Phys Lecture 14 Impulse Transmision #1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Graded potentials
Changing membrane potentials, can vary on distance
Graded potentials pt.2
Generally involve and INPUT via neurotransmitter receptors
receptors are on dendrites and cell body
Amplitude decreases with distance from activation
Can be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing
DEPOLARIZING: activate action potential
HYPERPOLARIZING: restrict action potential
Axon hillock decides
2 primary neuro-receptors
Ionotropic receptors: ligand-gated channels
Metabotrophic receptors: coupled to ion channels
Voltage gated channels
Na+, K+, and Ca2+ -calcium influx
Action potentials
Generated by changes in membrane
Propagation of the action potential
Propagation of a DEPOLARIZING electric potential along the plasma membrane (neurons, muscle, and some endocrine cells)
an action potential is SELF PROPAGATING (continues like a row of falling dominos)
Threshold of depolarization
Activates at -55 mV - NA+ is depolarizer
Propagation of depolarization
Depolarization: rising phase of Action potential
Voltage gated sodium channels open
1) Influx of NA+ ions depolarizes atonal membrane (graded potential)
2) if depolarization reaches threshold:
voltage gated Na+ channels open :INFLUX of Na+ ions (faster)
Positive feedback loop: depolarization
Membrane REPOLARIZATION
REPOLARIZATION: falling phase of action potential
1) voltage gated Na+ channels inactivate (around 1ms)
stops influx of Na+ ions
Na+ channels now inactive: channel plugged
2) voltage gated K+ channels open K+ rushes out of cell (membrane potential becomes more negative) Repolarization the membrane potential (slower)
Voltage gated K+ channels open slowly
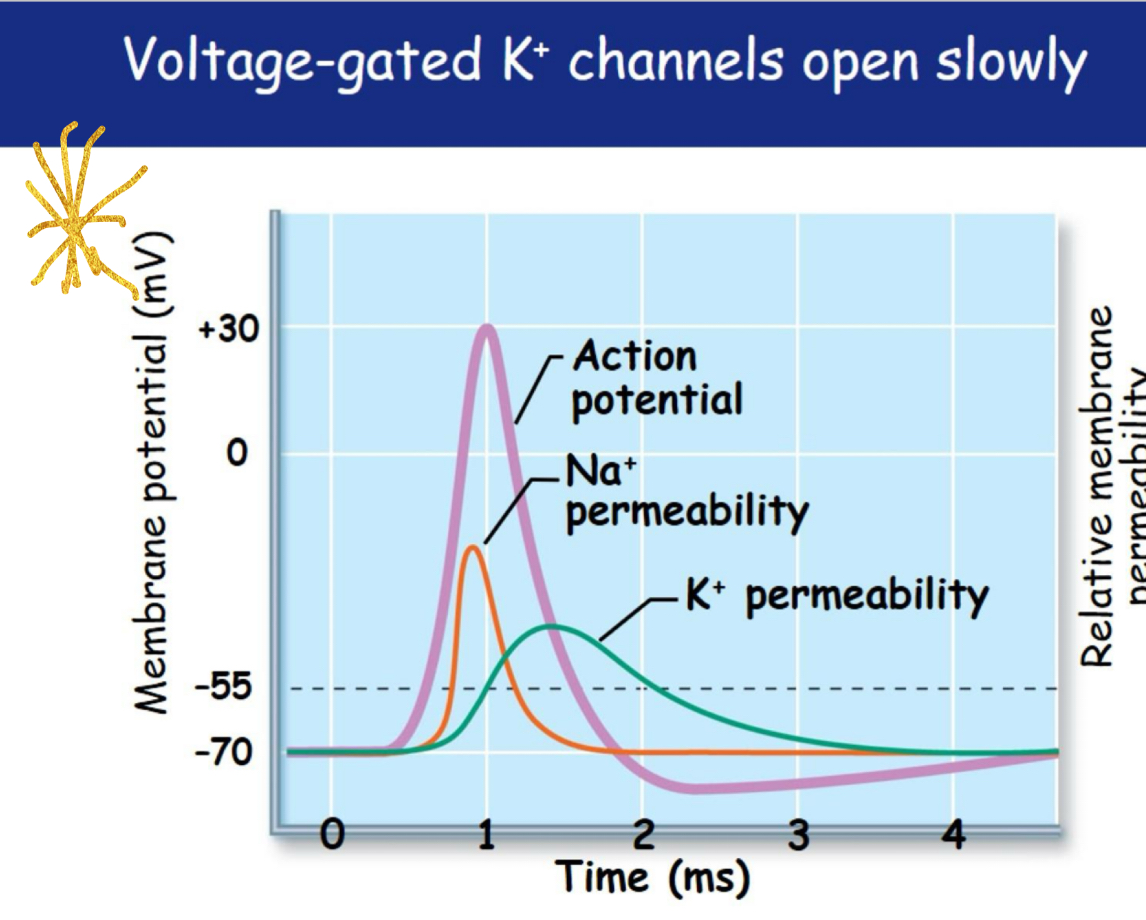
Reaching resting membrane potentials
HYPERPOLARIZATION (undershoot phase of AP)
1) with Na+ channels closed and more K+ channels opened the membrane potential will become more negitive then the resting potential of -70mV
2) voltage gated K+ channels close moving membrane potentials back to rest
Action potentials are all or none
For an action potential to occur, axon must be depolarized by about 15mv (-70mV —> -55mV)
if too few Na+ ions enter the cell NO action potential will occur
Absolute refractory period
Neurons can’t respond to another stimulus when Na+ channels are either open or inactivated
Ensures that each AP is a discrete event
Enforces one way transmission of AP
Relative refractory period
Immediately after the absolute refractory period
Na+ channels reactivate ready to be opened for release of Na+ intracellular to extracellular
How do neurons code for stimulus intensity?
