N209 - Vascular Periphery
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
claudification
= pain when walking
Modified Allen test
= assessment of adequacy of collateral circulation that is done before cannulating the radial artery
occlude both the radial and ulnar artery, have the pt make a fist multiple times until the hand blanches
open the hand and release only the ulnar artery
Hand should return to normal color in <7 seconds
What are the steps of a Modified Allen Test? What should normally happen?
Normal findings in the upper extremeties
pink & warm bilaterally
2+ radial pulses
elastic turgor
feels soft, blunt, sharp sensations
free of edema, lesions or pain
Abnormal findings in the upper extremities
cold, cool or hot
0, 1+ or 3+ radial pulse
poor turgor
paresthesia (pins & needles) or absent sensation
paralysis/weakness
edema, lesions, pain
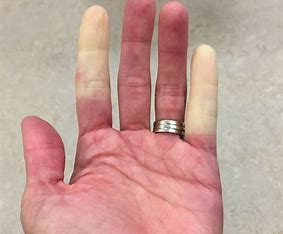
Raynaud Phenomenon
= episodes of abrupt, progressive tricolor change of the fingers in response to cold, vibration, or stress
White (pallor) at the fingertips
Blue (cyanosis) in the lower figure
Red (rubor) in the heel of the hand
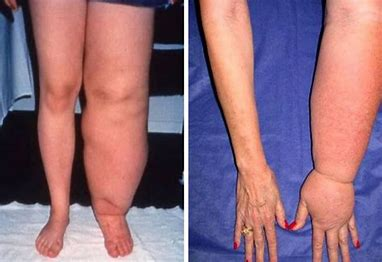
chronic lymphedema
= chronic progressive accumulation of protein rich fluid in the interstitial spaces
From a blockage in the lymphatic system
Femoral artery
Which lower extremity pulse is located just below inguinal ligament halfway between pubis and anterior superior iliac spines?
Dorsalis Pedis
Which lower extremity pulse is lateral to and parallel with the extensor tendon of the big toe?
Popliteal
Which lower extremity pulse is located by anchoring your thumb on the knee and curling your fingers around into the popliteal fossa?
posterior tibial
Which lower extremity pulse is located by curving your fingers around the medial malleolus?
60-100 bpm
What is the normal rate of a pulse?
Asystole
= absent pulse (no palpable pulse or waveform)
Causes:
Arterial line disconnected
cardiac arrest
Weak/thready
= 1+ intensity; may wax and wane; difficult to find
Causes:
shock
decreased cardiac output
peripheral arterial disease
aortic valve stenosis

Bounding
= 3+ intensity easy to observe near skin surface; very easy to palpate & difficult to obliterate with fingertips
Causes:
hyperkinetic states (exercise, anxiety, fever)
anemia
hyperthyroidism
increased CO
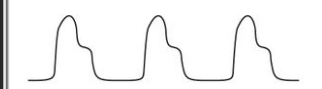
Pulsus Bisferiens
= each pulse has 2 strong systolic peaks with a dip in between
causes:
aortic regurgitation
aortic stenosis
cardiomyopathy
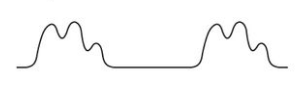
Pulsus Alternans
= alternating strong and weak pulses; rhythm regular
causes:
aortic regurgitation
left ventricular heart failure
systemic hypertension

Pulsus Bigeminus
= rhythm is coupled; every other beat comes in early or a normal beat is followed by a premature beat.
causes:
conduction disturbances
PVCs (premature ventricular contractions)
PACs (premature atrial contractions)

