Embryology 7 | Teratogens and Birth Defects
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
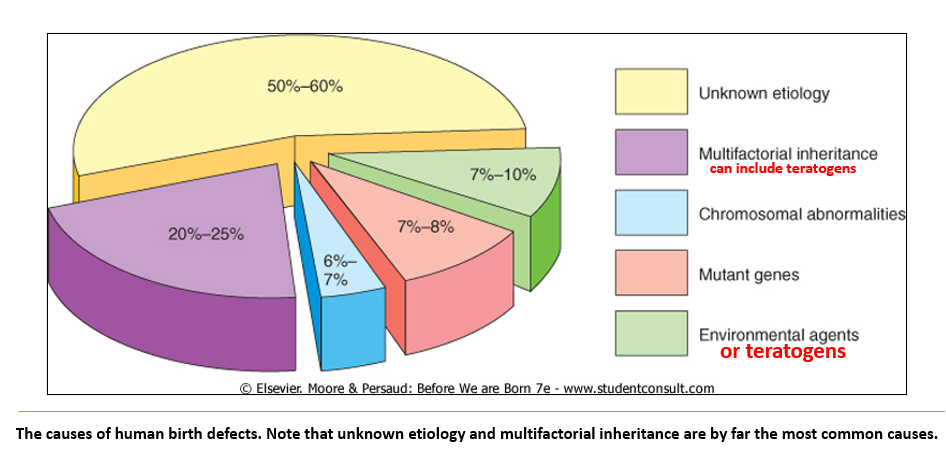
What are the main causes of birth defects and their approximate contributions?
Unknown etiology: 50–60%
Multifactorial inheritance: 20–25%
Chromosomal abnormalities: 6–7%
Mutant genes: 7–8%
Environmental agents: 7–10%
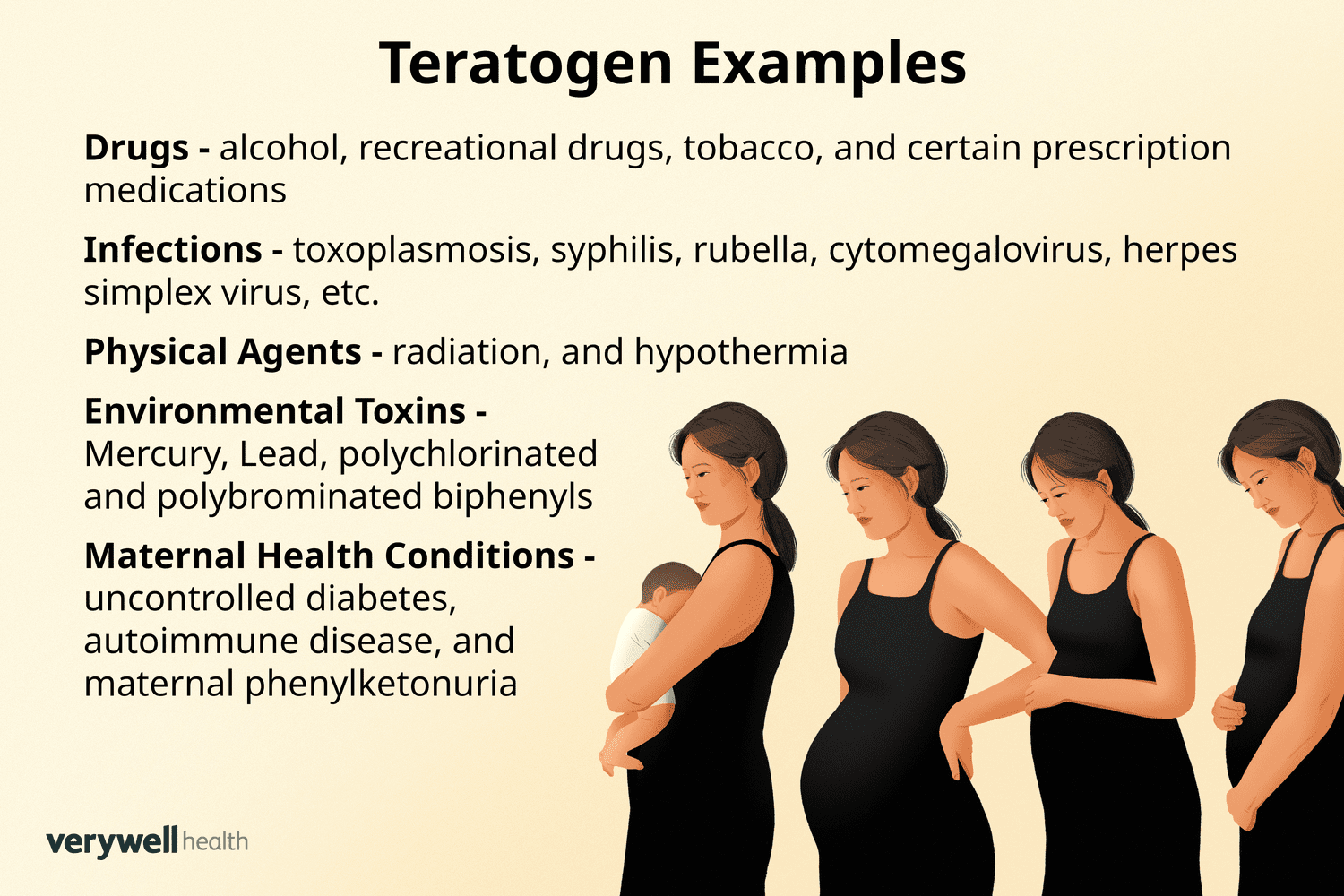
What is a teratogen?
A teratogen is any agent that causes birth defects.
What determines how susceptible a developing baby is to teratogens?
Susceptibility depends on the genotype of both the mother and the embryo (conceptus). Some individuals may be more sensitive to certain teratogens due to genetic differences.
