The Nervous System
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Nervous system is split up into
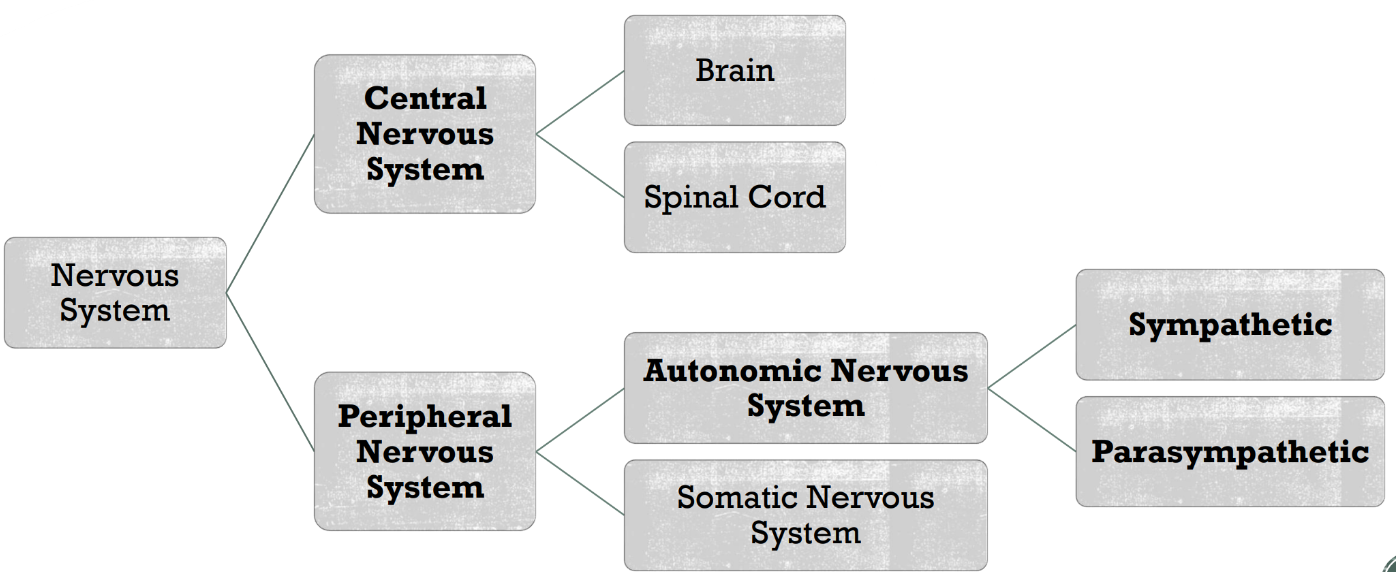
Peripheral Nervous System
relay information to and the from the CNS
cranial nerves → to the brain; concern head, neck and face
spinal nerves → come from spinal chord, enter through dorsal side, form dorsal root ganglion, leave through ventral, ventral root (in spinal chord)
serve somatic (voluntary)
autonomic (involuntary
advantage of autonomic nervous system
involuntarily and automatically control internal and involuntary activities
visceral reflex
involuntary response - maintains homeostasis
what is ANS controlled by
medulla oblongata and hypothalamus
preganglionic neuron and postganglionic neuron
pre → relays information to the ganglia from the CNS - myelinated
post → relays information to effector from ganglia - unmyelinated
what does ANS consist of
2 antagonistic divisions
parasympathetic
sympathetic
Parasympathetic Nervous System (not responses)
slows down activity of visceral organs
activated during rest and digest
response is localized
neurotransmittor is acetylcholine
ganglia is close to organs being innervated
preganglionic neurons start from cranium and tip of spinal chord
Responses of Parasympathetic Nervous System
slower heart rate
stimulation of flow of saliva
bladder contracts
stimulates peristalsis and secretion
release of bile
Sympathetic nervous system
accelerates activity of all visceral organs
during fight or flight → stress response
ganglia are far from organs being innervated
neurotransmitter is noradrenaline
preganglionic neurons originate from spinal chord
response is diffused
Responses of sympathetic Nervous System
dilates pupils
accelerates heartbeat
stimulates conversion of glycogen into glucose
inhibits peristalsis
inhibits flow of saliva
inhibits bladder contraction
dilates bronchi
central nervous system is protected by
bones
Meninges
CSF - cerebrospinal fluid
Bones
cranium and vertebrae
Meninges
3 layered membrane
line skull and cover brain
protect it from being bruised + friction
nourish CNS tissues (grey + white matter)
bacterium → meningitis (inflammation)
where is csf produced
choroid plexus -network of blood vessels and epithelial cells in the ventricles of the brain
produce csf
Cerebrospinal Fluid
central canal between spinal chord and also in ventricles of brain
fills space between meninges
blood vessels which supply nutrients and oxygen to brain
lymphocytes → immunity
lubrication
removes waste from brain and spinal chord
shock absorbed