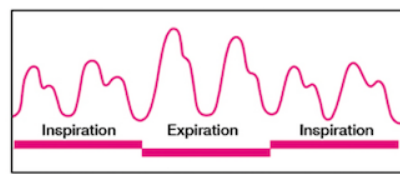
Pulsus Paradoxus (paradoxical pulse)
= reduced intensity of pulse during inspiration and stronger with expiration
causes:
cardiac tamponade
pericarditis
chronic lung disease
acute pulmonary embolus
hypovolemic shock
pregnancy
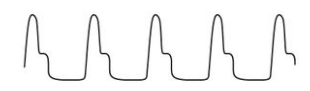
Waterhammer or Corrigan’s pulse
= 3+ intensity; rapid systolic upstroke and then suddenly collapses
causes:
aortic regurgitation
patent ductus arteriosus
Unequal Pulses
= different intensity b/t right and left pulses
causes:
dissecting aneurysm (location determines where felt)
Normal findings in the lower extremities
pink & warm bilaterally
elastic turgor
venous pattern is flat & barely visible
intact sensation
symmetrical size
free of lesions, pain, edema
abnormal findings in the lower extremeties
cold, cool or hot
tents for >3 sec
severe/multiple varicosities/broken veins
paresthesia/pain
intermittent claudication
paralysis/hemiparesis
lesions, ulcers, color changes
no edema is indicated by the fingers leaving no indentation
What is a normal finding for checking for edema?
Brawny Edema
= result of lymphatic obstruction & hemosiderin deposition
nonpitting and hard
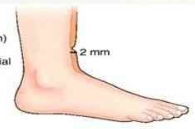
Mild Pitting (1+)
slight indentation (2mm)
no perceptible swelling of the leg
returns to normal quickly
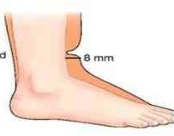
Moderate Pitting (2+)
indentation ~4mm (1/4 in)
contour appears normal
returns to normal in 13-15 seconds
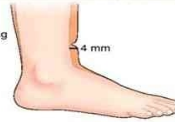
Deep Pitting (3+)
indents 6mm (1/4-1/2 in)
returns to normal in 1-2 minutes
looks edematous
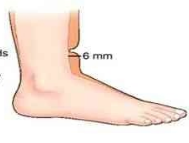
Very Deep Pitting (4+)
indentation 8mm (1/2-1 in)
returns to normal in 2-5 minutes
grossly edematous
raise the legs about 30 cm (12 in) and have the pt. wag there feet to drain off venous blood
skin now reflects only arterial blood (should still be pink)
have the pt. sit w legs dangling
should take 10 sec or less for color to return to feet
should take 15 sec for superficial veins around the feet to fill
How would you assess the legs if you suspect arterial deficit?
pallor
rubor
cyanosis
mottled
What are abnormal colors you might see in the lower legs?
Varicose Veins
= legs have dilated bc of chronic increased veinous pressure & reflux of blood back towards the legs (instead of heart) from incompetent valves
severe PAD
What does an ABI of <0.40 indicate?
moderate PAD
What does an ABI of 0.41-0.70 indicate?
Mild PAD
What does an ABI of 0.71-0.90 indicate?
borderline risk
What does an ABI of 0.91-0.99 indicate?
normal
What does an ABI of 1.0-1.4 indicate?
counterclockwise (right arm, right PT, right DP, left DP, left PT, left arm)
What order would you perform and ankle-brachial index (ABI)?
Phlebitis
= inflammation of a vein
note redness, enlargement of extremity, heat, pain, & tenderness
Thrombophlebitis
= inflammation with clot formation
Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis (DVT)
= a deep vein is occluded by a thrombus, causing inflammation, blocked venous return, cyanosis, edema
requires emergency referral bc of risk for pulmonary embolism
Arterial abnormalities
dec/absent pulses
pale w elevation and rubor
cold temp
no edema
shiny/thick nails
ulcers on toes
pain w exercise & cold
decreased sensations
Venous abnormalities
palpable pulses
pink to cyanotic color
warm temp
pitting edema
ulcers/thick dark skin
pain w standing & relief when lying
Pediatric Variations
Transient acrocyanosis & mottling at birth can occur
Pulse force should be normal and symmetric in both UE & LE
Palpable lymph nodes occur often in healthy infants & children
Small, firm (shotty), mobile, and nontender
Vaccinations can produce local lymphadenopathy
OA Variations
Arteriosclerosis (hardening) and Atherosclerosis (plaques)
DP and PT pulses may become more difficult to find
Trophic changes associated with arterial insufficiency may be seen:
Thin, shiny skin
Thick, ridged nails
Loss of hair on lower legs
What are trophic changes associated with arterial insufficiency?
Thin, shiny skin
Thick, ridged nails
Loss of hair on lower legs