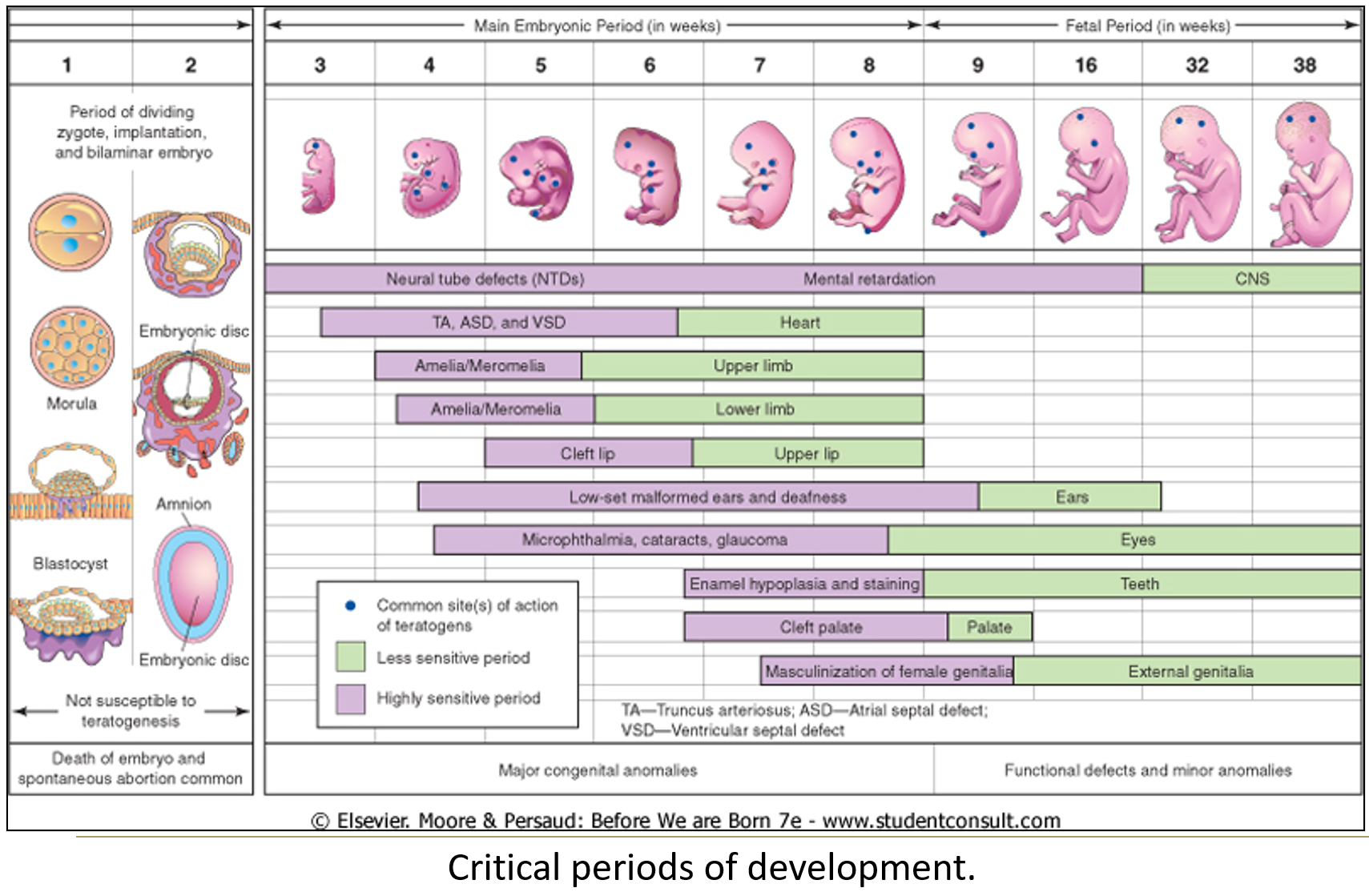
When is the embryo most vulnerable to teratogens?
The critical period is between 3–8 weeks of embryonic development, when major organs are forming.
Exposure during the blastula or gastrula stage (earlier) is often lethal.
The brain and some organs have longer critical periods.
Mnemonic: Teratogen = T (third), E (eighth) = to remember weeks 3 to 8.
What other factors influence the effect of a teratogen?
Dose
Duration of exposure
Genetic makeup of the conceptus
All affect the severity and manifestation of the defect.
What is required to prove a substance has teratogenic potential?
There must be:
