Glycolysis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
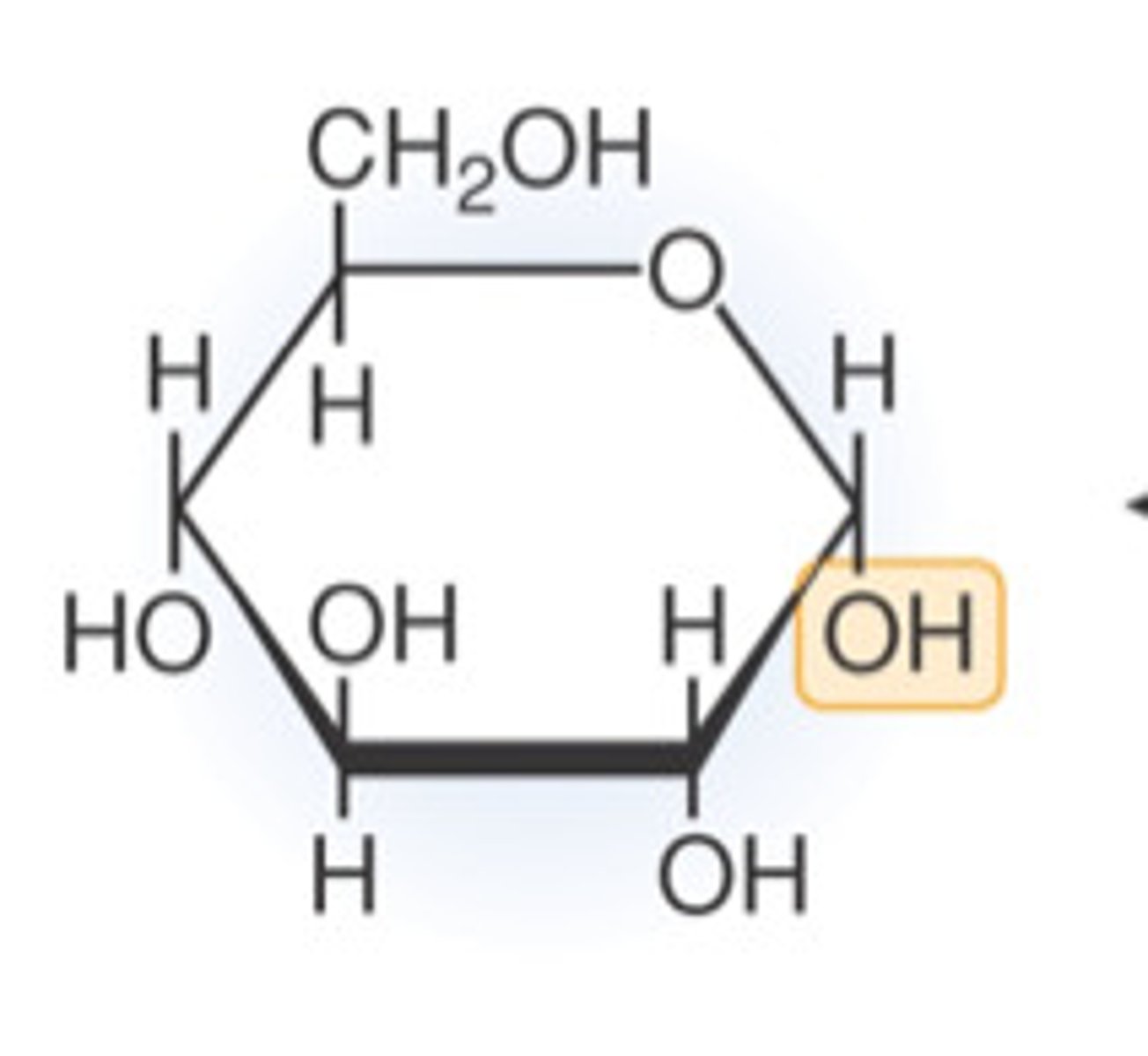
Glucose
A 6 carbon sugar that is used in Cellular Respiration to make ATP.
