ABG Analysis
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
what 5 components do ABGs examine
1. arterial pH (acid-base balance)
2. PaCO2 (ventilation)
3. PaO2 (oxygenation)
4. bicarbonate (HCO3-)
5. base excess
what is the normal value for ARTERIAL pH
7.35-7.45
what is the normal value for PaCO2
35-45 mmHg
what is the normal value for PaO2
80-100 mmHg
what is the normal value for HCO3-
22-26 mEq/L
how are ABGs reported
PaO2/PaCO2/pH/HCO3-
followed by a +/- number (BE)
what is HIGH pH called
alkalosis
what is LOW pH called
acidosis
ALKALOSIS (high pH) is caused by (2)
1. decreased PaCO2
2. increased HCO3-
ACIDOSIS (low pH) is caused by (2)
1. increased PaCO2
2. decreased HCO3-
what is PaCO2
partial pressure of carbon dioxide in plasma
what does PaCO2 reflect
adequacy of alveolar ventilation
what do HIGH PaCO2 LEVELS cause
low pH (acidic) = hypoventilation
what do LOW PaCO2 LEVELS cause
high pH (basic) = hyperventilation
what does HYPOVENTILATION result in
low pH (acidic)
what does HYPERVENTILATION result in
high pH (basic)
what is PaO2
partial pressure of oxygen in plasma
what does PaO2 reflect
circulating oxygen available for tissues to use
what does HCO3- act as
a buffer to prevent extreme fluctuations in acid-base balance
what do significant changes in blood pH >7.8 or <6.8 interfere with
cellular functioning
(if uncorrected = death)
what 2 ORGANS take on the role of REGULATING ACID-BASE BALANCES
1. lungs
2. kidneys
how do the LUNGS regulate acid-base balance
by blowing off (hyperventilation)/retaining (hypoventilation) PaCO2
when does RESPIRATORY COMPENSATION begin
within second by alveolar hyper/hypoventilation
how do the KIDNEYS regulate acid-base balance
by retaining/excreting bicarbonate + hydrogen ions
what does RENAL COMPENSATION require to significantly effect pH
at least 12-24 hours
what are 4 ACID-BASE STATES
1. respiratory acidosis
2. respiratory alkalosis
3. metabolic acidosis
4. metabolic alkalosis
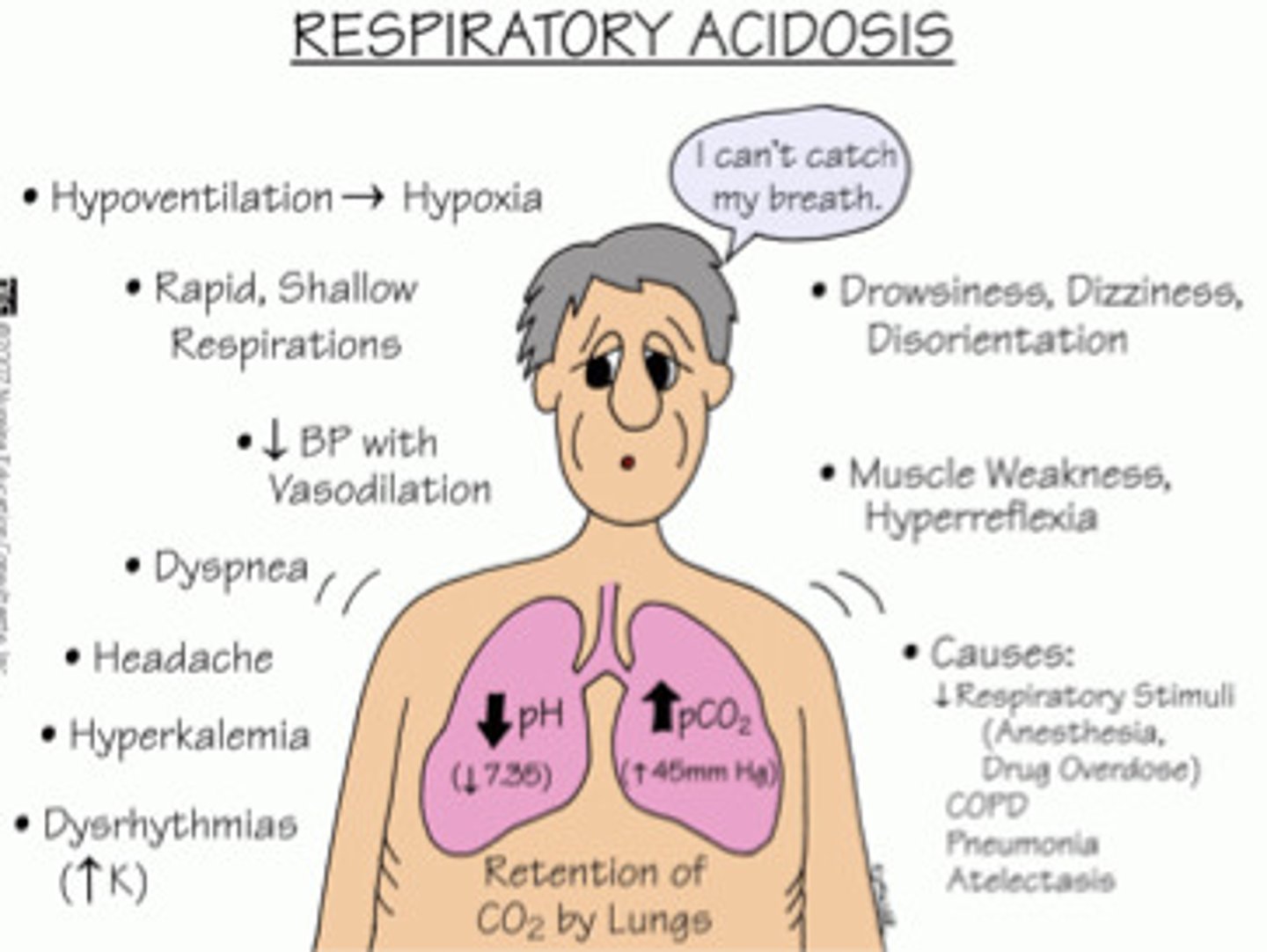
what is the MAJOR CAUSE of RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
high PaCO2
what is HIGH PaCO2 due to
alveolar hypoventilation
what are 2 FEATURES of RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
1. pH < 7.35
2. PaCO2 > 45 mmHg
what are 5 COMMON CAUSES of RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
1. CNS depression (TBI, narcotics, sedatives, anesthesia)
2. impaired respiratory muscle function (SCI, neuromuscular diseases)