More birth defects than usual in babies exposed to it during pregnancy, or
Mothers of babies with birth defects must have a higher exposure to the agent than mothers of healthy babies.
Why is proving teratogenic potential difficult?
Exposure often occurs months before birth, making data collection difficult.
Animal studies may not accurately reflect human outcomes, especially due to differences in dosage or nutrition.
How does cigarette smoke act as a teratogen?
Smoke causes intrauterine growth restriction
Nicotine constricts uterine blood vessels
Carbon monoxide binds to maternal and fetal hemoglobin
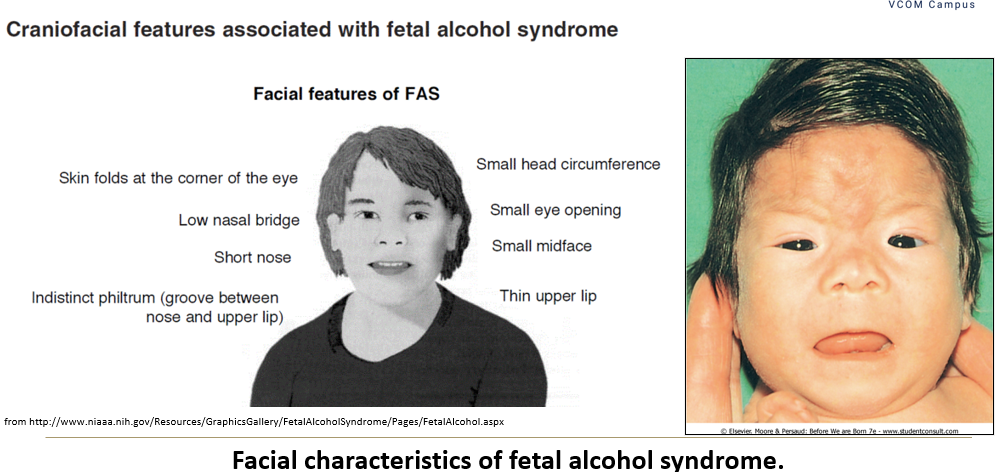
What are the effects of alcohol on fetal development?