Pyruvate
1/2 of a glucose molecule. Has 3 carbons.
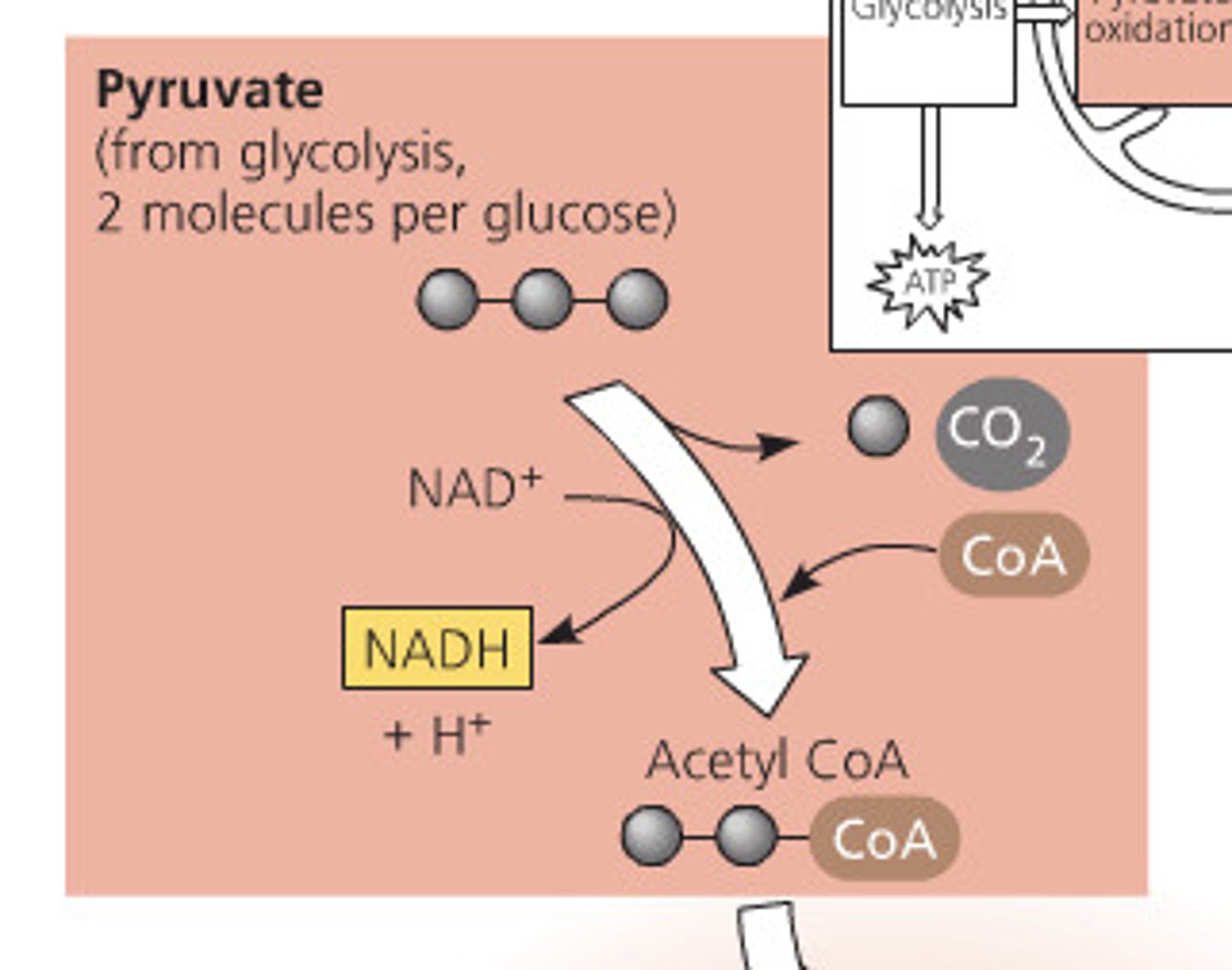
Acetyl CoA
A molecule created when a carbon is moved from pyruvate. That removed carbon is released as CO2. This is the molecule that enters the Krebs cycle.