3. pulmonary disorders (atelectasis, pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, bronchial obstruction, COPD)
4. massive pulmonary embolus
5. hypoventilation (pain, chest wall injury/deformity, rib fractures, abdominal distention, sleep apnea)
what are 3 SIGNS + SYMPTOMS of RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
1. pulmonary
- dyspnea
- respiratory distress
- shallow respirations
2. neurological
- HA
- restlessness
- drowsiness
- lethargy
- confusion
- altered mental status
- tremor
- coma
3. cardiovascular
- tachycardia
- dysrhythmia
- HTN
what is the MAJOR CAUSE of RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
low PaCO2
what is LOW PaCO2 due to
alveolar hyperventilation
what are 2 FEATURES of RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
1. pH > 7.45
2. PaCO2 < 35 mmHg
what are 6 COMMON CAUSES of RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
1. psychological responses (anxiety/fear)
2. pain
3. increased metabolic demands (fever, sepsis, pregnancy)
4. medications (respiratory stimulants)
5. CNS lesions
6. cardiopulmonary (CHF, PE, asthma, ARDS, hypoxia)
what are 4 SIGNS + SYMPTOMS of RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
1. neurological
- light-headedness
- numbness/tingling
- confusion
- inability to concentrate
- blurred vision
2. cardiovascular
- palpitations
- dysrhythmia
- diaphoresis (excessive sweating)
3. dry mouth
4. tetanic spasm of arms/legs
what is the MAJOR CAUSE of METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
low HCO3-
what are 2 FEATURES of METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
1. pH < 7.35
2. HCO3- < 22 mEq/L
what are 5 COMMON CAUSES of METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
1. renal failure
2. diabetes/DKA
3. anaerobic metabolism (lactic acidosis)
4. starvation
5. alcoholism
6. diarrhea
7. ostomy drainage
8. parenteral nutrition (extended need)
9. salicylate intoxication (aspirin)
what are 4 SIGNS + SYMPTOMS of METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
1. pulmonary
- Kussmaul respirations
2. neurological
- HA
- restlessness
- drowsiness
- lethargy
- confusion
- coma
3. cardiovascular
- dysrhythmia
4. warm + flushed skin
what are KUSSMAUL RESPIRATIONS
deep desperate breathing
- attempt to increase pH by removing CO2
what is the MAJOR CAUSE of METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
high HCO3-
what are 2 FEATURES of METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
1. pH >7.45
2. HCO3- > 26 mEq/L