Fetal alcohol effects include behavioral and learning issues from moderate use or binge episodes
Fetal alcohol syndrome: physical, mental, and growth anomalies from chronic alcoholism
Abstinence from alcohol is recommended during pregnancy
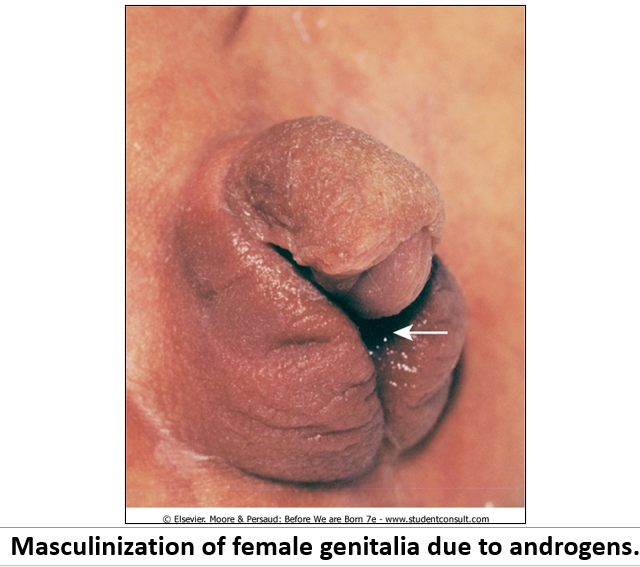
How do sex hormones impact fetal development?
Androgens cause masculinization of female fetuses
Progesterone (in birth control) is linked to VACTERL syndrome
Diethylstilbestrol leads to genital tract anomalies and vaginal adenocarcinoma in offspring
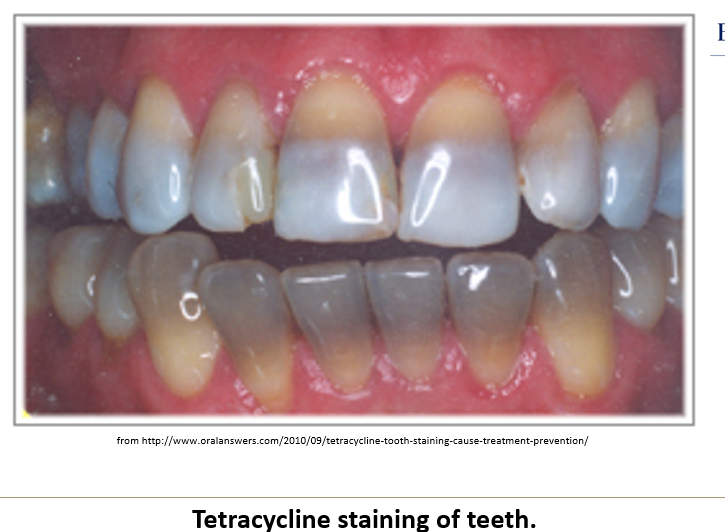
Which antibiotics are teratogenic and how?
Tetracycline causes tooth discoloration, low enamel, and bone growth delay
Streptomycin has been linked to 8th cranial nerve damage
Why is thalidomide a classic teratogen?
Used to treat morning sickness (1957–61)
Caused meromelia (limb reduction defects)
Still used, but only in non-childbearing women
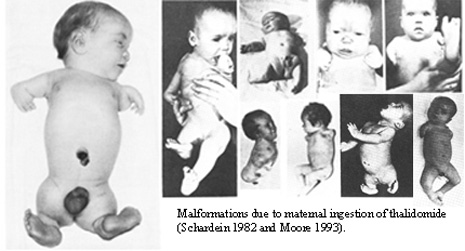
Are prescription drugs also teratogenic?
