segments are there?
1 (Co).
Each spinal cord segment is associated with what?
A set of spinal nerves.
What are the three spinal meninges (from internal to external)?
Pia mater → Arachnoid → Dura mater.
What is the pia mater in the spinal cord?
Closely adhered to the surface of the SC.
What is the arachnoid in the spinal cord?
Loosely surrounds pia mater, attached to dura.
What is the dura mater in the spinal cord anchored by?
Denticulate ligaments & spinal nerve roots.
What is the dural sac?
A sac inferior to the SC spanning LV1–SV2, part of the subarachnoid space.
What anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx?
Filum terminale (“terminal thread”).
What is the cauda equina?
Roots of lumbar and sacral nerves within the dural sac.
What fluid fills the dural sac?
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid).
What procedure removes CSF from the lumbar region?
Lumbar tap.
What does “cauda equina” mean?
Latin for “horse’s tail.”
Which nerves make up the cauda equina?
2nd–5th lumbar pairs, 1st–5th sacral pairs, and the coccygeal nerve.
Where do the cauda equina nerves originate?
Conus medullaris (end of the SC proper).
Where do cauda equina nerves descend to?
To the level of their namesake vertebrae or sacrum.
What does “cauda equina” mean in Latin?
Horse’s tail.
What happens at the cauda equina?
The spinal cord ends, but nerve roots descend and exit at the level of their namesake vertebrae.
What are the two types of spinal nerve roots?
Dorsal and ventral roots.
Dorsal
Sensory/Afferent
Ventral
Motor/Efferent
How many roots does each spinal cord segment have?
Four (a pair of dorsal roots and a pair of ventral roots).
How are roots attached to the spinal cord?
By rootlets.
What happens when dorsal and ventral roots unite?
They form spinal nerves.
Why are spinal nerves considered mixed?
They contain both sensory and motor fibers.
What is the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord?
A groove that houses the anterior spinal artery.
What is the posterior median sulcus of the spinal cord?
A groove along the posterior midline.
What emerges from the anterolateral sulci?
Anterior (ventral) rootlets.
What emerges from the posterolateral sulci?
Posterior (dorsal) rootlets.
What does the external portion of the spinal cord consist of?
White matter (myelinated axons → whitish color).
What does the internal portion of the spinal cord consist of?
Gray matter (cell bodies/nuclei, dendrites, capillaries, glia → lack of myelin = grayish color).
What does the posterior funiculus (dorsal column) contain?
Only ascending axons for somatic sensory input.
What tract in the posterior funiculus carries input from the lower limbs and trunk?
Gracile tract. (grass)
What tract in the posterior funiculus carries input from the upper limbs and trunk?
Cuneate tract.
What does the lateral funiculus contain?
Ascending and descending tracts for sensorimotor control.
What does the anterior funiculus contain?
Ascending tracts (pain/temp) and descending tracts (axial muscles, posture).
How many divisions are in the spinal cord gray matter?
Four
What is the function of the dorsal (posterior) horns?
Sensory processing.
What is the function of the ventral (anterior) horns?
Voluntary movement.
What is the function of the intermediate zones?
Contain associative interneurons for reflex modulation and intersegmental integration.
What is the function of the lateral horns?
Sympathetic nervous system control.
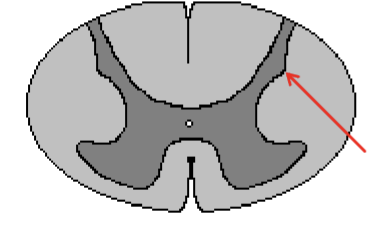
Cervical
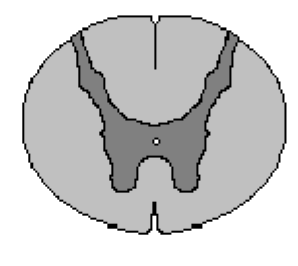
Thoracic
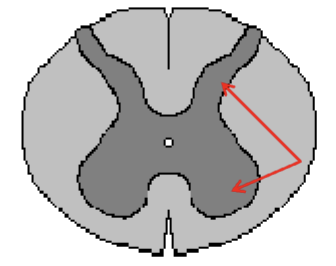
Lumbar
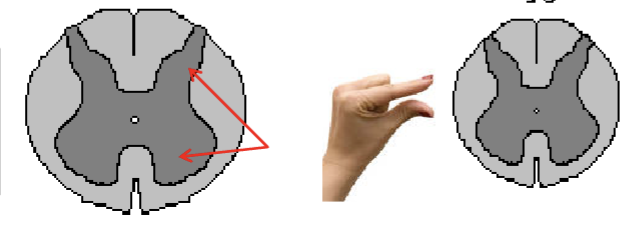
Sacral; coccygeal