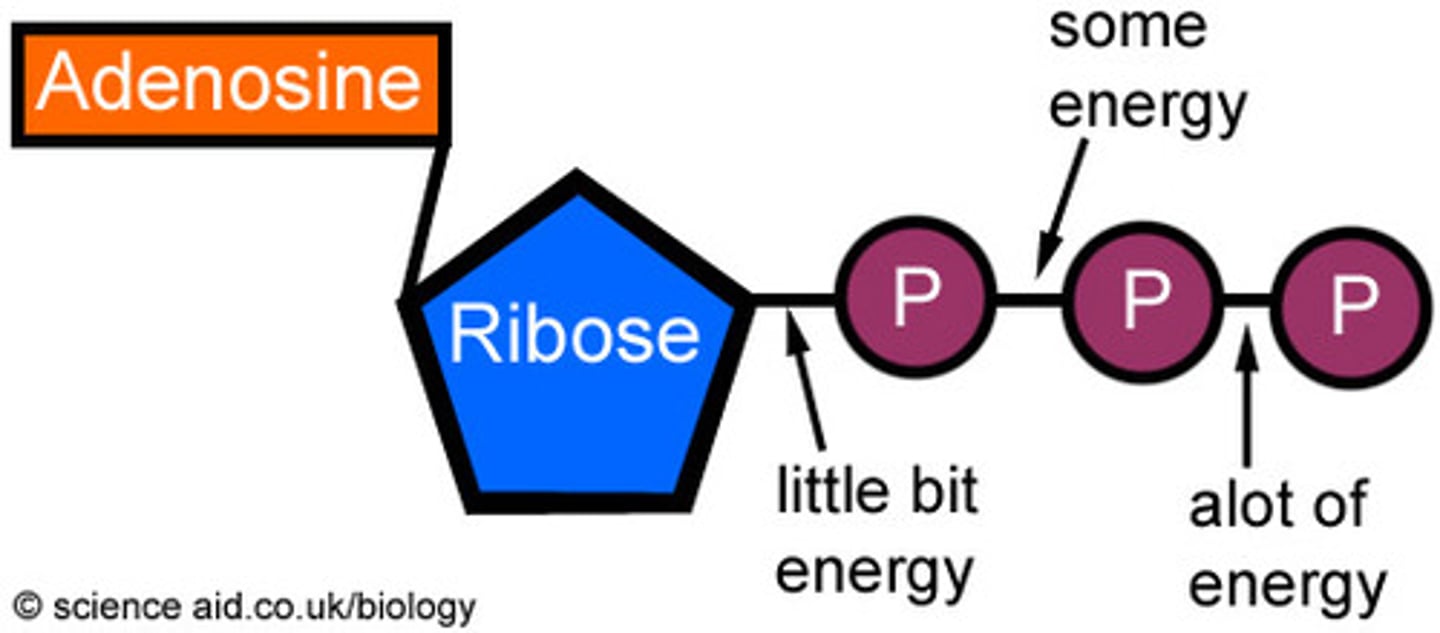
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate. Our energy "coin" that is required to run all of our cellular machinery
Cellular Respiration
Process that breaks down glucose into CO2, H2O, and makes energy in the form of ATP.