Yes, several prescription drugs (e.g., anticonvulsants, lithium, antihypertensives, retinoic acid, anti-cancer agents) and illicit drugs are known teratogens.
How does mercury act as a teratogen?
Causes mental retardation and motor dysfunctions, most commonly from fish and seafood consumption.

What are the effects of lead exposure during pregnancy?
Increased miscarriage, anomalies, IUGR, and functional deficits
Sub-clinical exposure can cause neurobehavioral and psychomotor issues
Most common source is old paint dust or chips (pre-1978), though many others exist
What are polychlorinated biphenyls and how do they affect development?
Polychlorinated biphenyls are highly carcinogenic, cause intrauterine growth retardation and skin discoloration.
They were used as coolants/insulators until 1979 and are still found in the environment and sports fish.

What birth defects are caused by rubella?
Rubella (German measles) interferes with eye and/or ear development.
What is the concern with cytomegalovirus in pregnancy?
Cytomegalovirus is usually asymptomatic in mothers, but can cause mental retardation or be lethal in infants.
How does Toxoplasma gondii cause birth defects?
Toxoplasma gondii affects the CNS in infants. It’s asymptomatic in mothers and is contracted through raw meats or cat feces.
Which infectious agents have low teratogenic potential?
Herpes simplex, syphilis, varicella, and HIV have low teratogenic potential. Hyperthermia from maternal infection with pyrogenic viruses is also linked to low risk.
Can radiation cause birth defects?
High-dose radiation kills rapidly dividing cells and acts as a mutagen. Diagnostic levels are safe unless the uterus is involved and exposure is limited.
How does poorly controlled diabetes affect pregnancy?
Increases the risk of birth defects, stillbirth, neonatal death, and macrosomia by 3-4 times.
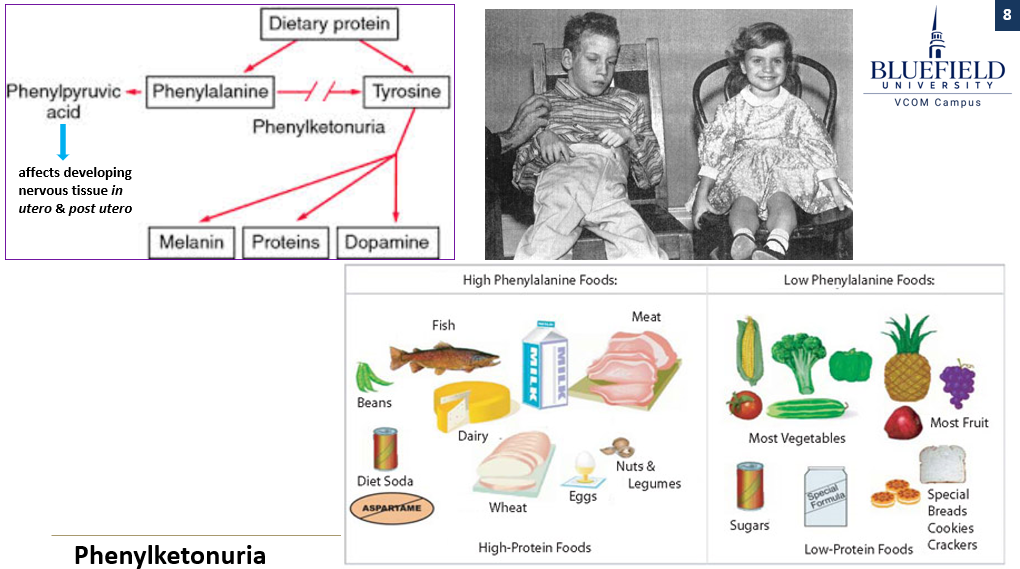
What are the effects of phenylketonuria in pregnancy?
High maternal phenylalanine levels are teratogenic, leading to mental retardation, microcephaly, and heart defects. Risk is reduced with a low-phenylalanine diet.