what are 4 COMMON CAUSES of METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
1. excess base
- excess ingestion of antacids
- excess use of bicarbonate
- use of lactate in dialysis
2. loss of acids
- vomiting
- nasogastric suction
- hypochloremia (decreased Cl-)
- hypokalemia
- excess diuretics
- high levels of aldosterone (steroids)
3. banked blood transfusions
4. cushing's syndrome (overactive adrenal gland)
what are 4 SIGNS + SYMPTOMS of METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
1. neurological
- dizziness
- lethargy
- disorientation
- seizures
- coma
2. pulmonary
- respiratory depression (try to retain PaCO2 to decrease pH)
3. musculoskeletal
- weakness
- muscle twitching
- muscle cramps
- tetany
4. gastrointestinal
- nausea
- vomiting
what are 2 features of FULLY COMPENSATED ABGs
1. pH normal range
2. both PaCO2 + HCO3- out of range
what are 2 features of PARTIALLY COMPENSATED ABGs
1. pH out of normal range (but moving near normal)
2. both PaCO2 + HCO3- out of range
what are 2 features of UNCOMPENSATED ABGs
1. pH out of normal range
2. only PaCO2 or HCO3- out of range (not both)
practice #1
pH: 7.30
PaCO2: 55 mmHg
HCO3-: 26 mEq/L
uncompensated respiratory acidosis
explanation:
pH: low
PaCO2: high
HCO3-: normal range
- respiratory acidosis = high PaCO2 + low pH (acidic)
- uncompensated = only PaCO2 out of range + pH out of range
practice #2
pH: 7.48
PaCO2: 44 mmHg
HCO3-: 32 mEq/L
uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
explanation
pH: high
PaCO2: normal range
HCO3-: high
- metabolic alkalosis = high pH + high HCO3-
- uncompensated = pH out of range + only HCO3- out of range
practice #3
pH: 7.38
PaCO2: 56 mmHg
HCO3-: 35 mEq/L
fully compensated respiratory acidosis
explanation:
pH: normal (lower end of range)
PaCO2: high
HCO3-: high
- respiratory acidosis = high PaCO2 + pH lower end of range
- full compensated = pH normal range + both PaCO2 and HCO3- out of range
practice #4
pH: 7.33
PaCO2: 62 mmHg
HCO3-: 35 mEq/L
partially compensated respiratory acidosis
explanation
pH: low
PaCO2: high
HCO3-: high
- respiratory acidosis = high PaCO2 + low pH
- partially compensated = pH outside normal (moving to normal) + both PaCO2 and HCO3- out of range
practice #5
pH: 7.29
PaCO2: 30 mmHg
HCO3-: 18 mEq/L
partially compensated metabolic acidosis
explanation:
pH: low
PaCO2: low
HCO3-: low
- metabolic acidosis = low HCO3- + low pH
- partially compensated = pH outside normal (moving to normal) + both PaCO2 and HCO3- out of range