Glycolysis
The 1st step of Cellular Respiration. Breaks glucose into 2 pyruvates, creating 4 ATP, 2 NADH. 2 ATP are required to start the process. Occurs in the cytoplasm
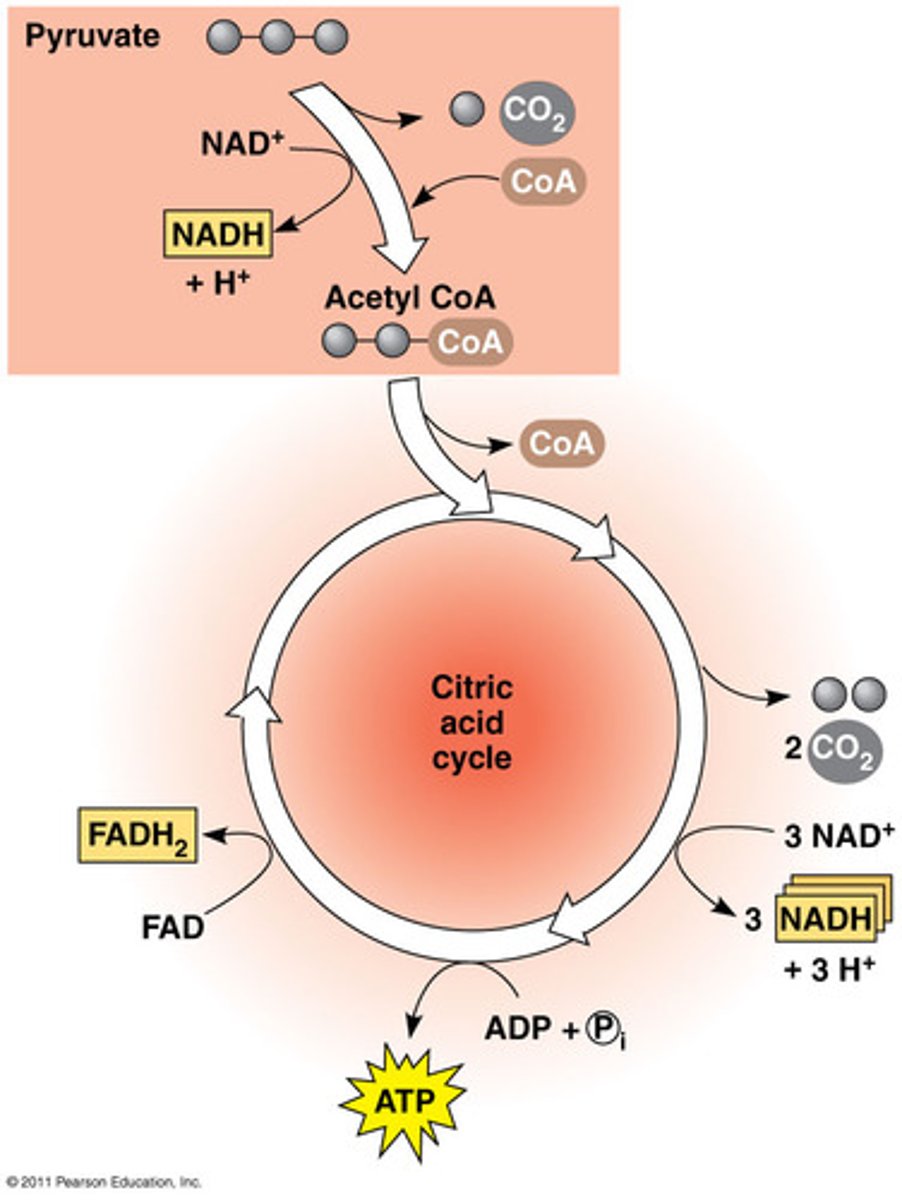
Krebs Cycle
Occurs in mitochondrial matrix. Completes the final breakdown of glucose. ATP, NADH, FADH2 are made. CO2 is released.
Electron Transport Chain
Occurs in inner mitochondrial membrane. Coverts NADH and FADH2 into ATP through a series of electron transport proteins located in the membrane.
Oxidation
The removal of electrons from a molecule.
Reduction
The addition of electrons to a molecule.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme that acts as a H+ pump, driving the production of ATP from ADP.
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell. Functions to generate ATP for cellular energy