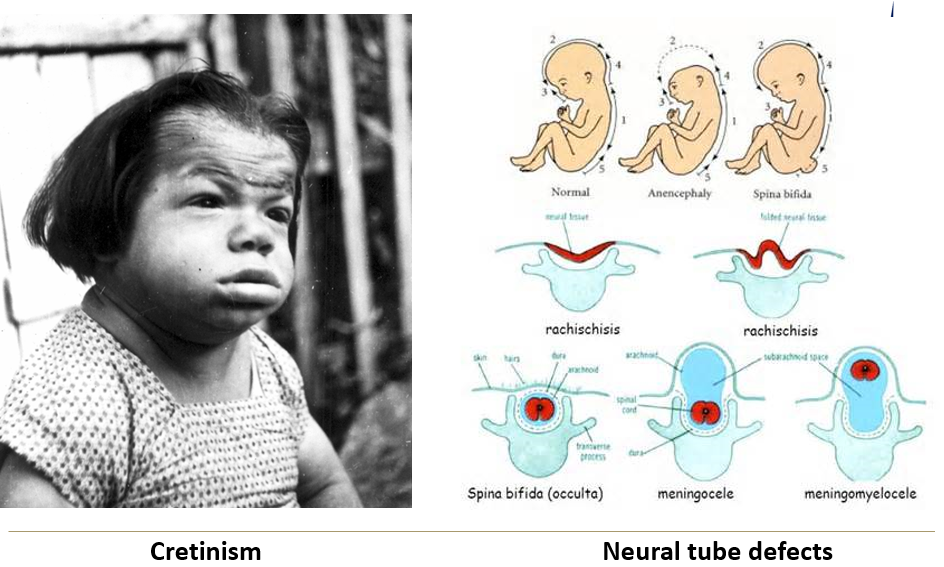
Which maternal nutritional deficiencies are widely accepted to cause cretinism and neural tube defects?
Iodine deficiency = congenital cretinism, brain development delay
Folate deficiency = neural tube defects
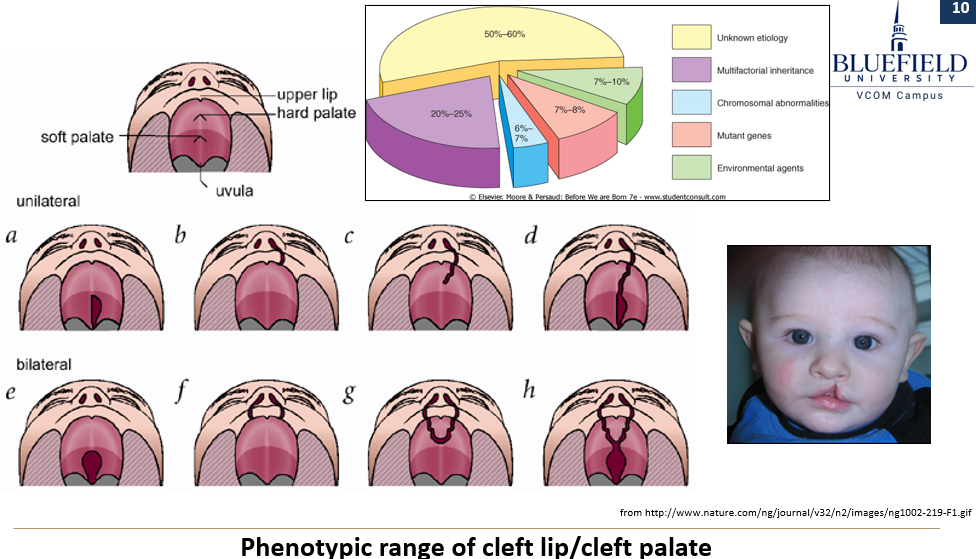
What characterizes birth defects caused by multifactorial inheritance?
It involves multiple genes and environmental factors. It explains variation in phenotypes such as cleft lip/palate and shows increased liability within families, though it does not follow a Mendelian pattern.