The amplitude of all action potentials is the same and is independent of stimulus intensity (all or none)
Stimulus intensity is encoded in FREQUENCY
the more intense the higher the frequency
Synapses (presynaptic neuron)
conducts impulses towards synapse
Synaptic vesicles
Stores NEUROTRANSMITTER
Synapses (synaptic cleft)
fluid filled space between pre and post synaptic membranes
Synapses (postsynaptic neuron)
-Neurotransmitter receptors
Synaptic transmission
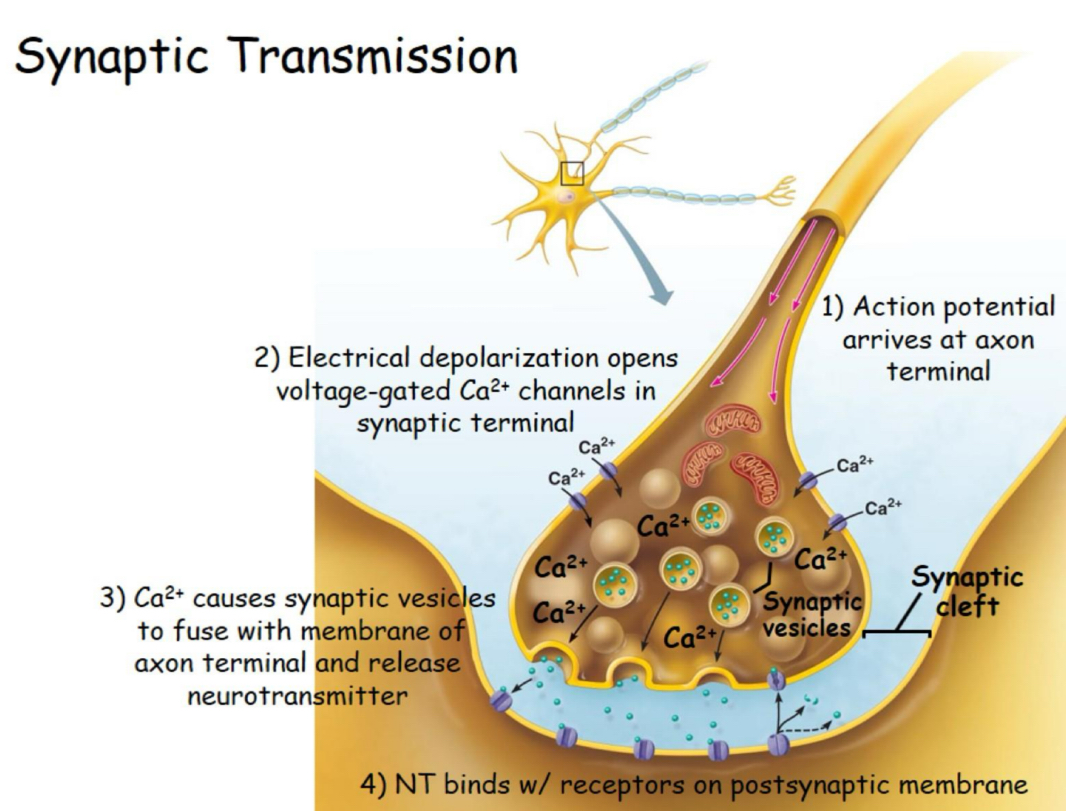
Ca2+ in synaptic transmission
Triggers the fusion pore opening
Termination of the neurotransmitter signal
Remove Ca2+ from the cytosol (stops neurotransmitter release)
Ca2+ ATPase
Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
Neurotransmitter removal
1) diffuses from synaptic cleft
2) degraded by an enzyme
3) taken up by presynaptic terminal or astrocyte
Recovery of resting membrane potential and ionic concentration
1) K+ leak channels
2) sodium/potassium pump
helps re-establish the Na+ and K+ ion concentrations inside and outside neuron
Helps maintain internally negative resting membrane potential